目录
24. 两两交换链表节点
19. 删除链表倒数第n个节点
方法一:普通写法
方法二:双指针法
面试题:找链表相交节点
142. 判断环形链表
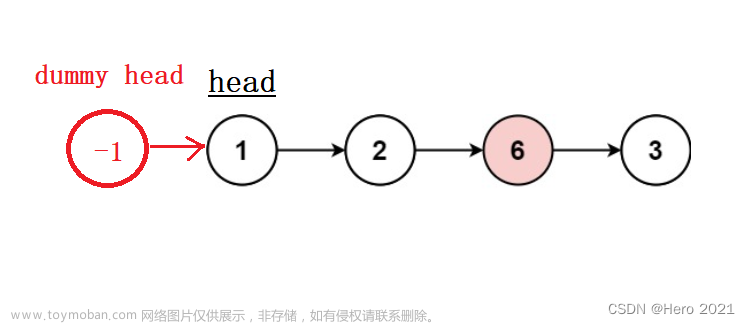
24. 两两交换链表节点
虚拟头节点的本质意义在于减少了特殊情况的处理。不用判断该节点是否在链表的第一位。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *pphead = new ListNode();
pphead->next = head;
ListNode *cur = pphead;
while(cur->next && cur->next->next){
ListNode *temp = cur->next;
ListNode *temp2 = cur->next->next->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
cur->next->next = temp;
temp->next = temp2;
cur = cur->next->next;
}
return pphead->next;
}
};19. 删除链表倒数第n个节点
方法一:普通写法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* pphead = new ListNode();
pphead->next = head;
int size = 0;
ListNode* cur = pphead;
while(cur->next){
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
cur = pphead;
while( size-n > 0){
size--;
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = cur->next->next;
return pphead->next;
}
};方法二:双指针法
定义快慢两个指针。
fast先走n步,再让fast和slow一起移动。则当fast指向末尾时,slow指向的即为倒数第n个元素。
而为了对该节点进行删除操作,所以本质上是找到倒数第n+1个节点,所以fast先走n+1步。
时间复杂度相同,但是思路比较优秀。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* pphead = new ListNode();
pphead->next = head;
ListNode* fast = pphead;
ListNode* slow = pphead;
int t = n+1;
while(t){
fast = fast->next;
t--;
}
while(fast){
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
slow->next = slow->next->next;
return pphead->next;
}
};面试题:找链表相交节点
本质:相交节点后的长度一定是相同的,所以只需要让他们从尾部对齐,从前向后遍历找相同节点即可。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if ( headA == NULL || headB == NULL)
return NULL;
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
ListNode* curA = headA;
ListNode* curB = headB;
while(curA){
a++;
curA = curA->next;
}
while(curB){
b++;
curB = curB->next;
}
if (a>b){
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
while(a>b){
a--;
curA = curA->next;
}
}
else{
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
while(b>a){
b--;
curB = curB->next;
}
}
while(curA){
if (curA == curB)
return curA;
curA = curA->next;
curB = curB->next;
}
return NULL;
}
};142. 判断环形链表
思路:建立快慢指针,相当于是追及问题。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-444739.html
相当考验数学功底,快指针速度设为2,慢指针速度设为1,则可以保证二者必然会相遇。因为速度差是1,其次,相遇点的位置和头节点到环入口的距离,在相差n圈环长度的意义下是相等的。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-444739.html
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast->next && fast->next->next){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (fast == slow){
ListNode* temp = head;
while(temp!=fast){
temp = temp->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return fast;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};到了这里,关于代码随想录算法训练day4 | 链表的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!