PS: 前面我们已经详细介绍了二叉树的概念以及二叉树的遍历的概念等,一些详细概念知识点可以在下面链接中的博客查看。本文主要需要使用代码自己实现二叉树及应用。
二叉树的概念及遍历
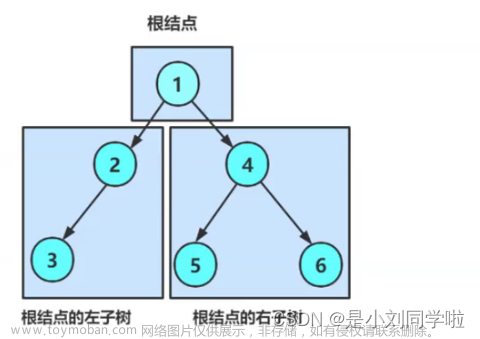
1. 构造二叉树
二叉树是由一个节点一个个连接而成的,每个节点最多连接两个节点,所以每个节点需要有一个数据元素和两个指向左右子树的指针,当没有左右子树时,可以为null。
public class MyTreeNode {
public int val;
public MyTreeNode left,right;
public MyTreeNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
public MyTreeNode(){}
}
因为编译器本身并不会自动构造二叉树,所以我们要编写程序来构造一个二叉树,并通过一个节点root记录根节点。
//构造Tree
public MyTreeNode root;
public MyTreeNode createTree(){
MyTreeNode node1 = new MyTreeNode(1);
MyTreeNode node2 = new MyTreeNode(2);
MyTreeNode node3 = new MyTreeNode(3);
MyTreeNode node4 = new MyTreeNode(4);
MyTreeNode node5 = new MyTreeNode(5);
MyTreeNode node6 = new MyTreeNode(6);
root = node1;
node1.left = node2;
node2.left = node3;
node1.right = node4;
node4.left = node5;
node4.right = node6;
return root;
}
如图
接下来应用将围绕此树进行。
2. 前序遍历
前序遍历的遍历顺序:访问根结点—>根的左子树—>根的右子树。
遍历结果:123456
2.1 前序遍历递归
参数root是当前节点,如果为null说明已经到叶子节点,直接返回。否则,我们先输出当前节点的值,然后递归遍历左子树,最后递归遍历右子树。
// 前序遍历递归
public void preOrder(MyTreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
2.2 前序遍历非递归
我们使用一个栈来辅助遍历。首先将根节点压入栈中,然后每次从栈中弹出一个节点,并输出它的值。如果该节点有右子树,我们就将右子树压入栈中,因为左子树后遍历,为了后遍历左子树,我们将左子树后入栈,所以先遍历右子树。如果该节点有左子树,我们就将左子树压入栈中,因为下一步要遍历左子树。这样,我们就依次访问了整个二叉树节点。
//前序遍历非递归
public void norPreOrder(MyTreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
Stack<MyTreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
MyTreeNode cur = stack.pop();
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
if(cur.right != null){
stack.push(cur.right);
}
if(cur.left != null){
stack.push(cur.left);
}
}
}
3. 中序遍历
根的左子树—>根节点—>根的右子树。
遍历结果:321546
3.1 中序遍历递归
用递归实现,先递归遍历左子树,遍历完后将节点值加入结果列表中,然后再递归遍历右子树。
// 中序遍历递归
public void inOrder(MyTreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
inOrder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
inOrder(root.right);
}
3.2 中序遍历非递归
借助辅助栈实现非递归中序遍历,首先检查当前节点是否为空以及是否有左子节点,如果有则将节点入栈,并将当前节点指向左子节点,继续进入循环,直到左子树遍历完毕,然后将节点出栈并添加到结果列表中,将当前节点指向右子节点,继续遍历。
//中序遍历非递归
public void norInOrder(MyTreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
Stack<MyTreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
MyTreeNode curr = root;
while(curr != null || !stack.empty()) {
while (curr != null) {
stack.push(curr);
curr = curr.left;
}
curr = stack.pop();
System.out.print(curr.val + " ");
curr = curr.right;
}
}
4. 后序遍历
根的左子树—>根的右子树—>根节点。
遍历结果:325641
4.1 后序遍历递归
用递归实现后序遍历,先递归遍历左子树,然后递归遍历右子树,最后将当前节点的值添加到结果列表中。
// 后序遍历递归
public void postOrder(MyTreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
}
4.2 后序遍历非递归
用辅助栈实现后序遍历,首先将根节点入栈,然后定义一个辅助栈,将根节点出栈并压入辅助栈中。然后依次将当前节点的左孩子和右孩子入栈,但先入右孩子再入左孩子,因为要保证左孩子后访问。重复这个过程直到栈为空,然后从辅助栈依次将节点的值添加到结果列表中。
//后序遍历非递归
public void norPostOrder(MyTreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<MyTreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<MyTreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<>();
stack1.push(root);
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
MyTreeNode cur = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(cur);
if (cur.left != null) {
stack1.push(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
stack1.push(cur.right);
}
}
while (!stack2.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(stack2.pop().val + " ");
}
}
5. 层序遍历
从根节点一层一层的遍历,借助队列的先进先出的特性实现.
//层序遍历
public void levelOrder(MyTreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
Queue<MyTreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
MyTreeNode cur = queue.poll();
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
if(cur.left != null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right != null){
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}
6. 节点个数
6.1 所有节点个数
直接递归,遍历整个树,递归一次加1.
// 获取树中节点的个数
public int size(MyTreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
return size(root.left) + root.size(root.right) + 1;
}
6.2 获得叶子节点个数
利用递归直接遍历,左右节点为null,则为叶子节点,加1.
// 获取叶子节点的个数
//叶子个数
static int countLeaf = 0;
public int sizeLeaf(MyTreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
countLeaf++;
}
sizeLeaf(root.left);
sizeLeaf(root.right);
return countLeaf;
}
7. 检测值为value的元素是否存在
遍历,寻找文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-479016.html
// 检测值为value的元素是否存在
public MyTreeNode find(MyTreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
if(root.val == val){
return root;
}
MyTreeNode left = find(root.left,val);
if(left != null){
return left;
}
MyTreeNode right = find(root.right,val);
if(right != null){
return right;
}
return null;
}
8.总结
这些实现都是经典的,类似这种可太多,我们平常可以多刷刷题,提升自己的代码能力,这样也可以更好的提升自己的代码能力.
大家可以也关注我的刷题集,每周更新经典好题,瑞思拜!
数据结构刷题集文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-479016.html
到了这里,关于【数据结构】一文带你掌握二叉树的构造与应用的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!