这里以五子棋为例,来说明开发过程
其中该项目包含3个文件,一个.h文件声明所用的函数,两个.c文件进行主要的代码书写。
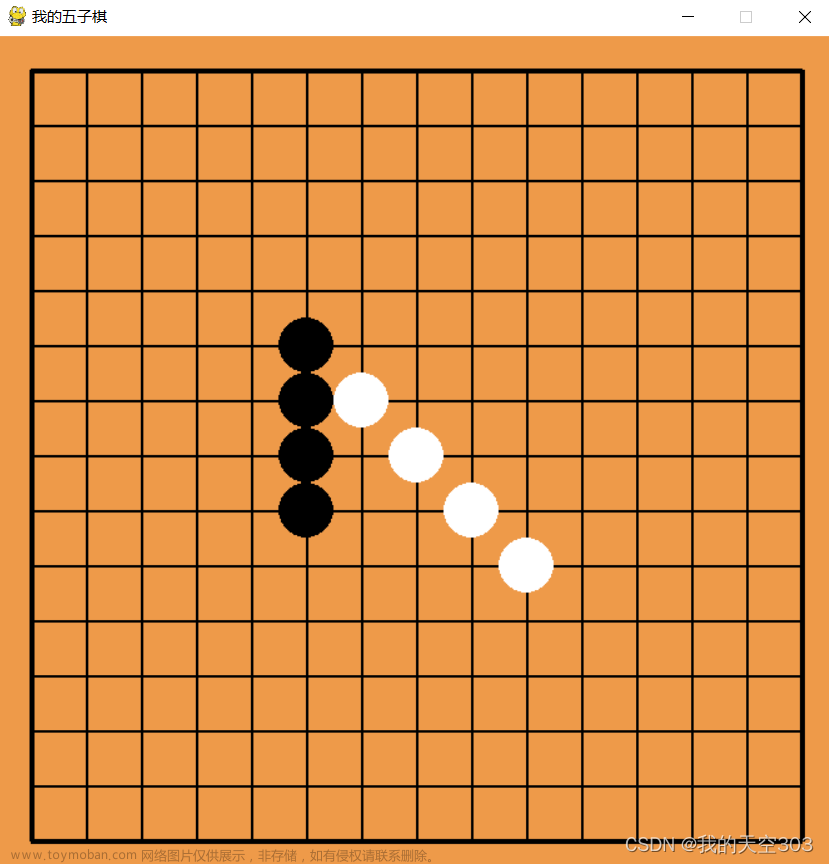
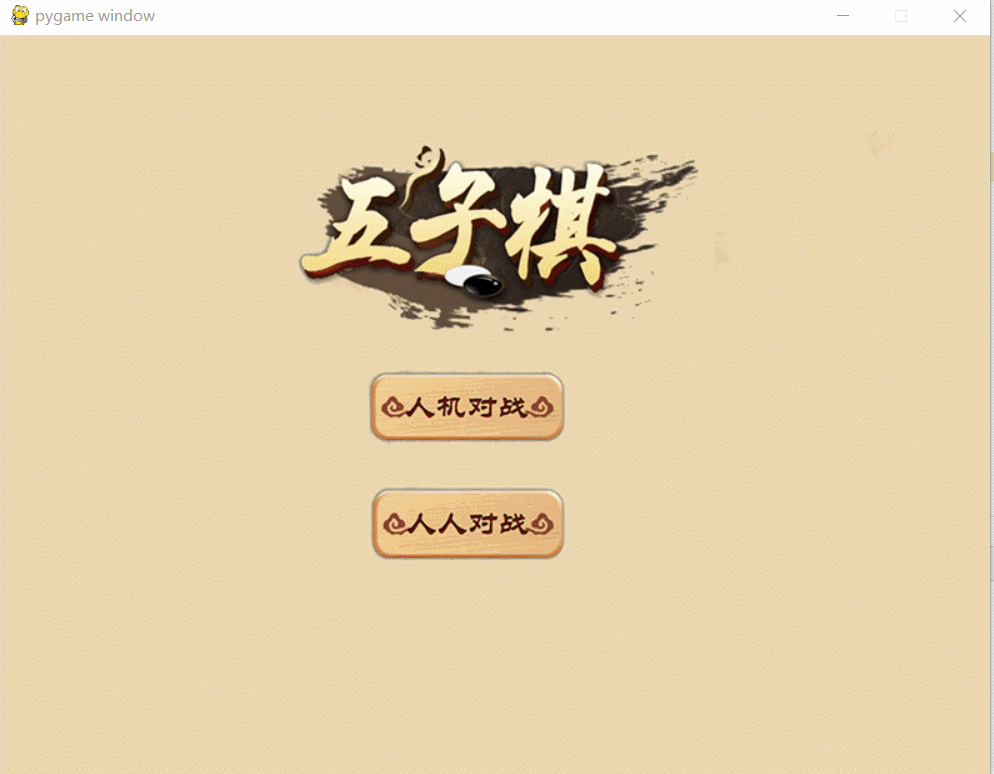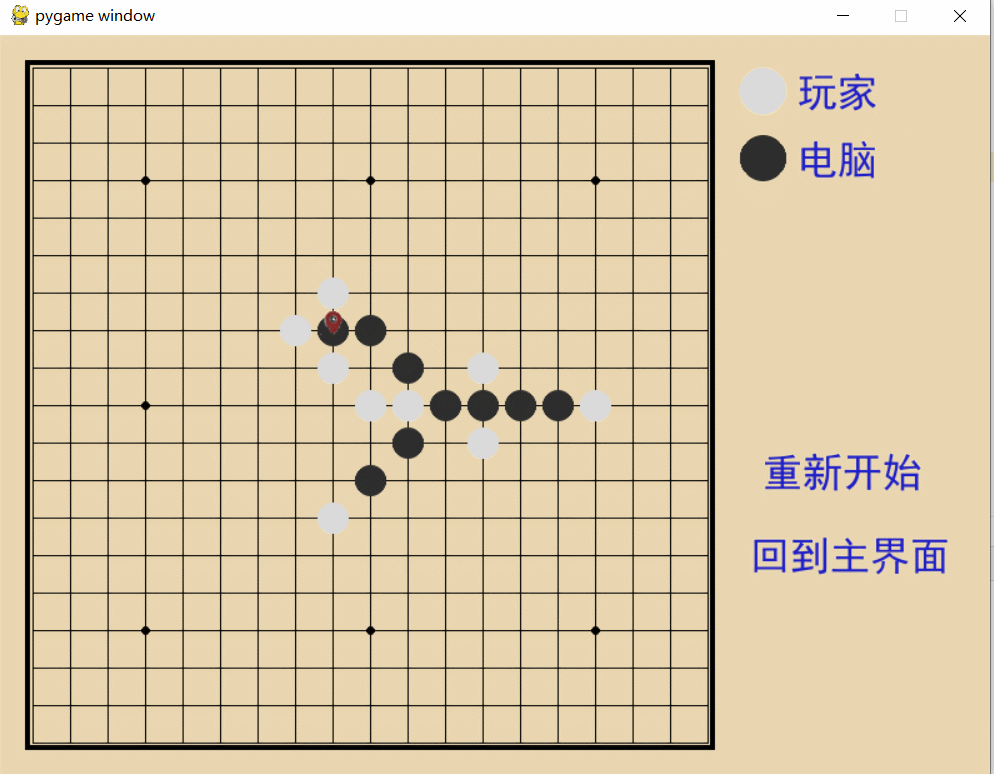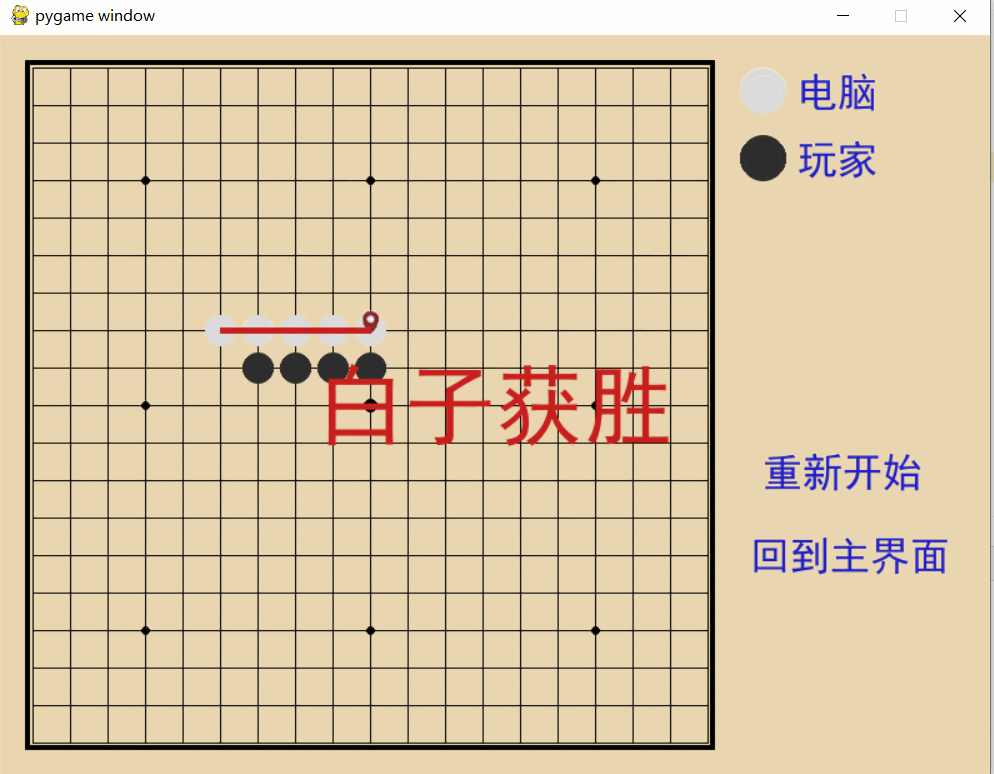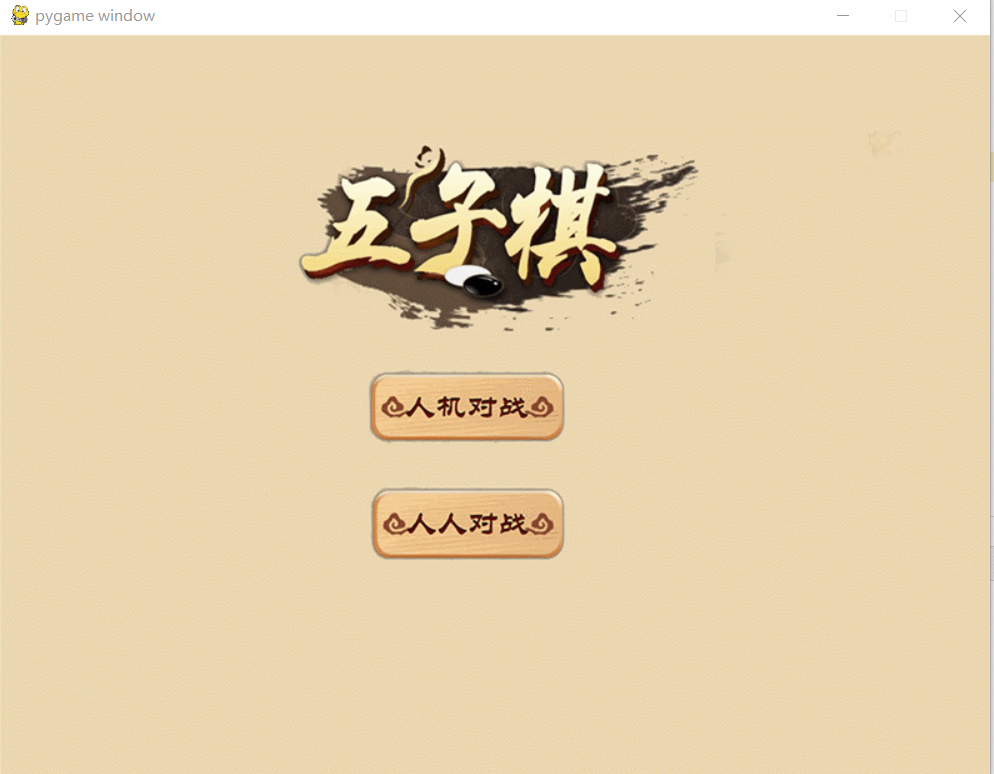
项目效果展示:

开发思路
- 菜单打印
- 棋盘的打印(二维数组)
- 棋子打印(下标)
- 电脑下棋(随机数)
- 判断输赢(竖,横,左斜,右斜…)
大致的思路就是这些,看过开发思路,脑海里应该就大致有了想法,有了主意。
接着,我们一步一步的进行开发。
菜单打印
菜单我们可以设计简单一些,同时把其放在一个函数中,这样便于调用。
该函数如下所示:
void menu()
{
printf("*********************\n");
printf("*** 1.play 0.exit ***\n");
printf("*********************\n");
}
这里我们要不断的去 接收用户的输入,当为1时,进入游戏,为0时,退出程序
直接就想到了 条件语句判断,这里我们用switch
不断的:用户完成游戏后,可以再次打印菜单供用户选择
这个操作当然是项目的核心部分了,放在 main()函数里
int main()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
// 设置随机数的生成起点(利用时间)
后面会讲随机数的使用
int input = 0;
do
{
menu();//打印菜单
printf("请选择->\n");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
game();
break;
case 0:
printf("退出游戏\n");
break;
default:
printf("输入错误!!!\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
棋盘的打印
我们是利用二维数组打印棋盘,观察效果展示后可以发现,打印棋子的地方上 空格,然后用 “|”和“_” 装饰地图
首先打印出空格,为了便于控制棋盘行列数量,我们直接定义一个变量,之后对其进行赋值操作。
row col
void Initboard(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
board[i][j] = ' ';
}
}
}
同时在 game.h头文件中声明其函数,并定义变量的值
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#define Row 10
#define Col 10
// 初始化棋盘
void Initboard(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col);
// 打印棋盘
void displayboard(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col);
最后,对棋盘进行装饰
void displayboard(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
// 打印数据
//printf(" %c | %c | %c | %c | %c \n",
//board[i][0], board[i][1]......board[i][4]);
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf(" %c ", board[i][j]);
if (j < col - 1)
{
printf("|");
}
}
printf("\n");
// 打印分割信息
//printf("---|---|---|---|---\n");
if (i < row - 1)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf("---");
if (j < col - 1)
{
printf("|");
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}
棋子的打印
棋子的打印分为两部分:
1.玩家输入棋子坐标进行下棋
2.电脑根据随机数进行下棋
首先,进行玩家下棋
思路:
让用户输入二维数组下标进行判断
如果是空格,就可以用一个字符代替棋子进行占用。
若不为空格,则说明该位置上有棋子,则让玩家重新输入坐标
void paly_move(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col)
{
// 玩家输入其坐标
int x = 0, y = 0;
printf("请玩家输入坐标(例如:1 1):\n");
while (1)
{
printf("请输入坐标->\n");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
// 坐标的合法性判断 1.范围 2.是否被占用
if (x >= 1 && x <= row && y >= 1 && y <= col)
{
// 玩家输入的1 1 ,在二维数组中对应的为0 0
// 二维数组坐标从0开始
if (board[x - 1][y - 1] == ' ')
{
board[x - 1][y - 1] = '*';
break;
}
else
{
printf("坐标已被占用,不能下棋,请选择其他位置\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("坐标非法,请重新输入->\n");
}
}
}
电脑下棋(随机数)
思路:
电脑下棋就是产生随机数–>随机坐标下棋
然后,判断该位置是否有棋子,若无则打印,若有则再次随机产生
随机数:
利用srand()time()函数
用法如下:
#include <time.h>
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
unsigned int 可以理解为自然数
这里是利用变化的时间作为种子,来进行产生随机数(注:如果调用的间隙过短,则是产生相同的值)
对应rand()的随机数范围是0~32767
void computer_move(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col)
{
printf("电脑下棋->\n");
int x = 0, y = 0;
// 判断并下棋
while (1)
{
// 利用随机数 返回test.c设置随机数的起点
x = rand() % row;
// rand()的随机数范围是0~32767 模上row(5) 就是0~5
y = rand() % col;
if (board[x][y] == ' ')
{
board[x][y] = '#';
break;
}
}
}
判断输赢
在循环下棋中,每次都去进行判断,所以有四种情况
我们可以 让其返回的值不同,然后就可以直接对返回值进行判断,进而判断输赢
-
玩家赢 (返回值):*
-
电脑赢 #
-
平局 Q
-
继续下棋 C
定义一个函数,判断棋盘是否满子
满子返回 1
未满返回 0
int full_board(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
if (board[i][j] == ' ')
{
return 0;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
判断:
char who_win(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
// 行
if (board[i][j] == board[i][j+1] && board[i][j+1] == board[i][j+2] && board[i][j+2] == board[i][j+3] && board[i][j+3] == board[i][j+4] && board[i][j+3] != ' ')
{
return board[i][j+2];
}
// 列
if (board[i][j] == board[i+1][j] && board[i+1][j] == board[i+2][j] && board[i+2][j] == board[i+3][j] && board[i+3][j] == board[i+4][j] && board[i+4][j] != ' ')
{
return board[i+1][j];
}
// 右斜
if(board[i][j] == board[i + 1][j + 1] && board[i + 1][j + 1] == board[i + 2][j + 2] && board[i + 2][j + 2] == board[i + 3][j + 3] && board[i + 3][j + 3] == board[i + 4][j + 4] && board[i + 3][j + 3] != ' ')
{
return board[i + 2][j + 2];
}
// 左斜
if (board[i][j + 4] == board[i + 1][j + 3] && board[i + 1][j + 3] == board[i + 2][j + 2] && board[i + 2][j + 2] == board[i + 3][j + 1] && board[i + 3][j + 1] == board[i + 4][j] && board[i + 2][j + 2] != ' ')
{
return board[i][j + 4];
}
}
}
// 棋盘满了,未分出胜负
if (full_board(board, row, col))
{
return 'Q';
}
// 游戏继续
return 'C';
}
到这里,整个项目的核心代码我们都已经分解好了,现在只剩下去整合了
我这里就直接上完整代码了
代码整合
test.c
# define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "game.h"
#include <time.h>
void menu()
{
printf("*********************\n");
printf("*** 1.play 0.exit ***\n");
printf("*********************\n");
}
void game()
{
char ret;
char board[Row][Col] = { 0 };
//初始化棋盘
Initboard(board, Row, Col);
displayboard(board, Row, Col);
//下棋
while (1)
{
//玩家
paly_move(board,Row, Col);
//判断输赢
ret = who_win(board, Row, Col);
if (ret != 'C')
{
break;
}
// 打印棋盘
displayboard(board, Row, Col);
//电脑
computer_move(board, Row, Col);
ret = who_win(board, Row, Col);
if (ret != 'C')
{
break;
}
// 打印棋盘
displayboard(board, Row, Col);
}
if (ret == '*')
{
printf("玩家赢\n");
}
else if (ret == '#')
{
printf("电脑赢\n");
}
else
{
printf("平局\n");
}
}
int main()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
// 设置随机数的生成起点(利用时间)
int input = 0;
do
{
menu();//打印菜单
printf("请选择->\n");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
game();
break;
case 0:
printf("退出游戏\n");
break;
default:
printf("输入错误!!!\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
game.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#define Row 10
#define Col 10
// 初始化棋盘
void Initboard(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col);
// 打印棋盘
void displayboard(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col);
// 玩家下棋
void paly_move(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col);
// 电脑下棋
// 找个空白的地方下棋
void computer_move(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col);
// 判断棋盘形式
// 可以设置其对应的返回值,便于判断,以及继续执行程序
// 玩家赢 电脑赢 平局 继续下棋 (四种情况)
// * # Q C 字符
char who_win(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col);
game.c
# define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "game.h"
void Initboard(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
board[i][j] = ' ';
}
}
}
void displayboard(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
// 打印数据
//printf(" %c | %c | %c | %c | %c \n", board[i][0], board[i][1]......board[i][4]);
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf(" %c ", board[i][j]);
if (j < col - 1)
{
printf("|");
}
}
printf("\n");
// 打印分割信息
//printf("---|---|---|---|---\n");
if (i < row - 1)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf("---");
if (j < col - 1)
{
printf("|");
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}
void paly_move(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col)
{
// 玩家输入其坐标
int x = 0, y = 0;
printf("请玩家输入坐标(例如:1 1):\n");
while (1)
{
printf("请输入坐标->\n");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
// 坐标的合法性判断 1.范围 2.是否被占用
if (x >= 1 && x <= row && y >= 1 && y <= col)
{
// 玩家输入的1 1 ,在二维数组中对应的为0 0
// 二维数组坐标从0开始
if (board[x - 1][y - 1] == ' ')
{
board[x - 1][y - 1] = '*';
break;
}
else
{
printf("坐标已被占用,不能下棋,请选择其他位置\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("坐标非法,请重新输入->\n");
}
}
}
void computer_move(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col)
{
printf("电脑下棋->\n");
int x = 0, y = 0;
// 判断并下棋
while (1)
{
// 利用随机数 返回test.c设置随机数的起点
x = rand() % row;
// rand()的随机数范围是0~32767 模上row(5) 就是0~5
y = rand() % col;
if (board[x][y] == ' ')
{
board[x][y] = '#';
break;
}
}
}
// 定义一个函数,判断棋盘是否满子
// 满子返回 1
// 未满返回 0
int full_board(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
if (board[i][j] == ' ')
{
return 0;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
char who_win(char board[Row][Col], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
// 行
if (board[i][j] == board[i][j+1] && board[i][j+1] == board[i][j+2] && board[i][j+2] == board[i][j+3] && board[i][j+3] == board[i][j+4] && board[i][j+3] != ' ')
{
return board[i][j+2];
}
// 列
if (board[i][j] == board[i+1][j] && board[i+1][j] == board[i+2][j] && board[i+2][j] == board[i+3][j] && board[i+3][j] == board[i+4][j] && board[i+4][j] != ' ')
{
return board[i+1][j];
}
// 右斜
if(board[i][j] == board[i + 1][j + 1] && board[i + 1][j + 1] == board[i + 2][j + 2] && board[i + 2][j + 2] == board[i + 3][j + 3] && board[i + 3][j + 3] == board[i + 4][j + 4] && board[i + 3][j + 3] != ' ')
{
return board[i + 2][j + 2];
}
// 左斜
if (board[i][j + 4] == board[i + 1][j + 3] && board[i + 1][j + 3] == board[i + 2][j + 2] && board[i + 2][j + 2] == board[i + 3][j + 1] && board[i + 3][j + 1] == board[i + 4][j] && board[i + 2][j + 2] != ' ')
{
return board[i][j + 4];
}
}
}
// 棋盘满了,未分出胜负
if (full_board(board, row, col))
{
return 'Q';
}
// 游戏继续
return 'C';
}
注意事项
整个项目中只能有 一个main()函数和#include <stdio.h>
这里,我把 stdio.h 头文件放在game.h中
之后再去调用game.h头文件,stdio.h 头文件也是包含其中的
我们可以控制row,col 的值改变棋盘的大小文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-462507.html
在判断输赢里,修改判断语句可以修改为三子棋等等文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-462507.html
到了这里,关于C语言三子棋,五子棋,n子棋的代码实现的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!