目录
一、简介
二、创建文件
三、写入文件
四、读取文件
五、复制文件
六、移动文件
七、重命名文件
八、删除文件
结束
一、简介
C#中的IO(Input/Output)操作包括读取和写入文件、读取和写入流、以及操作目录和文件夹等。这些操作都可以通过System.IO命名空间中的类实现。下面对C# IO相关的类和操作进行介绍。
文件操作
File类
File类提供了对文件的创建、读取、写入、复制、移动、重命名和删除等操作。
StreamReader和StreamWriter类
StreamReader和StreamWriter类用于读取和写入文本文件。
目录和文件夹操作
Directory和DirectoryInfo类
Directory和DirectoryInfo类提供了对目录和文件夹的创建、移动、重命名和删除等操作。
二、创建文件
要创建一个文件,可以使用System.IO.File.Create()方法。该方法接受一个文件路径和一个可选的缓冲区大小作为参数,然后返回一个FileStream对象,该对象可用于写入文件。
代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 文件操作
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
string filePath = @"E:\myFile.txt";
FileStream fileStream = File.Create(filePath);
fileStream.Close();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("创建文件失败:" + ex.Message);
}
Console.WriteLine("创建文件成功!");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
打开E盘,文件是创建成功了,只是这个 txt 文件里没有任何内容

三、写入文件
写入文件可以使用下面方式:
1. File.WriteAllText(FilePath,String)
2. File.WriteAllText(FilePath, String,Encoding) ----指定编码
3. File.WriteAllLines(FilePath,String[])
4. File.WriteAllLines(FilePath,String[],Encoding) ----指定编码
前面两种写入的是一个字符串,后面两种写入的是一个字符串数组。
使用 File.WriteAllText 或 File.WriteAllLines 方法时,如果指定的文件路径不存在,会创建一个新文件;如果文件已经存在,则会覆盖原文件。
第一种:字符串的写入
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 文件操作
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string filePath = @"E:\myFile.txt";
string content = "读取读取读取读取读取读取";
//第一种
//File.WriteAllText(filePath, content);
//第二种
File.WriteAllText(filePath, content, Encoding.UTF8);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
打开刚创建的 myFile.txt 文件:

第二种:多行字符串的写入
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 文件操作
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string filePath = @"E:\myFile.txt";
string[] contentArr = { "dddd", "eeeeee" };
//第一种
//File.WriteAllLines(filePath, contentArr);
//第二种
File.WriteAllLines(filePath, contentArr, Encoding.UTF8);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}上面写入的字符串现在已经被覆盖了

上面写入字符串都会覆盖原有的内容,下面就介绍如何追加字符串。
第三种:追加字符串
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Test1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string filePath = @"E:\myFile.txt";
string content = "423423423423";
File.AppendAllText(filePath, content);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}filePath 路径这个文件如果没有,C# 会自动生成这个文件,运行后找到这个文件,就可以看到添加的内容

下面我将内容做一下更改,再次运行
namespace Test1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string filePath = @"E:\myFile.txt";
string content = "dffsddgaadfasdfa";
File.AppendAllText(filePath, content);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}我们重写打开 myFile.txt 这个文件,发现文字是追加上去了,但是并没有换行

其实换行也非常的简单,直接在字符串里加转义字符 \n 就行了
namespace Test1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string filePath = @"E:\myFile.txt";
string content = "\n哇哈哈哈哈";
File.AppendAllText(filePath, content);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}效果:

第四种:追加多行字符串
按上面的套路,添加多行当然也是可以的,不过用的方法名要换一个了
使用 File.AppendAllLines 来添加多行文字。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Test1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string filePath = @"E:\myFile.txt";
string[] list = { "\n恭喜", "发财", "红包", "拿来" };
File.AppendAllLines(filePath, list, Encoding.UTF8);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}运行后:

四、读取文件
读取文件可以使用下面方式:
1.File.ReadAllText(FilePath)
2.File.ReadAllText(FilePath, Encoding) ----指定编码
3.File.ReadAllLines(FilePath)
4.File.ReadAllLines(FilePath, Encoding) ----指定编码
以字符串接收方式
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 文件操作
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string path = @"E:\myFile.txt";
//string content = File.ReadAllText(path);
string content = File.ReadAllText(path,Encoding.UTF8);
Console.WriteLine(content);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}以字符串数组接收的方式
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 文件操作
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string path = @"E:\myFile.txt";
//string[] content = File.ReadAllLines(path);
string[] content = File.ReadAllLines(path, Encoding.UTF8);
for (int i = 0; i < content.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(content[i]);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
采用流(Stream)的方式来读取内容
1.StreamReader(FilePath)
2.StreamReader(FilePath, Encoding)
3.StreamReader(FileStream)
4.StreamReader(FileStream, Encoding)
5.File.OpenText(FilePath)
6.FileInfo.OpenText()
基于StreamReader,一行一行读取
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 文件操作
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string path = @"E:\myFile.txt";
//StreamReader sr1 = new StreamReader(path);
//StreamReader sr2 = new StreamReader(path, Encoding.UTF8);
//初始化FileStream
FileStream fs = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read, FileShare.None);
//StreamReader sr3 = new StreamReader(fs);
StreamReader sr4 = new StreamReader(fs, Encoding.UTF8);
string line = string.Empty;
while((line = sr4.ReadLine()) != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(line);
}
sr4.Close();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
一次性读完
string path = @"E:\myFile.txt";
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(path, Encoding.UTF8);
string content = sr.ReadToEnd();
Console.WriteLine(content);
sr.Close();五、复制文件
要复制文件,可以使用System.IO.File.Copy()方法。该方法接受源文件路径和目标文件路径作为参数,并将源文件复制到目标文件。如果目标文件已存在,则将被覆盖。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 文件操作
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string sourceFilePath = @"E:\myFile.txt";
string destinationFilePath = @"E:\myFile_copy.txt";
File.Copy(sourceFilePath, destinationFilePath);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
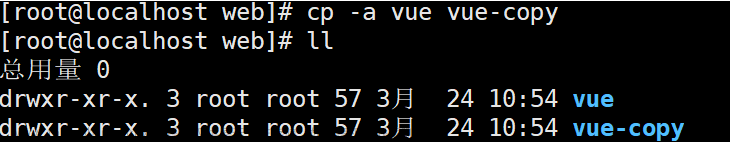
打开对应的目录,可以看到拷贝成功了,而且字节数也是一样的

六、移动文件
要移动文件,可以使用System.IO.File.Move()方法。该方法接受源文件路径和目标文件路径作为参数,并将源文件移动到目标文件。如果目标文件已存在,则将被覆盖。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 文件操作
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string sourceFilePath = @"E:\myFile.txt";
string destinationFilePath = @"D:\myFile.txt";
File.Move(sourceFilePath, destinationFilePath);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
七、重命名文件
要重命名文件,可以使用System.IO.File.Move()方法。该方法接受源文件路径和目标文件路径作为参数,并将源文件重命名为目标文件。如果目标文件已存在,则将被覆盖。
在上一节 移动文件 中,我们将 myFile.txt 文件移动到 D 盘了,执行下面操作之前,要先剪切回来再执行操作哦
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 文件操作
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string filePath = @"E:\myFile.txt";
string newFilePath = @"E:\myFile_new.txt";
File.Move(filePath, newFilePath);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}运行后,可以看到效果了


八、删除文件
要删除文件,可以使用System.IO.File.Delete()方法。该方法接受文件路径作为参数,并将该文件从磁盘上删除。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 文件操作
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string newFilePath = @"E:\myFile_new.txt";
File.Delete(newFilePath);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}结束
如果这个帖子对你有所帮助,欢迎 关注 + 点赞 + 留言文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-429892.html
end文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-429892.html
到了这里,关于C# 文件操作(复制、移动、重命名、创建、打开、删除)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!