笔记链接
谷粒商城笔记(详细版) IDEA2021 基础篇(1/3).
谷粒商城笔记(详细版) IDEA2021 基础篇(2/3).
ES6 VUE 基础篇前端笔记
谷粒商城笔记(详细版) IDEA2021 基础篇(3/3).
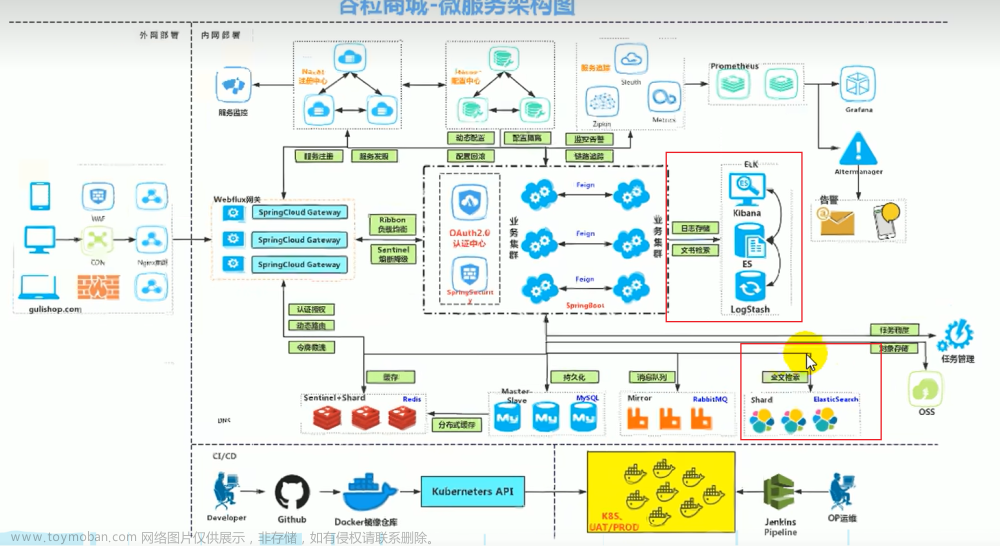
[谷粒商城笔记(详细版) IDEA2021 高级篇(第1篇)
1 全文检索 ElasticSearch 简介
1.1 基础简介



1.2 概念划分

索引对应mysql中的库
类型对应Mysql中的数据表
文档对应mysql中的一条条数据

在我们插入一条文档记录时
ElasticSearch会将其分成好几个单词存在一张倒排索引表中
在检索时 会对被检索的语句进行分词
到倒排索引表中查找 只要有单词命中就会查找出来对应的记录
看命中几次 会算出相关性得分 并进行排序
2 Docker 安装

2.1 拉取镜像
下载镜像
docker pull elasticsearch:7.4.2
下载可视化
docker pull kibana:7.4.2
下载后
查看所有镜像 docker images

2.2 创建实例 进行一定配置

2.2.1 在linux本机创建elasticsearch文件夹(后面将docker中的elastic配置文件与linux本机的配置文件绑定)
#Linux创建目录
mkdir -p /mydata/elasticsearch/config
mkdir -p /mydata/elasticsearch/data
mkdir -p /mydata/elasticsearch/plugins
# 将一条命令写入linux本机的创建的配置文件中
# es可以被远程任何机器访问
echo "http.host: 0.0.0.0" >/mydata/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml
# 递归更改权限,es需要访问
chmod -R 777 /mydata/elasticsearch/
关于这一行命令的具体解释
# 递归更改权限,es需要访问
chmod -R 777 /mydata/elasticsearch/
如果不加这一行会出现报错
报错解决
java.nio.file.AccessDeniedException: /usr/share/elasticsearch/data/nodes…
看错误我们会以为是es容器里的/usr/share/elasticsearch/data/nodes文件夹目录没有读写权限,其实给提示误导了,实际是挂载的目录没有读写权限
比如我们宿主主机的配置目录为:/usr/local/es/data,那么我们需要赋予它读写权限:
chmod 777 /usr/local/es/data
2.2.2 启动elasticsearch(将elasticsearch映射到本机)
# 9200是用户交互端口 9300是集群心跳端口
# -e指定是单阶段运行
# -e指定占用的内存大小,生产时可以设置32G
docker run --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 \
-e "discovery.type=single-node" \
-e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms64m -Xmx512m" \
-v /mydata/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml \
-v /mydata/elasticsearch/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data \
-v /mydata/elasticsearch/plugins:/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins \
-d elasticsearch:7.4.2
# 设置开机启动elasticsearch
docker update elasticsearch --restart=always
如果你买的是阿里云或者别的云服务器 记得在安全组里放行端口
接着远程ip访问9200端口

3 全文检索ElasticSearchsDocker安装Kibana

# 这里-e是自己的elasticsearch服务地址
docker run --name kibana -e ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS=http://192.168.56.10:9200 -p 5601:5601 -d kibana:7.4.2
# 设置开机启动kibana
docker update kibana --restart=always
如果是购买的服务器
放行你的端口后访问
服务器对应端口
4 _cat

给出一个例子
http://139.224.237.247:9200/_cat/indices

5 put&post新增数据
5 .1 put 方式发送
必须要求携带id
也是新增和修改二合一
这个id之前没有对应数据则 created创建
如果这个id之前有数据则会改为updated 更新
5 .2 Post 方式发送

不带id会随机给我们返回一个id 每次都不同 所以一直是新建created
带一个固定Id 第一次是created
接着以后是 updated
6 get查询数据&乐观锁宇段


乐观锁用法:通过“if_seq_no=1&if_primary_term=1”,当序列号匹配的时候,才进行修改,否则不修改。
7 更新文档 put&post修改数据
http://139.224.237.247:9200/customer/external/1/_update
POST customer/externel/1/_update
{
"doc":{
"name":"111"
}
}
或者
POST customer/externel/1
{
"doc":{
"name":"222"
}
}
或者
PUT customer/externel/1
{
"doc":{
"name":"222"
}
}
如果post更改数据带_update 会检查原数据 一样的话不做任何更改
版本号等都不会变
put更改数据不允许带_update
如果post put更改数据不带 _update 不会检查原数据 一旦更新版本号等各项都会改变
8 删除数据
删除文档 数据记录
DELETE customer/external/1
delete
http://139.224.237.xxx:9200/customer/external/1
{
"_index": "customer",
"_type": "external",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 18,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 17,
"_primary_term": 1
}
删除索引 数据库
DELETE customer
delete
http://139.224.237.xxx:9200/customer
{
"acknowledged": true
}
9 bulk批量操作

POST /customer/external/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":"1"}}
{"name":"a"}
{"index":{"_id":"2"}}
{"name":"b"}
新增两条数据
新增id为1的 对应 name为a
新增Id为2的 对应 name为b
语法格式
{action:{metadata}}\n
{request body }\n
{action:{metadata}}\n
{request body }\n
当某一条执行失败时 下一条仍能继续执行
{
"took" : 262,
"errors" : false,
"items" : [
{
"index" : {
"_index" : "customer", 索引
"_type" : "external", 类型
"_id" : "1", 文档
"_version" : 1, 版本
"result" : "created", 创建
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 201 新建成功
}
},
{
"index" : {
"_index" : "customer",
"_type" : "external",
"_id" : "2",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 1,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"status" : 201
}
}
]
}
POST /_bulk
{"delete":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog","_id":"123"}}
{"create":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog","_id":"123"}}
{"title":"my first blog post"}
{"index":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog"}}
{"title":"my second blog post"}
{"update":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog","_id":"123"}}
{"doc":{"title":"my updated blog post"}}
bank测试数据网址
https://gitee.com/xlh_blog/common_content/blob/master/es%E6%B5%8B%E8%AF%95%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE.json#
10 进阶:两种查询方式(Query DSL + 路径参数查询)
1 rest风格 + 参数在请求路径中
GET bank/_search?q=*&sort=account_number:asc
说明:
q=* # 查询所有
sort # 排序字段
asc #升序

2 rest风格 + 参数在请求体中 也被成为Query DSL
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match_all": {} },
"sort": [
{ "account_number": "asc" },
{ "balance":"desc"}
]
}
查询匹配所有
首先根据acconut number 升序排列
如果相同再 根据blance降序排列
11 进阶 QueryDSL
11.1 基本使用&match_all
基本结构
如果针对于某个字段,那么它的结构如下:
{
QUERY_NAME:{ # 使用的功能
FIELD_NAME:{ # 功能参数
ARGUMENT:VALUE,
ARGUMENT:VALUE,...
}
}
}
使用时不要加#注释内容
GET bank/_search
{
"query": { # 查询的字段
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0, # 从第几条文档开始查
"size": 5,
"_source":["account_number"], #指定只返回account_number字段
"sort": [
{
"account_number": { # 返回结果按哪个列排序
"order": "desc" # 降序
}
}
]
}
结果
11.2 query/match匹配查询
如果不是查询的值不是字符串则进行精确匹配
是字符串则进行全文检索
例1
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"account_number": "20"
}
}
}

例2
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "kings"
}
}
}
查询的结果相关性评分越高越靠前
这里相关性评分一致
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 5.9908285,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "20",
"_score" : 5.9908285,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 20,
"balance" : 16418,
"firstname" : "Elinor",
"lastname" : "Ratliff",
"age" : 36,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "282 Kings Place",
"employer" : "Scentric",
"email" : "elinorratliff@scentric.com",
"city" : "Ribera",
"state" : "WA"
}
},
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "722",
"_score" : 5.9908285,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 722,
"balance" : 27256,
"firstname" : "Roberts",
"lastname" : "Beasley",
"age" : 34,
"gender" : "F",
"address" : "305 Kings Hwy",
"employer" : "Quintity",
"email" : "robertsbeasley@quintity.com",
"city" : "Hayden",
"state" : "PA"
}
}
]
}
}
11.3 query/match_phrase [不拆分匹配]
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"address": "mill road"
}
}
}
match_phrase 即不拆分匹配
相当于只查询mill road都包含的address
而不进行拆分查询
结果
只查出一条mill road都包含的文档
{
"took" : 25,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 8.926605,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "970",
"_score" : 8.926605,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 970,
"balance" : 19648,
"firstname" : "Forbes",
"lastname" : "Wallace",
"age" : 28,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "990 Mill Road", 只查出一条mill road都包含的文档
"employer" : "Pheast",
"email" : "forbeswallace@pheast.com",
"city" : "Lopezo",
"state" : "AK"
}
}
]
}
}
11.4 query/multi_math【多字段匹配】
查询state 字段 或者 address字段中
有mill的文档
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "mill",
"fields": [
"state",
"address"
]
}
}
}
11.5 bool复合查询
must:必须达到must所列举的所有条件
must_not:必须不匹配must_not所列举的所有条件。
should:应该满足should所列举的条件。满足条件最好,不满足也可以,满足得分更高
特别注意
should:应该达到should列举的条件,如果到达会增加相关文档的评分,并不会改变查询的结果。如果query中只有should且只有一种匹配规则,那么should的条件就会被作为默认匹配条件并且改变查询结果
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"gender": "M"
}
},
{
"match": {
"address": "mill"
}
}
],
"must_not": [
{
"match": {
"age": "18"
}
}
],
"should": [
{
"match": {
"lastname": "Wallace"
}
}
]
}
}
}
11.6 query/filter【结果过滤】
使用规则和must must_not一样
只不过满足filter不会提供相关性得分
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": {"address": "mill" } }
],
"filter": { # query.bool.filter
"range": {
"balance": { # 哪个字段
"gte": "10000",
"lte": "20000"
}
}
}
}
}
}
这里先是查询所有匹配address=mill的文档,然后再根据10000<=balance<=20000进行过滤查询结果
11.7 term查询
和match用法一样。匹配某个属性的值。
全文检索字段用match,
其他非text字段匹配用term。
-全文检索字段用match,其他非text字段匹配用term
11.8 属性.keyword
“term”: {
“name.keyword”: “测试名称”
}
相当于对 测试名称进行不分词查询
实现完全匹配
12 aggregations聚合分析
聚合相当于对hits中的数据进行一定分析
并返回结果
有点相似mysql中的group By
"aggs":{ # 聚合
"aggs_name":{ # 这次聚合的名字,方便展示在结果集中
"AGG_TYPE":{} # 聚合的类型(avg,term,terms)
}
}
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "Mill"
}
},
"aggs": {
"ageAgg": { #聚合名称 自定义
"terms": { #聚合类型 terms类型 值统计 会返回有哪些值 这些值有多少
"field": "age",
"size": 10
}
},
"ageAvg": { # 聚合名 自定义
"avg": { #算平均值
"field": "age" #算age的平均值
}
},
"balanceAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
13 映射mapping创建
Mapping(映射)是用来定义一个文档(document),以及它所包含的属性(field)是如何存储和索引的。
mapping可以查看属性类型
类型
在我们添加数据的时候elasticsearch会自动判断数据类型
查看mapping信息:GET bank/_mapping
{
"bank" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"account_number" : {
"type" : "long" # long类型
},
"address" : {
"type" : "text", # 文本类型,会进行全文检索,进行分词
"fields" : {
"keyword" : { # addrss.keyword
"type" : "keyword", # 该字段必须全部匹配到
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"age" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"balance" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"city" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"email" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"employer" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"firstname" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"gender" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"lastname" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"state" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
ElasticSearch7-去掉type概念
Elasticsearch 8.x 不再支持URL中的type参数。
创建映射
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"email": {
"type": "keyword" # 指定为keyword
},
"name": {
"type": "text" # 全文检索。保存时候分词,检索时候进行分词匹配
}
}
}
}
注意映射被创建后只能增加不能被更改 新增映射语法如下
添加新的字段映射
PUT /my_index/_mapping
PUT /my_index/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"employee-id": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": false # 字段不能被检索。检索
}
}
}
14 数据迁移
对于已经存在的字段映射,我们不能更新。更新必须创建新的索引,进行数据迁移
相当于把一个表数据传给另一个表
不过另一个表的mapping映射规则可能不同于原表
因为新版本的elasticsearch去除了类型和这个概念
于是数据迁移的写法如下
新写法
POST reindex
{
"source":{
"index":"twitter"
},
"dest":{
"index":"new_twitters"
}
}
老写法
POST reindex
{
"source":{
"index":"twitter",
"twitter":"twitter"
},
"dest":{
"index":"new_twitters"
}
}
15 分词:安装ik分词
标准的分词器对中文支持较差
我们安装IK分词器
docker exec -it 87a /bin/bash
进入对应的容器中
cd到plugins目录下 准备安装分词器
wget https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases/download/v7.4.2/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.4.2.zip
发现提示没有wget
我们已经把主机和容器的plugins做映射
于是cd 到 主机的plugins进行安装
wget压缩文件然后解压
接着渠去到容器内部
查看是否安装成功
接着重启
docker restart 容器id
然后来到kibana再次进行ik分词测试
智能分词完成
16 分词 自定义扩展词库
修改/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins/ik/config中的IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE properties SYSTEM "http://java.sun.com/dtd/properties.dtd">
<properties>
<comment>IK Analyzer 扩展配置</comment>
<!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展字典 -->
<entry key="ext_dict"></entry>
<!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展停止词字典-->
<entry key="ext_stopwords"></entry>
<!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展字典 -->
<!-- <entry key="remote_ext_dict">words_location</entry> -->
<!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展停止词字典-->
<!-- <entry key="remote_ext_stopwords">words_location</entry> -->
</properties>
主要配置自己的远程扩展字典
使用Nginx做反向代理后就可以实现
17 SpringBoot整合high-everclient


由于spring-data-ES 在8.0以后不再被支持
也因为其他连接工具(JestClient RestTemplate)的非官方 封装不完善的特性 我们最终选用 ES-Rest-Client
首先创建一个新moudle
接着在pom文件中引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>7.4.2</version>
</dependency>
接着
spring-boot-dependencies中所依赖的ES版本位6.8.5,要改掉 否则会和你加的7.4.2版本冲突
我这里直接把maven仓库里的配置改了

重新刷新maven仓库
然后配置appliction.yml 注册到nacos 配置端口和名称
spring:
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
application:
name: gulimall-search
server:
port: 10002
logging:
level:
com.atguigu.gulimall: debug
配置启动类
主要排除数据库先关依赖 因为这个模块基于common
和开启eureka服务与注册
package com.atguigu.gulimall.search;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class GulimallSearchApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(GulimallSearchApplication.class, args);
}
}

接着编写config
返回一个RestHighLevelClient到LOC容器中
package com.atguigu.gulimall.search;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClientBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class GuliESConfig {
// public static final RequestOptions COMMON_OPTIONS;
//
// static {
// RequestOptions.Builder builder = RequestOptions.DEFAULT.toBuilder();
//
// COMMON_OPTIONS = builder.build();
// }
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient esRestClient() {
RestClientBuilder builder = null;
// 可以指定多个es
builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("139.224.237.24",9200,"http"));
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
return client;
}
}
创建一个controller测试注入是否成功
package com.atguigu.gulimall.search;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@RequestMapping("/search/test")
public class TestController {
@Autowired
GuliESConfig guliESConfig;
@RequestMapping("/1")
public void test1(){
System.out.println(guliESConfig);
}
}
打印出来了注入的对象
18 学习Java High Level REST Client的Api(官方文档)
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/java-rest/7.16/java-rest-high-document-index.html
18 ElasticSearch测试新增数据(api 里的index api)
官方文档
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/java-rest/7.16/java-rest-high.html
package com.atguigu.gulimall.search;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import lombok.Data;
import net.minidev.json.JSONArray;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.io.IOException;
@SpringBootTest
class GulimallSearchApplicationTests {
@Autowired
RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient;
@Test
public void indexData() throws IOException {
//1 创建 Indexrequest 记得加上在哪个索引下进行初始化
IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("users"); //哪个索引下
//2 设置 Indexrequest 的数据 Id
indexRequest.id("1"); //数据的id
User user = new User();
user.setAge(18);
user.setUsername("yyl");
String s = JSON.toJSONString(user); //要保存的内容
//3 设置 Indexrequest 的要保存的数据 这里使用json格式
indexRequest.source(s, XContentType.JSON);
//4 调用客户端 执行操作 执行index 添加
IndexResponse index = restHighLevelClient.index(indexRequest, GuliESConfig.COMMON_OPTIONS);
//提取有用的响应数据
System.out.println("es的响应数据是");
System.out.println(index);
}
@Data
class User{
private String username;
private Integer age;
}
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println("打印的是");
System.out.println(restHighLevelClient);
}
}
执行结果
使用Kibana 查看 数据添加成功文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-407085.html
GET users/_search
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-407085.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-407085.html
总结
到了这里,关于谷粒商城笔记(详细版) IDEA2021 高级篇1(2022/11/9)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!