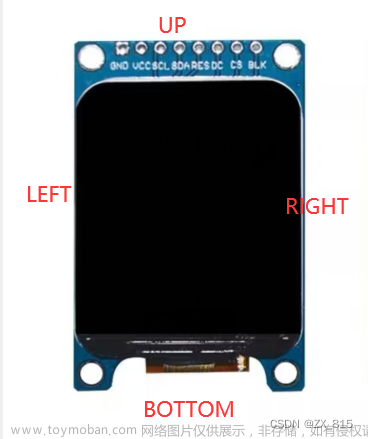
1.环境配置
Arduino下载TFT_eSPI和JPEGDecoder库
步骤:项目->加载库->管理库

修改User_Setup.h
驱动
#define ST7789_DRIVER
屏尺寸(我的是240*240)
#define TFT_WIDTH 240
#define TFT_HEIGHT 240
连接引脚
#define TFT_CS PIN_D8 // Chip select control pin D8
#define TFT_DC PIN_D3 // Data Command control pin
#define TFT_RST PIN_D4 // Reset pin (could connect to NodeMCU RST, see next line)
#define TFT_BL PIN_D1 // LED back-light (only for ST7789 with backlight control pin)


2.示例显示图片
选择示例:
文件->TFT_eSPI->160×128->TFT_flas_jpg
其中jpeg1.h,jpeg2.h,jpeg3.h,jpeg4.h几个头文件里存的是图片的数据信息。
3.显示自己的图片
首先要注意一下自己图片的格式,我用的是png格式的(图片大小不要太大)。在线调整图像像素。
图片信息获取工具:https://notisrac.github.io/FileToCArray/
点击Copy to clipboard,复制框内的图片数据,粘贴到之前jpeg1.h中。
3.1 修改示例代码
删除jpeg2.h,jpeg3.h,jpeg4.h三个头文件,如果想多显示几张可以增加到后几个头文件中

其他的我没有修改,需要其他功能的再百度吧,俺还不会。
3.2 引脚连接
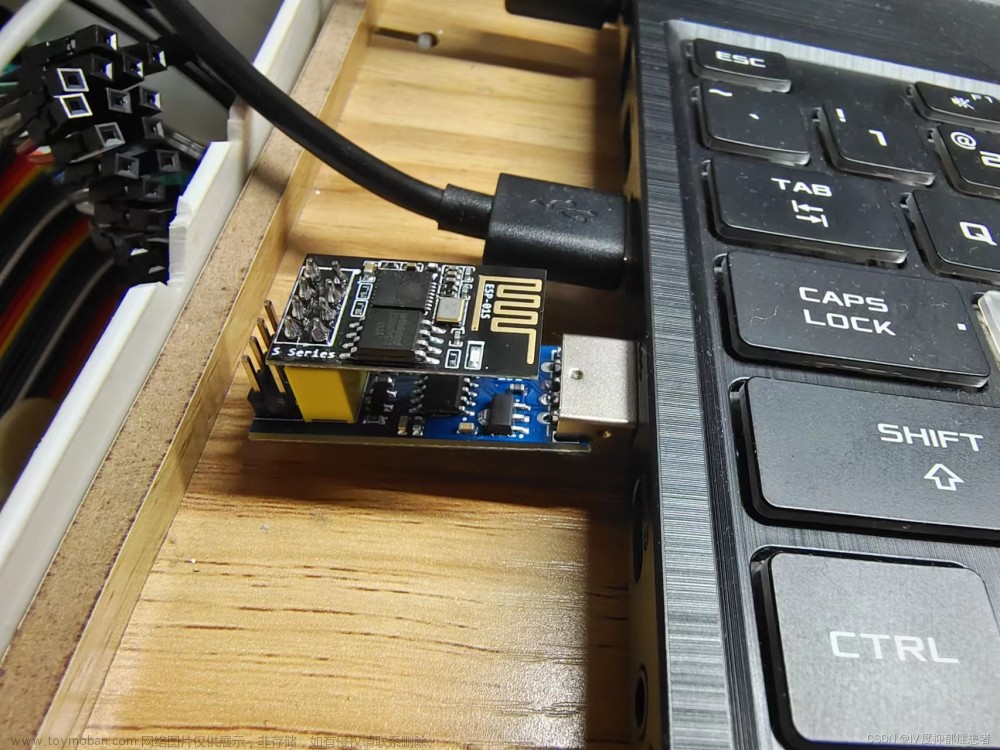
引脚连接
实物图展示
3.3 编译下载
工具设置
下载程序: 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-424586.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-424586.html
3.4 代码
这里不提供给jpeg1.h的代码啦,反正你们也能自己生成,对吧文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-424586.html
#include <SPI.h>
#include <TFT_eSPI.h>
TFT_eSPI tft = TFT_eSPI();
// JPEG decoder library
#include <JPEGDecoder.h>
// Return the minimum of two values a and b
#define minimum(a,b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b))
// Include the sketch header file that contains the image stored as an array of bytes
// More than one image array could be stored in each header file.
#include "jpeg1.h"
// Count how many times the image is drawn for test purposes
uint32_t icount = 0;
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//####################################################################################################
// Setup
//####################################################################################################
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
tft.begin();
}
//####################################################################################################
// Main loop
//####################################################################################################
void loop() {
drawArrayJpeg(_1661000196384, sizeof(_1661000196384), 0, 0); // Draw a jpeg image stored in memory at x,y
delay(2000);
}
//####################################################################################################
// Draw a JPEG on the TFT pulled from a program memory array
//####################################################################################################
void drawArrayJpeg(const uint8_t arrayname[], uint32_t array_size, int xpos, int ypos) {
int x = xpos;
int y = ypos;
JpegDec.decodeArray(arrayname, array_size);
jpegInfo(); // Print information from the JPEG file (could comment this line out)
renderJPEG(x, y);
Serial.println("#########################");
}
//####################################################################################################
// Draw a JPEG on the TFT, images will be cropped on the right/bottom sides if they do not fit
//####################################################################################################
// This function assumes xpos,ypos is a valid screen coordinate. For convenience images that do not
// fit totally on the screen are cropped to the nearest MCU size and may leave right/bottom borders.
void renderJPEG(int xpos, int ypos) {
// retrieve infomration about the image
uint16_t *pImg;
uint16_t mcu_w = JpegDec.MCUWidth;
uint16_t mcu_h = JpegDec.MCUHeight;
uint32_t max_x = JpegDec.width;
uint32_t max_y = JpegDec.height;
// Jpeg images are draw as a set of image block (tiles) called Minimum Coding Units (MCUs)
// Typically these MCUs are 16x16 pixel blocks
// Determine the width and height of the right and bottom edge image blocks
uint32_t min_w = minimum(mcu_w, max_x % mcu_w);
uint32_t min_h = minimum(mcu_h, max_y % mcu_h);
// save the current image block size
uint32_t win_w = mcu_w;
uint32_t win_h = mcu_h;
// record the current time so we can measure how long it takes to draw an image
uint32_t drawTime = millis();
// save the coordinate of the right and bottom edges to assist image cropping
// to the screen size
max_x += xpos;
max_y += ypos;
// read each MCU block until there are no more
while (JpegDec.readSwappedBytes()) {
// save a pointer to the image block
pImg = JpegDec.pImage ;
// calculate where the image block should be drawn on the screen
int mcu_x = JpegDec.MCUx * mcu_w + xpos; // Calculate coordinates of top left corner of current MCU
int mcu_y = JpegDec.MCUy * mcu_h + ypos;
// check if the image block size needs to be changed for the right edge
if (mcu_x + mcu_w <= max_x) win_w = mcu_w;
else win_w = min_w;
// check if the image block size needs to be changed for the bottom edge
if (mcu_y + mcu_h <= max_y) win_h = mcu_h;
else win_h = min_h;
// copy pixels into a contiguous block
if (win_w != mcu_w)
{
uint16_t *cImg;
int p = 0;
cImg = pImg + win_w;
for (int h = 1; h < win_h; h++)
{
p += mcu_w;
for (int w = 0; w < win_w; w++)
{
*cImg = *(pImg + w + p);
cImg++;
}
}
}
// draw image MCU block only if it will fit on the screen
if (( mcu_x + win_w ) <= tft.width() && ( mcu_y + win_h ) <= tft.height())
{
tft.pushRect(mcu_x, mcu_y, win_w, win_h, pImg);
}
else if ( (mcu_y + win_h) >= tft.height()) JpegDec.abort(); // Image has run off bottom of screen so abort decoding
}
// calculate how long it took to draw the image
drawTime = millis() - drawTime;
// print the results to the serial port
Serial.print(F( "Total render time was : ")); Serial.print(drawTime); Serial.println(F(" ms"));
Serial.println(F(""));
}
//####################################################################################################
// Print image information to the serial port (optional)
//####################################################################################################
void jpegInfo() {
Serial.println(F("==============="));
Serial.println(F("JPEG image info"));
Serial.println(F("==============="));
Serial.print(F( "Width :")); Serial.println(JpegDec.width);
Serial.print(F( "Height :")); Serial.println(JpegDec.height);
Serial.print(F( "Components :")); Serial.println(JpegDec.comps);
Serial.print(F( "MCU / row :")); Serial.println(JpegDec.MCUSPerRow);
Serial.print(F( "MCU / col :")); Serial.println(JpegDec.MCUSPerCol);
Serial.print(F( "Scan type :")); Serial.println(JpegDec.scanType);
Serial.print(F( "MCU width :")); Serial.println(JpegDec.MCUWidth);
Serial.print(F( "MCU height :")); Serial.println(JpegDec.MCUHeight);
Serial.println(F("==============="));
}
//####################################################################################################
// Show the execution time (optional)
//####################################################################################################
// WARNING: for UNO/AVR legacy reasons printing text to the screen with the Mega might not work for
// sketch sizes greater than ~70KBytes because 16 bit address pointers are used in some libraries.
// The Due will work fine with the HX8357_Due library.
void showTime(uint32_t msTime) {
//tft.setCursor(0, 0);
//tft.setTextFont(1);
//tft.setTextSize(2);
//tft.setTextColor(TFT_WHITE, TFT_BLACK);
//tft.print(F(" JPEG drawn in "));
//tft.print(msTime);
//tft.println(F(" ms "));
Serial.print(F(" JPEG drawn in "));
Serial.print(msTime);
Serial.println(F(" ms "));
}
到了这里,关于Arduino+esp8266+1.3寸TFT屏(st7789驱动)显示图片教程的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!