目录
树的定义
二叉树的定义
二叉树的存储表示
二叉树的创建和前中后序遍历
通过中序遍历和先序遍历来构建树
通过后序遍历加先序遍历构建树
链式存储的树 将其中序遍历
非递归后序遍历
非递归后序遍历第二种方法
非递归中序遍历
非递归前序遍历
层次遍历
求二叉树节点个数
求二叉树深度
判断一个数是不是满二叉树
判断一个数是不是完全二叉树
树的定义
树是由n个结点组成的有限集合,如果 n=0 ,称为空树,如果n>0则
1、有一个特定的称之为根(root)的结点,它只有直接后继,但没有直接前驱;
2、除根以外的其他结点划分为m(m>=0)个互不交互的有限集合,每个集合又是一棵树,称为子树。每个子树的根节点只有一个直接前驱。
节点的度:一个节点含有的子树的个数
树的度:最大节点的度称为树的度
叶节点:度为零的节点
分支节点:度不为零
兄弟节点:含有相同父节点的节点
节点的层次:从根开始定义起,根为第一层,根的子节点为第二层
深度:对于任意节点n,n的深度为从根到n的唯一路径长,根的深度为0;
二叉树的定义
一棵二叉树是结点的一个有限集合,是由一个根节点加上两颗分别称为左子树和右子树的、互不相交的二叉树组成。
二叉树的性质:
每一个结点最多有两个子结点
高度为k的二叉树节点数最多为2的k+1次方-1
满二叉树:
每一层都达到了结点的最大个数
完全二叉树:
高度为h的树,共有h+1层,除h层以外,都达到最大个数,第h层从右向左连续缺若干结点,这就是完全二叉树。
二叉树的存储表示
顺序存储:当从0下标开始时,左孩子:i*2+1 右孩子:i*2+2 父节点:(i-1)/2
假设只有右孩子 就会导致很多下标处没有数据 太浪费空间 所以存在第二种存储方式,一般只有完全二叉树才用数组存放文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-446763.html
链式存储 :分为二叉链表和三叉,区别是结构体里有没有parent指针 便于回溯文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-446763.html
二叉树的创建和前中后序遍历
typedef char Elemtype;
typedef struct BtNode
{
struct BtNode* leftchild;
struct BtNode* rightchild;
Elemtype data;
}BtNode,*BinartTree;
void InOrder(BtNode* ptr)//中序遍历
{
if (ptr == NULL) { return; }
InOrder(ptr->leftchild);
cout << ptr->data << endl;
InOrder(ptr->rightchild);
}
void PreOrder(BtNode* ptr)//先序遍历
{
if (ptr == NULL) { return; }
cout << ptr->data << endl;
PreOrder(ptr->leftchild);
PreOrder(ptr->rightchild);
}
void PastOrder(BtNode* ptr)//后序遍历
{
if (ptr == NULL) { return; }
PastOrder(ptr->leftchild);
PastOrder(ptr->rightchild);
cout << ptr->data << endl;
}
BtNode* BuyNode()
{
BtNode* ptr = (BtNode*)malloc(sizeof(BtNode));
if (ptr == nullptr)exit(1);
memset(ptr, 0, sizeof(BtNode));
return ptr;
}
BtNode* CreatTree(const char*& str)
{
if (str == nullptr && strlen(str) <= 0) { return nullptr; }
BtNode* s = nullptr;
if (*str != '#') {
s = BuyNode();
s->data = *str;
s->leftchild = CreatTree(++str);
s->rightchild = CreatTree(++str);
}
return s;
}
int main()
{
const char* str = "ABC##DE##F##G#H##";
BinartTree root = CreatTree(str);
PastOrder(root);
PreOrder(root);
InOrder(root);
return 0;
}通过中序遍历和先序遍历来构建树
int Findpos(const char* ptr, int n, char first)
{
int pos = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (ptr[i] == first) { pos = i; break; }
}
return pos;
}
BtNode* CreateBTreePI(const char* str, const char* ptr, int n)
{
BtNode* s = nullptr;
if (n > 0)
{
s = BuyNode();
s->data = str[0];
int pos = Findpos(ptr, n, str[0]);
if (pos == -1) { exit(1); }
s->leftchild = CreateBTreePI(str+1, ptr, pos);
s->rightchild = CreateBTreePI(str+pos+1, ptr+pos+1, n-pos-1);
}
return s;
}
BtNode* CreatBinartTreePI(const char* str, const char* ptr)
{
int n = strlen(str);
int m = strlen(ptr);
if (nullptr == ptr || nullptr == str || n < 1 || m < 1 || n != m) { return nullptr; }
else { return CreateBTreePI(str, ptr,n); }
}
int main()
{
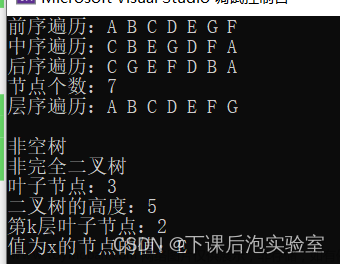
const char* str = "ABCDEFGH";
const char* ptr = "CBEDFAGH";
BinartTree root = CreatBinartTreePI(str, ptr);
return 0;
}通过后序遍历加先序遍历构建树
int Findpos(const char* ptr, int n, char first)
{
int pos = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (ptr[i] == first) { pos = i; break; }
}
return pos;
}
BtNode* CreateBTreePL(const char* ptr, const char* ltr, int n)
{
BtNode* s = nullptr;
if (n > 0)
{
s = BuyNode();
s->data = ltr[n-1];
int pos = Findpos(ptr, n, ltr[n-1]);
if (pos == -1) { exit(1); }
s->leftchild = CreateBTreePL(ptr, ltr, pos);
s->rightchild = CreateBTreePL(ptr + pos+1 , ltr + pos, n - pos - 1);
}
return s;
}
BtNode* CreatBinartTreePL(const char* ptr, const char* ltr)
{
int n = strlen(ptr);
int m = strlen(ltr);
if (nullptr == ptr || nullptr == ltr || n < 1 || m < 1 || n != m) { return nullptr; }
else { return CreateBTreePL(ptr, ltr, n); }
}
int main()
{
const char* str = "ABCDEFGH";
const char* ptr = "CBEDFAGH";
const char* ltr = "CEFDBHGA";
BinartTree root = CreatBinartTreePL(ptr, ltr);
return 0;
}
链式存储的树 将其中序遍历
void InOrder_Ar(const int* ar, int n, int i)
{
if (i < n) {
InOrder_Ar(ar, n, i * 2 + 1);
if (ar[i] != -1)
{
cout << ar[i] << " ";
}
InOrder_Ar(ar, n, i * 2 + 2);
}
}
int main()
{
int ar[] = { 31,23,12,66,-1,5,17,70,62,-1,-1,-1,88,-1,55 };
int n = sizeof(ar) / sizeof(ar[0]);
InOrder_Ar(ar, n, 0);
return 0;
}非递归后序遍历
if (nullptr == ptr) { return; }
stack<BtNode*> st;
BtNode* tag = nullptr;
while (!st.empty() || ptr != nullptr) {
while (ptr != nullptr)
{
st.push(ptr);
ptr = ptr->leftchild;
}
ptr = st.top();
st.pop();
if (ptr->rightchild == nullptr || ptr->rightchild == tag)
{
cout << ptr->data << " ";
tag = ptr;
ptr = nullptr;
}
else
{
st.push(ptr);
ptr = ptr->rightchild;
}
}非递归后序遍历第二种方法
struct StkNode
{
BtNode* Pnode;
int popnum;
};
void NicePastOrder_2(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (ptr == nullptr) { return; }
stack<StkNode>st;
st.push(StkNode{ ptr,0 });
while (!st.empty())
{
StkNode node = st.top(); st.pop();
if (++node.popnum == 3)
{
cout << node.Pnode->data << " ";
}
else
{
st.push(node);
if (node.popnum == 1 &&node.Pnode->leftchild != nullptr)
{
st.push(StkNode{ node.Pnode->leftchild,0 });
}
else if(node.popnum == 2 &&node.Pnode->rightchild!=nullptr)
{
st.push(StkNode{ node.Pnode->rightchild,0 });
}
}
}
cout << endl;
}非递归中序遍历
void NiceInOrder(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (nullptr == ptr) {return;}
stack<BtNode*> st;
while (!st.empty() || ptr != nullptr) {
while (ptr != nullptr)
{
st.push(ptr);
ptr = ptr->leftchild;
}
ptr = st.top();
st.pop();
cout << ptr->data << " ";
ptr = ptr->rightchild;
}
}非递归前序遍历
void NicePerOrder(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (nullptr == ptr) { return; }
stack<BtNode*>st;
st.push(ptr);
while (!st.empty())
{
ptr = st.top();
st.pop();
cout << ptr->data << " ";
if (ptr->rightchild != nullptr)
{
st.push(ptr->rightchild);
}
if(ptr->leftchild!= nullptr)
{
st.push(ptr->leftchild);
}
}
cout << endl;
}层次遍历
void LevelOrder(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (ptr == nullptr)return;
queue<BtNode*> qu;
qu.push(ptr);
while (!qu.empty())
{
ptr = qu.front();
qu.pop();
cout << ptr->data << " ";
if (ptr->leftchild != nullptr)
{
qu.push(ptr->leftchild);
}
if (ptr->rightchild != nullptr)
{
qu.push(ptr->rightchild);
}
}
cout << endl;
}求二叉树节点个数
int GetSize(BtNode *ptr)
{
if (ptr == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
return GetSize(ptr->leftchild) + GetSize(ptr->rightchild) + 1;
}求二叉树深度
int Max(const int a, const int b)
{
return a > b ? a : b;
}
int GetDepth(BtNode* ptr)
{
if (ptr == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
return Max(GetDepth(ptr->leftchild) , GetDepth(ptr->rightchild))+1;
}判断一个数是不是满二叉树
bool IfFullBinartTree(BtNode* ptr)
{
bool ret = true;
if (ptr == nullptr)return ret;
queue<BtNode*>qua;
queue<BtNode*>qub;
int i = 0;
int n = 1;
qua.push(ptr);
while (!qua.empty() || !qub.empty())
{
for (; i < n && !qua.empty(); i++)
{
ptr = qua.front(); qua.pop();
if (ptr->leftchild != nullptr)
{
qub.push(ptr->leftchild);
}
if (ptr->rightchild != nullptr)
{
qub.push(ptr->rightchild);
}
}
if (i < n)
{
ret == false;
break;
}
if (qub.empty())break;
n += n;
for (i = 0; i < n && !qub.empty(); i++)
{
ptr = qub.front(); qub.pop();
if (ptr->leftchild != nullptr)
{
qua.push(ptr->leftchild);
}
if (ptr->rightchild != nullptr)
{
qua.push(ptr->rightchild);
}
}
if (i < n)
{
ret = false;
break;
}
if (qua.empty())break;
n += n;
}
return ret;
}判断一个数是不是完全二叉树
bool isfull(BtNode* ptr)
{
bool ret = true;
if (ptr != nullptr)return 0;
queue<BtNode*>qu1;
qu1.push(ptr);
while (!qu1.empty())
{
ptr = qu1.front(); qu1.pop();
if (ptr == nullptr)break;
qu1.push(ptr->leftchild);
qu1.push(ptr->rightchild);
}
while (!qu1.empty())
{
if (qu1.front() != nullptr) {
ret = false;
break;
}
qu1.pop();
}
return ret;
}到了这里,关于二叉树的存储方式、遍历、构建、判定的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!