个人主页:平行线也会相交
欢迎 点赞👍 收藏✨ 留言✉ 加关注💓本文由 平行线也会相交 原创
收录于专栏【数据结构初阶(C实现)】
二叉树遍历
什么是二叉树遍历:
二叉树遍历就是按照某种特定的规则,依次堆二叉树中的结点进行相应的操作,并且每个结点只操作一次。访问结点所做的操作依赖于具体的应用问题。遍历是二叉树上最重要的运算之一,也是二叉树上进行其它运算的基础。
我们以后看到二叉树应该这样去看待:把他看成根、左子树、右子树。
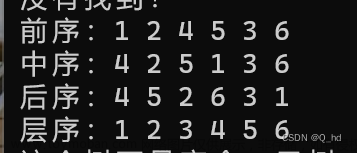
二叉树的遍历有:前序、中序、后序、层序遍历的递归结构遍历:
1.前序遍历(Preorder Traversal),也叫前根遍历:
2.中序遍历(Inorder Traversal),也叫中根遍历:
3.后序遍历(Post orderTraversal)也叫后根遍历:
4.层序遍历
前序遍历
下面是前序遍历的动态图。
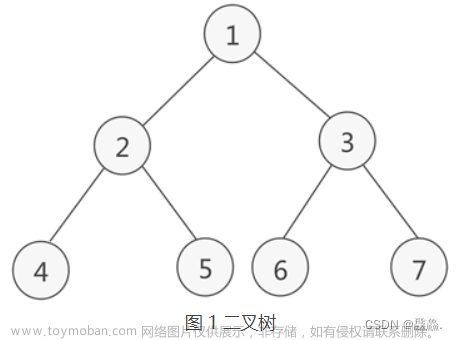
以下图为例进行代码的编写:
请看代码:
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PreOrder(root->left);
PreOrder(root->right);
}
这是运行结果:
中序遍历
请看中序遍历的动态图:

还是以下图进行举例:
请看代码:
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
下面是运行结果:
后序遍历
下面是后序遍历的动态图:
还是以下图进行举例:
//后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
请看运行结果:
前中后序总代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
//新建结点
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BTNode* CreatTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
return node1;
}
//前序遍历
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PreOrder(root->left);
PreOrder(root->right);
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
//后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatTree();
//PreOrder(root);//前序遍历
//InOrder(root);//中序遍历
//PostOrder(root);//后序遍历
return 0;
}
最后,其实前序、中序、后序的过程基本上就是一样的,即前序、中序、后序的递归过程是一样的,不一样的就是访问根的时机不一样。
层序遍历
层序遍历的话可以利用队列先进先出的特点来进行实现,出上一层,带入下一层。
所以这里的层序遍历就是利用队列来实现的。

注意队列中的结点里面的data存的是树结点的指针。
层序遍历总代码
Queue.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode* QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QueueNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QueueNode* head;
QueueNode* tail;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq,QDataType x);//插入数据
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);//删除数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);//取队头的数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);//取队尾的数据
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);//有多少个数据
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);//判断队列是否为空
Queue.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Queue.h"
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = NULL;
pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QueueNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = cur->next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
//删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
//if (pq->head == NULL)
//{
// return;
//}//温柔的处理
QueueNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->tail=NULL;
}
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)//取队尾的数据
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)//取队头的数据
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)//有多少个数据
{
assert(pq);
int n = 0;
QueueNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
n++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return n;
}
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include"Queue.h"
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
//新建结点
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BTNode* CreatTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
return node1;
}
//前序遍历
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PreOrder(root->left);
PreOrder(root->right);
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
//后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
int size = 0;
求树中结点个数法1
//int TreeSize(BTNode* root,int* psize)
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// return;
// (*psize)++;
// TreeSize(root->left, psize);
// TreeSize(root->right, psize);
//}
//求树的结点个数法2
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 :
TreeSize(root->left)
+ TreeSize(root->right)
+ 1;
}
//求树的高度
int TreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int leftHeight = TreeHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight = TreeHeight(root->right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
int TreeKLevel(BTNode* root, int k)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (k == 1)
return 1;
int leftK = TreeKLevel(root->left, k - 1);
int rightK = TreeKLevel(root->right, k - 1);
return leftK + rightK;
}
//二叉树查找值为x的结点
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data == x)
return root;
BTNode* lret = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);
if (lret)
return lret;
BTNode* rret = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);
if (rret)
return rret;
return NULL;
}
//层序遍历
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
//front指向的不是队列的结点,而是树的结点
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", front->data);
if (front->left)
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
if (front->right)
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
QueueDestory(&q);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatTree();
//PreOrder(root);//前序遍历
//InOrder(root);//中序遍历
//PostOrder(root);//后序遍历
求树的结点法1
/*int size1 = 0;
TreeSize(root, &size1);
printf("TreeSize:%d\n", size1);
int size2 = 0;
TreeSize(root, &size2);
printf("TreeSize:%d\n", size2);*/
求树的结点法2
//printf("TreeSize:%d\n", TreeSize(root));
//printf("TreeSize:%d\n", TreeSize(root));
//printf("TreeSize:%d\n", TreeSize(root));
求树的高度
//printf("TreeHeight:%d\n", TreeHeight(root));
//printf("TreeKLevel:%d\n", TreeKLevel(root, 1));
二叉树查找值为x的结点
//printf("BinaryTreeFind:%p\n", BinaryTreeFind(root, 5));
//printf("BinaryTreeFind:%p\n", BinaryTreeFind(root, 0));
//层序遍历
LevelOrder(root);
return 0;
}
 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-408463.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-408463.html
以上就是二叉树遍历的四种方式(前序、中序、后序、层序)。说实话,内容还是有些难度的,这就更需要我们认真的进行学习并复习了。
加油,各位!!!文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-408463.html
到了这里,关于【数据结构入门】二叉树的遍历(前序、中序、后序、层序)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!