哈希表封装unordered系列
前言
本篇文章的大框架部分详解见红黑树封装map和set那篇博客,大框架我就不细讲了,主要说明一下小细节,源码采用哈希桶并且哈希桶的方式能够更好的解决冲突问题,因此再次以哈希桶为基准进行改良进而封unodered_set 和unordered_map。
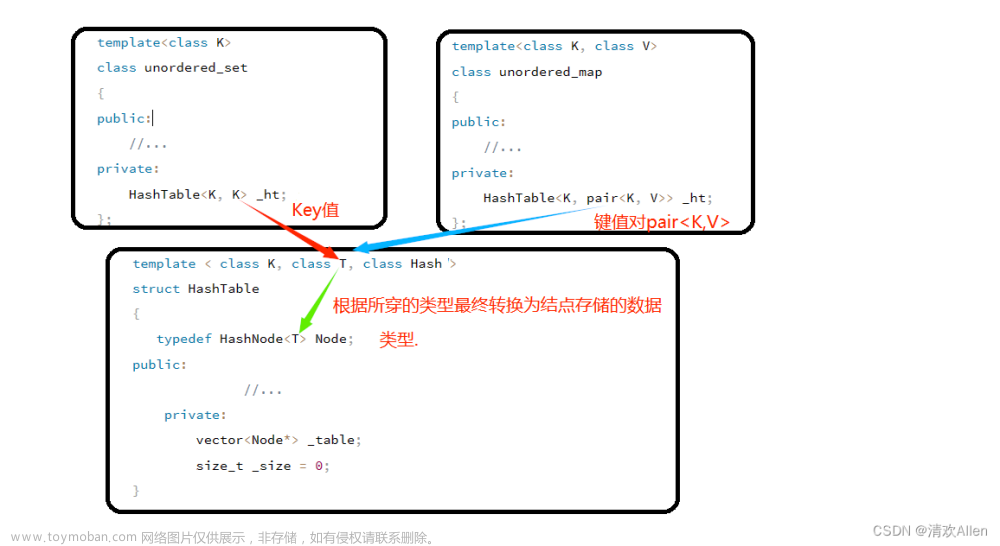
1. 改良后的类和节点
还是像map和set部分一样,节点模板参数改为T, 对于unodered_set存储的是Key,对于unordered_map存储pair的键值对哈希表类第一个模板参数是Key, 第二模板参数是T,unodered_set传过来是Key,unordered_map传来是pair的键值对, 同时提供一个仿函数将T中的K提取出来
2. 迭代器
1. begin 和 end
begin()就是返回第一个不为空的桶中的第一个元素,end是返回哈希表中最后一个元素的下一个
iterator begin() //返回第一个不为空的桶中的第一个元素
{
Node *cur = nullptr;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
cur = _tables[i];
if (cur)
{
break;
}
}
return iterator(cur, this);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
2. operator++()
思路: 先在一个桶内向下迭代,如果碰到空,那就需要转移到另一个桶的头结点,当然了,如果剩下的头节点都为空,那么迭代器最终就走到了end(),也变成了空。
需要注意的是,在迭代器的封装中,利用了HashTable,HashTable中又引用了迭代器,两个类互相引用, 需要前置声明,因为在封装的迭代器中需要有如下HT* _ ht 这样类型的成员变量,只有通过这个变量才能在operator++时找到下一个桶。在映射时我们发现,也会用到_tables.size();,这是HashTable中私有成员的成员函数,为了可以访问,有两种方式,其一是在HashTable中再封装一个公有函数返回这个值,其二是在HashTable中写出迭代器的友元,下面用到的就是友元的方式访问。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-459726.html
//++it 迭代器++还是迭代器
Self &operator++()
{
if (_node->_next != nullptr)
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else
{
// 思路: 找出下一个不为空的桶
KeyofT kot;
Hash hash;
// 1. 计算当前桶所在位置
size_t hashi = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size();
++hashi; // 要从下一个桶开始找
while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size())
{
if (_ht->_tables[hashi]) // 找到了不为空的桶
{
_node = _ht->_tables[hashi];
break;
}
else
{
++hashi;
}
}
// 没有找到不为空的桶
if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size())
{
_node = nullptr;
}
}
return *this;
}
3. const迭代器
const迭代器里面,库中实现的是把普通迭代器和const迭代器分开实现,我们这里仍然采用封装map和set时的方法,多给两个模板参数让const迭代器直接复用普通迭代器即可文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-459726.html
//哈希表引用迭代器,迭代器引用哈希表的类型,相互引用,需要先前置声明
template<class K, class T, class KeyofT, class Hash>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr,class KeyofT, class Hash>
struct __HashIterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef HashTable<K, T, KeyofT, Hash> HT;
typedef __HashIterator<K, T,Ref,Ptr, KeyofT, Hash> Self;
typedef __HashIterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyofT, Hash> Iterator;
Node* _node;
const HT* _ht; //迭代器遍历哈希表, 不会修改哈希表
__HashIterator(Node* node, const HT* ht)
:_node(node)
, _ht(ht)
{
}
//...
}
3. 整体代码
3.1 hashtable.h
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
HashNode<T>* _next;
T _data;
HashNode(const T& data)
:_next(nullptr)
, _data(data)
{
}
};
//整型系列本身可以转换
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
//模板特化 --- 实现字符串比较不用自己显示传仿函数, 和库里保持一致
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
//BKDR算法
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : s)
{
hash += ch;
hash *= 31;
}
return hash;
}
};
//哈希表引用迭代器,迭代器引用哈希表的类型,相互引用,需要先前置声明
template<class K, class T, class KeyofT, class Hash>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr,class KeyofT, class Hash>
struct __HashIterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef HashTable<K, T, KeyofT, Hash> HT;
typedef __HashIterator<K, T,Ref,Ptr, KeyofT, Hash> Self;
typedef __HashIterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyofT, Hash> Iterator;
Node* _node;
const HT* _ht; //迭代器遍历哈希表, 不会修改哈希表
__HashIterator(Node* node, const HT* ht)
:_node(node)
, _ht(ht)
{
}
__HashIterator(const Iterator&it)
:_node(it._node)
, _ht(it._ht)
{
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) //用节点的指针比较
{
return _node != s._node;
}
//++it 迭代器++还是迭代器
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next != nullptr)
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else
{
//思路: 找出下一个不为空的桶
KeyofT kot;
Hash hash;
//1. 计算当前桶所在位置
size_t hashi = hash(kot(_node->_data))% _ht->_tables.size();
++hashi; //要从下一个桶开始找
while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size())
{
if (_ht->_tables[hashi]) //找到了不为空的桶
{
_node = _ht->_tables[hashi];
break;
}
else
{
++hashi;
}
}
//没有找到不为空的桶
if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size())
{
_node = nullptr;
}
}
return *this;
}
};
template<class K, class T, class KeyofT, class Hash>
class HashTable
{
template<class K, class T, class Ref,class Ptr, class KeyofT, class Hash>
friend struct __HashIterator; //是模板,要添加模板参数
public:
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef __HashIterator<K, T, T&,T*, KeyofT, Hash> iterator;
typedef __HashIterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, KeyofT, Hash> const_iterator;
iterator begin() //返回第一个不为空的桶中的第一个元素
{
Node* cur = nullptr;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
cur = _tables[i];
if (cur)
{
break;
}
}
return iterator(cur, this);
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
Node* cur = nullptr;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
cur = _tables[i];
if (cur)
{
break;
}
}
return const_iterator(cur, this);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
const iterator end()const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
}
//size_t newsize = GetNextPrime(_tables.size());
size_t GetNextPrime(size_t prime)
{
// SGI --- 除留余数法模素数
static const int __stl_num_primes = 28;
static const unsigned long __stl_prime_list[__stl_num_primes] =
{
53, 97, 193, 389, 769,
1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433,
1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843,
50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457,
1610612741, 3221225473, 4294967291
};
size_t i = 0;
for (; i < __stl_num_primes; ++i)
{
if (__stl_prime_list[i] > prime)
return __stl_prime_list[i];
}
return __stl_prime_list[i];
}
~HashTable() //保存下一个位置,释放当前位置
{
for (auto& cur : _tables)
{
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
cur = nullptr;
}
}
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
Hash hash;
if (_tables.size() == 0)
return end();
KeyofT kot;
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
{
return iterator(cur,this);
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return end();
}
bool Erase(const K& key) //从链表中删除
{
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
Node* prev = nullptr; //保存前一个节点
KeyofT kot;
while (cur) //链表头删的过程
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return false;
}
pair<iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
KeyofT kot;
//元素已经存在不能插入
iterator it = Find(kot(data));
if (it != end())
{
return make_pair(it,false);
}
Hash hash;
//负载因子等于1时扩容
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
//size_t newsize =_tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
size_t newsize = GetNextPrime(_tables.size()); //模素数
vector<Node*> newtables(newsize, nullptr);
for (auto& cur : _tables)
{
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
//需要重新计算映射关系
size_t hashi = hash(kot(data)) % _tables.size();
//头插到新表
cur->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
}
_tables.swap(newtables);
}
size_t hashi = hash(kot(data)) % _tables.size();
//直接插入就行 —— 这里用头插
Node* newnode = new Node(data);
newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode, this), false);
}
//最大桶
size_t MaxBucketSize()
{
size_t max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
size_t size = 0;
while (cur)
{
++size;
cur = cur->_next;
}
printf("[%d]->[%d]\n", i, size);
if (size > max)
{
max = size;
}
}
return max;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables; //vector里面挂节点(链表),是指针数组类型
size_t _n = 0; //存储有效数据个数
};
3.2 unordered_set.h
namespace yj
{
template<class K, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{
public:
//将T中的K提取出来
struct SetKeyofT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
//取这个类模板中的内嵌类型 HashTables<K, K, SetofT, Hash>
typedef typename HashTable<K, K, SetKeyofT, Hash>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename HashTable<K, K, SetKeyofT, Hash>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Insert(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
private:
HashTable<K, K, SetKeyofT, Hash> _ht;
};
}
3.3 unordered_map.h
namespace yj
{
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{
public:
//将T中的K提取出来
struct MapKeyofT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
typedef typename HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyofT, Hash>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyofT, Hash>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return _ht.Insert(kv);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second; //找到ret(make_pair<iterator,bool>)的first,解引用找到节点value
}
private:
HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyofT, Hash> _ht;
};
}
到了这里,关于哈希表封装unordered系列的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!






![[C++]哈希表实现,unordered_map\set封装](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/475233-1.png)





