相关链接
1. YOLOV7 + 单目测距(python)
2. YOLOV5 + 单目跟踪(python)
3. YOLOV7 + 单目跟踪(python)
4. YOLOV5 + 双目测距(python)
5. YOLOV7 + 双目测距(python)
6. 具体实现效果已在Bilibili发布,点击跳转
本篇博文工程源码下载
链接1:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_45077760/87708260
链接2:https://github.com/up-up-up-up/yolov5_Monocular_ranging
更多有关单目(尺寸测量,跟踪、碰撞检测等)的文章请见:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45077760/category_12312107.html文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-453784.html
1. 相关配置
系统:win 10
YOLO版本:yolov5 6.1
拍摄视频设备:安卓手机
电脑显卡:NVIDIA 2080Ti(CPU也可以跑,GPU只是起到加速推理效果)
2. 测距原理
单目测距原理相较于双目十分简单,无需进行立体匹配,仅需利用下边公式线性转换即可:
D = (F*W)/P
其中D是目标到摄像机的距离, F是摄像机焦距(焦距需要自己进行标定获取), W是目标的宽度或者高度(行人检测一般以人的身高为基准), P是指目标在图像中所占据的像素
了解基本原理后,下边就进行实操阶段
3. 相机标定
3.1:标定方法1
可以参考张学友标定法获取相机的焦距
3.2:标定方法2
直接使用代码获得焦距,需要提前拍摄一个矩形物体,拍摄时候相机固定,距离被拍摄物体自行设定,并一直保持此距离,背景为纯色,不要出现杂物;最后将拍摄的视频用以下代码检测:
import cv2
win_width = 1920
win_height = 1080
mid_width = int(win_width / 2)
mid_height = int(win_height / 2)
foc = 1990.0 # 根据教程调试相机焦距
real_wid = 9.05 # A4纸横着的时候的宽度,视频拍摄A4纸要横拍,镜头横,A4纸也横
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
w_ok = 1
capture = cv2.VideoCapture('5.mp4')
capture.set(3, win_width)
capture.set(4, win_height)
while (True):
ret, frame = capture.read()
# frame = cv2.flip(frame, 1)
if ret == False:
break
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 140, 200, 60) # 扫描不到纸张轮廓时,要更改阈值,直到方框紧密框住纸张
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3))
binary = cv2.dilate(binary, kernel, iterations=2)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# cv2.drawContours(frame, contours, -1, (0, 255, 0), 2) # 查看所检测到的轮框
for c in contours:
if cv2.contourArea(c) < 1000: # 对于矩形区域,只显示大于给定阈值的轮廓,所以一些微小的变化不会显示。对于光照不变和噪声低的摄像头可不设定轮廓最小尺寸的阈值
continue
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c) # 该函数计算矩形的边界框
if x > mid_width or y > mid_height:
continue
if (x + w) < mid_width or (y + h) < mid_height:
continue
if h > w:
continue
if x == 0 or y == 0:
continue
if x == win_width or y == win_height:
continue
w_ok = w
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x + 1, y + 1), (x + w_ok - 1, y + h - 1), (0, 255, 0), 2)
dis_inch = (real_wid * foc) / (w_ok - 2)
dis_cm = dis_inch * 2.54
# os.system("cls")
# print("Distance : ", dis_cm, "cm")
frame = cv2.putText(frame, "%.2fcm" % (dis_cm), (5, 25), font, 0.8, (0, 255, 0), 2)
frame = cv2.putText(frame, "+", (mid_width, mid_height), font, 1.0, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.namedWindow('res', 0)
cv2.namedWindow('gray', 0)
cv2.resizeWindow('res', win_width, win_height)
cv2.resizeWindow('gray', win_width, win_height)
cv2.imshow('res', frame)
cv2.imshow('gray', binary)
c = cv2.waitKey(40)
if c == 27: # 按退出键esc关闭窗口
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
反复调节 ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 140, 200, 60)这一行里边的三个参数,直到线条紧紧包裹住你所拍摄视频的物体,然后调整相机焦距直到左上角距离和你拍摄视频时相机到物体的距离接近为止
然后将相机焦距写进测距代码distance.py文件里,这里行人用高度表示,根据公式 D = (F*W)/P,知道相机焦距F、行人的高度66.9(单位英寸→170cm/2.54)、像素点距离 h,即可求出相机到物体距离D。 这里用到h-2是因为框的上下边界像素点不接触物体
foc = 1990.0 # 镜头焦距
real_hight_person = 66.9 # 行人高度
real_hight_car = 57.08 # 轿车高度
# 自定义函数,单目测距
def person_distance(h):
dis_inch = (real_hight_person * foc) / (h - 2)
dis_cm = dis_inch * 2.54
dis_cm = int(dis_cm)
dis_m = dis_cm/100
return dis_m
def car_distance(h):
dis_inch = (real_hight_car * foc) / (h - 2)
dis_cm = dis_inch * 2.54
dis_cm = int(dis_cm)
dis_m = dis_cm/100
return dis_m
4. 相机测距
4.1 测距添加
主要是把测距部分加在了画框附近,首先提取边框的像素点坐标,然后计算边框像素点高度,在根据 公式 D = (F*W)/P 计算目标距离
for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):
if save_txt: # Write to file
xywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4)) / gn).view(-1).tolist() # normalized xywh
line = (cls, *xywh, conf) if save_conf else (cls, *xywh) # label format
with open(txt_path + '.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(('%g ' * len(line)).rstrip() % line + '\n')
if save_img or save_crop or view_img: # Add bbox to image
x1 = int(xyxy[0]) #获取四个边框坐标
y1 = int(xyxy[1])
x2 = int(xyxy[2])
y2 = int(xyxy[3])
h = y2-y1
if names[int(cls)] == "person":
c = int(cls) # integer class 整数类 1111111111
label = None if hide_labels else (
names[c] if hide_conf else f'{names[c]} {conf:.2f}') # 111
dis_m = person_distance(h) # 调用函数,计算行人实际高度
label += f' {dis_m}m' # 将行人距离显示写在标签后
txt = '{0}'.format(label)
annotator.box_label(xyxy, txt, color=colors(c, True))
if names[int(cls)] == "car":
c = int(cls) # integer class 整数类 1111111111
label = None if hide_labels else (
names[c] if hide_conf else f'{names[c]} {conf:.2f}') # 111
dis_m = car_distance(h) # 调用函数,计算汽车实际高度
label += f' {dis_m}m' # 将汽车距离显示写在标签后
txt = '{0}'.format(label)
annotator.box_label(xyxy, txt, color=colors(c, True))
if save_crop:
save_one_box(xyxy, imc, file=save_dir / 'crops' / names[c] / f'{p.stem}.jpg', BGR=True)
4.2 细节修改(可忽略)
到上述步骤就已经实现了单目测距过程,下边是一些小细节修改,可以不看
为了实时显示画面,对运行的py文件点击编辑配置,在形参那里输入–view-img --save-txt
但实时显示画面太大,我们对显示部分做了修改,这部分也可以不要,具体是把代码
if view_img:
cv2.imshow(str(p), im0)
cv2.waitKey(1) # 1 millisecond
替换成
if view_img:
cv2.namedWindow("Webcam", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.resizeWindow("Webcam", 1280, 720)
cv2.moveWindow("Webcam", 0, 100)
cv2.imshow("Webcam", im0)
cv2.waitKey(1)
4.3 主代码
# YOLOv5 🚀 by Ultralytics, GPL-3.0 license
"""
Run inference on images, videos, directories, streams, etc.
Usage - sources:
$ python path/to/detect.py --weights yolov5s.pt --source 0 # webcam
img.jpg # image
vid.mp4 # video
path/ # directory
path/*.jpg # glob
'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc' # YouTube
'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4' # RTSP, RTMP, HTTP stream
Usage - formats:
$ python path/to/detect.py --weights yolov5s.pt # PyTorch
yolov5s.torchscript # TorchScript
yolov5s.onnx # ONNX Runtime or OpenCV DNN with --dnn
yolov5s.xml # OpenVINO
yolov5s.engine # TensorRT
yolov5s.mlmodel # CoreML (MacOS-only)
yolov5s_saved_model # TensorFlow SavedModel
yolov5s.pb # TensorFlow GraphDef
yolov5s.tflite # TensorFlow Lite
yolov5s_edgetpu.tflite # TensorFlow Edge TPU
"""
import argparse
import os
import sys
from pathlib import Path
import cv2
import torch
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
FILE = Path(__file__).resolve()
ROOT = FILE.parents[0] # YOLOv5 root directory
if str(ROOT) not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(str(ROOT)) # add ROOT to PATH
ROOT = Path(os.path.relpath(ROOT, Path.cwd())) # relative
from models.common import DetectMultiBackend
from utils.datasets import IMG_FORMATS, VID_FORMATS, LoadImages, LoadStreams
from utils.general import (LOGGER, check_file, check_img_size, check_imshow, check_requirements, colorstr,
increment_path, non_max_suppression, print_args, scale_coords, strip_optimizer, xyxy2xywh)
from utils.plots import Annotator, colors, save_one_box
from utils.torch_utils import select_device, time_sync
from distance import person_distance,car_distance
@torch.no_grad()
def run(weights=ROOT / 'yolov5s.pt', # model.pt path(s)
source=ROOT / 'data/images', # file/dir/URL/glob, 0 for webcam
data=ROOT / 'data/coco128.yaml', # dataset.yaml path
imgsz=(640, 640), # inference size (height, width)
conf_thres=0.25, # confidence threshold
iou_thres=0.45, # NMS IOU threshold
max_det=1000, # maximum detections per image
device='', # cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu
view_img=False, # show results
save_txt=False, # save results to *.txt
save_conf=False, # save confidences in --save-txt labels
save_crop=False, # save cropped prediction boxes
nosave=False, # do not save images/videos
classes=None, # filter by class: --class 0, or --class 0 2 3
agnostic_nms=False, # class-agnostic NMS
augment=False, # augmented inference
visualize=False, # visualize features
update=False, # update all models
project=ROOT / 'runs/detect', # save results to project/name
name='exp', # save results to project/name
exist_ok=False, # existing project/name ok, do not increment
line_thickness=3, # bounding box thickness (pixels)
hide_labels=False, # hide labels
hide_conf=False, # hide confidences
half=False, # use FP16 half-precision inference
dnn=False, # use OpenCV DNN for ONNX inference
):
source = str(source)
save_img = not nosave and not source.endswith('.txt') # save inference images
is_file = Path(source).suffix[1:] in (IMG_FORMATS + VID_FORMATS)
is_url = source.lower().startswith(('rtsp://', 'rtmp://', 'http://', 'https://'))
webcam = source.isnumeric() or source.endswith('.txt') or (is_url and not is_file)
if is_url and is_file:
source = check_file(source) # download
# Directories
save_dir = increment_path(Path(project) / name, exist_ok=exist_ok) # increment run
(save_dir / 'labels' if save_txt else save_dir).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # make dir
# Load model
device = select_device(device)
model = DetectMultiBackend(weights, device=device, dnn=dnn, data=data)
stride, names, pt, jit, onnx, engine = model.stride, model.names, model.pt, model.jit, model.onnx, model.engine
imgsz = check_img_size(imgsz, s=stride) # check image size
# Half
half &= (pt or jit or onnx or engine) and device.type != 'cpu' # FP16 supported on limited backends with CUDA
if pt or jit:
model.model.half() if half else model.model.float()
# Dataloader
if webcam:
view_img = check_imshow()
cudnn.benchmark = True # set True to speed up constant image size inference
dataset = LoadStreams(source, img_size=imgsz, stride=stride, auto=pt)
bs = len(dataset) # batch_size
else:
dataset = LoadImages(source, img_size=imgsz, stride=stride, auto=pt)
bs = 1 # batch_size
vid_path, vid_writer = [None] * bs, [None] * bs
# Run inference
model.warmup(imgsz=(1 if pt else bs, 3, *imgsz), half=half) # warmup
dt, seen = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0], 0
for path, im, im0s, vid_cap, s in dataset:
t1 = time_sync()
im = torch.from_numpy(im).to(device)
im = im.half() if half else im.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
im /= 255 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
if len(im.shape) == 3:
im = im[None] # expand for batch dim
t2 = time_sync()
dt[0] += t2 - t1
# Inference
visualize = increment_path(save_dir / Path(path).stem, mkdir=True) if visualize else False
pred = model(im, augment=augment, visualize=visualize)
t3 = time_sync()
dt[1] += t3 - t2
# NMS
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres, iou_thres, classes, agnostic_nms, max_det=max_det)
dt[2] += time_sync() - t3
# Second-stage classifier (optional)
# pred = utils.general.apply_classifier(pred, classifier_model, im, im0s)
# Process predictions
for i, det in enumerate(pred): # per image
seen += 1
if webcam: # batch_size >= 1
p, im0, frame = path[i], im0s[i].copy(), dataset.count
s += f'{i}: '
else:
p, im0, frame = path, im0s.copy(), getattr(dataset, 'frame', 0)
p = Path(p) # to Path
save_path = str(save_dir / p.name) # im.jpg
txt_path = str(save_dir / 'labels' / p.stem) + ('' if dataset.mode == 'image' else f'_{frame}') # im.txt
s += '%gx%g ' % im.shape[2:] # print string
gn = torch.tensor(im0.shape)[[1, 0, 1, 0]] # normalization gain whwh
imc = im0.copy() if save_crop else im0 # for save_crop
annotator = Annotator(im0, line_width=line_thickness, example=str(names))
if len(det):
# Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 size
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(im.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
# Print results
for c in det[:, -1].unique():
n = (det[:, -1] == c).sum() # detections per class
s += f"{n} {names[int(c)]}{'s' * (n > 1)}, " # add to string
# Write results
for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):
if save_txt: # Write to file
xywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4)) / gn).view(-1).tolist() # normalized xywh
line = (cls, *xywh, conf) if save_conf else (cls, *xywh) # label format
with open(txt_path + '.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(('%g ' * len(line)).rstrip() % line + '\n')
if save_img or save_crop or view_img: # Add bbox to image
x1 = int(xyxy[0])
y1 = int(xyxy[1])
x2 = int(xyxy[2])
y2 = int(xyxy[3])
h = y2-y1
if names[int(cls)] == "person":
c = int(cls) # integer class 整数类 1111111111
label = None if hide_labels else (
names[c] if hide_conf else f'{names[c]} {conf:.2f}') # 111
dis_m = person_distance(h)
label += f' {dis_m}m'
txt = '{0}'.format(label)
# annotator.box_label(xyxy, txt, color=(255, 0, 255))
annotator.box_label(xyxy, txt, color=colors(c, True))
if names[int(cls)] == "car":
c = int(cls) # integer class 整数类 1111111111
label = None if hide_labels else (
names[c] if hide_conf else f'{names[c]} {conf:.2f}') # 111
dis_m = car_distance(h)
label += f' {dis_m}m'
txt = '{0}'.format(label)
# annotator.box_label(xyxy, txt, color=(255, 0, 255))
annotator.box_label(xyxy, txt, color=colors(c, True))
if save_crop:
save_one_box(xyxy, imc, file=save_dir / 'crops' / names[c] / f'{p.stem}.jpg', BGR=True)
# Stream results
im0 = annotator.result()
'''if view_img:
cv2.imshow(str(p), im0)
cv2.waitKey(1) # 1 millisecond'''
if view_img:
cv2.namedWindow("Webcam", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.resizeWindow("Webcam", 1280, 720)
cv2.moveWindow("Webcam", 0, 100)
cv2.imshow("Webcam", im0)
cv2.waitKey(1)
# Save results (image with detections)
if save_img:
if dataset.mode == 'image':
cv2.imwrite(save_path, im0)
else: # 'video' or 'stream'
if vid_path[i] != save_path: # new video
vid_path[i] = save_path
if isinstance(vid_writer[i], cv2.VideoWriter):
vid_writer[i].release() # release previous video writer
if vid_cap: # video
fps = vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
w = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
h = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
else: # stream
fps, w, h = 30, im0.shape[1], im0.shape[0]
save_path = str(Path(save_path).with_suffix('.mp4')) # force *.mp4 suffix on results videos
vid_writer[i] = cv2.VideoWriter(save_path, cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v'), fps, (w, h))
vid_writer[i].write(im0)
# Print time (inference-only)
LOGGER.info(f'{s}Done. ({t3 - t2:.3f}s)')
# Print results
t = tuple(x / seen * 1E3 for x in dt) # speeds per image
LOGGER.info(f'Speed: %.1fms pre-process, %.1fms inference, %.1fms NMS per image at shape {(1, 3, *imgsz)}' % t)
if save_txt or save_img:
s = f"\n{len(list(save_dir.glob('labels/*.txt')))} labels saved to {save_dir / 'labels'}" if save_txt else ''
LOGGER.info(f"Results saved to {colorstr('bold', save_dir)}{s}")
if update:
strip_optimizer(weights) # update model (to fix SourceChangeWarning)
def parse_opt():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--weights', nargs='+', type=str, default=ROOT / 'yolov5s.pt', help='model path(s)')
parser.add_argument('--source', type=str, default=ROOT / 'data/images/1.mp4', help='file/dir/URL/glob, 0 for webcam')
parser.add_argument('--data', type=str, default=ROOT / 'data/coco128.yaml', help='(optional) dataset.yaml path')
parser.add_argument('--imgsz', '--img', '--img-size', nargs='+', type=int, default=[640], help='inference size h,w')
parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.25, help='confidence threshold')
parser.add_argument('--iou-thres', type=float, default=0.45, help='NMS IoU threshold')
parser.add_argument('--max-det', type=int, default=1000, help='maximum detections per image')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--view-img', action='store_true', help='show results')
parser.add_argument('--save-txt', action='store_true', help='save results to *.txt')
parser.add_argument('--save-conf', action='store_true', help='save confidences in --save-txt labels')
parser.add_argument('--save-crop', action='store_true', help='save cropped prediction boxes')
parser.add_argument('--nosave', action='store_true', help='do not save images/videos')
parser.add_argument('--classes', nargs='+', type=int, help='filter by class: --classes 0, or --classes 0 2 3')
parser.add_argument('--agnostic-nms', action='store_true', help='class-agnostic NMS')
parser.add_argument('--augment', action='store_true', help='augmented inference')
parser.add_argument('--visualize', action='store_true', help='visualize features')
parser.add_argument('--update', action='store_true', help='update all models')
parser.add_argument('--project', default=ROOT / 'runs/detect', help='save results to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--name', default='exp', help='save results to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--exist-ok', action='store_true', help='existing project/name ok, do not increment')
parser.add_argument('--line-thickness', default=3, type=int, help='bounding box thickness (pixels)')
parser.add_argument('--hide-labels', default=False, action='store_true', help='hide labels')
parser.add_argument('--hide-conf', default=False, action='store_true', help='hide confidences')
parser.add_argument('--half', action='store_true', help='use FP16 half-precision inference')
parser.add_argument('--dnn', action='store_true', help='use OpenCV DNN for ONNX inference')
opt = parser.parse_args()
opt.imgsz *= 2 if len(opt.imgsz) == 1 else 1 # expand
print_args(FILE.stem, opt)
return opt
def main(opt):
check_requirements(exclude=('tensorboard', 'thop'))
run(**vars(opt))
if __name__ == "__main__":
opt = parse_opt()
main(opt)
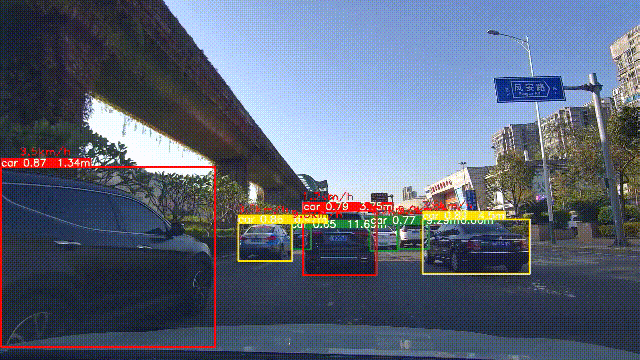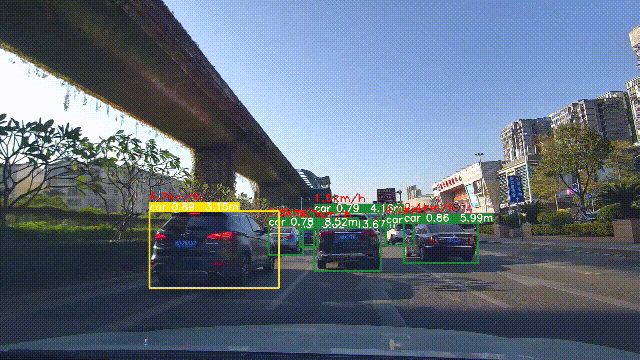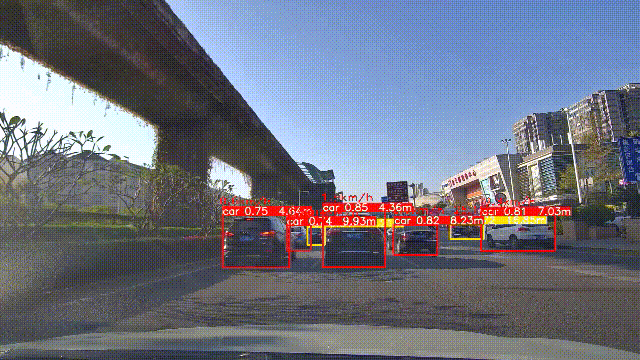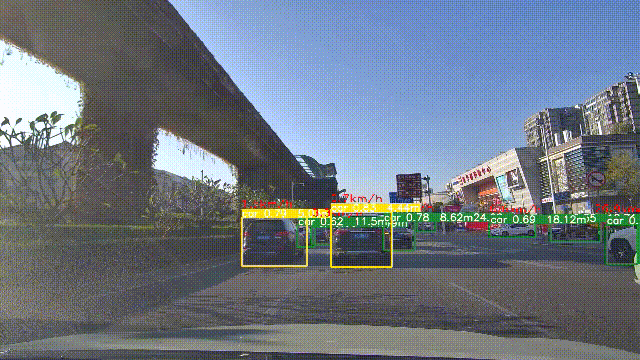
5. 实验效果
实验效果如下
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-453784.html
更多有关单目(尺寸测量,跟踪、碰撞检测等)的文章请见:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45077760/category_12312107.html
到了这里,关于YOLOv5+单目测距(python)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!