前言
嗨喽,大家好呀~这里是爱看美女的茜茜呐

开发环境:
首先我们先来安装一下写代码的软件(对没安装的小白说)
-
Python 3.8 / 编译器
-
Pycharm 2021.2版本 / 编辑器
-
专业版是付费的 <文章下方名片可获取魔法永久用~>
-
社区版是免费的
-
第三方模块使用:
-
requests >>> pip install requests 数据请求
-
parsel >>> pip install parsel 数据解析
-
csv <表格文件> 内置模块 保存数据
python第三方模块安装:
-
win + R 输入 cmd 点击确定, 输入安装命令 pip install 模块名 (pip install requests) 回车
-
在pycharm中点击Terminal(终端) 输入安装命令
(如果你觉得安装速度比较慢, 你可以切换国内镜像源)
代码步骤:
-
发送请求
-
获取数据
-
解析数据
-
保存数据
python资料、源码、教程: 点击此处跳转文末名片获取
采集代码展示:
# 导入数据请求模块 --> 第三方模块, 需要安装 pip install requests
import requests
# 导入数据解析模块 --> 第三方模块, 需要安装 pip install parsel
import parsel
# 导入csv模块
import csv
for page in range(1, 26):
请求链接
url = f'http://****m/books/bestsellers/01.00.00.00.00.00-recent30-0-0-1-{page}'
伪装 模拟 --> 请求头 字典数据类型
headers = {
# User-Agent 用户代理 表示浏览器基本身份信息
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/101.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
发送请求 等号左边都是自定义变量名
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers)
selector = parsel.Selector(response.text)
第一次提取 获取所有书籍所对应li标签
lis = selector.css('.bang_list_mode li')
for循环遍历
for li in lis:
“”"
提取具体数据信息
css选择器 --> 可以直接复制粘贴就好了
get 获取第一个标签数据内容
“”"
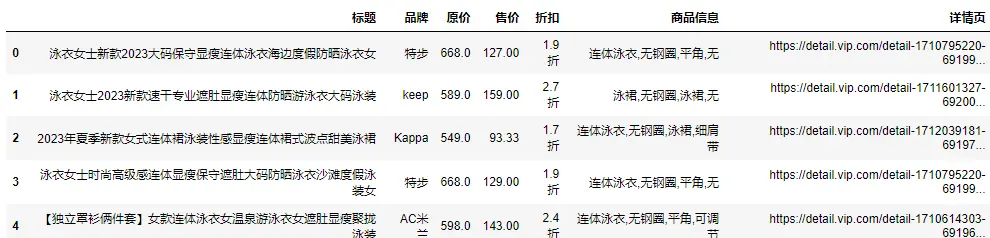
title = li.css('.name a::attr(title)').get() # 书名
star = li.css('.star a::text').get() # 评论
recommend = li.css('.tuijian::text').get() # 推荐
writer = li.css('.publisher_info a::text').get() # 作者
date = li.css('.publisher_info span::text').get() # 时间
publisher = li.css('div:nth-child(6) a::text').get() # 出版社
price_n = li.css('.price .price_n::text').get() # 售价
price_r = li.css('.price .price_r::text').get() # 原价
price_s = li.css('.price .price_s::text').get() # 折扣
price_e = li.css('.price_e .price_n::text').get() # 电子书
href = li.css('.name a::attr(href)').get() # 详情页
创建字典
dit = {
'书名': title,
'评论': star,
'推荐': recommend,
'作者': writer,
'时间': date,
'出版社': publisher,
'售价': price_n,
'原价': price_r,
'折扣': price_s,
'电子书': price_e,
'详情页': href,
}
csv_writer.writerow(dit)
print(title, star, recommend, writer, date, publisher, price_n, price_r, price_s, price_e, href)
创建表格保存数据
f = open('书籍.csv', mode='a', encoding='utf-8', newline='')
csv_writer = csv.DictWriter(f, fieldnames=[
'书名',
'评论',
'推荐',
'作者',
'时间',
'出版社',
'售价',
'原价',
'折扣',
'电子书',
'详情页',
])
写入表头
csv_writer.writeheader()
可视化代码展示:
1.导入模块
import pandas as pd
from pyecharts.charts import *
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType#设定主题
from pyecharts.commons.utils import JsCode
import pyecharts.options as opts
2.导入数据
df = pd.read_csv('data.csv', encoding='utf-8', engine='python')
df.head()

3.数据处理
df['书名'] = df['书名'].apply(lambda x:x.split('(')[0])
df.head()

df['书籍简介'] = df['书名'].str.extract('.*?((.*?))')
df['书籍简介'].fillna('无', inplace=True)
df.head(1)

提取评论数
data = df.apply(lambda x:x['评论'].split('条评论')[0], axis=1)
df['评论数'] = data.astype('int64')
df.head(1)

原价、售价、电子书价格 数值化
df['原价'] = df['原价'].str.replace('¥', '')
df['售价'] = df['售价'].str.replace('¥', '')
df['电子书价格'] = df['电子书'].str.replace('¥', '')
df.head(1)

df.info()
df['原价'] = df['原价'].str.replace(',', '').astype('float64')
df['售价'] = df['售价'].str.replace(',', '').astype('float64')
缺失值

电子书价格列额外处理


4.数据可视化
书籍总体价格区间
def tranform_price(x):
if x <= 50.0:
return '0~50元'
elif x <= 100.0:
return '51~100元'
elif x <= 500.0:
return '101~500元'
elif x <= 1000.0:
return '501~1000元'
else:
return '1000以上'
df['价格分级'] = df['原价'].apply(lambda x:tranform_price(x))
price_1 = df['价格分级'].value_counts()
datas_pair_1 = [(i, int(j)) for i, j in zip(price_1.index, price_1.values)]
df['售价价格分级'] = df['售价'].apply(lambda x:tranform_price(x))
price_2 = df['售价价格分级'].value_counts()
datas_pair_2 = [(i, int(j)) for i, j in zip(price_2.index, price_2.values)]
pie1 = (
Pie(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme='dark',width='1000px',height='600px'))
.add('', datas_pair_1, radius=['35%', '60%'])
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}:{d}%"))
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(
title="书籍\n\n原价价格区间",
pos_left='center',
pos_top='center',
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(
color='#F0F8FF',
font_size=20,
font_weight='bold'
),
)
)
.set_colors(['#EF9050', '#3B7BA9', '#6FB27C', '#FFAF34', '#D8BFD8', '#00BFFF', '#7FFFAA'])
)
pie1.render_notebook()

pie1 = (
Pie(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme='dark',width='1000px',height='600px'))
.add('', datas_pair_2, radius=['35%', '60%'])
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}:{d}%"))
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(
title="书籍\n\n售价价格区间",
pos_left='center',
pos_top='center',
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(
color='#F0F8FF',
font_size=20,
font_weight='bold'
),
)
)
.set_colors(['#EF9050', '#3B7BA9', '#6FB27C', '#FFAF34', '#D8BFD8', '#00BFFF', '#7FFFAA'])
)
pie1.render_notebook()

各个出版社书籍数量柱状图
counts = df.groupby('出版社')['书名'].count().sort_values(ascending=False).head(20)
bar=(
Bar(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(height='500px',width='1000px',theme='dark'))
.add_xaxis(counts.index.tolist())
.add_yaxis(
'出版社书籍数量',
counts.values.tolist(),
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True,position='top'),
itemstyle_opts=opts.ItemStyleOpts(
color=JsCode("""new echarts.graphic.LinearGradient(
0, 0, 0, 1,[{offset: 0,color: 'rgb(255,99,71)'}, {offset: 1,color: 'rgb(32,178,170)'}])
"""
)
)
)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(
title='各个出版社书籍数量柱状图'),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name='书籍名称',
type_='category',
axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(rotate=90),
),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(
name='数量',
min_=0,
max_=29.0,
splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts(is_show=True,linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts(type_='dash'))
),
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(trigger='axis',axis_pointer_type='cross')
)
.set_series_opts(
markline_opts=opts.MarkLineOpts(
data=[
opts.MarkLineItem(type_='average',name='均值'),
opts.MarkLineItem(type_='max',name='最大值'),
opts.MarkLineItem(type_='min',name='最小值'),
]
)
)
)
bar.render_notebook()

电子书版本占比
per = df['电子书'].value_counts()['无电子书版本']/len(df)
c = (
Liquid()
.add("lq", [1-per], is_outline_show=False)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="电子书版本占比"))
)
c.render_notebook()


bar=(
Bar(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(height='500px',width='1000px',theme='dark'))
.add_xaxis(price_top.index.tolist())
.add_yaxis(
'书籍单价',
price_top.values.tolist(),
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True,position='top'),
itemstyle_opts=opts.ItemStyleOpts(
color=JsCode("""new echarts.graphic.LinearGradient(
0, 0, 0, 1,[{offset: 0,color: 'rgb(255,99,71)'}, {offset: 1,color: 'rgb(32,178,170)'}])
"""
)
)
)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(
title='单价最高的书籍详细柱状图'),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name='书籍名称',
type_='category',
axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(rotate=90),
),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(
name='单价/元',
min_=0,
max_=1080.0,
splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts(is_show=True,linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts(type_='dash'))
),
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(trigger='axis',axis_pointer_type='cross')
)
.set_series_opts(
markline_opts=opts.MarkLineOpts(
data=[
opts.MarkLineItem(type_='average',name='均值'),
opts.MarkLineItem(type_='max',name='最大值'),
opts.MarkLineItem(type_='min',name='最小值'),
]
)
)
)
bar.render_notebook()



import pyecharts.options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
“”"
目前无法实现的功能:
1、迷之颜色映射的问题
“”"
content = df['出版社'].value_counts()
# x = content.index.tolist()[:10]
# y = content.values.tolist()[:10]
x_data = content.index.tolist()[:10]
y_data = content.values.tolist()[:10]
data_pair = [list(z) for z in zip(x_data, y_data)]
data_pair.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
c = (
Pie(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width="1600px", height="800px", bg_color="#2c343c"))
.add(
series_name="访问来源",
data_pair=data_pair,
rosetype="radius",
radius="55%",
center=["50%", "50%"],
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False, position="center"),
)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(
title="前10出版社, 书籍占比",
pos_left="center",
pos_top="20",
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color="#fff"),
),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=False),
)
.set_series_opts(
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(
trigger="item", formatter="{a} <br/>{b}: {c} ({d}%)"
),
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(color="rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.3)"),
)
)
c.render_notebook()

from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
content = df['出版社'].value_counts() # 读取出版社的数据
x_data = content.index.tolist()[:10]
y_data = content.values.tolist()[:10]
data_pair = [list(z) for z in zip(x_data, y_data)]
data_pair
# x_data = content.index.tolist()[:10] #
# y_data = content.values.tolist()[:10]
# data_pair = [list(z) for z in zip(x_data, y_data)]
c = (
Pie()
.add(
"",
data_pair,
radius=["40%", "75%"],
)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="出版社前10名"),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(orient="vertical", pos_top="15%", pos_left="2%"),
)
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {c}"))
)
c.render_notebook()

尾语
感谢你观看我的文章呐~本次航班到这里就结束啦 🛬
希望本篇文章有对你带来帮助 🎉,有学习到一点知识~
躲起来的星星🍥也在努力发光,你也要努力加油(让我们一起努力叭)。
 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-441301.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-441301.html
最后,宣传一下呀~👇👇👇更多源码、资料、素材、解答、交流皆点击下方名片获取呀👇👇👇文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-441301.html
到了这里,关于当~python批量获取某电商:商品数据并作可视化的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!