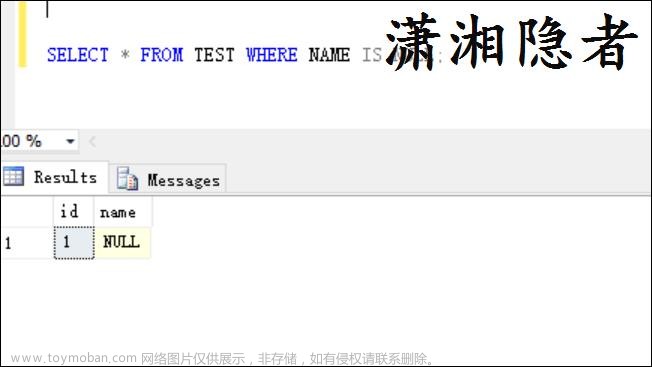
1、schema。
pg中的schema表示当前db中数据库对象的命名空间(namespace),数据库对象包括但不限于表、函数、视图、索引等。
对于熟悉mysql的人来说,在第一次看到pg中的schema的概念时,可能会疑惑,schema不是表示database的吗?
注:mysql中schema和database是一个概念。create database 和create schema的效果是相同的。
Oracle 中的schema的和用户名相同,schema用于 存放对象包括但不限于表、函数、视图、索引等。
schama 在PG中概念最小,在mysql中概念最大
需要注意的是PostgreSQL中的用户(和角色)是全局对象,不是在数据库中定义的,而是在实例级别定义的。(oracle cdb的root# )schema由用户在特定数据库中创建,并包含数据库对象。
Oracle CDB之前一个实例或者多个实例(RAC)对应一个数据库,其他数据库都是默认一个实例多个数据库。这样用户就是数据库专用的,CDB后和其他数据库对齐。
做个测试:

但是在pg中schema并不等同于database。pg中一个db可以有一个或多个模式,不同模式可以有具有相同名称的各种对象。如下图所示:

图片来源:
https://blog.dbi-services.com/a-schema-and-a-user-are-not-the-same-in-postgresql/
2、怎么列出当前db中的所有模式?
psql 中使用\dn+
postgres=# \dn+List of schemasName | Owner | Access privileges | Description--------+----------+----------------------+------------------------public | postgres | postgres=UC/postgres+| standard public schema| | =UC/postgres |(1 row)
在pg中数据库对象都是指向特定的schema的。默认情况下每个pg的数据库都有一个名为public的schema,如果create语句没有指定模式,新对象将默认属于该模式。 类似sqlserver的dbo
postgres=# create table t1(id int);CREATE TABLEpostgres=# \dt+List of relationsSchema | Name | Type | Owner | Persistence | Access method | Size | Description--------+------+-------+----------+-------------+---------------+---------+-------------public | t1 | table | postgres | permanent | heap | 0 bytes |(1 row)
可以看到t1表的模式是public。也可以通过查询pg_tables表的schemaname字段来查看表的模式。
postgres=# select schemaname from pg_tables where tablename = 't1';schemaname------------public(1 row)
3、怎么删除一个模式?
我们可以删除public模式吗?
可以。
试一下:
postgres=# drop schema public cascade;NOTICE: drop cascades to 4 other objectsDETAIL: drop cascades to function add(integer,integer)drop cascades to function add1(integer,integer)drop cascades to function add2(integer,integer)drop cascades to table t1DROP SCHEMA
因为我们删除了public,所以此时portgres数据库中没有任何的模式了,这时候我们再create table看看会发生什么。
postgres=# \dn+List of schemasName | Owner | Access privileges | Description------+-------+-------------------+-------------(0 rows)postgres=# create table t1(id int);ERROR: no schema has been selected to create inLINE 1: create table t1(id int);^
可以看到提示:ERROR: no schema has been selected to create in。这也说明了数据库对象必须指向一个schema。
4、怎么创建模式?
postgres=# create schema my_schema;CREATE SCHEMApostgres=# \dn+List of schemasName | Owner | Access privileges | Description-----------+----------+-------------------+-------------my_schema | postgres | |(1 row)
这时候我们再创建表t1,就可以指定schema。
create table my_schema.t1 ( a int );
此时我们使用\d命令列出所有表。会提示Did not find any relations.原因是search_path中没有设置my_schema。
postgres=# \dDid not find any relations.
将my_schema添加到search_path中,即可显示出来。

5、什么是search_path?
search_path类似于linux的path环境变量。它是一个模式名列表,当我们不使用数据库对象的限定名时,pg会检查这些模式名。例如,当我们执行select * from mytable; 没有指定模式。此时pg会在search_path中列出的模式中查找这个表。它选择它找到的第一个匹配项。默认是$user,public。
怎么修改search_path?
set search_path = "$user", public, my_schema
6、pg中的user。
默认的pg安装后会包含一个postgres的超级用户。我们如果需要创建新用户,需要以postgres用户连接到pg, 然后使用create user(或create role)创建其他用户。
postgres=# \du+List of rolesRole name | Attributes | Member of | Description-----------+------------------------------------------------------------+-----------+-------------postgres | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLS | {} |
用户和角色的区别是什么?官网上的描述是:
别名
CREATE USER is now an alias for CREATE ROLE. The only difference is that when the command is spelled CREATE USER, LOGIN is assumed by default, whereas NOLOGIN is assumed when the command is spelled CREATE ROLE.
也就是说user和role是相同的概念,唯一的区别是create user默认有login权限,而create role没有。
postgres=# \du+List of rolesRole name | Attributes | Member of | Description-----------+------------------------------------------------------------+-----------+-------------postgres | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLS | {} |u1 | | {} |u2 | Cannot login | {} |
需要注意的是PostgreSQL中的用户(和角色)是全局对象,不是在数据库中定义的,而是在实例级别定义的。模式由用户在特定数据库中创建,并包含数据库对象。
我们创建了新用户后,如果想使用它, 使用u1用户连接数据库。
/usr/local/postgresql/bin/psql -U u1 -h 127.0.01 -p 5432 -d postgres
登陆成功后,我们创建一个名为testdb的数据库。
postgres=> create database testdb;ERROR: permission denied to create databasepostgres=>
提示没有权限。如果想要有create database的权限应该怎么做?
使用postgres用户连接数据库,执行alter user u1 with createdb;
postgres=# alter user u1 with createdb;ALTER ROLEpostgres=# \du+List of rolesRole name | Attributes | Member of | Description-----------+------------------------------------------------------------+-----------+-------------postgres | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLS | {} |u1 | Create DB | {} |u2 | Cannot login | {} |
然后重新使用u1连接数据库。
postgres=> create database testdb;CREATE DATABASEpostgres=> \l+List of databasesName | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges | Size | Tablespace | Description-----------+----------+----------+-------------+-------------+-----------------------+---------+------------+--------------------------------------------postgres | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | 8673 kB | pg_default | default administrative connection databasetemplate0 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +| 8417 kB | pg_default | unmodifiable empty database| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres | | |template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +| 8417 kB | pg_default | default template for new databases| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres | | |testdb | u1 | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | 8417 kB | pg_default |(4 rows)
你会发现这个testdb的Owner的是u1。这里需要注意这个owner的概念。
删除一个对象或以任何方式改变其定义的权利不被视为可授予的特权,它是owner所固有的。不能被授予或撤销。
怎么理解这句话?
举个例子,我们以另外一个非superuser用户u2来连接数据库,尝试去删除testdb,看看会发生什么。
[ops@test ~]$ /usr/local/postgresql/bin/psql -U u2 -h 127.0.01 -p 5432 -d postgrespsql (14beta1)Type "help" for help.postgres=> \l+List of databasesName | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges | Size | Tablespace | Description-----------+----------+----------+-------------+-------------+-----------------------+---------+------------+--------------------------------------------postgres | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | 8673 kB | pg_default | default administrative connection databasetemplate0 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +| 8417 kB | pg_default | unmodifiable empty database| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres | | |template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +| 8417 kB | pg_default | default template for new databases| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres | | |testdb | u1 | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | 8417 kB | pg_default |(4 rows)postgres=> drop database testdb;ERROR: must be owner of database testdb
如果我们把testdb的所有权限赋予给u2这个用户呢?
postgres=# GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE "testdb" to u2;GRANT
重新用u2来连接数据库,并删除testdb。
postgres=> drop database testdb;ERROR: must be owner of database testdb
依然报错。
也就是说如果我们想删除一个数据库对象,必须是该对象的owner才行。
7、user的privilges。
在上面的例子中,我使用u1创建了testdb,并使用
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE "testdb" to u2;
将testdb的权限授予给了u2。
但是这个时候,u2真正拥有了这个testdb的所有权限了吗?
使用u1连接数据库,列出所有的表。
testdb=> \c testdbYou are now connected to database "testdb" as user "u2".testdb=> \d+List of relationsSchema | Name | Type | Owner | Persistence | Access method | Size | Description--------+------+-------+-------+-------------+---------------+---------+-------------public | t1 | table | u2 | permanent | heap | 0 bytes |public | t2 | table | u1 | permanent | heap | 0 bytes |(2 rows)
发现其中表t1的owner是u2,表t2的Owenr的是u1,我们看下u2能否访问1、t2表。
[ops@test~]$ /usr/local/postgresql/bin/psql -U u2 -h 127.0.01 -p 5432 -d postgrespsql (14beta1)Type "help" for help.postgres=> \c testdbYou are now connected to database "testdb" as user "u2".testdb=> select * from t1;id----(0 rows)testdb=> select * from t2;ERROR: permission denied for table t2
可以发现,u2可以查询t1,但是不能查询t2。这个时候要怎么办?
以postgres用户连接数据库testdb。然后执行:GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO u2;
[ops@test ~]$ usr/local/postgresql/bin/psql -U postgres -h 127.0.01 -p 5432 -d postgrespsql (14beta1)Type "help" for help.postgres=# \c testdbYou are now connected to database "testdb" as user "postgres".testdb=# GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO u2;GRANT
这时候再使用t2连接到testdb。
[ops@testdb ~]$ usr/local/postgresql/bin/psql -U u2 -h 127.0.01 -p 5432 -d postgrespsql (14beta1)Type "help" for help.postgres=> \c testdbYou are now connected to database "testdb" as user "u2".testdb=> select * from t1;id----(0 rows)testdb=> select * from t2;id----(0 rows)
发现t2表可以访问了。
在创建新角色并授予它们访问各种数据库对象的权限的过程中,权限必须在
数据库、模式和模式对象
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE "testdb" to u2;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO u2;
---------------------其实着一个数据库就相当于早期的一个oracle实例,建了多个用户,对应多个schema,各个用户访问对方的表要授权一个道理。 只是这个库有一个专用的用户,之前oracle的库没有专有用户。 专用用户对这个库什么都能干。别人可以借用库,但是访问就不行。
那反过来 库是u1的,u1是不是随便访问u2呢? 下面的结果发现也是不能的,所以数据库的owner是谁不重要,owner只能删库,但是不是查看表。
我使用u1创建了testdb,并使用 将testdb的权限授予给了u2。
表t1的owner是u2,表t2的Owenr的是u1,我们看下u2能否访问1、t2表。
u2可以查询t1,但是不能查询t2
反之也然,对方只是借用了你的库,但是你没权限访问
[postgres@pg-192-134 ~]$ psql -U u1 -d testdb
psql (14.7)
Type "help" for help.
testdb=> \l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
------------+------------+----------+-------------+-------------+-----------------------
ecology | ecology | UTF8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 |
keepalived | keepalived | UTF8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 |
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 |
template0 | postgres | UTF8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | UTF8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
testdb | u1 | UTF8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | =Tc/u1 +
| | | | | u1=CTc/u1 +
| | | | | u2=CTc/u1
(6 rows)
testdb=> \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------+-------+-------
public | t1 | table | u1
public | t2 | table | u2
(2 rows)
testdb=> select *from t1;
id
----
(0 rows)
testdb=> select * from t2;
ERROR: permission denied for table t2
testdb=> exit
[postgres@pg-192-134 ~]$ psql -U u2 -d testdb
psql (14.7)
Type "help" for help.
testdb=> \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------+-------+-------
public | t1 | table | u1
public | t2 | table | u2
(2 rows)
testdb=> \l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
------------+------------+----------+-------------+-------------+-----------------------
ecology | ecology | UTF8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 |
keepalived | keepalived | UTF8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 |
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 |
template0 | postgres | UTF8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | UTF8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
testdb | u1 | UTF8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | zh_CN.UTF-8 | =Tc/u1 +
| | | | | u1=CTc/u1 +
| | | | | u2=CTc/u1
(6 rows)
testdb=> select * from t2;
id
----
(0 rows)
testdb=> select * from t1;
ERROR: permission denied for table t1
testdb=> 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-473866.html
级别分别授予。例如,如果需要授予对表的访问权,还必须确保角色对表所在的数据库和模式具有访问权。如果缺少任何权限,则该角色无法访问表。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-473866.html
到了这里,关于pg mysql oracle 中的schema的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!