引言
💡 作者简介:专注于C/C++高性能程序设计和开发,理论与代码实践结合,让世界没有难学的技术。包括C/C++、Linux、MySQL、Redis、TCP/IP、协程、网络编程等。
👉
🎖️ CSDN实力新星,社区专家博主
👉
🔔 专栏介绍:从零到c++精通的学习之路。内容包括C++基础编程、中级编程、高级编程;掌握各个知识点。
👉
🔔 专栏地址:C++从零开始到精通
👉
🔔 博客主页:https://blog.csdn.net/Long_xu
🔔 上一篇:【022】C++的结构体、共用体以及枚举详解(最全讲解)
一、链表的概述
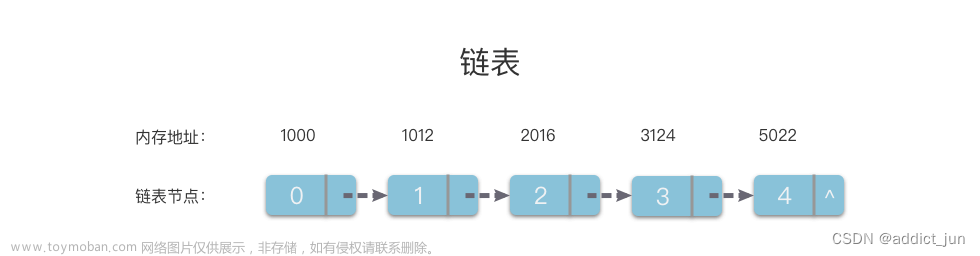
链表(Linked List)是一种常见的数据结构,它由若干个节点(Node)组成,每个节点包含一个数据元素和指向下一个节点的指针。相邻两个节点之间通过指针连接起来,形成了链式结构。
链表可以分为单向链表、双向链表和循环链表三种类型。其中单向链表每个节点只有一个指向下一个节点的指针;双向链表每个节点除了有指向下一个节点的指针外,还有指向前一个节点的指针;循环链表则是将最后一个节点的指针指向头结点,使得整个链条形成了一个闭环。
单向链表是由一个一个节点组成,节点没有名字,每个节点从堆区动态申请,节点间物理上是非连续的,但是每个节点通过指针保存下一个节点的位置达到逻辑上的连续。
数组和链表的优缺点:
- 静态数组:缺点是必须事先知道数组元素个数,设置过多了浪费内存空间,设置过少容易溢出,插入、删除数据效率低;优点是遍历元素效率高,支持随机访问。
- 动态数组:不需要实现知道元素的个数,在使用中动态申请,插入、删除数据效率低;优点是遍历元素效率高,支持随机访问。
- 链表:优点是不需要实现知道元素的个数,在使用中动态申请,插入、删除数据不需要移动数据;缺点是遍历效率低。
二、利用链表设计一个学生管理系统
通过实战的方式掌握链表的使用。
2.1、设计主函数main()
首先是一个帮助函数和main()函数的实现:
void help()
{
cout << "*************************************" << endl;
cout << "1) help:" << endl;
cout << "2) insert:" << endl;
cout << "3) print:" << endl;
cout << "4) search:" << endl;
cout << "5) delete:" << endl;
cout << "6) free:" << endl;
cout << "7) quit:" << endl;
cout << "*************************************" << endl;
}
int main() {
help();
struct Student *head=NULL;
while (1)
{
char cmd[64] = { 0 };
cout << "请输入指令:";
cin >> cmd;
if (strcmp(cmd, "help")==0)
{
help();
}
else if (strcmp(cmd, "insert")==0)
{
cout << "请输入节点信息(id, name):";
struct Student *tmp=new struct Student;
cin >> tmp->id >> tmp->name;
head=insert_link(head,tmp);
}
else if (strcmp(cmd, "print")==0)
{
print_link(head);
}
else if (strcmp(cmd, "search") == 0)
{
char name[32] = { 0 };
cout << "请输入查询的姓名:";
cin >> name;
struct Student *res=search_link(head, name);
if (res != NULL)
{
cout << "查询结果:"<<res->id << " " << res->name << endl;
}
else
{
cout << name << "不存在" << endl;
}
}
else if (strcmp(cmd, "delete") == 0)
{
cout << "请输入要删除的节点学号:";
int num;
cin >> num;
head = delete_link(head, num);
}
else if (strcmp(cmd, "free") == 0)
{
head=free_link(head);
if (head == NULL)
cout << "已完成释放" << endl;
}
else if (strcmp(cmd, "quit") == 0)
{
head = free_link(head);
if (head == NULL)
cout << "已完成释放" << endl;
cout << "已退出系统" << endl;
return 0;
}
else
{
cout << "不识别的指令,请正确输入指令。" << endl;
help();
}
}
return 0;
}
2.2、实现插入节点
插入节点的方式有三种:
- 头部插入。
- 尾部插入。
- 有序插入(双指针法)。
// 插入链表
struct Student * insert_link(struct Student *head, struct Student *node)
{
#if 0
//头插法
// 链表不存在时;
if (head == NULL)
{
head = node;
head->next = NULL;
}
else
{
// 链表串联起来。头插法
node->next = head;
head = node;
}
return head;
#elif 0
// 尾插法
if (head == NULL)
{
head = node;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
// 查找末尾
struct Student *cur = head;
while (cur->next != NULL)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
// 尾部插入
cur->next = node;
node->next = NULL;
return head;
#else
// 有序插入
if (head == NULL)
{
head = node;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
// 双指针法
struct Student *cur = head;
struct Student *pre = head;
while (cur->id < node->id && cur->next != NULL)
{
// 保存cur记录
pre = cur;
// cur移动到下一个
cur = cur->next;
}
// 判断插入点的位置
if (cur->id > node->id)
{
if (cur == head)//头部插入
{
node->next = head;
head = node;
}
else//中部插入
{
pre->next = node;
node->next = cur;
}
}
else
{
// 尾部插入
cur->next = node;
node->next = NULL;
}
#endif
}
2.3、实现链表的遍历
// 遍历链表
void print_link(struct Student *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
cout << "link is empty." << endl;
return;
}
// 循环遍历链表
struct Student *cur;
cur = head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
cout << cur->id << " " << cur->name << endl;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
2.4、实现链表的查找
struct Student *search_link(struct Student *head,const char *name)
{
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
struct Student *cur = head;
while (cur->next != NULL && strcmp(cur->name, name) != 0)
cur = cur->next;
if (strcmp(cur->name, name) == 0)
return cur;
return NULL;
}
2.5、实现删除某个节点
struct Student *delete_link(struct Student *head,int num)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
cout << "链表不存在" << endl;
return NULL;
}
struct Student *cur = head;
struct Student *pre = head;
// 查找节点
while (cur->next != NULL && cur->id != num)
{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur->id == num)
{
cout << "找到节点,并删除了。" << endl;
if (cur == head)//头部删除
{
head = cur->next;
}
else//中尾部删除
pre->next = cur->next;
delete cur;
}
else
{
cout << "节点不存在" << endl;
}
return head;
}
2.6、实现释放链表
struct Student *free_link(struct Student *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
cout << "链表不存在" << endl;
return NULL;
}
struct Student *cur = head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
head = head->next;
delete cur;
cur = head;
}
return head;
}
2.7、完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
void help()
{
cout << "*************************************" << endl;
cout << "1) help:" << endl;
cout << "2) insert:" << endl;
cout << "3) print:" << endl;
cout << "4) search:" << endl;
cout << "5) delete:" << endl;
cout << "6) free:" << endl;
cout << "7) quit:" << endl;
cout << "*************************************" << endl;
}
struct Student {
int id;
char name[16];
struct Student *next;
};
// 插入链表
struct Student * insert_link(struct Student *head, struct Student *node)
{
#if 0
//头插法
// 链表不存在时;
if (head == NULL)
{
head = node;
head->next = NULL;
}
else
{
// 链表串联起来。头插法
node->next = head;
head = node;
}
return head;
#elif 0
// 尾插法
if (head == NULL)
{
head = node;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
// 查找末尾
struct Student *cur = head;
while (cur->next != NULL)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
// 尾部插入
cur->next = node;
node->next = NULL;
return head;
#else
// 有序插入
if (head == NULL)
{
head = node;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
// 双指针法
struct Student *cur = head;
struct Student *pre = head;
while (cur->id < node->id && cur->next != NULL)
{
// 保存cur记录
pre = cur;
// cur移动到下一个
cur = cur->next;
}
// 判断插入点的位置
if (cur->id > node->id)
{
if (cur == head)//头部插入
{
node->next = head;
head = node;
}
else//中部插入
{
pre->next = node;
node->next = cur;
}
}
else
{
// 尾部插入
cur->next = node;
node->next = NULL;
}
#endif
}
// 遍历链表
void print_link(struct Student *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
cout << "link is empty." << endl;
return;
}
// 循环遍历链表
struct Student *cur;
cur = head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
cout << cur->id << " " << cur->name << endl;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
struct Student *search_link(struct Student *head,const char *name)
{
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
struct Student *cur = head;
while (cur->next != NULL && strcmp(cur->name, name) != 0)
cur = cur->next;
if (strcmp(cur->name, name) == 0)
return cur;
return NULL;
}
struct Student *delete_link(struct Student *head,int num)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
cout << "链表不存在" << endl;
return NULL;
}
struct Student *cur = head;
struct Student *pre = head;
// 查找节点
while (cur->next != NULL && cur->id != num)
{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur->id == num)
{
cout << "找到节点,并删除了。" << endl;
if (cur == head)//头部删除
{
head = cur->next;
}
else//中尾部删除
pre->next = cur->next;
delete cur;
}
else
{
cout << "节点不存在" << endl;
}
return head;
}
struct Student *free_link(struct Student *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
cout << "链表不存在" << endl;
return NULL;
}
struct Student *cur = head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
head = head->next;
delete cur;
cur = head;
}
return head;
}
int main() {
help();
struct Student *head=NULL;
while (1)
{
char cmd[64] = { 0 };
cout << "请输入指令:";
cin >> cmd;
if (strcmp(cmd, "help")==0)
{
help();
}
else if (strcmp(cmd, "insert")==0)
{
cout << "请输入节点信息(id, name):";
struct Student *tmp=new struct Student;
cin >> tmp->id >> tmp->name;
head=insert_link(head,tmp);
}
else if (strcmp(cmd, "print")==0)
{
print_link(head);
}
else if (strcmp(cmd, "search") == 0)
{
char name[32] = { 0 };
cout << "请输入查询的姓名:";
cin >> name;
struct Student *res=search_link(head, name);
if (res != NULL)
{
cout << "查询结果:"<<res->id << " " << res->name << endl;
}
else
{
cout << name << "不存在" << endl;
}
}
else if (strcmp(cmd, "delete") == 0)
{
cout << "请输入要删除的节点学号:";
int num;
cin >> num;
head = delete_link(head, num);
}
else if (strcmp(cmd, "free") == 0)
{
head=free_link(head);
if (head == NULL)
cout << "已完成释放" << endl;
}
else if (strcmp(cmd, "quit") == 0)
{
head = free_link(head);
if (head == NULL)
cout << "已完成释放" << endl;
cout << "已退出系统" << endl;
return 0;
}
else
{
cout << "不识别的指令,请正确输入指令。" << endl;
help();
}
}
return 0;
}
总结
链表(Linked List)是一种常见的数据结构,它由若干个节点(Node)组成,每个节点包含一个数据元素和指向下一个节点的指针。相邻两个节点之间通过指针连接起来,形成了链式结构。
链表可以分为单向链表、双向链表和循环链表三种类型。其中单向链表每个节点只有一个指向下一个节点的指针;双向链表每个节点除了有指向下一个节点的指针外,还有指向前一个节点的指针;循环链表则是将最后一个节点的指针指向头结点,使得整个链条形成了一个闭环。
相比于数组等线性存储结构,链表具有以下优点:
-
链表可以动态扩展,不需要预先定义大小。
-
插入和删除操作非常高效,只需要修改相邻两个节点之间的指针即可。
-
对于大规模数据存储时空效率更高。
但是也存在一些缺点:
-
随机访问元素比较困难,需要遍历整个链条才能找到对应位置的元素。
-
存储多余的地址信息会占用额外空间。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-477029.html
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-477029.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-477029.html
到了这里,关于【023】C/C++数据结构之链表及其实战应用的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!