RabbitMQ系列
RabbitMQ系列-概念及安装
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-461250.html
1. Exchange
RabbitMQ系列-概念及安装 提到AMQP 0-9-1协议默认支持四种exchange,分别是Direct Exchange,Fanout Exchange,Topic Exchange,Headers Exchange
除了交换类型之外,交换还声明了许多属性
- Name,交换机名称,唯一的
- Durability,持久性,RabbitMQ Server重启后依旧存在
- Auto-delete,自动删除,没有队列绑定到交换机时,交换机自动删除
- Arguments,可选参数, 用于插件和一些特定功能
1.1 Direct Exchange
Direct Exchange根据路由信息将消息送到指定队列
工作流程如下
- 消息队列绑定到Direct Exchange,并指定路由字符串K,该Direct Exchange名称为E
-
当具有路由键R的新消息到达交换机E时,如果K = R,则交换机将消息副本拷贝到队列
- 继续遍历剩余绑定到交换机E的队列,如果K = R,则交换机将消息副本拷贝到队列
Direct Exchange模型如下图所示

队列queue1和direct exchange的绑定路由有info和warn,类似的queue2和direct exchange的绑定路由有debug,queue3和direct exchange的绑定路由有error
当消息生产者producer发布路由值为info或者warn的消息时,根据绑定关系,该消息将被送到queue1,并被consumer1接收处理
同理,当消息生产者producer发布路由值为debug的消息时,根据绑定关系,该消息将被送到queue2,并被consumer2接收处理
当消息生产者producer发布路由值为error消息时,根据绑定关系,该消息将被送到queue3,并被consumer3接收处理
1.2 Fanout Exchange
Fanout Exchange忽略路由且将消息副本推送到所有绑定到该交换机的队列,假设有N个队列绑定到Fanout Exchange,生产者发送到消息经过该交换机处理,将消息副本发送到这个N个队列。
因此Fanout Exchange适用于广播的场景,Fanout Exchange模型如下图所示

队列queue1、queue2、queue3均绑定到了fanout类型的交换机,消息生产者producer发布的消息将被fanout exchange分发到queue1、queue2、queue3,最后被各自的消费者消费。
1.3 Topic Exchange
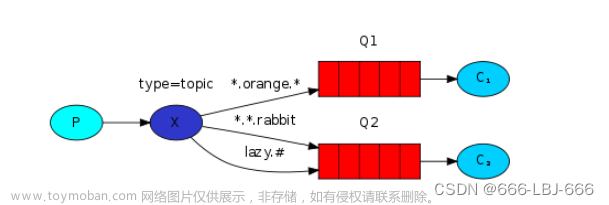
topic exchange对消息"分发范围"介于direct exchange和fanout exchange之间,direct exchage要求消息的路由键和队列的绑定路由键完全一致才分发,fanout exchange将消息分发到所有具有绑定关系的队列上
一般情况下,topic exchange的路由键由用英文逗号隔开的多个单词构成。其中,有两个单词比较特殊,*可以代表任意的一个单词,#可以代表0个或多个单词
假设,有路由键<地区.新闻种类.子种类>的新闻分发系统,系统模型如下图所示

其中,队列queue1和topic交换机的绑定关系有两个,<us.sport.*>表示关注美国地区所有体育主题相关的消息,<*.food.apple>表示关注所有地区关于苹果这种水果主题的消息
队列queue1与topic交换机绑定路由键<cn.car.byd>表示关注中国地区下汽车类主题下关于比亚迪的消息。
队列queue3与topic交换机的绑定关系为<#.huawei>表示关注所有地区关于华为的所有主题的消息。
1.4 Headers Exchange
headers交换机忽略路由键,利用x-match参数和多个可选的headers键值对参数来路由消息。x-match有两种类型值all和any
当x-math=all时,所有的headers键值对参数需要全部匹配,当x-math=any时,只需要headers键值对参数中的一个匹配即可
假设,有学生信息订阅系统使用的时headers类型的交换机,模型如下图所示

其中,队列queue1和headers交换机的绑定关系的x-math=any,键值对参数为age=18和height=170,因此当生产者发布的消息包含age=18或height=170时,消息将被路由到queue1
队列queue2和headers交换机的绑定关系的x-math=all,键值对参数为age=22和height=180,因此当生产者发布的消息包含age=22和height=180时,消息将被路由到queue2
队列queue3和headers交换机的绑定关系的x-math=all,键值对参数为gender=male和score=60,因此当生产者发布的消息包含gender=male和score=60时,消息将被路由到queue3
以amqp091-go为例,使用Direct Exchange说明Direct Exchange的基本使用方法。
2. 消费者代码
以amqp091-go为例,使用Direct Exchange说明消息者端的基本流程。
2.1 连接到RabbitMQ Server
conn, err := amqp.Dial("amqp://guest:guest@localhost:5672/")
failOnError(err, "Failed to connect to RabbitMQ")
defer conn.Close()Dial接收AMQP URI格式的字符串,建立和RabbitMQ Server的TCP连接,并返回连接Connection。TCP握手的超时时间默认为30s
2.2 建立轻量级连接Channel
ch, err := conn.Channel()
failOnError(err, "Failed to open a channel")
defer ch.Close()通过和RabbitMQ Server一次网络往返交互,建立一个唯一的轻量级连接Connection
当Channel不在需要时,需要手动调用Channel.Close关闭Channel,以释放Channel占用的资源,避免内存泄漏
当Channel所属的Connection关闭时,Channel也会被关闭。
2.3 声明交换机Exchange
err = ch.ExchangeDeclare(
"log_direct", // name
amqp.ExchangeDirect, // type
true, // durable
false, // auto-deleted
false, // internal
false, // no-wait
nil, // arguments
)
failOnError(err, "Failed to declare an exchange")生产者发布的消息会先到达Exchange,在根据Exchange类型和绑定关系将消息路由到特定队列。
ExchangeDeclare共有6个参数,这里重点看下其中几个参数
func (ch *Channel) ExchangeDeclare(name, kind string, durable, autoDelete, internal, noWait bool, args Table) error
第二个参数type/kind 类型,AMQP 0-9-1 broker提供了四种类型,分别是direct,fanout,topic和headers,这里使用的是direct
第三个参数durable 是否持久化,第四个参数autoDelete 是否自动删除
- 当持久化且不自动删除时,当RabbitMQ重启或者没有队列绑定时,Exchange依旧存在
- 当非持久化且自动删除时,当RabbitMQ重启或者Exchange没有队列绑定时,Exchange会自动删除
- 当非持久化且不自动删除时,当RabbitMQ重启后,Exchange会消失,当Exchange没有队列绑定时,Exchange会存在。即RabbitMQ不重启,Exchange就会一直存在
- 当持久化且自动删除时,当RabbitMQ重启后,Exchange依旧存在,但当Exchange没有队列绑定时,Exchange会被删除
第六个参数noWait 是否等待服务器的确认应答,当该参数no-wait为true是,应当给通过Channel.NotifyClose异步处理异常。
2.4 声明队列Queue
q, err := ch.QueueDeclare(
"", // name
false, // durable
false, // delete when unused
true, // exclusive
false, // no-wait
nil, // arguments
)
failOnError(err, "Failed to declare a queue")队列Queue充当了Exchange和消费者之间缓冲区的角色
func (ch *Channel) QueueDeclare(name string, durable, autoDelete, exclusive, noWait bool, args Table) (Queue, error)
如果队列不存在则创建,如果存在时需要确保参数和已经存在的Queue一致,否则会返回错误
当name为空时,RabbitMQ Server会生成唯一的名称,并返回给q
第二个参数durable 是否持久化,第三个参数autoDelete 是否自动删除
- 当持久化且不自动删除时,当RabbitMQ重启或者没有与消费者的绑定关系时,Queue依旧存在,只有持久化的Exchange才能声明这种Queue
- 当非持久化且自动删除时,当RabbitMQ重启或者没有消费者时,Queue会自动删除,只有非持久化的Exchange才能声明这种Queue
- 当非持久化且不自动删除时,当RabbitMQ重启后,Queue会消失,当没有消费者时,Queue依旧存在。即RabbitMQ不重启,Queue就会一直存在,只有非持久化的Exchange才能声明这种Queue
- 当持久化且自动删除时,当RabbitMQ重启后,Queue依旧存在,但当没有消费者时,Queue会被删除
第四个参数exclusive 是否独占,当该参数为true时,该队列只能被声明这个Queue的Connection访问,并且在Connection关闭时,队列会被删除
第五个参数noWait是否等待服务器的确认应答,当该参数no-wait为true是,应当给通过Channel.NotifyClose异步处理异常。
当QueueDeclare返回错误时,说明Queue创建失败,同时Channel也会被关闭
2.5 绑定关系Binding
err = ch.QueueBind(
q.Name, // queue name
s, // routing key
"log_direct", // exchange
false, // noWait
nil // args
)
failOnError(err, "Failed to bind a queue")使用路由建立交换机和队列的绑定关系,可以使用多个路由建立交换机和队列的绑定关系,交换机根据路由判断是否将消息推送到队列
func (ch *Channel) QueueBind(name, key, exchange string, noWait bool, args Table) error
第一个参数是队列名称name,第三个参数是交换机名称exchange,第二个参数时队列和交换机绑定关系的表示
第三个参数noWait是否等待服务器的确认应答,当该参数no-wait为true是,应当给通过Channel.NotifyClose异步处理异常。
当建立绑定关系QueueBind失败时,会返回错误并且Channel会被关闭。
2.6 Consume参数说明
msgs, err := ch.Consume(
q.Name, // queue
"", // consumer tag
true, // auto-ack
false, // exclusive
false, // no-local
false, // no-wait
nil, // args
)
failOnError(err, "Failed to register a consumer")开始接受来自队列的消息
func (ch *Channel) Consume(queue, consumer string, autoAck, exclusive, noLocal, noWait bool, args Table) (<-chan Delivery, error)
Channel.Consume返回<-chan Delivery,消费者不断从需要该Channel上接受消息,需要注意的是,消费者需要及时处理消息,否则将阻塞Channel所属Connection上的任何操作
第三个参数 autoAck 是否自动向确认RabbitMQ确认成功投递 当该参数为true时,写入TCP套接字即向abbitMQ确认成功投递。当该参数为false,则需要消费者手动发出确认信息,即调用Delivery.Ack
第四个参数exclusive 是否独占,当该参数为true时,消费者独占该队列,当该参数为false是,RabbitMQ Server将在多个消费者之间公平地分配交付
第五个参数noWait是否等待服务器的确认应答,当该参数no-wait为true是,应当给通过Channel.NotifyClose异步处理异常。
2.7 消费者汇总代码
查看代码
func failOnError(err error, msg string) {
if err != nil {
log.Panicf("%s: %s", msg, err)
}
}
// routingKeys 绑定的路由: debug info warning error
func RecvMsg(routingKeys []string) {
conn, err := amqp.Dial("amqp://guest:guest@localhost:5672/")
failOnError(err, "Failed to connect to RabbitMQ")
defer conn.Close()
ch, err := conn.Channel()
failOnError(err, "Failed to open a channel")
defer ch.Close()
err = ch.ExchangeDeclare(
"log_direct", // name
amqp.ExchangeDirect, // type
true, // durable
false, // auto-deleted
false, // internal
false, // no-wait
nil, // arguments
)
failOnError(err, "Failed to declare an exchange")
q, err := ch.QueueDeclare(
"", // name
false, // durable
false, // delete when unused
true, // exclusive
false, // no-wait
nil, // arguments
)
failOnError(err, "Failed to declare a queue")
if len(routingKeys) < 1 {
log.Printf("Usage: %s [info] [warning] [error]", routingKeys)
os.Exit(0)
}
for _, s := range routingKeys {
log.Printf("Binding queue %s to exchange %s with routing key %s",
q.Name, "fruit_direct", s)
err = ch.QueueBind(
q.Name, // queue name
s, // routing key
"log_direct", // exchange
false,
nil)
failOnError(err, "Failed to bind a queue")
}
msgs, err := ch.Consume(
q.Name, // queue
"", // consumer
true, // auto-ack
false, // exclusive
false, // no-local
false, // no-wait
nil, // args
)
failOnError(err, "Failed to register a consumer")
var forever chan struct{}
go func() {
for d := range msgs {
log.Printf(" [x] %s", d.Body)
}
}()
log.Printf(" [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C")
<-forever
}
3. 生产者代码
同样以amqp091-go为例,说明消息生产者端的基本流程
3.1 建立连接
和消费端一样,需要通过amqp.Dial建立TCP连接,通过Connection.Channel建立一个轻量级连接
conn, err := amqp.Dial("amqp://guest:guest@localhost:5672/")
failOnError(err, "Failed to connect to RabbitMQ")
defer conn.Close()
ch, err := conn.Channel()
failOnError(err, "Failed to open a channel")
defer ch.Close()
3.2 声明交换机Exchange
和消费端一样需要声明交换机Exchange,需要注意的是,生产者和消费者都声明了相同名称的Exchange,需要保持两者的参数是一致的,否则会报错
err = ch.ExchangeDeclare(
"log_direct", // name
amqp091.ExchangeDirect, // type
true, // durable
false, // auto-deleted
false, // internal
false, // no-wait
nil, // arguments
)
failOnError(err, "Failed to declare an exchange")
3.3 发布消息
err = ch.PublishWithContext(ctx,
"log_direct", // exchange
severityFrom(msg), // routing key
false, // mandatory
false, // immediate
amqp.Publishing{
ContentType: "text/plain",
Body: []byte(msg),
})
failOnError(err, "Failed to publish a message")采用异步的方式将消息发送到RabbitMQ server到交换机
第三个参数 mandatory 是否强制送达 当该参数为true时,且消费端队列和交换机没有对应的绑定路由时,消息就无法发出,可通过Channel.NotifyReturn处理这种被退回的消息
第三个参数 immediate 是否理解接收 当该参数为true时,且匹配的消费端队列没有准备好接受此消息时,消息就无法发出,可通过Channel.NotifyReturn处理这种被退回的消息
3.4 生产者汇总代码
查看代码
import (
"context"
"log"
"strings"
"time"
amqp "github.com/rabbitmq/amqp091-go"
)
func failOnError(err error, msg string) {
if err != nil {
log.Panicf("%s: %s", msg, err)
}
}
func SendMsg(msg string) {
conn, err := amqp.Dial("amqp://guest:guest@localhost:5672/")
failOnError(err, "Failed to connect to RabbitMQ")
defer conn.Close()
ch, err := conn.Channel()
failOnError(err, "Failed to open a channel")
defer ch.Close()
err = ch.ExchangeDeclare(
"log_direct", // name
amqp.ExchangeDirect, // type
true, // durable
false, // auto-deleted
false, // internal
false, // no-wait
nil, // arguments
)
failOnError(err, "Failed to declare an exchange")
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 5*time.Second)
defer cancel()
err = ch.PublishWithContext(ctx,
"log_direct", // exchange
severityFrom(msg), // routing key
false, // mandatory
false, // immediate
amqp.Publishing{
ContentType: "text/plain",
Body: []byte(msg),
})
failOnError(err, "Failed to publish a message")
log.Printf(" [x] Sent %s", msg)
}
func severityFrom(msg string) string {
var s string
if strings.Contains(msg, "debug") {
s = "debug"
} else if strings.Contains(msg, "error") {
s = "error"
} else if strings.Contains(msg, "warn") {
s = "warn"
} else {
s = "info"
}
return s
}文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-461250.html
到了这里,关于RabbitMQ系列-Exchange介绍的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!