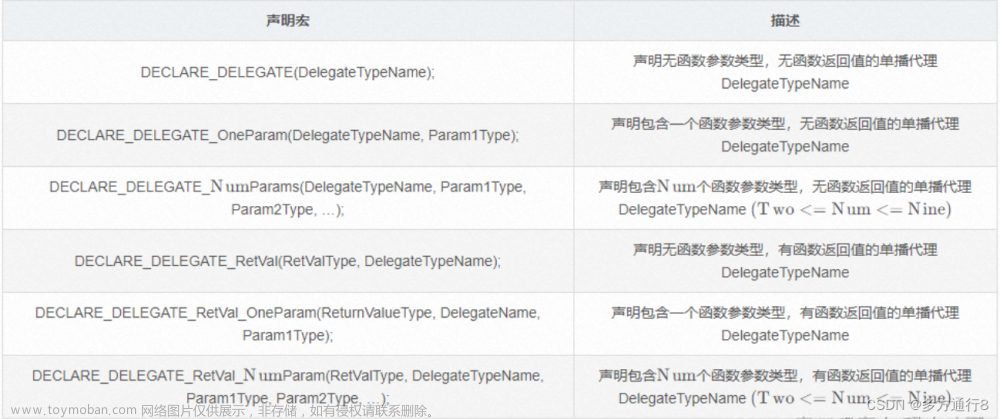
什么是委托
C# 中的委托(Delegate)类似于 C 或 C++ 中函数的指针。委托(Delegate) 是存有对某个方法的引用的一种引用类型变量。引用可在运行时被改变。
声明委托
委托声明决定了可由该委托引用的方法。委托可指向一个与其具有相同标签的方法。
语法
修饰符 delegate 返回值类型 委托名 ( 参数列表 );
delegate void IntMethodInvoker(intx);
定义了一个委托叫做 IntMethodInvoker ,这个委托可以指向带有一个int类型的参数,并且返回值是void的一个方法。
定义一个委托要定义方法的参数和返回值,使用delegate定义
delegate void FirstInvoke(int x);实例化委托
在定义好委托后就可以实例化委托,命名方法委托在实例化委托时必须带入方法的具体名称或者是null。
委托名 委托对象名 = new 委托名 ( 方法名 );
delegate void FirstInvoke(int x);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
FirstInvoke firstInvoke = new FirstInvoke(PutOutX);
}
public static void PutOutX(int x)
{
Console.WriteLine(x);
}委托的实现方法
delegate void FirstInvoke(int x);
delegate string Str();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
FirstInvoke firstInvoke = new FirstInvoke(PutOutX);
firstInvoke(3);
Str str = 872.ToString;
Console.WriteLine(str());
}
public static void PutOutX(int x)
{
Console.WriteLine(x);
}委托数组
委托名[] 委托对象名 = {委托的方法1,......};
FuncArray[] funcArray = { DoubleValue, AreaValue };委托做完函数的参数
访问类型 static 返回类型 方法名(委托类型 委托参数,参数.....)
public static void FuncAry(FuncArray func, int value) public delegate int FuncArray(int x);
public static void Test2()
{
//委托数组
FuncArray[] funcArray = { DoubleValue, AreaValue };
foreach(FuncArray func in funcArray)
{
FuncAry(func, 3);
}
}
public static int DoubleValue(int x)
{
return x * 2;
}
public static int AreaValue(int x)
{
return x * x;
}
/// <summary>
/// 委托可以作为参数使用
/// </summary>
/// <param name="func">委托</param>
/// <param name="value">传入的值</param>
public static void FuncAry(FuncArray func, int value)
{
Console.WriteLine("这是方法" + func + "值是" + func(value));
}Action
Action是.NET Framework内置的泛型委托,可以使用Action委托以参数形式传递方法,而不用显示声明自定义的委托。封装的方法必须与此委托定义的方法签名相对应。也就是说,封装的方法必须具有一个通过值传递给它的参数,并且不能有返回值。
Action<参数类型> 委托对象名 = 方法名
Action<int> action2 = Func2; public static void Test3()
{
Action action1 = Func1;
action1();
Action<int> action2 = Func2;
action2(1);
}
public static void Func1()
{
Console.WriteLine("0");
}
public static void Func2(int value)
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
} 
Func
参数最后一位就是返回值类型(返回值的类型和Func输出参数类型相同)
Func<参数,返回类型> 委托对象名 = 方法名
Func<int, int> func2 = Func4; Func<int> func1 = Func3;
Console.WriteLine(func1());
Func<int, int> func2 = Func4;
Console.WriteLine(func2(1));
public static int Func3()
{
return 0;
}
public static int Func4(int value)
{
return value;
}委托实现实例的排序
public static void Test4()
{
Employee[] employees =
{
new Employee("A",8),
new Employee("B",3),
new Employee("C",1),
new Employee("D",4),
new Employee("E",1),
new Employee("F",7),
new Employee("G",2),
};
Sort<Employee>(employees, Employee.Compare);
foreach(Employee e in employees)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Name + ":" + e.Salary);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 对雇员类按照制定排序方法排序
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">排序数据的类型</typeparam>
/// <param name="data">排序的对象</param>
/// <param name="compare">排序的方法</param>
public static void Sort<T>(T[] data,Func<T,T,bool> compare)
{
bool swapped = true;
do
{
swapped = false;
for (int i = 0; i < data.Length - 1; i++)
{
if (compare(data[i], data[i + 1]))
{
T temp = data[i];
data[i] = data[i + 1];
data[i + 1] = temp;
swapped = true;
}
}
} while (swapped );
}
}
internal class Employee
{
public string Name { get; private set; }
public double Salary { get; private set; }
public Employee(string name, double salary)
{
Name = name;
Salary = salary;
}
//雇员的比较方法
public static bool Compare(Employee e1,Employee e2)
{
return e1.Salary > e2.Salary;
}
}多播委托
委托可以包含多个方法,这种委托叫做多播委托。使用多播委托就可以按照顺序调用多个方法,多播委托只能得到调用的最后一个方法的结果,一般我们把多播委托的返回类型声明为void。
Action action1 = Test1;
action2 += Test2;
action2 -= Test1
//获取委托列表
Delegate[] delegate = action1.GetInvocationList();
public static void Test5()
{
FirstInvoke firstInvoke = null;
firstInvoke += PutOutX;
firstInvoke += DoubleValue;
firstInvoke(4);
} 
匿名方法
不用去定义一个方法,而是在后面直接使用匿名的方法。相当于直接把要引用的方法直接写在了后面,优点是减少了要编写的代码,减少代码的复杂性。
Func<T> 委托对象名 = delegate(方法参数){
方法体
};
public static void Test6()
{
Func<int, int, int> plue = delegate (int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
};
int res = plue(1, 2);
Console.WriteLine(res);
}事件
事件(Event)是类或者对象向其他类或对象通知发送的事情的一种特殊签名的委托
事件的声明
public event 委托类型 事件名;
事件使用event关键词来声明,他的返回值是一个委托类型
通常事件的命名,以名字+Event 作为他的名称,在编码中尽量使用规范命名,增加代码可读性。
工具人类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace _03_事件
{
//定义委托,可以让其他构造函数调用
delegate void DownStairDelegate();
/// <summary>
/// 工具人类
/// </summary>
class ToolMan
{
public string Name { get;private set; }
//声明委托,event可以让外部无法直接访问这个委托
public event DownStairDelegate DownStairDelegate = null;
public ToolMan(string name)
{
Name = name;
}
public void DownStair()
{
Console.WriteLine("工具人" + Name + "下楼了");
//在调用委托之前先检测委托是否为空
if (DownStairDelegate != null)
DownStairDelegate();
}
}
}
懒人类文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-413790.html
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace _03_事件
{
/// <summary>
/// 懒人的构造函数
/// </summary>
class LazyMan
{
public string Name { get;private set; }
public LazyMan(string name)
{
Name = name;
}
public void TakeFood()
{
Console.WriteLine("给" + Name + "拿了外卖");
}
public void TakePackage()
{
Console.WriteLine("给" + Name+"拿了快递");
}
}
}
主方法文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-413790.html
using System;
namespace _03_事件
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ToolMan toolMan = new ToolMan("A");
LazyMan lazyMan1 = new LazyMan("B");
LazyMan lazyMan2 = new LazyMan("C");
LazyMan lazyMan3 = new LazyMan("D");
toolMan.DownStair();
toolMan.DownStairDelegate += lazyMan1.TakeFood;
toolMan.DownStairDelegate += lazyMan2.TakePackage;
toolMan.DownStairDelegate += lazyMan3.TakeFood;
toolMan.DownStair();
toolMan.DownStairDelegate -= lazyMan1.TakeFood;
toolMan.DownStairDelegate -= lazyMan2.TakePackage;
toolMan.DownStair();
//toolMan.DownStairDelegate();
}
}
}
到了这里,关于C#——委托的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!