1. AQS 源码
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984972572414691L;
/**
* Creates a new {@code AbstractQueuedSynchronizer} instance
* with initial synchronization state of zero.
*/
protected AbstractQueuedSynchronizer() {
}
/**
* Wait queue node class.
* <p>
* 不管是条件队列,还是CLH等待队列
* 都是基于Node类
* <p>
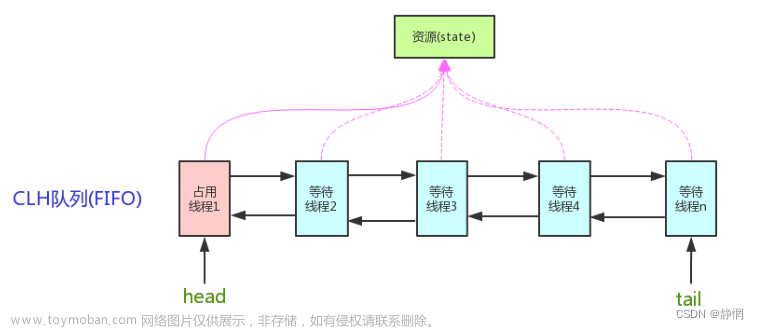
* AQS当中的同步等待队列也称CLH队列,CLH队列是Craig、Landin、Hagersten三人
* 发明的一种基于双向链表数据结构的队列,是FIFO先入先出线程等待队列,Java中的
* CLH队列是原CLH队列的一个变种,线程由原自旋机制改为阻塞机制。
*/
static final class Node {
/**
* 标记节点未共享模式
*/
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
/**
* 标记节点为独占模式
*/
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
/**
* 在同步队列中等待的线程等待超时或者被中断,需要从同步队列中取消等待
*/
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
/**
* 后继节点的线程处于等待状态,而当前的节点如果释放了同步状态或者被取消,
* 将会通知后继节点,使后继节点的线程得以运行。
*/
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
/**
* 节点在等待队列中,节点的线程等待在Condition上,当其他线程对Condition调用了signal()方法后,
* 该节点会从等待队列中转移到同步队列中,加入到同步状态的获取中
*/
static final int CONDITION = -2;
/**
* 表示下一次共享式同步状态获取将会被无条件地传播下去
*/
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
/**
* 标记当前节点的信号量状态 (1,0,-1,-2,-3)5种状态
* 使用CAS更改状态,volatile保证线程可见性,高并发场景下,
* 即被一个线程修改后,状态会立马让其他线程可见。
*/
volatile int waitStatus;
/**
* 前驱节点,当前节点加入到同步队列中被设置
*/
volatile Node prev;
/**
* 后继节点
*/
volatile Node next;
/**
* 节点同步状态的线程
*/
volatile Thread thread;
/**
* 等待队列中的后继节点,如果当前节点是共享的,那么这个字段是一个SHARED常量,
* 也就是说节点类型(独占和共享)和等待队列中的后继节点共用同一个字段。
*/
Node nextWaiter;
/**
* Returns true if node is waiting in shared mode.
*/
final boolean isShared() {
return nextWaiter == SHARED;
}
/**
* 返回前驱节点
*/
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
Node p = prev;
if (p == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
else
return p;
}
//空节点,用于标记共享模式
Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker
}
//用于同步队列CLH
Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiter
this.nextWaiter = mode;
this.thread = thread;
}
//用于条件队列
Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Condition
this.waitStatus = waitStatus;
this.thread = thread;
}
}
/**
* 指向同步等待队列的头节点
*/
private transient volatile Node head;
/**
* 指向同步等待队列的尾节点
*/
private transient volatile Node tail;
/**
* 同步资源状态
*/
private volatile int state;
protected final int getState() {
return state;
}
protected final void setState(int newState) {
state = newState;
}
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update);
}
static final long spinForTimeoutThreshold = 1000L;
/**
* 节点加入CLH同步队列
*/
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (; ; ) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
//队列为空需要初始化,创建空的头节点
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
//set尾部节点
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {//当前节点置为尾部
t.next = node; //前驱节点的next指针指向当前节点
return t;
}
}
}
}
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 1. 将当前线程构建成Node类型
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
// 2. 1当前尾节点是否为null?
if (pred != null) {
// 2.2 将当前节点尾插入的方式
node.prev = pred;
// 2.3 CAS将节点插入同步队列的尾部
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
private void setHead(Node node) {
head = node;
node.thread = null;
node.prev = null;
}
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
//获取wait状态
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);// 将等待状态waitStatus设置为初始值0
/**
* 若后继结点为空,或状态为CANCEL(已失效),则从后尾部往前遍历找到最前的一个处于正常阻塞状态的结点
* 进行唤醒
*/
Node s = node.next; //head.next = Node1 ,thread = T3
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);//唤醒线程,T3唤醒
}
/**
* 把当前结点设置为SIGNAL或者PROPAGATE
* 唤醒head.next(B节点),B节点唤醒后可以竞争锁,成功后head->B,然后又会唤醒B.next,一直重复直到共享节点都唤醒
* head节点状态为SIGNAL,重置head.waitStatus->0,唤醒head节点线程,唤醒后线程去竞争共享锁
* head节点状态为0,将head.waitStatus->Node.PROPAGATE传播状态,表示需要将状态向后继节点传播
*/
private void doReleaseShared() {
for (; ; ) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {//head是SIGNAL状态
/* head状态是SIGNAL,重置head节点waitStatus为0,E这里不直接设为Node.PROPAGAT,
* 是因为unparkSuccessor(h)中,如果ws < 0会设置为0,所以ws先设置为0,再设置为PROPAGATE
* 这里需要控制并发,因为入口有setHeadAndPropagate跟release两个,避免两次unpark
*/
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; //设置失败,重新循环
/* head状态为SIGNAL,且成功设置为0之后,唤醒head.next节点线程
* 此时head、head.next的线程都唤醒了,head.next会去竞争锁,成功后head会指向获取锁的节点,
* 也就是head发生了变化。看最底下一行代码可知,head发生变化后会重新循环,继续唤醒head的下一个节点
*/
unparkSuccessor(h);
/*
* 如果本身头节点的waitStatus是出于重置状态(waitStatus==0)的,将其设置为“传播”状态。
* 意味着需要将状态向后一个节点传播
*/
} else if (ws == 0 && !compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) //如果head变了,重新循环
break;
}
}
/**
* 把node节点设置成head节点,且Node.waitStatus->Node.PROPAGATE
*/
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {
Node h = head; //h用来保存旧的head节点
setHead(node);//head引用指向node节点
/* 这里意思有两种情况是需要执行唤醒操作
* 1.propagate > 0 表示调用方指明了后继节点需要被唤醒
* 2.头节点后面的节点需要被唤醒(waitStatus<0),不论是老的头结点还是新的头结点
*/
if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ||
(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.isShared())//node是最后一个节点或者 node的后继节点是共享节点
/* 如果head节点状态为SIGNAL,唤醒head节点线程,重置head.waitStatus->0
* head节点状态为0(第一次添加时是0),设置head.waitStatus->Node.PROPAGATE表示状态需要向后继节点传播 */
doReleaseShared();
}
}
/**
* 终结掉正在尝试去获取锁的节点
*
* @param node the node
*/
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
// Ignore if node doesn't exist
if (node == null)
return;
node.thread = null;
// 剔除掉一件被cancel掉的节点
Node pred = node.prev;
while (pred.waitStatus > 0)
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
Node predNext = pred.next;
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) {
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);
} else {
int ws;
if (pred != head && ((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL || (ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) && pred.thread != null) {
Node next = node.next;
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0)
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next);
} else {
unparkSuccessor(node);
}
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}
/**
*
*/
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
//若前驱结点的状态是SIGNAL,意味着当前结点可以被安全地park
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
//前驱节点状态如果被取消状态,将被移除出队列
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/* 当前驱节点waitStatus为 0 or PROPAGATE状态时
* 将其设置为SIGNAL状态,然后当前结点才可以可以被安全地park */
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
/**
* 中断当前线程
*/
static void selfInterrupt() {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
/**
* 阻塞当前节点,返回当前Thread的中断状态
* LockSupport.park 底层实现逻辑调用系统内核功能 pthread_mutex_lock 阻塞线程
*/
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);//阻塞
return Thread.interrupted();
}
/**
* 已经在队列当中的Thread节点,准备阻塞等待获取锁
*/
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (; ; ) {//死循环
final Node p = node.predecessor();//找到当前结点的前驱结点
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {//如果前驱结点是头结点,才tryAcquire,其他结点是没有机会tryAcquire的。
setHead(node);//获取同步状态成功,将当前结点设置为头结点。
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
/**
* 如果前驱节点不是Head,通过shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire判断是否应该阻塞
* 前驱节点信号量为-1,当前线程可以安全被parkAndCheckInterrupt用来阻塞线程
*/
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
/**
* 与acquireQueued逻辑相似,唯一区别节点还不在队列当中需要先进行入队操作
*/
private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);//以独占模式放入队列尾部
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (; ; ) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
/**
* 独占模式定时获取
*/
private boolean doAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException {
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);//加入队列
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (; ; ) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return true;
}
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;//超时直接返回获取失败
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && nanosTimeout > spinForTimeoutThreshold)
//阻塞指定时长,超时则线程自动被唤醒
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
if (Thread.interrupted())//当前线程中断状态
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
/**
* 尝试获取共享锁
*/
private void doAcquireShared(int arg) {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);//入队
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (; ; ) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();//前驱节点
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg); //非公平锁实现,再尝试获取锁
//state==0时tryAcquireShared会返回>=0(CountDownLatch中返回的是1)。
// state为0说明共享次数已经到了,可以获取锁了
if (r >= 0) {//r>0表示state==0,前继节点已经释放锁,锁的状态为可被获取
//这一步设置node为head节点设置node.waitStatus->Node.PROPAGATE,然后唤醒node.thread
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
if (interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
failed = false;
return;
}
}
//前继节点非head节点,将前继节点状态设置为SIGNAL,通过park挂起node节点的线程
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (; ; ) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
private boolean doAcquireSharedNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException {
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (; ; ) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return true;
}
}
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && nanosTimeout > spinForTimeoutThreshold)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// Main exported methods
/**
* 尝试获取独占锁,可指定锁的获取数量
*/
protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* 尝试释放独占锁,在子类当中实现
*/
protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* 共享式:共享式地获取同步状态。对于独占式同步组件来讲,同一时刻只有一个线程能获取到同步状态,
* 其他线程都得去排队等待,其待重写的尝试获取同步状态的方法tryAcquire返回值为boolean,这很容易理解;
* 对于共享式同步组件来讲,同一时刻可以有多个线程同时获取到同步状态,这也是“共享”的意义所在。
* 本方法待被之类覆盖实现具体逻辑
* 1.当返回值大于0时,表示获取同步状态成功,同时还有剩余同步状态可供其他线程获取;
* <p>
* 2.当返回值等于0时,表示获取同步状态成功,但没有可用同步状态了;
* 3.当返回值小于0时,表示获取同步状态失败。
*/
protected int tryAcquireShared(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* 释放共享锁,具体实现在子类当中实现
*/
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* 当前线程是否持有独占锁
*/
protected boolean isHeldExclusively() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* 获取独占锁
*/
public final void acquire(int arg) {
//尝试获取锁
if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))//独占模式
selfInterrupt();
}
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (!tryAcquire(arg))
doAcquireInterruptibly(arg);
}
/**
* 获取独占锁,设置最大等待时间
*/
public final boolean tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
return tryAcquire(arg) ||
doAcquireNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}
/**
* 释放独占模式持有的锁
*/
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {//释放一次锁
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);//唤醒后继结点
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 请求获取共享锁
*/
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)//返回值小于0,获取同步状态失败,排队去;获取同步状态成功,直接返回去干自己的事儿。
doAcquireShared(arg);
}
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
public final boolean hasQueuedThreads() {
return head != tail;
}
public final boolean hasContended() {
return head != null;
}
public final Thread getFirstQueuedThread() {
// handle only fast path, else relay
return (head == tail) ? null : fullGetFirstQueuedThread();
}
private Thread fullGetFirstQueuedThread() {
Node h, s;
Thread st;
if (((h = head) != null && (s = h.next) != null && s.prev == head && (st = s.thread) != null) || ((h = head) != null && (s = h.next) != null && s.prev == head && (st = s.thread) != null))
return st;
Node t = tail;
Thread firstThread = null;
while (t != null && t != head) {
Thread tt = t.thread;
if (tt != null)
firstThread = tt;
t = t.prev;
}
return firstThread;
}
/**
* 判断当前线程是否在队列当中
*/
public final boolean isQueued(Thread thread) {
if (thread == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev)
if (p.thread == thread)
return true;
return false;
}
final boolean apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive() {
Node h, s;
return (h = head) != null && (s = h.next) != null && !s.isShared() && s.thread != null;
}
/**
* 判断当前节点是否有前驱节点
*/
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
Node t = tail; // Read fields in reverse initialization order
Node h = head;
Node s;
return h != t && ((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
}
/**
* 同步队列长度
*/
public final int getQueueLength() {
int n = 0;
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (p.thread != null)
++n;
}
return n;
}
/**
* 获取队列等待thread集合
*/
public final Collection<Thread> getQueuedThreads() {
ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
Thread t = p.thread;
if (t != null)
list.add(t);
}
return list;
}
/**
* 获取独占模式等待thread线程集合
*/
public final Collection<Thread> getExclusiveQueuedThreads() {
ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (!p.isShared()) {
Thread t = p.thread;
if (t != null)
list.add(t);
}
}
return list;
}
/**
* 获取共享模式等待thread集合
*/
public final Collection<Thread> getSharedQueuedThreads() {
ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (p.isShared()) {
Thread t = p.thread;
if (t != null)
list.add(t);
}
}
return list;
}
/**
* 判断节点是否在同步队列中
*/
final boolean isOnSyncQueue(Node node) {
//快速判断1:节点状态或者节点没有前置节点
//注:同步队列是有头节点的,而条件队列没有
if (node.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION || node.prev == null)
return false;
//快速判断2:next字段只有同步队列才会使用,条件队列中使用的是nextWaiter字段
if (node.next != null) // If has successor, it must be on queue
return true;
//上面如果无法判断则进入复杂判断
return findNodeFromTail(node);
}
private boolean findNodeFromTail(Node node) {
Node t = tail;
for (; ; ) {
if (t == node)
return true;
if (t == null)
return false;
t = t.prev;
}
}
/**
* 将节点从条件队列当中移动到同步队列当中,等待获取锁
*/
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
/*
* 修改节点信号量状态为0,失败直接返回false
*/
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
/*
* 加入同步队列尾部当中,返回前驱节点
*/
Node p = enq(node);
int ws = p.waitStatus;
//前驱节点不可用 或者 修改信号量状态失败
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL))
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread); //唤醒当前节点
return true;
}
final boolean transferAfterCancelledWait(Node node) {
if (compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0)) {
enq(node);
return true;
}
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node))
Thread.yield();
return false;
}
/**
* 入参就是新创建的节点,即当前节点
*/
final int fullyRelease(Node node) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
//这里这个取值要注意,获取当前的state并释放,这从另一个角度说明必须是独占锁
//可以考虑下这个逻辑放在共享锁下面会发生什么?
int savedState = getState();
if (release(savedState)) {
failed = false;
return savedState;
} else {
//如果这里释放失败,则抛出异常
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
}
} finally {
/**
* 如果释放锁失败,则把节点取消,由这里就能看出来上面添加节点的逻辑中
* 只需要判断最后一个节点是否被取消就可以了
*/
if (failed)
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
}
}
public final boolean hasWaiters(ConditionObject condition) {
if (!owns(condition))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Not owner");
return condition.hasWaiters();
}
/**
* 获取条件队列长度
*/
public final int getWaitQueueLength(ConditionObject condition) {
if (!owns(condition))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Not owner");
return condition.getWaitQueueLength();
}
/**
* 获取条件队列当中所有等待的thread集合
*/
public final Collection<Thread> getWaitingThreads(ConditionObject condition) {
if (!owns(condition))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Not owner");
return condition.getWaitingThreads();
}
/**
* 条件对象,实现基于条件的具体行为
*/
public class ConditionObject implements Condition, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1173984872572414699L;
/**
* First node of condition queue.
*/
private transient Node firstWaiter;
/**
* Last node of condition queue.
*/
private transient Node lastWaiter;
public ConditionObject() {
}
/**
* 1.与同步队列不同,条件队列头尾指针是firstWaiter跟lastWaiter
* 2.条件队列是在获取锁之后,也就是临界区进行操作,因此很多地方不用考虑并发
*/
private Node addConditionWaiter() {
Node t = lastWaiter;
//如果最后一个节点被取消,则删除队列中被取消的节点
//至于为啥是最后一个节点后面会分析
if (t != null && t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) {
//删除所有被取消的节点
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
t = lastWaiter;
}
//创建一个类型为CONDITION的节点并加入队列,由于在临界区,所以这里不用并发控制
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION);
if (t == null)
firstWaiter = node;
else
t.nextWaiter = node;
lastWaiter = node;
return node;
}
/**
* 发信号,通知遍历条件队列当中的节点转移到同步队列当中,准备排队获取锁
*/
private void doSignal(Node first) {
do {
if ((firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null)
lastWaiter = null;
first.nextWaiter = null;
} while (!transferForSignal(first) && //转移节点
(first = firstWaiter) != null);
}
/**
* 通知所有节点移动到同步队列当中,并将节点从条件队列删除
*/
private void doSignalAll(Node first) {
lastWaiter = firstWaiter = null;
do {
Node next = first.nextWaiter;
first.nextWaiter = null;
transferForSignal(first);
first = next;
} while (first != null);
}
/**
* 删除条件队列当中被取消的节点
*/
private void unlinkCancelledWaiters() {
Node t = firstWaiter;
Node trail = null;
while (t != null) {
Node next = t.nextWaiter;
if (t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) {
t.nextWaiter = null;
if (trail == null)
firstWaiter = next;
else
trail.nextWaiter = next;
if (next == null)
lastWaiter = trail;
} else
trail = t;
t = next;
}
}
/**
* 发新号,通知条件队列当中节点到同步队列当中去排队
*/
public final void signal() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())//节点不能已经持有独占锁
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;
if (first != null)
/**
* 发信号通知条件队列的节点准备到同步队列当中去排队
*/
doSignal(first);
}
/**
* 唤醒所有条件队列的节点转移到同步队列当中
*/
public final void signalAll() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;
if (first != null)
doSignalAll(first);
}
public final void awaitUninterruptibly() {
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
boolean interrupted = false;
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
LockSupport.park(this);
if (Thread.interrupted())
interrupted = true;
}
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) || interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
}
/**
* 该模式表示在退出等待时重新中断
*/
private static final int REINTERRUPT = 1;
/**
* 异常中断
*/
private static final int THROW_IE = -1;
/**
* 这里的判断逻辑是:
* 1.如果现在不是中断的,即正常被signal唤醒则返回0
* 2.如果节点由中断加入同步队列则返回THROW_IE,由signal加入同步队列则返回REINTERRUPT
*/
private int checkInterruptWhileWaiting(Node node) {
return Thread.interrupted() ? (transferAfterCancelledWait(node) ? THROW_IE : REINTERRUPT) : 0;
}
/**
* 根据中断时机选择抛出异常或者设置线程中断状态
*/
private void reportInterruptAfterWait(int interruptMode)
throws InterruptedException {
if (interruptMode == THROW_IE)
throw new InterruptedException();
else if (interruptMode == REINTERRUPT)
selfInterrupt();
}
/**
* 加入条件队列等待,条件队列入口
*/
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
//T2进来
//如果当前线程被中断则直接抛出异常
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
//把当前节点加入条件队列
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
//释放掉已经获取的独占锁资源
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);//T2释放锁
int interruptMode = 0;
//如果不在同步队列中则不断挂起
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
LockSupport.park(this);//T1被阻塞
//这里被唤醒可能是正常的signal操作也可能是中断
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
}
/**
* 走到这里说明节点已经条件满足被加入到了同步队列中或者中断了
* 这个方法很熟悉吧?就跟独占锁调用同样的获取锁方法,从这里可以看出条件队列只能用于独占锁
* 在处理中断之前首先要做的是从同步队列中成功获取锁资源
*/
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
//走到这里说明已经成功获取到了独占锁,接下来就做些收尾工作
//删除条件队列中被取消的节点
if (node.nextWaiter != null) // clean up if cancelled
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
//根据不同模式处理中断
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
}
public final boolean await(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long nanosTimeout = unit.toNanos(time);
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
boolean timedout = false;
int interruptMode = 0;
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L) {
timedout = transferAfterCancelledWait(node);
break;
}
if (nanosTimeout >= spinForTimeoutThreshold)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
}
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
if (node.nextWaiter != null)
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
return !timedout;
}
final boolean isOwnedBy(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer sync) {
return sync == AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.this;
}
protected final boolean hasWaiters() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
for (Node w = firstWaiter; w != null; w = w.nextWaiter) {
if (w.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION)
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final int getWaitQueueLength() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
int n = 0;
for (Node w = firstWaiter; w != null; w = w.nextWaiter) {
if (w.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION)
++n;
}
return n;
}
/**
* 得到同步队列当中所有在等待的Thread集合
*/
protected final Collection<Thread> getWaitingThreads() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
ArrayList<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (Node w = firstWaiter; w != null; w = w.nextWaiter) {
if (w.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION) {
Thread t = w.thread;
if (t != null)
list.add(t);
}
}
return list;
}
}
/**
* unsafe魔法类,直接绕过虚拟机内存管理机制,修改内存
*/
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
//偏移量
private static final long stateOffset;
private static final long headOffset;
private static final long tailOffset;
private static final long waitStatusOffset;
private static final long nextOffset;
static {
try {
//状态偏移量
stateOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("state"));
//head指针偏移量,head指向CLH队列的头部
headOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("head"));
tailOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("tail"));
waitStatusOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(Node.class.getDeclaredField("waitStatus"));
nextOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(Node.class.getDeclaredField("next"));
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new Error(ex);
}
}
/**
* CAS 修改头部节点指向. 并发入队时使用.
*/
private final boolean compareAndSetHead(Node update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, headOffset, null, update);
}
/**
* CAS 修改尾部节点指向. 并发入队时使用.
*/
private final boolean compareAndSetTail(Node expect, Node update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, tailOffset, expect, update);
}
/**
* CAS 修改信号量状态.
*/
private static final boolean compareAndSetWaitStatus(Node node, int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(node, waitStatusOffset,
expect, update);
}
/**
* 修改节点的后继指针.
*/
private static final boolean compareAndSetNext(Node node, Node expect, Node update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(node, nextOffset, expect, update);
}
}2. AQS 框架具体实现 - 独占锁实现 ReentrantLock 源码
实现 ReentrantLock 的三大核心原理:文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-419967.html
- LocksSuport:加锁解锁
- 自旋:如果没有加锁成功就一直自旋
- CAS:保证只能有一个线程可以加锁成功
- queue 队列:用容器保存上面未加锁成功的阻塞线程,要解锁的时候从容器中拿出线程进行解锁(为什么选择队列?因为ReentrantLock要实现公平与非公平锁,所以选择先进先出的队列)
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984872572414699L;
/**
* 内部调用AQS的动作,都基于该成员属性实现
*/
private final Sync sync;
/**
* ReentrantLock锁同步操作的基础类,继承自AQS框架.
* 该类有两个继承类,1、NonfairSync 非公平锁,2、FairSync公平锁
*/
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5179523762034025860L;
/**
* 加锁的具体行为由子类实现
*/
abstract void lock();
/**
* 尝试获取非公平锁
*/
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
//acquires = 1
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
/**
* 不需要判断同步队列(CLH)中是否有排队等待线程
* 判断state状态是否为0,不为0可以加锁
*/
if (c == 0) {
//unsafe操作,cas修改state状态
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
//独占状态锁持有者指向当前线程
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
/**
* state状态不为0,判断锁持有者是否是当前线程,
* 如果是当前线程持有 则state+1
*/
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
//加锁失败
return false;
}
/**
* 释放锁
*/
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
/**
* 判断持有独占锁的线程是否是当前线程
*/
protected final boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getExclusiveOwnerThread() == Thread.currentThread();
}
//返回条件对象
final ConditionObject newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}
final Thread getOwner() {
return getState() == 0 ? null : getExclusiveOwnerThread();
}
final int getHoldCount() {
return isHeldExclusively() ? getState() : 0;
}
final boolean isLocked() {
return getState() != 0;
}
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
setState(0); // reset to unlocked state
}
}
/**
* 非公平锁
*/
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
/**
* 加锁行为
*/
final void lock() {
/**
* 第一步:直接尝试加锁
* 与公平锁实现的加锁行为一个最大的区别在于,此处不会去判断同步队列(CLH队列)中
* 是否有排队等待加锁的节点,上来直接加锁(判断state是否为0,CAS修改state为1)
* ,并将独占锁持有者 exclusiveOwnerThread 属性指向当前线程
* 如果当前有人占用锁,再尝试去加一次锁
*/
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
//AQS定义的方法,加锁
acquire(1);
}
/**
* 父类AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.acquire()中调用本方法
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
}
/**
* 公平锁
*/
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
/**
* 重写aqs中的方法逻辑
* 尝试加锁,被AQS的acquire()方法调用
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
/**
* 与非公平锁中的区别,需要先判断队列当中是否有等待的节点
* 如果没有则可以尝试CAS获取锁
*/
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
//独占线程指向当前线程
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
} else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* 默认构造函数,创建非公平锁对象
*/
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
/**
* 根据要求创建公平锁或非公平锁
*/
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
/**
* 加锁
*/
public void lock() {
sync.lock();
}
/**
* 尝试获去取锁,获取失败被阻塞,线程被中断直接抛出异常
*/
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
/**
* 尝试加锁
*/
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.nonfairTryAcquire(1);
}
/**
* 指定等待时间内尝试加锁
*/
public boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
/**
* 尝试去释放锁
*/
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
/**
* 返回条件对象
*/
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition();
}
/**
* 返回当前线程持有的state状态数量
*/
public int getHoldCount() {
return sync.getHoldCount();
}
/**
* 查询当前线程是否持有锁
*/
public boolean isHeldByCurrentThread() {
return sync.isHeldExclusively();
}
/**
* 状态表示是否被Thread加锁持有
*/
public boolean isLocked() {
return sync.isLocked();
}
/**
* 是否公平锁?是返回true 否则返回 false
*/
public final boolean isFair() {
return sync instanceof FairSync;
}
/**
* 获取持有锁的当前线程
*/
protected Thread getOwner() {
return sync.getOwner();
}
/**
* 判断队列当中是否有在等待获取锁的Thread节点
*/
public final boolean hasQueuedThreads() {
return sync.hasQueuedThreads();
}
/**
* 当前线程是否在同步队列中等待
*/
public final boolean hasQueuedThread(Thread thread) {
return sync.isQueued(thread);
}
/**
* 获取同步队列长度
*/
public final int getQueueLength() {
return sync.getQueueLength();
}
/**
* 返回Thread集合,排队中的所有节点Thread会被返回
*/
protected Collection<Thread> getQueuedThreads() {
return sync.getQueuedThreads();
}
/**
* 条件队列当中是否有正在等待的节点
*/
public boolean hasWaiters(Condition condition) {
if (condition == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (!(condition instanceof AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not owner");
return sync.hasWaiters((AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject) condition);
}
}文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-419967.html
到了这里,关于并发编程 - AQS 源码的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!