基于图像的裂缝分割与裂缝宽度计算(正交骨架线法)
From https://subce.gitee.io/htmls/essays/crack_width_calculation.html
分割
可以使用 opencv 的阈值分割,或者使用 CNN 等深度学习的方法进行裂缝分割,一般得到的分割结果如下,这里不再赘述。

寻找边缘
寻找边缘有两种方法,如下
- scikit-image skimage.measure.find_contours, 官方的示例如下:

- 另一种可以使用 Delaunay 三角网加上 alpha shape 进行边缘的提取,可以参考: Delaunay三角网 alpha shape 2D点集边缘线提取
中轴变换
为了计算裂缝的宽度,一般使用正交骨架线法,所以还需要计算裂缝的骨架线,这里一般使用中轴变换,同样可以使用 scikit-image 库中的算法,参见:Skeletonize — skimage v0.18.0 docs (scikit-image.org),官方示例:

宽度计算
下面是最重要的一部分,主要包括法向量估计和宽度计算,主要参见下面的两个函数 estimate_normal_for_pos() 和 get_crack_ctrlpts()
-
法向量估计
这里主要是查找给定点的 K 近邻点,可以使用 kd-tree 算法,然后使用 奇异值分解 (SVD)计算骨架线的法向量。然后,裂缝的宽度计算就是在这个方向量的方向上计算的。

-
宽度计算
这里的主要思想是: 对弈给定的一个位置,根据上方,估计此位置骨架线的方向量,并将此作为局部坐标系的y轴方向,x轴方向与此垂直,然后把裂缝的边缘线变换到这个局部坐标系中,然后在局部坐标系中,查找到骨架线法向量最近的两个裂缝边缘线点,并计算这两个点所形成的线段与骨架线法向量的交点。对于左右侧的两个裂缝边缘线,分别计算。(这一部分具体可参见代码实现,后续会补充具体的图解)

- 代码解释
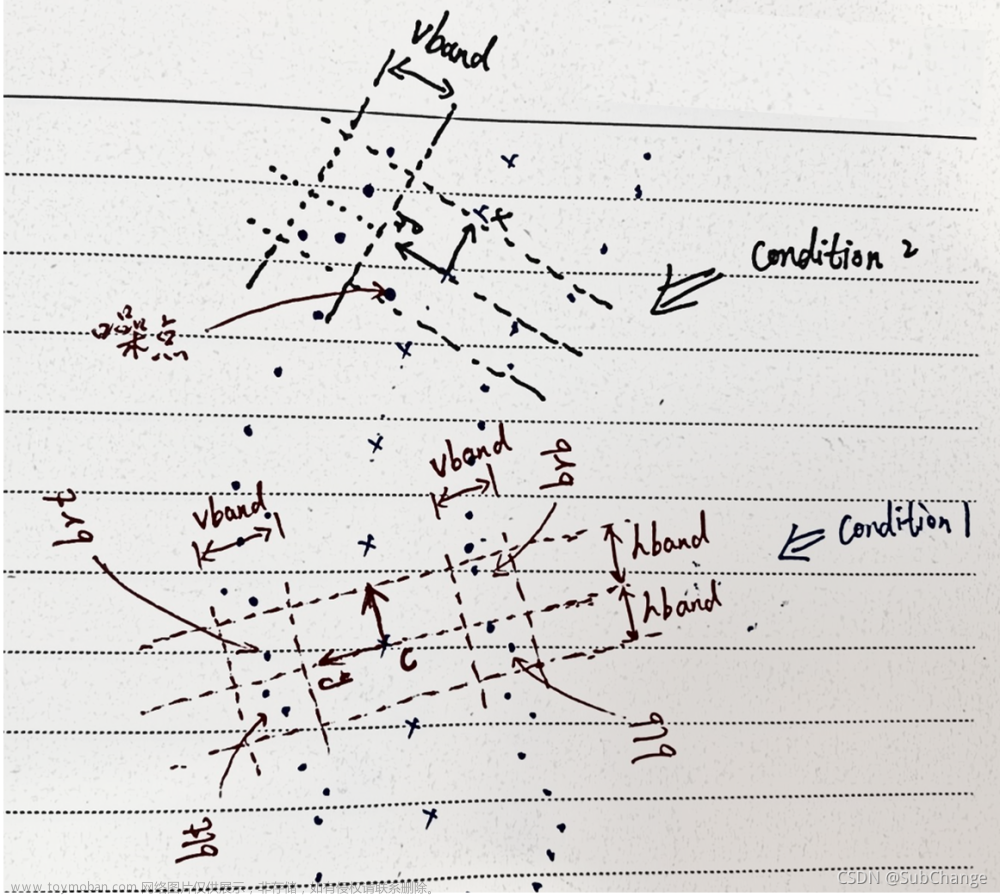
如上图所示,两条圆点线为边缘线,叉号线为骨架线,也即中心线,中心线上任意一点的法向量可以通过对邻域点集拟合直线得到。对于Condition1,中心线上一点 c c c, 根据 c c c 点的法向量建立局部坐标系,如上所示,根据 c c c 点的局部坐标系,可将裂缝边缘线上的点分为四个象限,为了找到每一个象限内离 y y y 轴最近的点,定义参数hband(见下面代码),然后只保留点到y轴的距离小于hband的点,也就是上图中三条虚线内的点,即保留中心点 c c c 两侧一定带宽内的点,然后vband是为了规定边缘线的粗细的参数,当发现 c c c 上方或者下方(两条边缘线)任意一侧点集的 y y y 坐标的极差(np.ptp)大于vband,说明这时候检测到的边缘线存在噪点,因为噪点为导致边缘线在 y y y 方向的极差变大,如图中Condition2中所标识处的噪点,噪点在vband带宽外,需要进一步过滤,过滤的方法是对存在噪点的地方,计算 y y y 坐标的均值,然后保留 y y y 坐标大于均值的点。通过hband,vband连个参数将中心点 c c c 处的边缘线分为4块区域,即图中的 b l t , b l b , b r t , b r b blt,blb,brt,brb blt,blb,brt,brb,最后,再在4块去区域中分别计算到 y y y 轴最近的点,即可以从来计算交点啦。
注:使用hband,vband主要是将c点附近的边缘线先初步框定出来。
代码
import numpy as np
from skimage import io
from skimage.morphology import medial_axis, skeletonize
from skimage import measure
from skimage import data
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.neighbors import KDTree
def show_2dpoints(pointcluster,s=None,quivers=None,qscale=1):
# pointcluster should be a list of numpy ndarray
# This functions would show a list of pint cloud in different colors
n = len(pointcluster)
nmax = n
if quivers is not None:
nq = len(quivers)
nmax = max(n,nq)
colors = ['r','g','b','c','m','y','k','tomato','gold']
if nmax < 10:
colors = np.array(colors[0:nmax])
else:
colors = np.random.rand(nmax,3)
fig = plt.figure(num=1)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
if s is None:
s = np.ones(n)*2
for i in range(n):
ax.scatter(pointcluster[i][:,0],pointcluster[i][:,1],s=s[i],c=[colors[i]],alpha=0.6)
if quivers is not None:
for i in range(nq):
ax.quiver(quivers[i][:,0],quivers[i][:,1],quivers[i][:,2],quivers[i][:,3],color=[colors[i]],scale=qscale)
plt.show()
def SVD(points):
# 二维,三维均适用
# 二维直线,三维平面
pts = points.copy()
# 奇异值分解
c = np.mean(pts, axis=0)
A = pts - c # shift the points
A = A.T #3*n
u, s, vh = np.linalg.svd(A, full_matrices=False, compute_uv=True) # A=u*s*vh
normal = u[:,-1]
# 法向量归一化
nlen = np.sqrt(np.dot(normal,normal))
normal = normal / nlen
# normal 是主方向的方向向量 与PCA最小特征值对应的特征向量是垂直关系
# u 每一列是一个方向
# s 是对应的特征值
# c >>> 点的中心
# normal >>> 拟合的方向向量
return u,s,c,normal
def calcu_dis_from_ctrlpts(ctrlpts):
if ctrlpts.shape[1]==4:
return np.sqrt(np.sum((ctrlpts[:,0:2]-ctrlpts[:,2:4])**2,axis=1))
else:
return np.sqrt(np.sum((ctrlpts[:,[0,2]]-ctrlpts[:,[3,5]])**2,axis=1))
def estimate_normal_for_pos(pos,points,n):
# estimate normal vectors at a given point
pts = np.copy(points)
tree = KDTree(pts, leaf_size=2)
idx = tree.query(pos, k=n, return_distance=False, dualtree=False, breadth_first=False)
#pts = np.concatenate((np.concatenate((pts[0].reshape(1,-1),pts),axis=0),pts[-1].reshape(1,-1)),axis=0)
normals = []
for i in range(0,pos.shape[0]):
pts_for_normals = pts[idx[i,:],:]
_,_,_,normal = SVD(pts_for_normals)
normals.append(normal)
normals = np.array(normals)
return normals
def estimate_normals(points,n):
pts = np.copy(points)
tree = KDTree(pts, leaf_size=2)
idx = tree.query(pts, k=n, return_distance=False, dualtree=False, breadth_first=False)
#pts = np.concatenate((np.concatenate((pts[0].reshape(1,-1),pts),axis=0),pts[-1].reshape(1,-1)),axis=0)
normals = []
for i in range(0,pts.shape[0]):
pts_for_normals = pts[idx[i,:],:]
_,_,_,normal = SVD(pts_for_normals)
normals.append(normal)
normals = np.array(normals)
return normals
def get_crack_ctrlpts(centers,normals,bpoints,hband=5,vband=2):
# main algorithm to obtain crack width
cpoints = np.copy(centers)
cnormals = np.copy(normals)
xmatrix = np.array([[0,1],[-1,0]])
cnormalsx = np.dot(xmatrix,cnormals.T).T # the normal of x axis
N = cpoints.shape[0]
interp_segm = []
widths = []
for i in range(N):
try:
ny = cnormals[i]
nx = cnormalsx[i]
tform = np.array([nx,ny])
bpoints_loc = np.dot(tform,bpoints.T).T
cpoints_loc = np.dot(tform,cpoints.T).T
ci = cpoints_loc[i]
bl_ind = (bpoints_loc[:,0]-(ci[0]-hband))*(bpoints_loc[:,0]-ci[0])<0
br_ind = (bpoints_loc[:,0]-ci[0])*(bpoints_loc[:,0]-(ci[0]+hband))<=0
bl = bpoints_loc[bl_ind] # left points
br = bpoints_loc[br_ind] # right points
blt = bl[bl[:,1]>np.mean(bl[:,1])]
if np.ptp(blt[:,1])>vband:
blt = blt[blt[:,1]>np.mean(blt[:,1])]
blb = bl[bl[:,1]<np.mean(bl[:,1])]
if np.ptp(blb[:,1])>vband:
blb = blb[blb[:,1]<np.mean(blb[:,1])]
brt = br[br[:,1]>np.mean(br[:,1])]
if np.ptp(brt[:,1])>vband:
brt = brt[brt[:,1]>np.mean(brt[:,1])]
brb = br[br[:,1]<np.mean(br[:,1])]
if np.ptp(brb[:,1])>vband:
brb = brb[brb[:,1]<np.mean(brb[:,1])]
#bh = np.vstack((bl,br))
#bmax = np.max(bh[:,1])
#bmin = np.min(bh[:,1])
#blt = bl[bl[:,1]>bmax-vband] # left top points
#blb = bl[bl[:,1]<bmin+vband] # left bottom points
#brt = br[br[:,1]>bmax-vband] # right top points
#brb = br[br[:,1]<bmin+vband] # right bottom points
t1 = blt[np.argsort(blt[:,0])[-1]]
t2 = brt[np.argsort(brt[:,0])[0]]
b1 = blb[np.argsort(blb[:,0])[-1]]
b2 = brb[np.argsort(brb[:,0])[0]]
interp1 = (ci[0]-t1[0])*((t2[1]-t1[1])/(t2[0]-t1[0]))+t1[1]
interp2 = (ci[0]-b1[0])*((b2[1]-b1[1])/(b2[0]-b1[0]))+b1[1]
if interp1-ci[1]>0 and interp2-ci[1]<0:
widths.append([i,interp1-ci[1],interp2-ci[1]])
interps = np.array([[ci[0],interp1],[ci[0],interp2]])
interps_rec = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(tform),interps.T).T
#show_2dpoints([bpointsxl_loc1,bpointsxl_loc2,bpointsxr_loc1,bpointsxr_loc2,np.array([ptsl_1,ptsl_2]),np.array([ptsr_1,ptsr_2]),interps,ci.reshape(1,-1)],s=[1,1,1,1,20,20,20,20])
interps_rec = interps_rec.reshape(1,-1)[0,:]
interp_segm.append(interps_rec)
except:
print("the %d-th was wrong" % i)
continue
interp_segm = np.array(interp_segm)
widths = np.array(widths)
# check
# show_2dpoints([np.array([[ci[0],interp1],[ci[0],interp2]]),np.array([t1,t2,b1,b2]),cpoints_loc,bl,br],[10,20,15,2,2])
return interp_segm, widths
path = "E:/Users/SubChange/Desktop/"
image = io.imread(path+"7Q3A9060-18.png", as_gray=True)
iw,ih = image.shape
blobs = np.copy(image)
blobs[blobs<128] = 0
blobs[blobs>128] = 1
blobs = blobs.astype(np.uint8)
# Generate the data
#blobs = data.binary_blobs(200, blob_size_fraction=.2,
#volume_fraction=.35, seed=1)
# using scikit-image
## Compute the medial axis (skeleton) and the distance transform
#skel, distance = medial_axis(blobs, return_distance=True)
## Distance to the background for pixels of the skeleton
#dist_on_skel = distance * skel
# Compare with other skeletonization algorithms
skeleton = skeletonize(blobs)
#skeleton_lee = skeletonize(blobs, method='lee')
x, y = np.where(skeleton>0)
centers = np.hstack((x.reshape(-1,1),y.reshape(-1,1)))
normals = estimate_normals(centers,3)
# search contours of the crack
contours = measure.find_contours(blobs, 0.8)
bl = contours[0]
br = contours[1]
bpoints = np.vstack((bl,br))
#interp_segm, widths = get_crack_ctrlpts(centers,normals,bpoints,hband=2,vband=2)
bpixel = np.zeros((iw,ih,3),dtype=np.uint8)
bpoints = bpoints.astype(np.int)
bpixel[bpoints[:,0],bpoints[:,1],0] = 255
skeleton_pixel = np.zeros((iw,ih,3),dtype=np.uint8)
skeleton_pixel[skeleton,1] = 255
bpixel_and_skeleton = np.copy(bpixel)
bpixel_and_skeleton[skeleton,1] = 255
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,3, figsize=(8, 8))
ax = axes.ravel()
ax[0].imshow(blobs, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[0].axis('off')
ax[1].imshow(bpixel_and_skeleton)
#for contour in contours:
# ax[1].plot(contour[:, 1], contour[:, 0], linewidth=2)
#for i in range(interp_segm.shape[0]):
# ax[1].plot([interp_segm[i,1],interp_segm[i,3]],[interp_segm[i,0],interp_segm[i,2]],'-b')
#ax[1].set_title('medial_axis')
ax[1].axis('off')
# ================ small window ==================
pos = np.array([191, 291]).reshape(1,-1) # input (x,y) where need to calculate crack width
# pos = np.array([142, 178]).reshape(1,-1)
posn = estimate_normal_for_pos(pos,centers,3)
interps, widths2 = get_crack_ctrlpts(pos,posn,bpoints,hband=1.5,vband=2)
sx = pos[0,0] - 20
sy = pos[0,1] - 20
ax[2].imshow(bpixel_and_skeleton)
for i in range(interps.shape[0]):
ax[2].plot([interps[i,1],interps[i,3]],[interps[i,0],interps[i,2]],c='c',ls='-',lw=5,marker='o',ms=8,mec='c',mfc='c')
ax[2].set_ylim(sx,sx+40)
ax[2].set_xlim(sy,sy+40)
#ax[2].set_title('skeletonize')
ax[2].axis('off')
print(interps)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
结果


另外,附上另外一张图片,是整条裂缝的宽度计算结果:
更新
针对裂缝形状比较复杂,即不是单条裂缝,图像中有多条裂缝,且裂缝的宽度在一定的范围的,可以做如下改进:
针对裂缝坐标下的四个象限的裂缝边缘线的点,设置一个预估计的裂缝宽度,并在四个象限中,删除宽度超出预估裂缝宽度的边缘像素点,这样便能够筛选离中轴线最近的边缘线了,具体看下面代码,即添加 est_width参数。
def get_crack_ctrlpts(centers,normals,bpoints,hband=5,vband=2,est_width=0):
# main algorithm to obtain crack width
cpoints = np.copy(centers)
cnormals = np.copy(normals)
xmatrix = np.array([[0,1],[-1,0]])
cnormalsx = np.dot(xmatrix,cnormals.T).T # the normal of x axis
N = cpoints.shape[0]
interp_segm = []
widths = []
for i in range(N):
try:
ny = cnormals[i]
nx = cnormalsx[i]
tform = np.array([nx,ny])
bpoints_loc = np.dot(tform,bpoints.T).T
cpoints_loc = np.dot(tform,cpoints.T).T
ci = cpoints_loc[i]
bl_ind = (bpoints_loc[:,0]-(ci[0]-hband))*(bpoints_loc[:,0]-ci[0])<0
br_ind = (bpoints_loc[:,0]-ci[0])*(bpoints_loc[:,0]-(ci[0]+hband))<=0
bl = bpoints_loc[bl_ind] # left points
br = bpoints_loc[br_ind] # right points
if est_width>0:
# 下面的数值 est_width 是预估计的裂缝宽度
half_est_width = est_width / 2
blt = bl[(bl[:,1]-(ci[1]+half_est_width))*(bl[:,1]-ci[1])<0]
blb = bl[(bl[:,1]-(ci[1]-half_est_width))*(bl[:,1]-ci[1])<0]
brt = br[(br[:,1]-(ci[1]+half_est_width))*(br[:,1]-ci[1])<0]
brb = br[(br[:,1]-(ci[1]-half_est_width))*(br[:,1]-ci[1])<0]
else:
blt = bl[bl[:,1]>np.mean(bl[:,1])]
if np.ptp(blt[:,1])>vband:
blt = blt[blt[:,1]>np.mean(blt[:,1])]
blb = bl[bl[:,1]<np.mean(bl[:,1])]
if np.ptp(blb[:,1])>vband:
blb = blb[blb[:,1]<np.mean(blb[:,1])]
brt = br[br[:,1]>np.mean(br[:,1])]
if np.ptp(brt[:,1])>vband:
brt = brt[brt[:,1]>np.mean(brt[:,1])]
brb = br[br[:,1]<np.mean(br[:,1])]
if np.ptp(brb[:,1])>vband:
brb = brb[brb[:,1]<np.mean(brb[:,1])]
# blt = bl[bl[:,1]>np.mean(bl[:,1])]
# if np.ptp(blt[:,1])>vband:
# blt = blt[blt[:,1]<ci[1]+50]
# #blt = blt[blt[:,1]>np.mean(blt[:,1])] (外侧)
# #blt = blt[blt[:,1]<(np.max(blt[:,1])-0.5*np.ptp(blt[:,1]))] (内侧)
# blb = bl[bl[:,1]<np.mean(bl[:,1])]
# if np.ptp(blb[:,1])>vband:
# blb = blb[blb[:,1]>ci[1]-50]
# #blb = blb[blb[:,1]<np.mean(blb[:,1])]
# #blb = blb[blb[:,1]>(np.min(blb[:,1])+0.5*np.ptp(blb[:,1]))]
# brt = br[br[:,1]>np.mean(br[:,1])]
# if np.ptp(brt[:,1])>vband:
# brt = brt[brt[:,1]<ci[1]+50]
# #brt = brt[brt[:,1]>np.mean(brt[:,1])]
# #brt = brt[brt[:,1]<(np.max(brt[:,1])-0.5*np.ptp(brt[:,1]))]
# brb = br[br[:,1]<np.mean(br[:,1])]
# if np.ptp(brb[:,1])>vband:
# brb = brb[brb[:,1]>ci[1]-50]
# # brb = brb[brb[:,1]<np.mean(brb[:,1])]
# # brb = brb[brb[:,1]>(np.min(brb[:,1])+0.5*np.ptp(brb[:,1]))]
#bh = np.vstack((bl,br))
#bmax = np.max(bh[:,1])
#bmin = np.min(bh[:,1])
#blt = bl[bl[:,1]>bmax-vband] # left top points
#blb = bl[bl[:,1]<bmin+vband] # left bottom points
#brt = br[br[:,1]>bmax-vband] # right top points
#brb = br[br[:,1]<bmin+vband] # right bottom points
t1 = blt[np.argsort(blt[:,0])[-1]]
t2 = brt[np.argsort(brt[:,0])[0]]
b1 = blb[np.argsort(blb[:,0])[-1]]
b2 = brb[np.argsort(brb[:,0])[0]]
interp1 = (ci[0]-t1[0])*((t2[1]-t1[1])/(t2[0]-t1[0]))+t1[1]
interp2 = (ci[0]-b1[0])*((b2[1]-b1[1])/(b2[0]-b1[0]))+b1[1]
if interp1-ci[1]>0 and interp2-ci[1]<0:
widths.append([i,interp1-ci[1],interp2-ci[1]])
interps = np.array([[ci[0],interp1],[ci[0],interp2]])
interps_rec = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(tform),interps.T).T
#show_2dpoints([bpointsxl_loc1,bpointsxl_loc2,bpointsxr_loc1,bpointsxr_loc2,np.array([ptsl_1,ptsl_2]),np.array([ptsr_1,ptsr_2]),interps,ci.reshape(1,-1)],s=[1,1,1,1,20,20,20,20])
interps_rec = interps_rec.reshape(1,-1)[0,:]
interp_segm.append(interps_rec)
except:
print("the %d-th was wrong" % i)
continue
interp_segm = np.array(interp_segm)
widths = np.array(widths)
# check
# show_2dpoints([np.array([[ci[0],interp1],[ci[0],interp2]]),np.array([t1,t2,b1,b2]),cpoints_loc,bl,br],[10,20,15,2,2])
return interp_segm, widths
具体效果如下(注意骨架线和边缘线的提取与传参问题):
鉴于很多人询问怎么测量整条裂缝的宽度,这里我将代码进行了略微的调整,仍然是针对于最先给出的裂缝,可以直接运行的代码和结果如下,大家可以尝试看看效果,应该是可以直接跑的通的,请注意更换裂缝图像路径,跑通后大家再仔细看看里面是怎么调整的。个人水平有限,代码写的有点乱,请见谅,如果还不能跑通,可私信沟通文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-446746.html
import numpy as np
from skimage import io
from skimage.morphology import medial_axis, skeletonize
from skimage import measure
from skimage import data
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.neighbors import KDTree
def show_2dpoints(pointcluster,s=None,quivers=None,qscale=1):
# pointcluster should be a list of numpy ndarray
# This functions would show a list of pint cloud in different colors
n = len(pointcluster)
nmax = n
if quivers is not None:
nq = len(quivers)
nmax = max(n,nq)
colors = ['r','g','b','c','m','y','k','tomato','gold']
if nmax < 10:
colors = np.array(colors[0:nmax])
else:
colors = np.random.rand(nmax,3)
fig = plt.figure(num=1)
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
if s is None:
s = np.ones(n)*2
for i in range(n):
ax.scatter(pointcluster[i][:,0],pointcluster[i][:,1],s=s[i],c=[colors[i]],alpha=0.6)
if quivers is not None:
for i in range(nq):
ax.quiver(quivers[i][:,0],quivers[i][:,1],quivers[i][:,2],quivers[i][:,3],color=[colors[i]],scale=qscale)
plt.show()
def SVD(points):
# 二维,三维均适用
# 二维直线,三维平面
pts = points.copy()
# 奇异值分解
c = np.mean(pts, axis=0)
A = pts - c # shift the points
A = A.T #3*n
u, s, vh = np.linalg.svd(A, full_matrices=False, compute_uv=True) # A=u*s*vh
normal = u[:,-1]
# 法向量归一化
nlen = np.sqrt(np.dot(normal,normal))
normal = normal / nlen
# normal 是主方向的方向向量 与PCA最小特征值对应的特征向量是垂直关系
# u 每一列是一个方向
# s 是对应的特征值
# c >>> 点的中心
# normal >>> 拟合的方向向量
return u,s,c,normal
def calcu_dis_from_ctrlpts(ctrlpts):
if ctrlpts.shape[1]==4:
return np.sqrt(np.sum((ctrlpts[:,0:2]-ctrlpts[:,2:4])**2,axis=1))
else:
return np.sqrt(np.sum((ctrlpts[:,[0,2]]-ctrlpts[:,[3,5]])**2,axis=1))
def estimate_normal_for_pos(pos,points,n):
"""
计算pos处的法向量.
Input:
------
pos: nx2 ndarray 需要计算法向量的位置.
points: 骨架线的点集
n: 用到的近邻点的个数
Output:
------
normals: nx2 ndarray 在pos位置处的法向量.
"""
# estimate normal vectors at a given point
pts = np.copy(points)
tree = KDTree(pts, leaf_size=2)
idx = tree.query(pos, k=n, return_distance=False, dualtree=False, breadth_first=False)
#pts = np.concatenate((np.concatenate((pts[0].reshape(1,-1),pts),axis=0),pts[-1].reshape(1,-1)),axis=0)
normals = []
for i in range(0,pos.shape[0]):
pts_for_normals = pts[idx[i,:],:]
_,_,_,normal = SVD(pts_for_normals)
normals.append(normal)
normals = np.array(normals)
return normals
def estimate_normals(points,n):
"""
计算points表示的曲线上的每一个点法向量.
等同于 estimate_normal_for_pos(points,points,n)
Input:
------
points: nx2 ndarray 曲线点集.
n: 用到的近邻点的个数
Output:
------
normals: nx2 ndarray 在points曲线上的每一处的法向量.
"""
pts = np.copy(points)
tree = KDTree(pts, leaf_size=2)
idx = tree.query(pts, k=n, return_distance=False, dualtree=False, breadth_first=False)
#pts = np.concatenate((np.concatenate((pts[0].reshape(1,-1),pts),axis=0),pts[-1].reshape(1,-1)),axis=0)
normals = []
for i in range(0,pts.shape[0]):
pts_for_normals = pts[idx[i,:],:]
_,_,_,normal = SVD(pts_for_normals)
normals.append(normal)
normals = np.array(normals)
return normals
def get_crack_ctrlpts(centers,normals,bpoints,hband=5,vband=2,est_width=0):
# main algorithm to obtain crack width
cpoints = np.copy(centers)
cnormals = np.copy(normals)
xmatrix = np.array([[0,1],[-1,0]])
cnormalsx = np.dot(xmatrix,cnormals.T).T # the normal of x axis
N = cpoints.shape[0]
interp_segm = []
widths = []
for i in range(N):
try:
ny = cnormals[i]
nx = cnormalsx[i]
tform = np.array([nx,ny])
bpoints_loc = np.dot(tform,bpoints.T).T
cpoints_loc = np.dot(tform,cpoints.T).T
ci = cpoints_loc[i]
bl_ind = (bpoints_loc[:,0]-(ci[0]-hband))*(bpoints_loc[:,0]-ci[0])<0
br_ind = (bpoints_loc[:,0]-ci[0])*(bpoints_loc[:,0]-(ci[0]+hband))<=0
bl = bpoints_loc[bl_ind] # left points
br = bpoints_loc[br_ind] # right points
if est_width>0:
# 下面的数值 est_width 是预估计的裂缝宽度
half_est_width = est_width / 2
blt = bl[(bl[:,1]-(ci[1]+half_est_width))*(bl[:,1]-ci[1])<0]
blb = bl[(bl[:,1]-(ci[1]-half_est_width))*(bl[:,1]-ci[1])<0]
brt = br[(br[:,1]-(ci[1]+half_est_width))*(br[:,1]-ci[1])<0]
brb = br[(br[:,1]-(ci[1]-half_est_width))*(br[:,1]-ci[1])<0]
else:
blt = bl[bl[:,1]>np.mean(bl[:,1])]
if np.ptp(blt[:,1])>vband:
blt = blt[blt[:,1]>np.mean(blt[:,1])]
blb = bl[bl[:,1]<np.mean(bl[:,1])]
if np.ptp(blb[:,1])>vband:
blb = blb[blb[:,1]<np.mean(blb[:,1])]
brt = br[br[:,1]>np.mean(br[:,1])]
if np.ptp(brt[:,1])>vband:
brt = brt[brt[:,1]>np.mean(brt[:,1])]
brb = br[br[:,1]<np.mean(br[:,1])]
if np.ptp(brb[:,1])>vband:
brb = brb[brb[:,1]<np.mean(brb[:,1])]
# blt = bl[bl[:,1]>np.mean(bl[:,1])]
# if np.ptp(blt[:,1])>vband:
# blt = blt[blt[:,1]<ci[1]+50]
# #blt = blt[blt[:,1]>np.mean(blt[:,1])] (外侧)
# #blt = blt[blt[:,1]<(np.max(blt[:,1])-0.5*np.ptp(blt[:,1]))] (内侧)
# blb = bl[bl[:,1]<np.mean(bl[:,1])]
# if np.ptp(blb[:,1])>vband:
# blb = blb[blb[:,1]>ci[1]-50]
# #blb = blb[blb[:,1]<np.mean(blb[:,1])]
# #blb = blb[blb[:,1]>(np.min(blb[:,1])+0.5*np.ptp(blb[:,1]))]
# brt = br[br[:,1]>np.mean(br[:,1])]
# if np.ptp(brt[:,1])>vband:
# brt = brt[brt[:,1]<ci[1]+50]
# #brt = brt[brt[:,1]>np.mean(brt[:,1])]
# #brt = brt[brt[:,1]<(np.max(brt[:,1])-0.5*np.ptp(brt[:,1]))]
# brb = br[br[:,1]<np.mean(br[:,1])]
# if np.ptp(brb[:,1])>vband:
# brb = brb[brb[:,1]>ci[1]-50]
# # brb = brb[brb[:,1]<np.mean(brb[:,1])]
# # brb = brb[brb[:,1]>(np.min(brb[:,1])+0.5*np.ptp(brb[:,1]))]
#bh = np.vstack((bl,br))
#bmax = np.max(bh[:,1])
#bmin = np.min(bh[:,1])
#blt = bl[bl[:,1]>bmax-vband] # left top points
#blb = bl[bl[:,1]<bmin+vband] # left bottom points
#brt = br[br[:,1]>bmax-vband] # right top points
#brb = br[br[:,1]<bmin+vband] # right bottom points
t1 = blt[np.argsort(blt[:,0])[-1]]
t2 = brt[np.argsort(brt[:,0])[0]]
b1 = blb[np.argsort(blb[:,0])[-1]]
b2 = brb[np.argsort(brb[:,0])[0]]
interp1 = (ci[0]-t1[0])*((t2[1]-t1[1])/(t2[0]-t1[0]))+t1[1]
interp2 = (ci[0]-b1[0])*((b2[1]-b1[1])/(b2[0]-b1[0]))+b1[1]
if interp1-ci[1]>0 and interp2-ci[1]<0:
widths.append([i,interp1-ci[1],interp2-ci[1]])
interps = np.array([[ci[0],interp1],[ci[0],interp2]])
interps_rec = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(tform),interps.T).T
#show_2dpoints([bpointsxl_loc1,bpointsxl_loc2,bpointsxr_loc1,bpointsxr_loc2,np.array([ptsl_1,ptsl_2]),np.array([ptsr_1,ptsr_2]),interps,ci.reshape(1,-1)],s=[1,1,1,1,20,20,20,20])
interps_rec = interps_rec.reshape(1,-1)[0,:]
interp_segm.append(interps_rec)
except:
print("the %d-th was wrong" % i)
continue
interp_segm = np.array(interp_segm)
widths = np.array(widths)
# check
# show_2dpoints([np.array([[ci[0],interp1],[ci[0],interp2]]),np.array([t1,t2,b1,b2]),cpoints_loc,bl,br],[10,20,15,2,2])
return interp_segm, widths
path = "e:/Users/subchange/Downloads/"
image = io.imread(path+"20210706162948837.png", as_gray=True)
iw,ih = image.shape
blobs = np.copy(image)
#blobs[blobs<128] = 0
#blobs[blobs>128] = 1
blobs = blobs.astype(np.uint8)
# Generate the data
#blobs = data.binary_blobs(200, blob_size_fraction=.2,
#volume_fraction=.35, seed=1)
# using scikit-image
## Compute the medial axis (skeleton) and the distance transform
#skel, distance = medial_axis(blobs, return_distance=True)
## Distance to the background for pixels of the skeleton
#dist_on_skel = distance * skel
# Compare with other skeletonization algorithms
skeleton = skeletonize(blobs)
#skeleton_lee = skeletonize(blobs, method='lee')
x, y = np.where(skeleton>0)
centers = np.hstack((x.reshape(-1,1),y.reshape(-1,1)))
normals = estimate_normals(centers, 9) # 这个用于估计法向量的KNN
# search contours of the crack
contours = measure.find_contours(blobs, 0.8)
bl = contours[0]
br = contours[1]
bpoints = np.vstack((bl,br))
#interp_segm, widths = get_crack_ctrlpts(centers,normals,bpoints,hband=2,vband=2)
bpixel = np.zeros((iw,ih,3),dtype=np.uint8)
bpoints = bpoints.astype(np.int64)
bpixel[bpoints[:,0],bpoints[:,1],0] = 255
skeleton_pixel = np.zeros((iw,ih,3),dtype=np.uint8)
skeleton_pixel[skeleton,1] = 255
bpixel_and_skeleton = np.copy(bpixel)
bpixel_and_skeleton[skeleton,1] = 255
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,2, figsize=(8, 8))
ax = axes.ravel()
ax[0].imshow(blobs, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax[0].axis('off')
ax[1].imshow(bpixel_and_skeleton)
#for contour in contours:
# ax[1].plot(contour[:, 1], contour[:, 0], linewidth=2)
#for i in range(interp_segm.shape[0]):
# ax[1].plot([interp_segm[i,1],interp_segm[i,3]],[interp_segm[i,0],interp_segm[i,2]],'-b')
#ax[1].set_title('medial_axis')
ax[1].axis('off')
interps, widths = get_crack_ctrlpts(centers, normals, bpoints, hband=2, vband=2, est_width=30)
interps_show = interps[np.random.choice(interps.shape[0], 120, replace=False),:] # 由于太多,这里随机采样120个测量位置,进行显示
for i in range(interps_show.shape[0]):
ax[1].plot([interps_show[i,1],interps_show[i,3]],[interps_show[i,0],interps_show[i,2]],c='c', ls='-', lw=2, marker='o',ms=4,mec='c',mfc='c')
## ================ small window ==================
#pos = np.array([191, 291]).reshape(1,-1) # input (x,y) where need to calculate crack width
## pos = np.array([142, 178]).reshape(1,-1)
#posn = estimate_normal_for_pos(pos,centers,3)
#interps, widths2 = get_crack_ctrlpts(pos,posn,bpoints,hband=1.5,vband=2)
#sx = pos[0,0] - 20
#sy = pos[0,1] - 20
#ax[2].imshow(bpixel_and_skeleton)
#for i in range(interps.shape[0]):
# ax[2].plot([interps[i,1],interps[i,3]],[interps[i,0],interps[i,2]],c='c',ls='-',lw=5,marker='o',ms=8,mec='c',mfc='c')
#ax[2].set_ylim(sx,sx+40)
#ax[2].set_xlim(sy,sy+40)
##ax[2].set_title('skeletonize')
#ax[2].axis('off')
#print(interps)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-446746.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-446746.html
到了这里,关于基于图像的裂缝分割与裂缝宽度计算(正交骨架线法)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!