近期忙于写论文,分享一下论文中表格数据的计算方法。
目录
一、FLOPS、FLOPs和GFLOPs的概念
二、计算VGG16的GFLOPs和参数量
三、计算DETR的GFLOPs和参数量
四、整理数据表格
一、FLOPS、FLOPs和GFLOPs的概念
- FLOPS:注意S是大写,是 “每秒所执行的浮点运算次数”(floating-point operations per second)的缩写。它常被用来估算电脑的执行效能,尤其是在使用到大量浮点运算的科学计算领域中。正因为FLOPS字尾的那个S,代表秒,而不是复数,所以不能省略掉。
- FLOPs:注意s小写,是floating point operations的缩写(s表复数),意指浮点运算数,理解为计算量。可以用来衡量算法/模型的复杂度。
- GFLOPs:一个GFLOPs等于每秒十亿(=10^9)次的浮点运算。
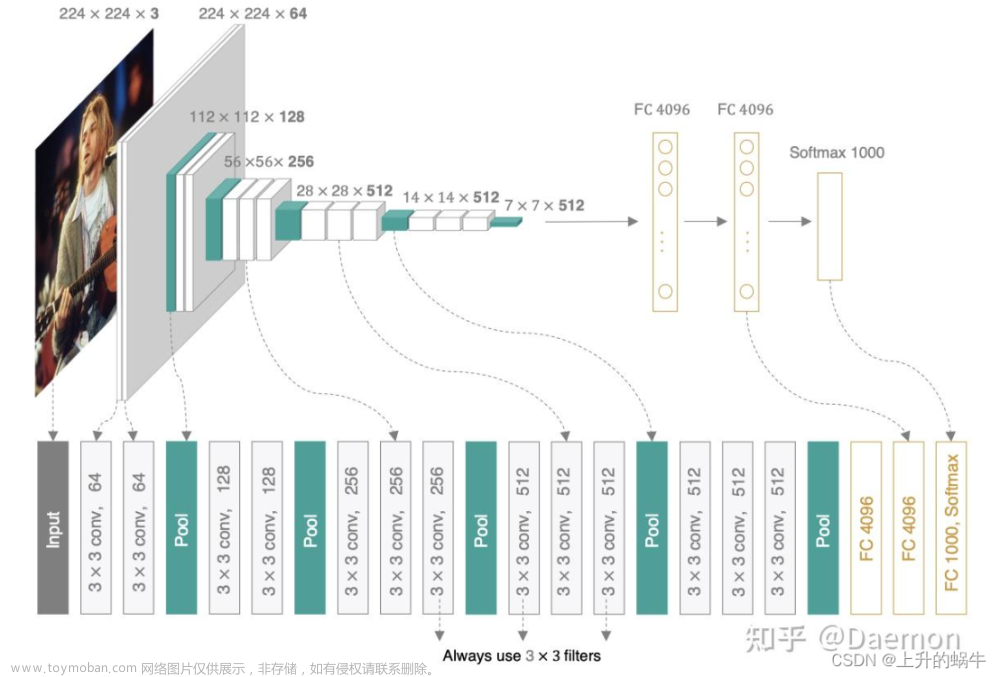
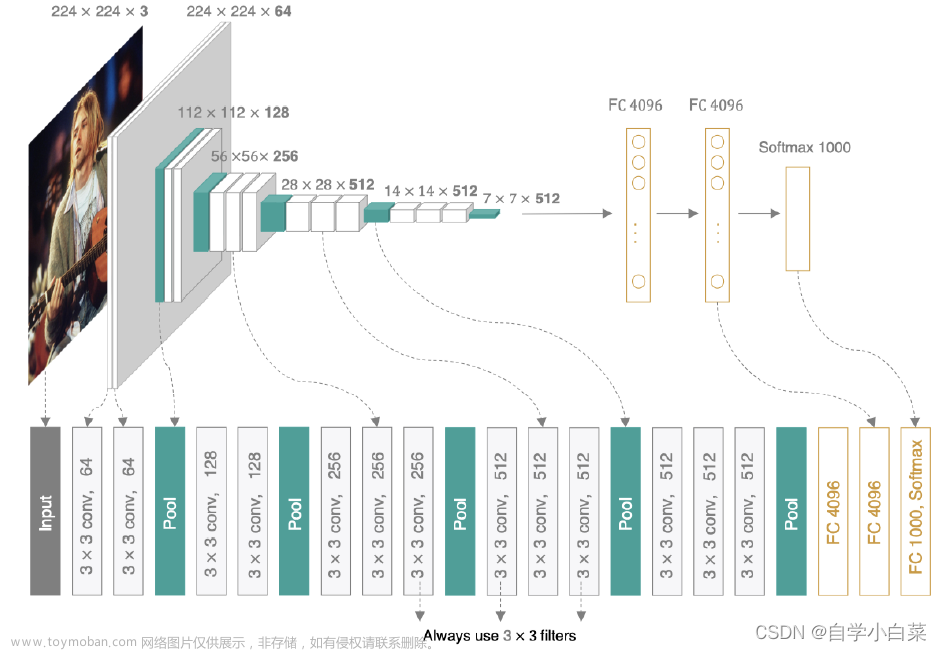
二、计算VGG16的GFLOPs和参数量
from thop import profile
import torch
import torchvision.models as models
model = models.vgg16()
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model.to(device)
input = torch.zeros((1, 3, 224, 224)).to(device)
flops, params = profile(model.to(device), inputs=(input,))
print("参数量:", params)
print("FLOPS:", flops)>>>output
参数量: 138357544.0
FLOPS: 15470314496.0
三、计算DETR的GFLOPs和参数量
- 首先,访问网址:GitHub - facebookresearch/detr: End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers
- 然后,下载DETR源码压缩包,调通源码。
- 最后,把下面的代码封装到py文件中,放到DETR源码的根目录即可。
import os
import time
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as T
torch.set_grad_enabled(False)
from models import build_model
import argparse
from torch.nn.functional import dropout,linear,softmax
def get_args_parser():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser('Set transformer detector', add_help=False)
parser.add_argument('--lr', default=1e-4, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--lr_backbone', default=1e-5, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--batch_size', default=1, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--weight_decay', default=1e-4, type=float)
# parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=300, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=100, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--lr_drop', default=200, type=int)
parser.add_argument('--clip_max_norm', default=0.1, type=float,
help='gradient clipping max norm')
# Model parameters
parser.add_argument('--frozen_weights', type=str, default=None,
help="Path to the pretrained model. If set, only the mask head will be trained")
# * Backbone
parser.add_argument('--backbone', default='resnet50', type=str,
help="Name of the convolutional backbone to use")
parser.add_argument('--dilation', action='store_true',
help="If true, we replace stride with dilation in the last convolutional block (DC5)")
parser.add_argument('--position_embedding', default='sine', type=str, choices=('sine', 'learned'),
help="Type of positional embedding to use on top of the image features")
# * Transformer
parser.add_argument('--enc_layers', default=6, type=int,
help="Number of encoding layers in the transformer")
parser.add_argument('--dec_layers', default=6, type=int,
help="Number of decoding layers in the transformer")
parser.add_argument('--dim_feedforward', default=2048, type=int,
help="Intermediate size of the feedforward layers in the transformer blocks")
parser.add_argument('--hidden_dim', default=256, type=int,
help="Size of the embeddings (dimension of the transformer)")
parser.add_argument('--dropout', default=0.1, type=float,
help="Dropout applied in the transformer")
parser.add_argument('--nheads', default=8, type=int,
help="Number of attention heads inside the transformer's attentions")
parser.add_argument('--num_queries', default=40, type=int,
help="Number of query slots") # 论文中对象查询为100
parser.add_argument('--pre_norm', action='store_true')
# * Segmentation
parser.add_argument('--masks', action='store_true',
help="Train segmentation head if the flag is provided")
# Loss
parser.add_argument('--no_aux_loss', dest='aux_loss', action='store_false',
help="Disables auxiliary decoding losses (loss at each layer)")
# * Matcher
parser.add_argument('--set_cost_class', default=1, type=float,
help="Class coefficient in the matching cost")
parser.add_argument('--set_cost_bbox', default=5, type=float,
help="L1 box coefficient in the matching cost")
parser.add_argument('--set_cost_giou', default=2, type=float,
help="giou box coefficient in the matching cost")
# * Loss coefficients
parser.add_argument('--mask_loss_coef', default=1, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--dice_loss_coef', default=1, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--bbox_loss_coef', default=5, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--giou_loss_coef', default=2, type=float)
parser.add_argument('--eos_coef', default=0.1, type=float,
help="Relative classification weight of the no-object class")
# dataset parameters
parser.add_argument('--dataset_file', default='coco')
parser.add_argument('--coco_path', default='', type=str)
parser.add_argument('--coco_panoptic_path', type=str)
parser.add_argument('--remove_difficult', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--output_dir', default='E:\project_yd\paper_sci_one_yd\Transformer\DETR\detr\\runs\\train',
help='path where to save, empty for no saving')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='cuda',
help='device to use for training / testing')
parser.add_argument('--seed', default=42, type=int)
# ============================================================================= #
parser.add_argument('--resume', default='', help='resume from checkpoint')
# ============================================================================= #
parser.add_argument('--start_epoch', default=0, type=int, metavar='N',
help='start epoch')
parser.add_argument('--eval', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--num_workers', default=2, type=int)
# distributed training parameters
parser.add_argument('--world_size', default=1, type=int,
help='number of distributed processes')
parser.add_argument('--dist_url', default='env://', help='url used to set up distributed training')
return parser
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser('DETR training and evaluation script', parents=[get_args_parser()])
args = parser.parse_args()
# 建立模型
model, criterion, postprocessors = build_model(args)
model.to('cuda:0')
url = r'detr-r50-dc5-f0fb7ef5.pth'
state_dict = torch.load(url)
# print(state_dict)
# 加载模型参数,以字典的形式表示
model.load_state_dict(state_dict['model'])
model.eval() # 把字符串类型转换成字典类型
# ==================================================== #
from thop import profile
import torchsummary
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model.to(device)
input = torch.zeros((1, 3, 800, 1422)).to(device)
flops, params = profile(model.to(device), inputs=(input,))
print("参数量:", params)
print("FLOPS:", flops)
# ==================================================== #>>> output
参数量: 36739785.0
FLOPS: 100937364480.0
四、整理数据表格
| Model | GFLOPs | Params |
|---|---|---|
| VGG16 | 15.47 | 13.84 M |
| DETR | 100.94 | 36.74 M |
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-406817.html
>>> 如有疑问,欢迎评论区一起探讨!文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-406817.html
到了这里,关于计算模型的GFLOPs和参数量 & 举例VGG16和DETR的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!