目录
1.什么是NIO
2.NIO结构
3.基于NIO下的聊天系统实现
4.Netty
1.什么是NIO
NIO:java non-blocking IO,同步非阻塞IO。
BIO是阻塞IO,即每一个事件都需要分配一个进程给他,如果客户端没有连接上,则一直阻塞等待。
而NIO,异步 I/O 是一种没有阻塞地读写数据的方法:该架构下我们可以注册对特定 I/O 事件诸如数据可读、新连接到来等等,而在发生这样感兴趣的事件时,系统将会告诉您,而不用一直等待。
打个比方:
五个人(请求)写作业,BIO架构下是五个老师(五个进程)看着写,学生直接在书上写(内存读写)。
NIO架构下则是一个老师(进程)看着写,要求学生先写在本子上(buffer,缓冲区),并且一直问助教(selector),写好的(事件就绪)交上来!
2.NIO结构
NIO主要有三大核心部分:Channel(通道),Buffer(缓冲区), Selector。
Channel:和IO中的Stream(流)类似。只不过Stream是单向的,channel是双向的,既可以用来进行读操作,又可以用来进行写操作。
Buffer:NIO中的缓冲区,本质上是一个可读取的内存块。当向buffer写入数据时,buffer会记录下写了多少数据。一旦要读取数据,需要通过flip()方法将Buffer从写模式切换到读模式,读取之前写入到buffer的所有数据。
NIO和java中普通IO最大的区别是数据打包和传输方式。传统IO基于字节流和字符流进行操作,而NIO基于Channel和Buffer(缓冲区)进行操作,数据总是从通道读取到缓冲区中,或者从缓冲区写入到通道中。

如上图所示:客户端/服务端将需要传输的数据存入到buffer缓冲区中,再通过java流获取对应的channel,然后使用channel写入/读取缓冲区中的数据,输出到对应的目标(文件/字节流)中。
selector:要使用Selector, 得向Selector注册Channel,然后调用它的select()方法进行监听:这个方法会一直阻塞到至少一个注册的通道有事件就绪;当事件就绪,会把对应的selectionKey(用于关联channel,每一个类型的事件对应一个selectionKey,可以帮助获得对应的channel进行后续操作)加入到内部集合,并返回;一旦这个方法返回,线程就可以处理这些事件。
注:select()方法是阻塞的,select(1000)方法阻塞1000毫秒;selectNow()方法是非阻塞的
当客户端发起一次请求事件过后,NIO架构的响应过程如下图所示:

首先,服务端会获得一个ServerSocketChannel并向selector注册,即可等待客户端连接。
客户端向服务端发起请求,selector通过select()方法监听到事件发生(如客户端读事件),分配线程处理该事件;服务端将事件类型对应的selectionKey返回,然后通过key获得处理的channel,通过channel.read()方法将数据写入buffer,并返回至客户端;客户端从buffer中读到需要的数据,请求结束。
Selector(选择区)用于监听多个通道的事件(比如:连接打开,数据到达),只有当 通道 真正有读写事件发生时,才会进行读写,大大减少系统开销,避免了多线程之间的上下文切换。这使得一个I/O线程可以并发处理多个客户端连接和读写操作,极大提升了性能。
3.基于NIO下的聊天系统实现
基于以上架构,我们可以根据NIO结构,编写一个聊天系统:
(1)服务端:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class ChatServer {
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
private Selector selector;
public static final int port = 8080;
public ChatServer(){
try {
//获取ServerSocketChannel供客户端连接,并开放端口
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//得到Selector,并注册channel
selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("服务器就绪");
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void listen(){
try {
while (true){
//阻塞2秒
int count = selector.select(2000);
if (count>0){
//有事件需要处理
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
//客户端连接事件,为客户端生成SocketChannel
if (key.isAcceptable()){
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
//非阻塞channel才能进行注册
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//注册,绑定事件读,并为该channel关联buffer
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
System.out.println("客户端:"+socketChannel.getRemoteAddress()+" 成功连接");
}
//读取事件
if (key.isReadable()){
readMessage(key);
}
//删除已处理key,避免重复操作
keyIterator.remove();
}
}else {
continue;
}
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//从客户端读取消息
private void readMessage(SelectionKey key){
SocketChannel channel = null;
try {
//通过key反向获取channel
channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
//获取该channel关联buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//从buffer中读取数据
int read = channel.read(buffer);
if (read>0){
String msg = new String(buffer.array()).trim();
//转发消息(排除自己)
transformMessage(msg,channel);
}
}catch (IOException e){
try {
System.out.println(channel.getRemoteAddress()+"下线");
//取消注册
key.cancel();
//关闭通道
channel.close();
}catch (Exception exception){
exception.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//转发消息给其他客户端
public void transformMessage(String msg, SocketChannel self) throws IOException {
System.out.println("服务器转发消息");
//遍历所有注册到selector的channel,进行转发
for (SelectionKey key:selector.keys()){
Channel targetChannel = key.channel();
//排除自己
if (targetChannel instanceof SocketChannel && targetChannel!=self){
//转发消息
SocketChannel dest = (SocketChannel) targetChannel;
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
dest.write(buffer);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChatServer chatServer = new ChatServer();
chatServer.listen();
}
}- 建立ServerSocketChannel,开放端口,并设置为非阻塞。
- 获取一个selector,并将channel注册进去,绑定触发事件及对应的SelectionKey
- 等待客户端连接。
- 当select()方法监听到事件,获取事件的selectionKey集合;遍历集合,处理事件。(连接事件则创建socketChannel连接;读事件则读取buffer中消息,并转发至其他客户端)
注:只有阻塞模式下,channel才可以向selector注册(serverSocketChannel.accept()获取的SocketChannel也需要设置);server端先生成一个ServerSocketChannel并注册后,客户端才可以用SocketChannel对其进行连接;
(2)客户端:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ChatClient implements Runnable{
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private final String host = "127.0.0.1";
private final int port = 8080;
private Selector selector;
private String username;
public ChatClient(){
try {
socketChannel=SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress(host, port));
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
selector=Selector.open();
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
username = socketChannel.getLocalAddress().toString().substring(1);
System.out.println("客户端就绪");
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//发送消息
public void sendMsg(String msg){
msg = username + ":" + msg;
try {
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//读取回复消息
public void readMsg(){
try {
int select = selector.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
if (key.isReadable()){
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
channel.read(buffer);
String str = new String(buffer.array());
System.out.println(str.trim());
}
iterator.remove();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
this.readMsg();
//每隔1秒监听一次
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChatClient chatClient = new ChatClient();
//启动线程读取
new Thread(chatClient).start();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()){
String str = scanner.nextLine();
chatClient.sendMsg(str);
}
}
}- 获取scocketServer连接服务端,设置非阻塞模式。
- 连接服务端。
- 发起事件:发送消息,将消息写入channel中。
- 读取服务器转发的其他客户单消息。
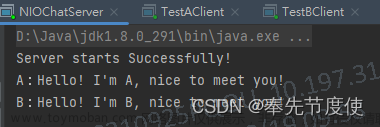
(3)运行效果:
服务端:

客户端1:

客户端2:

客户端3:

4.Netty
Netty是 一个异步事件驱动的网络应用程序框架(即基于NIO架构),用于快速开发可维护的高性能协议服务器和客户端。
为什么会有Netty?
- 1)NIO的类库和API繁杂,使用起来比较麻烦;
- 2)开发工作量和难度大,面临例如断连重连、半包读写、失败缓存等问题;
- 3)使用原生NIO编程需要掌握Reactor模型、多线程编程等额外技能,要求较高;
- 4)java原生NIO存在一定的bug,可能会影响NIO编程。
而Netty就是基于Reactor多线程模型 对 JDK 自带的 NIO 的 API 进行了良好的封装,解决了上述问题。且Netty拥有高性能、 吞吐量更高,延迟更低,减少资源消耗,最小化不必要的内存复制等优点。

其核心在于 可拓展事件驱动模型、全局交互API、零拷贝。
Netty快速使用,其使用形式类似于NIO架构,也是分为服务端、客户端:
(1)服务端:
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义线程组:BossEventLoop(负责连接) , WorkerEventLoop(负责业务读写)
EventLoopGroup bossEventLoop = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerEventLoop = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 1. ServerBootstrap:启动器,负责组装netty组件,启动服务器
new ServerBootstrap()
// 2.存入线程组
.group(bossEventLoop,workerEventLoop)
// 3.选择服务器的ServerSocketChannel实现
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
// 4. worker(child) , 决定了worker能执行什么操作(handler)
.childHandler(
// 5. channel 代表和客户端进行读写的通道 Initializer:初始化器,负责添加别的handler
new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// 6. 添加具体handler
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder()); //将 ByteBuf 转为字符串
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { //自定义handler
@Override //读事件
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(msg);
}
});
}
})
.bind(8080);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("客户端断开连接");
}
}
}(2)客户端:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-426297.html
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class NettyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
try {
// 1.启动类
new Bootstrap()
// 2.添加EventLoop
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
}
})
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost",8080))
.sync()
.channel()
//发送数据
.writeAndFlush("hello world");
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("服务器异常");
}
}
}上述代码实现了服务端创建ServerSocketChannel,客户端连接服务端并写入消息,服务端成功读取的功能。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-426297.html
到了这里,关于java网络编程——NIO架构的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!