目录
1.QR code介绍
1.1 通过split_train_val.py得到trainval.txt、val.txt、test.txt
1.2 通过voc_label.py得到适合yolov5训练需要的
2.基于yolov5的QR码检测
2.1配置 QR.yaml
2.2 修改yolov5s_QR.yaml
2.3 训练QR码检测模型
3.性能评价
4.QR码识别
4.1 转成onnx模型
4.2 基于opencv的QR码识别
4.3 基于zbar的QR码识别
5.代码上传
1.QR code介绍
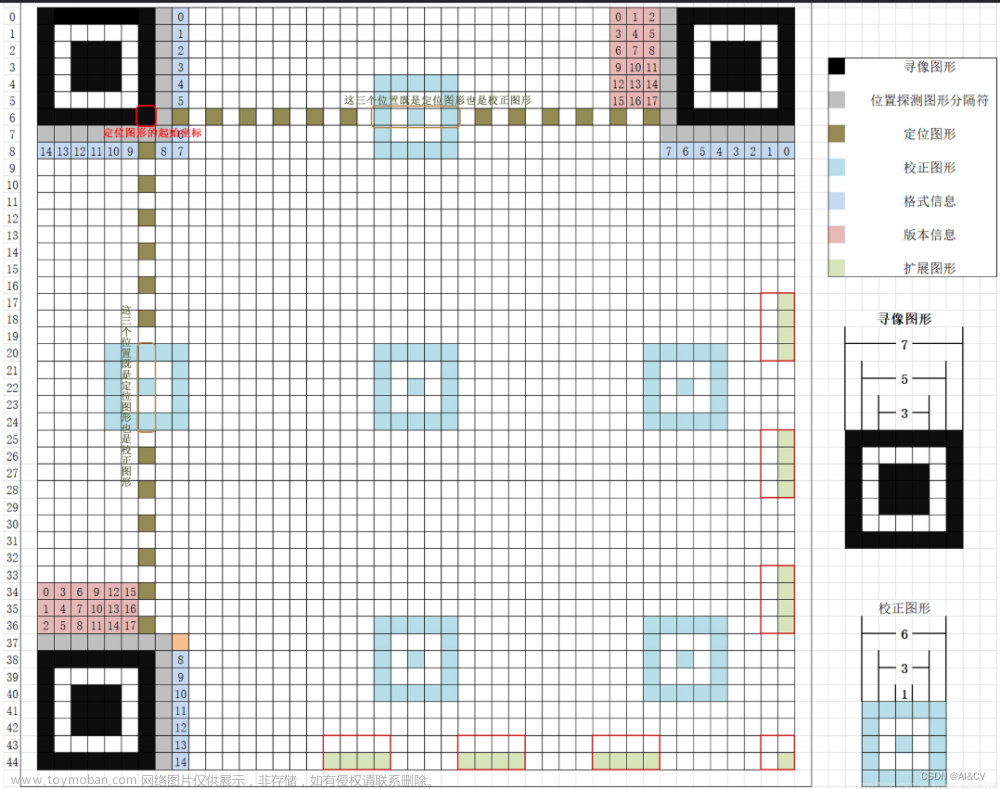
二维码被广泛的应用在我们日常生活中,比如微信和支付宝支付、火车票、商品标识等。二维码的出现极大的方便了我们日常的生活,同时也能将信息较为隐蔽的传输。二维码种类多种多样,有QR Code、Data Matrix、Code One等,日常生活中常用的二维码是QR二维码,该二维码样式以及每部分的作用在图7-30给出。二维码定点方向有三个较大的“回”字形区域用于对二维码进行定位,该区域最大的特别之处在于任何一条经过中心的直线其在黑色和白色区域的长度比值都为1:1:3:1:1。二维码中间具有多个较小的“回”字形区域用于二维码的对齐,根据二维码版本和尺寸的不同,对齐区域的数目也不尽相同。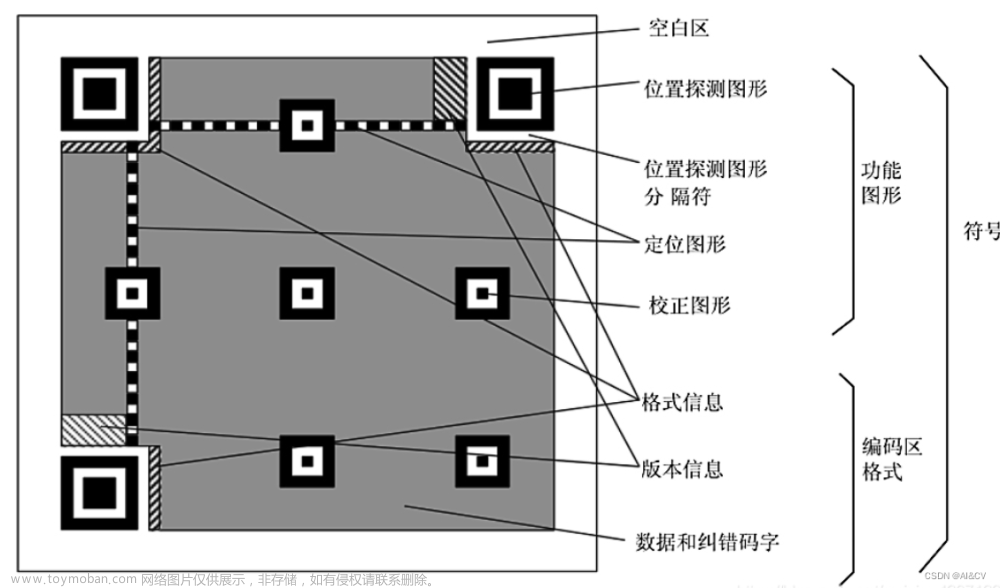
数据集 大小10,85张
数据集见:https://download.csdn.net/download/m0_63774211/87741216

1.1 通过split_train_val.py得到trainval.txt、val.txt、test.txt
# coding:utf-8
import os
import random
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
#xml文件的地址,根据自己的数据进行修改 xml一般存放在Annotations下
parser.add_argument('--xml_path', default='Annotations', type=str, help='input xml label path')
#数据集的划分,地址选择自己数据下的ImageSets/Main
parser.add_argument('--txt_path', default='ImageSets/Main', type=str, help='output txt label path')
opt = parser.parse_args()
trainval_percent = 0.9
train_percent = 0.8
xmlfilepath = opt.xml_path
txtsavepath = opt.txt_path
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
if not os.path.exists(txtsavepath):
os.makedirs(txtsavepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list_index = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list_index, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
file_trainval = open(txtsavepath + '/trainval.txt', 'w')
file_test = open(txtsavepath + '/test.txt', 'w')
file_train = open(txtsavepath + '/train.txt', 'w')
file_val = open(txtsavepath + '/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list_index:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
file_trainval.write(name)
if i in train:
file_train.write(name)
else:
file_val.write(name)
else:
file_test.write(name)
file_trainval.close()
file_train.close()
file_val.close()
file_test.close()1.2 通过voc_label.py得到适合yolov5训练需要的
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
from os import getcwd
sets = ['train', 'val']
classes = ["QR"] # 改成自己的类别
abs_path = os.getcwd()
print(abs_path)
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return x, y, w, h
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open('Annotations/%s.xml' % (image_id), encoding='UTF-8')
out_file = open('labels/%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
#difficult = obj.find('Difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
b1, b2, b3, b4 = b
# 标注越界修正
if b2 > w:
b2 = w
if b4 > h:
b4 = h
b = (b1, b2, b3, b4)
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
wd = getcwd()
for image_set in sets:
if not os.path.exists('labels/'):
os.makedirs('labels/')
image_ids = open('ImageSets/Main/%s.txt' % (image_set)).read().strip().split()
list_file = open('%s.txt' % (image_set), 'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
list_file.write(abs_path + '/images/%s.jpg\n' % (image_id))
convert_annotation(image_id)
list_file.close()2.基于yolov5的QR码检测
2.1配置 QR.yaml
# train and val data as 1) directory: path/images/, 2) file: path/images.txt, or 3) list: [path1/images/, path2/images/]
train: data/QR/train.txt # 16551 images
val: data/QR/val.txt # 4952 images
# number of classes
nc: 1
# class names
names: ['QR']2.2 修改yolov5s_QR.yaml
# YOLOv5 🚀 by Ultralytics, GPL-3.0 license
# Parameters
nc: 1 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3, [1024]],
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
2.3 训练QR码检测模型
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default=ROOT / 'weights/yolov5s.pt', help='initial weights path')
parser.add_argument('--cfg', type=str, default='models/yolov5s.yaml', help='model.yaml path')
parser.add_argument('--data', type=str, default=ROOT / 'data/QR.yaml', help='dataset.yaml path')
parser.add_argument('--hyp', type=str, default=ROOT / 'data/hyps/hyp.scratch-low.yaml', help='hyperparameters path')
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=100, help='total training epochs')
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=8, help='total batch size for all GPUs, -1 for autobatch')
parser.add_argument('--imgsz', '--img', '--img-size', type=int, default=640, help='train, val image size (pixels)')
parser.add_argument('--rect', action='store_true', help='rectangular training')
parser.add_argument('--resume', nargs='?', const=True, default=False, help='resume most recent training')
parser.add_argument('--nosave', action='store_true', help='only save final checkpoint')
parser.add_argument('--noval', action='store_true', help='only validate final epoch')
parser.add_argument('--noautoanchor', action='store_true', help='disable AutoAnchor')
parser.add_argument('--noplots', action='store_true', help='save no plot files')
parser.add_argument('--evolve', type=int, nargs='?', const=300, help='evolve hyperparameters for x generations')
parser.add_argument('--bucket', type=str, default='', help='gsutil bucket')
parser.add_argument('--cache', type=str, nargs='?', const='ram', help='image --cache ram/disk')
parser.add_argument('--image-weights', action='store_true', help='use weighted image selection for training')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--multi-scale', action='store_true', help='vary img-size +/- 50%%')
parser.add_argument('--single-cls', action='store_true', help='train multi-class data as single-class')
parser.add_argument('--optimizer', type=str, choices=['SGD', 'Adam', 'AdamW'], default='SGD', help='optimizer')
parser.add_argument('--sync-bn', action='store_true', help='use SyncBatchNorm, only available in DDP mode')
parser.add_argument('--workers', type=int, default=0, help='max dataloader workers (per RANK in DDP mode)')
parser.add_argument('--project', default=ROOT / 'runs/train_QR', help='save to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--name', default='exp', help='save to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--exist-ok', action='store_true', help='existing project/name ok, do not increment')
parser.add_argument('--quad', action='store_true', help='quad dataloader')
parser.add_argument('--cos-lr', action='store_true', help='cosine LR scheduler')
parser.add_argument('--label-smoothing', type=float, default=0.0, help='Label smoothing epsilon')
parser.add_argument('--patience', type=int, default=100, help='EarlyStopping patience (epochs without improvement)')
parser.add_argument('--freeze', nargs='+', type=int, default=[0], help='Freeze layers: backbone=10, first3=0 1 2')
parser.add_argument('--save-period', type=int, default=-1, help='Save checkpoint every x epochs (disabled if < 1)')
parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=0, help='Global training seed')
parser.add_argument('--local_rank', type=int, default=-1, help='Automatic DDP Multi-GPU argument, do not modify')开启python train.py
3.性能评价
map 为0.962

检测结果图:
4.QR码识别
4.1 转成onnx模型
python export.py --weights runs/train_QR/exp3/weights/best.pt --include onnx engine --device cpu4.2 基于opencv的QR码识别
import cv2
import time
import sys
import numpy as np
det = cv2.QRCodeDetector()
def build_model(is_cuda):
net = cv2.dnn.readNet("best.onnx")
if is_cuda:
print("Attempty to use CUDA")
net.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_CUDA)
net.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CUDA_FP16)
else:
print("Running on CPU")
net.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV)
net.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CPU)
return net
INPUT_WIDTH = 640
INPUT_HEIGHT = 640
SCORE_THRESHOLD = 0.2
NMS_THRESHOLD = 0.4
CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD = 0.4
def detect(image, net):
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(image, 1/255.0, (INPUT_WIDTH, INPUT_HEIGHT), swapRB=True, crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
preds = net.forward()
return preds
def load_classes():
class_list = []
with open("classes.txt", "r") as f:
class_list = [cname.strip() for cname in f.readlines()]
return class_list
class_list = load_classes()
def wrap_detection(input_image, output_data):
class_ids = []
confidences = []
boxes = []
rows = output_data.shape[0]
image_width, image_height, _ = input_image.shape
x_factor = image_width / INPUT_WIDTH
y_factor = image_height / INPUT_HEIGHT
for r in range(rows):
row = output_data[r]
confidence = row[4]
if confidence >= 0.4:
classes_scores = row[5:]
_, _, _, max_indx = cv2.minMaxLoc(classes_scores)
class_id = max_indx[1]
if (classes_scores[class_id] > .25):
confidences.append(confidence)
class_ids.append(class_id)
x, y, w, h = row[0].item(), row[1].item(), row[2].item(), row[3].item()
left = int((x - 0.5 * w) * x_factor)
top = int((y - 0.5 * h) * y_factor)
width = int(w * x_factor)
height = int(h * y_factor)
box = np.array([left, top, width, height])
boxes.append(box)
indexes = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, 0.25, 0.45)
result_class_ids = []
result_confidences = []
result_boxes = []
for i in indexes:
result_confidences.append(confidences[i])
result_class_ids.append(class_ids[i])
result_boxes.append(boxes[i])
return result_class_ids, result_confidences, result_boxes
def format_yolov5(frame):
row, col, _ = frame.shape
_max = max(col, row)
result = np.zeros((_max, _max, 3), np.uint8)
result[0:row, 0:col] = frame
return result
colors = [(255, 255, 0), (0, 255, 0), (0, 255, 255), (255, 0, 0)]
is_cuda = len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "cuda"
net = build_model(is_cuda)
start = time.time_ns()
frame_count = 0
total_frames = 0
fps = -1
frame = cv2.imread('QR-00345.jpg')
inputImage = format_yolov5(frame)
outs = detect(inputImage, net)
class_ids, confidences, boxes = wrap_detection(inputImage, outs[0])
for (classid, confidence, box) in zip(class_ids, confidences, boxes):
color = colors[int(classid) % len(colors)]
ROI=frame[(box[1]):(box[1]+box[3]),(box[0]):(box[0]+box[2])]
data, pts, st_code = det.detectAndDecode(ROI)
print(data)
cv2.rectangle(frame, box, color, 2)
#cv2.rectangle(frame, (box[0], box[1] - 20), (box[0] + box[2], box[1]), color, -1)
#cv2.putText(frame, class_list[classid], (box[0], box[1] - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, .5, (0,0,0))
cv2.putText(frame, str(data), (box[0], box[1] - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, .3, (0,0,0))
cv2.imshow("output", frame)
cv2.waitKey(10000)
检测结果文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-466292.html
4.3 基于zbar的QR码识别
import cv2
import time
import sys
import numpy as np
import zxing
from pyzbar import pyzbar
def build_model(is_cuda):
net = cv2.dnn.readNet("best.onnx")
if is_cuda:
print("Attempty to use CUDA")
net.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_CUDA)
net.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CUDA_FP16)
else:
print("Running on CPU")
net.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV)
net.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CPU)
return net
INPUT_WIDTH = 640
INPUT_HEIGHT = 640
SCORE_THRESHOLD = 0.2
NMS_THRESHOLD = 0.4
CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD = 0.4
def detect(image, net):
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(image, 1/255.0, (INPUT_WIDTH, INPUT_HEIGHT), swapRB=True, crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
preds = net.forward()
return preds
def load_capture():
capture = cv2.VideoCapture("sample.mp4")
return capture
def load_classes():
class_list = []
with open("classes.txt", "r") as f:
class_list = [cname.strip() for cname in f.readlines()]
return class_list
class_list = load_classes()
def wrap_detection(input_image, output_data):
class_ids = []
confidences = []
boxes = []
rows = output_data.shape[0]
image_width, image_height, _ = input_image.shape
x_factor = image_width / INPUT_WIDTH
y_factor = image_height / INPUT_HEIGHT
for r in range(rows):
row = output_data[r]
confidence = row[4]
if confidence >= 0.4:
classes_scores = row[5:]
_, _, _, max_indx = cv2.minMaxLoc(classes_scores)
class_id = max_indx[1]
if (classes_scores[class_id] > .25):
confidences.append(confidence)
class_ids.append(class_id)
x, y, w, h = row[0].item(), row[1].item(), row[2].item(), row[3].item()
left = int((x - 0.5 * w) * x_factor)
top = int((y - 0.5 * h) * y_factor)
width = int(w * x_factor)
height = int(h * y_factor)
box = np.array([left, top, width, height])
boxes.append(box)
indexes = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, 0.25, 0.45)
result_class_ids = []
result_confidences = []
result_boxes = []
for i in indexes:
result_confidences.append(confidences[i])
result_class_ids.append(class_ids[i])
result_boxes.append(boxes[i])
return result_class_ids, result_confidences, result_boxes
def format_yolov5(frame):
row, col, _ = frame.shape
_max = max(col, row)
result = np.zeros((_max, _max, 3), np.uint8)
result[0:row, 0:col] = frame
return result
colors = [(255, 255, 0), (0, 255, 0), (0, 255, 255), (255, 0, 0)]
is_cuda = len(sys.argv) > 1 and sys.argv[1] == "cuda"
net = build_model(is_cuda)
capture = load_capture()
start = time.time_ns()
frame_count = 0
total_frames = 0
fps = -1
frame = cv2.imread('QR-00345.jpg')
inputImage = format_yolov5(frame)
outs = detect(inputImage, net)
class_ids, confidences, boxes = wrap_detection(inputImage, outs[0])
for (classid, confidence, box) in zip(class_ids, confidences, boxes):
color = colors[int(classid) % len(colors)]
ROI=frame[(box[1]):(box[1]+box[3]),(box[0]):(box[0]+box[2])]
#barcode = zx.decode(ROI)
#print(barcode.parsed)
data = pyzbar.decode(ROI)
print(data)
cv2.rectangle(frame, box, color, 2)
#cv2.rectangle(frame, (box[0], box[1] - 20), (box[0] + box[2], box[1]), color, -1)
#cv2.putText(frame, class_list[classid], (box[0], box[1] - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, .5, (0,0,0))
cv2.putText(frame, str(data), (box[0], box[1] - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, .3, (0,0,0))
cv2.imshow("output", frame)
cv2.waitKey(10000)
5.代码上传
https://download.csdn.net/download/m0_63774211/87743400文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-466292.html
到了这里,关于基于Yolov5的二维码QR码识别的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!