说明:
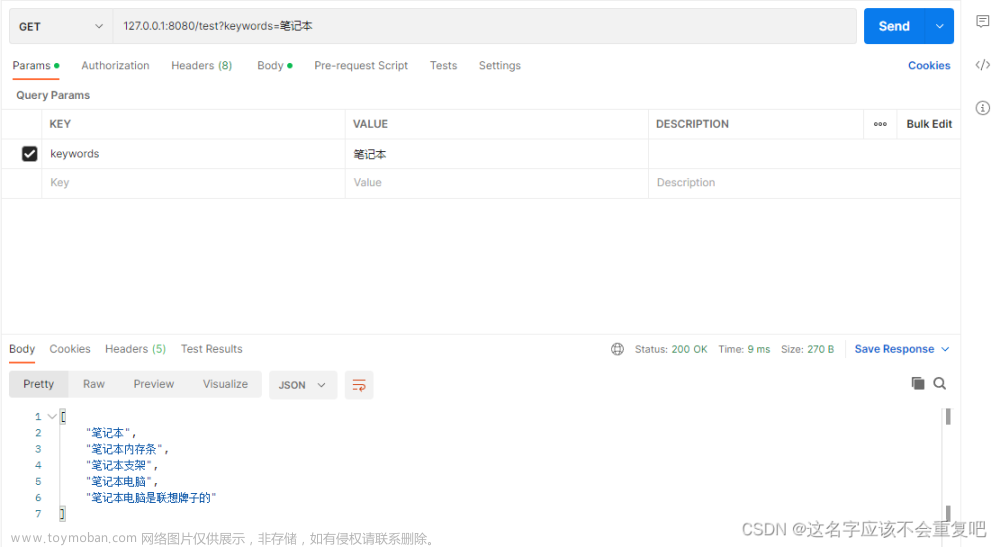
我们的项目中经常会遇到搜索的功能,最近也写过搜索的功能,用具体的python项目来实现
一.单表搜索
实现对于特定表中的某些字段的模糊搜索匹配
通过用orm查询操作来实现简单真的搜索,虽然比较简单方便但是效率不高,遇到大数据量的就会非常的吃力。
Article.objects.filter(title='文章标题')
二,全局搜索
解决数据库不能在数据量庞大高效实现全文搜索模糊匹配的,我们就选择合适的搜索引擎,现在主流的搜索引擎有:Lucene,Solr,ElasticSearch。python项目中还会经常用到一个纯python实现的全文搜索引擎whoosh,更加小巧简单。
在django项目中实现全文搜索,可以使用搜索框架haystack来实现,
haystack可以方便地在django中直接添加搜索功能,无需关注索引建立、搜索解析等细节问题。
方式一:haystack+whoosh+Jieba
安装和配置
- 安装:
pip install whoosh/django-haystack/jieba
因为whoosh他自带的是英文分词,对中文的分词不太友好,所以我们要把jieba替代whoosh的分词组件
2. 注册到Django的INSTALLED_APPS:
3.增加搜索引擎配置
'''配置haystack '''
# 全文检索框架配置
HAYSTACK_CONNECTIONS = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'djangoblog.whoosh_cn_backend.WhooshEngine',
'PATH': os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'whoosh_index'),
},
}
# Automatically update searching index# 添加此项,当数据库改变时,会自动更新索引,非常方便
HAYSTACK_SIGNAL_PROCESSOR = 'haystack.signals.RealtimeSignalProcessor'
- 创建搜索引

from haystack import indexes
from blog.models import Article
# 全局搜索
class ArticleIndex(indexes.SearchIndex, indexes.Indexable):
# 必须这么写
text = indexes.CharField(document=True, use_template=True)
def get_model(self):
# 重载get_model方法,必须要有!
return Article
def index_queryset(self, using=None):
return self.get_model().objects.filter(status='p')
5.然后在template下面建立 search/indexes/
前两个目录都是固定的,第blog三层是应用的名称,一一对应上,然后建立article_text.txt,名字是刚刚指定的类名的小写加_text.txt ,这里面就是对应哪个字段建立索引。例如:

6. 搜索模板
在templates/search/下面,建立一个search.html页面

{% extends 'share_layout/base.html' %}
{% load blog_tags %}
{% block header %}
<title>{{ SITE_NAME }} | {{ SITE_DESCRIPTION }}</title>
<meta name="description" content="{{ SITE_SEO_DESCRIPTION }}"/>
<meta name="keywords" content="{{ SITE_KEYWORDS }}"/>
<meta property="og:type" content="blog"/>
<meta property="og:title" content="{{ SITE_NAME }}"/>
<meta property="og:description" content="{{ SITE_DESCRIPTION }}"/>
<meta property="og:url" content="{{ SITE_BASE_URL }}"/>
<meta property="og:site_name" content="{{ SITE_NAME }}"/>
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
<div id="primary" class="site-content">
<div id="content" role="main">
{% if query %}
<header class="archive-header">
<h2 class="archive-title"> 搜索:<span style="color: red">{{ query }}</span></h2>
</header><!-- .archive-header -->
{% endif %}
{% if query and page.object_list %}
{% for article in page.object_list %}
{% load_article_detail article.object True user %}
{% endfor %}
{% if page.has_previous or page.has_next %}
<nav id="nav-below" class="navigation" role="navigation">
<h3 class="assistive-text">文章导航</h3>
{% if page.has_previous %}
<div class="nav-previous"><a
href="?q={{ query }}&page={{ page.previous_page_number }}"><span
class="meta-nav">←</span> 早期文章</a></div>
{% endif %}
{% if page.has_next %}
<div class="nav-next"><a href="?q={{ query }}&page={{ page.next_page_number }}">较新文章
<span
class="meta-nav">→</span></a>
</div>
{% endif %}
</nav><!-- .navigation -->
{% endif %}
{% else %}
<header class="archive-header">
<h1 class="archive-title">哎呀,关键字:<span>{{ query }}</span>没有找到结果,要不换个词再试试?</h1>
</header><!-- .archive-header -->
{% endif %}
</div><!-- #content -->
</div><!-- #primary -->
{% endblock %}
{% block sidebar %}
{% load_sidebar request.user 'i' %}
{% endblock %}
- 配置路由
我这是前后端不分离的项目
re_path(r'^search', include('haystack.urls'), name='search'),
8.替换成jieba分词
将haystack源码复制到项目中并改名
1.复制源码中文件并改名
将 C:\python37\Lib\site-packages\haystack\backends\whoosh_backend.py文件复制到项目中
并将 whoosh_backend.py改名为 whoosh_cn_backend.py 放在APP中如:whoosh_cn_backend.py
2.修改源码中文件
在全局引入的最后一行加入jieba分词器
from jieba.analyse import ChineseAnalyzer
修改为中文分词法
查找
analyzer=StemmingAnalyzer()
改为
analyzer=ChineseAnalyzer()
whoosh_cn_backend.py
# encoding: utf-8
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
import json
import os
import re
import shutil
import threading
import warnings
import six
from django.conf import settings
from django.core.exceptions import ImproperlyConfigured
from django.utils.datetime_safe import datetime
from django.utils.encoding import force_str
from haystack.backends import BaseEngine, BaseSearchBackend, BaseSearchQuery, EmptyResults, log_query
from haystack.constants import DJANGO_CT, DJANGO_ID, ID
from haystack.exceptions import MissingDependency, SearchBackendError, SkipDocument
from haystack.inputs import Clean, Exact, PythonData, Raw
from haystack.models import SearchResult
from haystack.utils import get_identifier, get_model_ct
from haystack.utils import log as logging
from haystack.utils.app_loading import haystack_get_model
from jieba.analyse import ChineseAnalyzer
from whoosh import index
from whoosh.analysis import StemmingAnalyzer
from whoosh.fields import BOOLEAN, DATETIME, IDLIST, KEYWORD, NGRAM, NGRAMWORDS, NUMERIC, Schema, TEXT
from whoosh.fields import ID as WHOOSH_ID
from whoosh.filedb.filestore import FileStorage, RamStorage
from whoosh.highlight import ContextFragmenter, HtmlFormatter
from whoosh.highlight import highlight as whoosh_highlight
from whoosh.qparser import QueryParser
from whoosh.searching import ResultsPage
from whoosh.writing import AsyncWriter
try:
import whoosh
except ImportError:
raise MissingDependency(
"The 'whoosh' backend requires the installation of 'Whoosh'. Please refer to the documentation.")
# Handle minimum requirement.
if not hasattr(whoosh, '__version__') or whoosh.__version__ < (2, 5, 0):
raise MissingDependency(
"The 'whoosh' backend requires version 2.5.0 or greater.")
# Bubble up the correct error.
DATETIME_REGEX = re.compile(
'^(?P<year>\d{4})-(?P<month>\d{2})-(?P<day>\d{2})T(?P<hour>\d{2}):(?P<minute>\d{2}):(?P<second>\d{2})(\.\d{3,6}Z?)?$')
LOCALS = threading.local()
LOCALS.RAM_STORE = None
class WhooshHtmlFormatter(HtmlFormatter):
"""
This is a HtmlFormatter simpler than the whoosh.HtmlFormatter.
We use it to have consistent results across backends. Specifically,
Solr, Xapian and Elasticsearch are using this formatting.
"""
template = '<%(tag)s>%(t)s</%(tag)s>'
class WhooshSearchBackend(BaseSearchBackend):
# Word reserved by Whoosh for special use.
RESERVED_WORDS = (
'AND',
'NOT',
'OR',
'TO',
)
# Characters reserved by Whoosh for special use.
# The '\\' must come first, so as not to overwrite the other slash
# replacements.
RESERVED_CHARACTERS = (
'\\', '+', '-', '&&', '||', '!', '(', ')', '{', '}',
'[', ']', '^', '"', '~', '*', '?', ':', '.',
)
def __init__(self, connection_alias, **connection_options):
super(
WhooshSearchBackend,
self).__init__(
connection_alias,
**connection_options)
self.setup_complete = False
self.use_file_storage = True
self.post_limit = getattr(
connection_options,
'POST_LIMIT',
128 * 1024 * 1024)
self.path = connection_options.get('PATH')
if connection_options.get('STORAGE', 'file') != 'file':
self.use_file_storage = False
if self.use_file_storage and not self.path:
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
"You must specify a 'PATH' in your settings for connection '%s'." %
connection_alias)
self.log = logging.getLogger('haystack')
def setup(self):
"""
Defers loading until needed.
"""
from haystack import connections
new_index = False
# Make sure the index is there.
if self.use_file_storage and not os.path.exists(self.path):
os.makedirs(self.path)
new_index = True
if self.use_file_storage and not os.access(self.path, os.W_OK):
raise IOError(
"The path to your Whoosh index '%s' is not writable for the current user/group." %
self.path)
if self.use_file_storage:
self.storage = FileStorage(self.path)
else:
global LOCALS
if getattr(LOCALS, 'RAM_STORE', None) is None:
LOCALS.RAM_STORE = RamStorage()
self.storage = LOCALS.RAM_STORE
self.content_field_name, self.schema = self.build_schema(
connections[self.connection_alias].get_unified_index().all_searchfields())
self.parser = QueryParser(self.content_field_name, schema=self.schema)
if new_index is True:
self.index = self.storage.create_index(self.schema)
else:
try:
self.index = self.storage.open_index(schema=self.schema)
except index.EmptyIndexError:
self.index = self.storage.create_index(self.schema)
self.setup_complete = True
def build_schema(self, fields):
schema_fields = {
ID: WHOOSH_ID(stored=True, unique=True),
DJANGO_CT: WHOOSH_ID(stored=True),
DJANGO_ID: WHOOSH_ID(stored=True),
}
# Grab the number of keys that are hard-coded into Haystack.
# We'll use this to (possibly) fail slightly more gracefully later.
initial_key_count = len(schema_fields)
content_field_name = ''
for field_name, field_class in fields.items():
if field_class.is_multivalued:
if field_class.indexed is False:
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = IDLIST(
stored=True, field_boost=field_class.boost)
else:
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = KEYWORD(
stored=True, commas=True, scorable=True, field_boost=field_class.boost)
elif field_class.field_type in ['date', 'datetime']:
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = DATETIME(
stored=field_class.stored, sortable=True)
elif field_class.field_type == 'integer':
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = NUMERIC(
stored=field_class.stored, numtype=int, field_boost=field_class.boost)
elif field_class.field_type == 'float':
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = NUMERIC(
stored=field_class.stored, numtype=float, field_boost=field_class.boost)
elif field_class.field_type == 'boolean':
# Field boost isn't supported on BOOLEAN as of 1.8.2.
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = BOOLEAN(
stored=field_class.stored)
elif field_class.field_type == 'ngram':
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = NGRAM(
minsize=3, maxsize=15, stored=field_class.stored, field_boost=field_class.boost)
elif field_class.field_type == 'edge_ngram':
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = NGRAMWORDS(minsize=2, maxsize=15, at='start',
stored=field_class.stored,
field_boost=field_class.boost)
else:
# schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = TEXT(stored=True, analyzer=StemmingAnalyzer(), field_boost=field_class.boost, sortable=True)
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname] = TEXT(
stored=True, analyzer=ChineseAnalyzer(), field_boost=field_class.boost, sortable=True)
if field_class.document is True:
content_field_name = field_class.index_fieldname
schema_fields[field_class.index_fieldname].spelling = True
# Fail more gracefully than relying on the backend to die if no fields
# are found.
if len(schema_fields) <= initial_key_count:
raise SearchBackendError(
"No fields were found in any search_indexes. Please correct this before attempting to search.")
return (content_field_name, Schema(**schema_fields))
def update(self, index, iterable, commit=True):
if not self.setup_complete:
self.setup()
self.index = self.index.refresh()
writer = AsyncWriter(self.index)
for obj in iterable:
try:
doc = index.full_prepare(obj)
except SkipDocument:
self.log.debug(u"Indexing for object `%s` skipped", obj)
else:
# Really make sure it's unicode, because Whoosh won't have it any
# other way.
for key in doc:
doc[key] = self._from_python(doc[key])
# Document boosts aren't supported in Whoosh 2.5.0+.
if 'boost' in doc:
del doc['boost']
try:
writer.update_document(**doc)
except Exception as e:
if not self.silently_fail:
raise
# We'll log the object identifier but won't include the actual object
# to avoid the possibility of that generating encoding errors while
# processing the log message:
self.log.error(
u"%s while preparing object for update" %
e.__class__.__name__,
exc_info=True,
extra={
"data": {
"index": index,
"object": get_identifier(obj)}})
if len(iterable) > 0:
# For now, commit no matter what, as we run into locking issues
# otherwise.
writer.commit()
def remove(self, obj_or_string, commit=True):
if not self.setup_complete:
self.setup()
self.index = self.index.refresh()
whoosh_id = get_identifier(obj_or_string)
try:
self.index.delete_by_query(
q=self.parser.parse(
u'%s:"%s"' %
(ID, whoosh_id)))
except Exception as e:
if not self.silently_fail:
raise
self.log.error(
"Failed to remove document '%s' from Whoosh: %s",
whoosh_id,
e,
exc_info=True)
def clear(self, models=None, commit=True):
if not self.setup_complete:
self.setup()
self.index = self.index.refresh()
if models is not None:
assert isinstance(models, (list, tuple))
try:
if models is None:
self.delete_index()
else:
models_to_delete = []
for model in models:
models_to_delete.append(
u"%s:%s" %
(DJANGO_CT, get_model_ct(model)))
self.index.delete_by_query(
q=self.parser.parse(
u" OR ".join(models_to_delete)))
except Exception as e:
if not self.silently_fail:
raise
if models is not None:
self.log.error(
"Failed to clear Whoosh index of models '%s': %s",
','.join(models_to_delete),
e,
exc_info=True)
else:
self.log.error(
"Failed to clear Whoosh index: %s", e, exc_info=True)
def delete_index(self):
# Per the Whoosh mailing list, if wiping out everything from the index,
# it's much more efficient to simply delete the index files.
if self.use_file_storage and os.path.exists(self.path):
shutil.rmtree(self.path)
elif not self.use_file_storage:
self.storage.clean()
# Recreate everything.
self.setup()
def optimize(self):
if not self.setup_complete:
self.setup()
self.index = self.index.refresh()
self.index.optimize()
def calculate_page(self, start_offset=0, end_offset=None):
# Prevent against Whoosh throwing an error. Requires an end_offset
# greater than 0.
if end_offset is not None and end_offset <= 0:
end_offset = 1
# Determine the page.
page_num = 0
if end_offset is None:
end_offset = 1000000
if start_offset is None:
start_offset = 0
page_length = end_offset - start_offset
if page_length and page_length > 0:
page_num = int(start_offset / page_length)
# Increment because Whoosh uses 1-based page numbers.
page_num += 1
return page_num, page_length
@log_query
def search(
self,
query_string,
sort_by=None,
start_offset=0,
end_offset=None,
fields='',
highlight=False,
facets=None,
date_facets=None,
query_facets=None,
narrow_queries=None,
spelling_query=None,
within=None,
dwithin=None,
distance_point=None,
models=None,
limit_to_registered_models=None,
result_class=None,
**kwargs):
if not self.setup_complete:
self.setup()
# A zero length query should return no results.
if len(query_string) == 0:
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
}
query_string = force_str(query_string)
# A one-character query (non-wildcard) gets nabbed by a stopwords
# filter and should yield zero results.
if len(query_string) <= 1 and query_string != u'*':
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
}
reverse = False
if sort_by is not None:
# Determine if we need to reverse the results and if Whoosh can
# handle what it's being asked to sort by. Reversing is an
# all-or-nothing action, unfortunately.
sort_by_list = []
reverse_counter = 0
for order_by in sort_by:
if order_by.startswith('-'):
reverse_counter += 1
if reverse_counter and reverse_counter != len(sort_by):
raise SearchBackendError("Whoosh requires all order_by fields"
" to use the same sort direction")
for order_by in sort_by:
if order_by.startswith('-'):
sort_by_list.append(order_by[1:])
if len(sort_by_list) == 1:
reverse = True
else:
sort_by_list.append(order_by)
if len(sort_by_list) == 1:
reverse = False
sort_by = sort_by_list[0]
if facets is not None:
warnings.warn(
"Whoosh does not handle faceting.",
Warning,
stacklevel=2)
if date_facets is not None:
warnings.warn(
"Whoosh does not handle date faceting.",
Warning,
stacklevel=2)
if query_facets is not None:
warnings.warn(
"Whoosh does not handle query faceting.",
Warning,
stacklevel=2)
narrowed_results = None
self.index = self.index.refresh()
if limit_to_registered_models is None:
limit_to_registered_models = getattr(
settings, 'HAYSTACK_LIMIT_TO_REGISTERED_MODELS', True)
if models and len(models):
model_choices = sorted(get_model_ct(model) for model in models)
elif limit_to_registered_models:
# Using narrow queries, limit the results to only models handled
# with the current routers.
model_choices = self.build_models_list()
else:
model_choices = []
if len(model_choices) > 0:
if narrow_queries is None:
narrow_queries = set()
narrow_queries.add(' OR '.join(
['%s:%s' % (DJANGO_CT, rm) for rm in model_choices]))
narrow_searcher = None
if narrow_queries is not None:
# Potentially expensive? I don't see another way to do it in
# Whoosh...
narrow_searcher = self.index.searcher()
for nq in narrow_queries:
recent_narrowed_results = narrow_searcher.search(
self.parser.parse(force_str(nq)), limit=None)
if len(recent_narrowed_results) <= 0:
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
}
if narrowed_results:
narrowed_results.filter(recent_narrowed_results)
else:
narrowed_results = recent_narrowed_results
self.index = self.index.refresh()
if self.index.doc_count():
searcher = self.index.searcher()
parsed_query = self.parser.parse(query_string)
# In the event of an invalid/stopworded query, recover gracefully.
if parsed_query is None:
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
}
page_num, page_length = self.calculate_page(
start_offset, end_offset)
search_kwargs = {
'pagelen': page_length,
'sortedby': sort_by,
'reverse': reverse,
}
# Handle the case where the results have been narrowed.
if narrowed_results is not None:
search_kwargs['filter'] = narrowed_results
try:
raw_page = searcher.search_page(
parsed_query,
page_num,
**search_kwargs
)
except ValueError:
if not self.silently_fail:
raise
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
'spelling_suggestion': None,
}
# Because as of Whoosh 2.5.1, it will return the wrong page of
# results if you request something too high. :(
if raw_page.pagenum < page_num:
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
'spelling_suggestion': None,
}
results = self._process_results(
raw_page,
highlight=highlight,
query_string=query_string,
spelling_query=spelling_query,
result_class=result_class)
searcher.close()
if hasattr(narrow_searcher, 'close'):
narrow_searcher.close()
return results
else:
if self.include_spelling:
if spelling_query:
spelling_suggestion = self.create_spelling_suggestion(
spelling_query)
else:
spelling_suggestion = self.create_spelling_suggestion(
query_string)
else:
spelling_suggestion = None
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
'spelling_suggestion': spelling_suggestion,
}
def more_like_this(
self,
model_instance,
additional_query_string=None,
start_offset=0,
end_offset=None,
models=None,
limit_to_registered_models=None,
result_class=None,
**kwargs):
if not self.setup_complete:
self.setup()
# Deferred models will have a different class ("RealClass_Deferred_fieldname")
# which won't be in our registry:
model_klass = model_instance._meta.concrete_model
field_name = self.content_field_name
narrow_queries = set()
narrowed_results = None
self.index = self.index.refresh()
if limit_to_registered_models is None:
limit_to_registered_models = getattr(
settings, 'HAYSTACK_LIMIT_TO_REGISTERED_MODELS', True)
if models and len(models):
model_choices = sorted(get_model_ct(model) for model in models)
elif limit_to_registered_models:
# Using narrow queries, limit the results to only models handled
# with the current routers.
model_choices = self.build_models_list()
else:
model_choices = []
if len(model_choices) > 0:
if narrow_queries is None:
narrow_queries = set()
narrow_queries.add(' OR '.join(
['%s:%s' % (DJANGO_CT, rm) for rm in model_choices]))
if additional_query_string and additional_query_string != '*':
narrow_queries.add(additional_query_string)
narrow_searcher = None
if narrow_queries is not None:
# Potentially expensive? I don't see another way to do it in
# Whoosh...
narrow_searcher = self.index.searcher()
for nq in narrow_queries:
recent_narrowed_results = narrow_searcher.search(
self.parser.parse(force_str(nq)), limit=None)
if len(recent_narrowed_results) <= 0:
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
}
if narrowed_results:
narrowed_results.filter(recent_narrowed_results)
else:
narrowed_results = recent_narrowed_results
page_num, page_length = self.calculate_page(start_offset, end_offset)
self.index = self.index.refresh()
raw_results = EmptyResults()
if self.index.doc_count():
query = "%s:%s" % (ID, get_identifier(model_instance))
searcher = self.index.searcher()
parsed_query = self.parser.parse(query)
results = searcher.search(parsed_query)
if len(results):
raw_results = results[0].more_like_this(
field_name, top=end_offset)
# Handle the case where the results have been narrowed.
if narrowed_results is not None and hasattr(raw_results, 'filter'):
raw_results.filter(narrowed_results)
try:
raw_page = ResultsPage(raw_results, page_num, page_length)
except ValueError:
if not self.silently_fail:
raise
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
'spelling_suggestion': None,
}
# Because as of Whoosh 2.5.1, it will return the wrong page of
# results if you request something too high. :(
if raw_page.pagenum < page_num:
return {
'results': [],
'hits': 0,
'spelling_suggestion': None,
}
results = self._process_results(raw_page, result_class=result_class)
searcher.close()
if hasattr(narrow_searcher, 'close'):
narrow_searcher.close()
return results
def _process_results(
self,
raw_page,
highlight=False,
query_string='',
spelling_query=None,
result_class=None):
from haystack import connections
results = []
# It's important to grab the hits first before slicing. Otherwise, this
# can cause pagination failures.
hits = len(raw_page)
if result_class is None:
result_class = SearchResult
facets = {}
spelling_suggestion = None
unified_index = connections[self.connection_alias].get_unified_index()
indexed_models = unified_index.get_indexed_models()
for doc_offset, raw_result in enumerate(raw_page):
score = raw_page.score(doc_offset) or 0
app_label, model_name = raw_result[DJANGO_CT].split('.')
additional_fields = {}
model = haystack_get_model(app_label, model_name)
if model and model in indexed_models:
for key, value in raw_result.items():
index = unified_index.get_index(model)
string_key = str(key)
if string_key in index.fields and hasattr(
index.fields[string_key], 'convert'):
# Special-cased due to the nature of KEYWORD fields.
if index.fields[string_key].is_multivalued:
if value is None or len(value) == 0:
additional_fields[string_key] = []
else:
additional_fields[string_key] = value.split(
',')
else:
additional_fields[string_key] = index.fields[string_key].convert(
value)
else:
additional_fields[string_key] = self._to_python(value)
del (additional_fields[DJANGO_CT])
del (additional_fields[DJANGO_ID])
if highlight:
sa = StemmingAnalyzer()
formatter = WhooshHtmlFormatter('em')
terms = [token.text for token in sa(query_string)]
whoosh_result = whoosh_highlight(
additional_fields.get(self.content_field_name),
terms,
sa,
ContextFragmenter(),
formatter
)
additional_fields['highlighted'] = {
self.content_field_name: [whoosh_result],
}
result = result_class(
app_label,
model_name,
raw_result[DJANGO_ID],
score,
**additional_fields)
results.append(result)
else:
hits -= 1
if self.include_spelling:
if spelling_query:
spelling_suggestion = self.create_spelling_suggestion(
spelling_query)
else:
spelling_suggestion = self.create_spelling_suggestion(
query_string)
return {
'results': results,
'hits': hits,
'facets': facets,
'spelling_suggestion': spelling_suggestion,
}
def create_spelling_suggestion(self, query_string):
spelling_suggestion = None
reader = self.index.reader()
corrector = reader.corrector(self.content_field_name)
cleaned_query = force_str(query_string)
if not query_string:
return spelling_suggestion
# Clean the string.
for rev_word in self.RESERVED_WORDS:
cleaned_query = cleaned_query.replace(rev_word, '')
for rev_char in self.RESERVED_CHARACTERS:
cleaned_query = cleaned_query.replace(rev_char, '')
# Break it down.
query_words = cleaned_query.split()
suggested_words = []
for word in query_words:
suggestions = corrector.suggest(word, limit=1)
if len(suggestions) > 0:
suggested_words.append(suggestions[0])
spelling_suggestion = ' '.join(suggested_words)
return spelling_suggestion
def _from_python(self, value):
"""
Converts Python values to a string for Whoosh.
Code courtesy of pysolr.
"""
if hasattr(value, 'strftime'):
if not hasattr(value, 'hour'):
value = datetime(value.year, value.month, value.day, 0, 0, 0)
elif isinstance(value, bool):
if value:
value = 'true'
else:
value = 'false'
elif isinstance(value, (list, tuple)):
value = u','.join([force_str(v) for v in value])
elif isinstance(value, (six.integer_types, float)):
# Leave it alone.
pass
else:
value = force_str(value)
return value
def _to_python(self, value):
"""
Converts values from Whoosh to native Python values.
A port of the same method in pysolr, as they deal with data the same way.
"""
if value == 'true':
return True
elif value == 'false':
return False
if value and isinstance(value, six.string_types):
possible_datetime = DATETIME_REGEX.search(value)
if possible_datetime:
date_values = possible_datetime.groupdict()
for dk, dv in date_values.items():
date_values[dk] = int(dv)
return datetime(
date_values['year'],
date_values['month'],
date_values['day'],
date_values['hour'],
date_values['minute'],
date_values['second'])
try:
# Attempt to use json to load the values.
converted_value = json.loads(value)
# Try to handle most built-in types.
if isinstance(
converted_value,
(list,
tuple,
set,
dict,
six.integer_types,
float,
complex)):
return converted_value
except BaseException:
# If it fails (SyntaxError or its ilk) or we don't trust it,
# continue on.
pass
return value
class WhooshSearchQuery(BaseSearchQuery):
def _convert_datetime(self, date):
if hasattr(date, 'hour'):
return force_str(date.strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S'))
else:
return force_str(date.strftime('%Y%m%d000000'))
def clean(self, query_fragment):
"""
Provides a mechanism for sanitizing user input before presenting the
value to the backend.
Whoosh 1.X differs here in that you can no longer use a backslash
to escape reserved characters. Instead, the whole word should be
quoted.
"""
words = query_fragment.split()
cleaned_words = []
for word in words:
if word in self.backend.RESERVED_WORDS:
word = word.replace(word, word.lower())
for char in self.backend.RESERVED_CHARACTERS:
if char in word:
word = "'%s'" % word
break
cleaned_words.append(word)
return ' '.join(cleaned_words)
def build_query_fragment(self, field, filter_type, value):
from haystack import connections
query_frag = ''
is_datetime = False
if not hasattr(value, 'input_type_name'):
# Handle when we've got a ``ValuesListQuerySet``...
if hasattr(value, 'values_list'):
value = list(value)
if hasattr(value, 'strftime'):
is_datetime = True
if isinstance(value, six.string_types) and value != ' ':
# It's not an ``InputType``. Assume ``Clean``.
value = Clean(value)
else:
value = PythonData(value)
# Prepare the query using the InputType.
prepared_value = value.prepare(self)
if not isinstance(prepared_value, (set, list, tuple)):
# Then convert whatever we get back to what pysolr wants if needed.
prepared_value = self.backend._from_python(prepared_value)
# 'content' is a special reserved word, much like 'pk' in
# Django's ORM layer. It indicates 'no special field'.
if field == 'content':
index_fieldname = ''
else:
index_fieldname = u'%s:' % connections[self._using].get_unified_index(
).get_index_fieldname(field)
filter_types = {
'content': '%s',
'contains': '*%s*',
'endswith': "*%s",
'startswith': "%s*",
'exact': '%s',
'gt': "{%s to}",
'gte': "[%s to]",
'lt': "{to %s}",
'lte': "[to %s]",
'fuzzy': u'%s~',
}
if value.post_process is False:
query_frag = prepared_value
else:
if filter_type in [
'content',
'contains',
'startswith',
'endswith',
'fuzzy']:
if value.input_type_name == 'exact':
query_frag = prepared_value
else:
# Iterate over terms & incorportate the converted form of
# each into the query.
terms = []
if isinstance(prepared_value, six.string_types):
possible_values = prepared_value.split(' ')
else:
if is_datetime is True:
prepared_value = self._convert_datetime(
prepared_value)
possible_values = [prepared_value]
for possible_value in possible_values:
terms.append(
filter_types[filter_type] %
self.backend._from_python(possible_value))
if len(terms) == 1:
query_frag = terms[0]
else:
query_frag = u"(%s)" % " AND ".join(terms)
elif filter_type == 'in':
in_options = []
for possible_value in prepared_value:
is_datetime = False
if hasattr(possible_value, 'strftime'):
is_datetime = True
pv = self.backend._from_python(possible_value)
if is_datetime is True:
pv = self._convert_datetime(pv)
if isinstance(pv, six.string_types) and not is_datetime:
in_options.append('"%s"' % pv)
else:
in_options.append('%s' % pv)
query_frag = "(%s)" % " OR ".join(in_options)
elif filter_type == 'range':
start = self.backend._from_python(prepared_value[0])
end = self.backend._from_python(prepared_value[1])
if hasattr(prepared_value[0], 'strftime'):
start = self._convert_datetime(start)
if hasattr(prepared_value[1], 'strftime'):
end = self._convert_datetime(end)
query_frag = u"[%s to %s]" % (start, end)
elif filter_type == 'exact':
if value.input_type_name == 'exact':
query_frag = prepared_value
else:
prepared_value = Exact(prepared_value).prepare(self)
query_frag = filter_types[filter_type] % prepared_value
else:
if is_datetime is True:
prepared_value = self._convert_datetime(prepared_value)
query_frag = filter_types[filter_type] % prepared_value
if len(query_frag) and not isinstance(value, Raw):
if not query_frag.startswith('(') and not query_frag.endswith(')'):
query_frag = "(%s)" % query_frag
return u"%s%s" % (index_fieldname, query_frag)
# if not filter_type in ('in', 'range'):
# # 'in' is a bit of a special case, as we don't want to
# # convert a valid list/tuple to string. Defer handling it
# # until later...
# value = self.backend._from_python(value)
class WhooshEngine(BaseEngine):
backend = WhooshSearchBackend
query = WhooshSearchQuery
'''2.修改源码中文件'''
# 在全局引入的最后一行加入jieba分词器
from jieba.analyse import ChineseAnalyzer
# 修改为中文分词法
# 查找
# analyzer=StemmingAnalyzer()
# 改为
analyzer=ChineseAnalyzer()
即可完成了。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-406799.html
方式二:haystack+ES
总结:
简单的搜索可以使用SQL语句,
whoosh是纯python实现的搜索引擎。whoosh在功能和性能上是比不上ES的,项目中使用es全局搜索,我们下次再来,每天进步一点点。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-406799.html
到了这里,关于【ElasticSearch和whoosh实现项目中搜索功能】的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!