前言
- 本文开始学习几何变换中的三维变换,对于各种变换的定义方法基本和二维变换一样,在此我就不过多赘述了。
- 三维变换矩阵
由于二维变换矩阵为三阶矩阵,所以三维变换矩阵为四阶矩阵 - 以下例子均在此正方体基础上
一、平移变换
-
坐标表示

-
矩阵表示

-
变换矩阵

#include "E_Point3.h"
class E_Transform3
{
public:
double T[4][4];
E_Point3* P;
int PtrNum;
public:
~E_Transform3() {}
E_Transform3(){}
void SetMatrix(E_Point3* P, int Pt);//获取顶点表和顶点个数
void E_Translate(double tx, double ty, double tz);//平移函数
void E_RotateX(double thet);//X轴旋转函数
void E_RotateY(double thet);//Y轴旋转函数
void E_RotateZ(double thet);//Z轴旋转函数
void E_RotatePX(double thet, E_Point3 P);//绕点旋转函数
void E_RotatePY(double thet, E_Point3 P);//绕点旋转函数
void E_RotatePZ(double thet, E_Point3 P);//绕点旋转函数
void E_RotatePXY(double thet, E_Point3 P);//绕点旋转函数
void E_Scale(double dx, double dy, double dz);//缩放函数
void E_ReflectZ();//Z轴反射
void E_ReflectX();//X轴反射
void E_ReflectY();//Y轴反射
void E_ReflectZOX();//ZOX面反射
void E_ReflectXOY();//XOY面反射
void E_ReflectYOZ();//YOZ面反射
void E_ShearX(double b, double c);//沿X方向错切变换
void E_ShearY(double b, double c);//沿Y方向错切变换
void E_ShearZ(double b, double c);//沿Z方向错切变换
void Identity();//对变换矩阵进行单位化
void MultiplyMatrix();//进行矩阵乘法
};
#include "E_Point3.h"
#include "E_Facet.h"
#include "E_Point.h"
#include<graphics.h>
class E_Cube
{
public:
E_Cube(){}
~E_Cube() {}
void GetPoint();//获取正方体各顶点坐标
void GetFacet();//根据面将顶点排序
E_Point3* GetVertexArrayName();//返回顶点数组
void Draw();//绘制正方体
private:
E_Point3 P[8];//八个顶点
E_Facet F[6];//六个面
};
- 核心代码
void E_Transform3::SetMatrix(E_Point3* P, int Pt)
{
this->P = P;
this->PtrNum = Pt;
}
void E_Transform3::E_Translate(double tx, double ty, double tz)
{
Identity();
T[0][3] = tx; T[1][3] = ty; T[2][3] = tz;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
///这是画正方体的函数
void E_Cube::Draw()
{
E_Point ScreenPoint, temp;
for (int nFacet = 0; nFacet < 6; nFacet++) {
for (int nPoint = 0; nPoint < 4; nPoint++) {
/*
获取每个面上的点
由于是直接投影到xoy平面所以本次投影为正交投影
F[nFacet].Index[nPoint]表示每个面上的点的索引
*/
ScreenPoint.x = P[F[nFacet].Index[nPoint]].x;
ScreenPoint.y = P[F[nFacet].Index[nPoint]].y;
if (0 == nPoint) {//获取每个面的起始点
moveto(ScreenPoint.x, ScreenPoint.y);
temp = ScreenPoint;
}
else {
lineto(ScreenPoint.x, ScreenPoint.y);
}
}
lineto(temp.x, temp.y);//最后闭合四边形
}
}
主函数
HWND hwnd = initgraph(500, 500);
setorigin(250, 250);
setaspectratio(1, -1);
setbkcolor(WHITE);
cleardevice();
setlinecolor(BLACK);
setlinestyle(PS_SOLID, 2);
E_Cube Cube;
E_Transform3 Translate;
Cube.GetPoint();
Cube.GetFacet();
for (; 1;) {
Cube.Draw();
Sleep(500);
cleardevice();
Translate.SetMatrix(Cube.GetVertexArrayName(), 8);
Translate.E_Translate(2,0,0);//沿x方向平移
}
closegraph();
return 0;
- 效果展示

二、比例变换
-
坐标表示

-
矩阵表示

-
变换矩阵

-
核心代码文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-483846.html
void E_Transform3::E_Scale(double dx, double dy, double dz)
{
Identity();
T[0][0] = dx; T[1][1] = dy; T[2][2] = dz;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
///主函数
HWND hwnd = initgraph(500, 500);
setorigin(250, 250);
setaspectratio(1, -1);
setbkcolor(WHITE);
cleardevice();
setlinecolor(BLACK);
setlinestyle(PS_SOLID, 2);
E_Cube Cube;
E_Transform3 Scale;
Cube.GetPoint();
Cube.GetFacet();
for (; 1;) {
Cube.Draw();
Sleep(1000);
cleardevice();
Scale.SetMatrix(Cube.GetVertexArrayName(), 8);
Scale.E_Scale(1.1,1.1,1.1);//正方体放大1.1倍
}
closegraph();
return 0;
- 效果展示

三、旋转变换
- 坐标表示
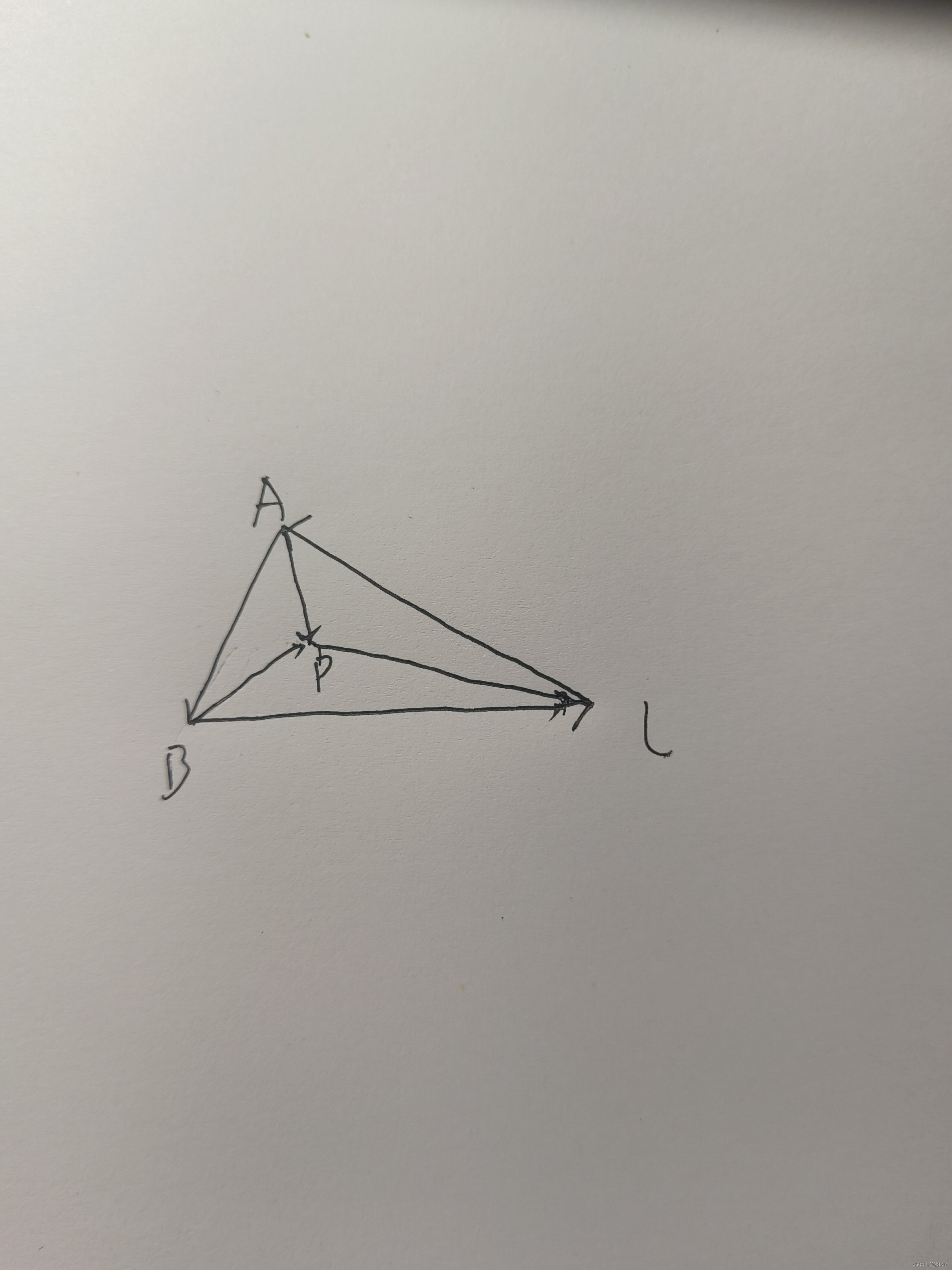
在此我从二维旋转推一下三维坐标旋转变换

从此图可以得出二维旋转变换的一系列表示

在此基础上加一个z轴旋转并没有发生什么改变,则此二维旋转便可以看作是绕z轴旋转,则可以得出三维旋转中的绕z轴旋转


从绕z轴的旋转变换便可以得出绕其它轴的变换,原理很简单,将x,y,z的位置交换但要符合右手坐标系,再来推一个绕y轴变换的




同理便可得出绕x轴旋转的坐标表示
-
矩阵表示
根据坐标表示便可得出矩阵表示,在此列出绕z轴的矩阵表示
-
变换矩阵
此处只列出绕z轴旋转的变换矩阵
-
核心代码
void E_Transform3::E_RotateX(double thet)
{
Identity();
T[1][1] = cos(thet); T[1][2] = -sin(thet); T[2][1] = sin(thet); T[2][2] = cos(thet);
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void E_Transform3::E_RotateY(double thet)
{
Identity();
T[0][0] = cos(thet); T[2][0] = -sin(thet); T[0][2] = sin(thet); T[2][2] = cos(thet);
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void E_Transform3::E_RotateZ(double thet)
{
Identity();
T[0][0] = cos(thet); T[0][1] = -sin(thet); T[1][0] = sin(thet); T[1][1] = cos(thet);
MultiplyMatrix();
}
///主函数
#include "E_Cube.h"
#include "E_Transform3.h"
#define PI 3.1415926
int main() {
HWND hwnd = initgraph(500, 500);
setorigin(250, 250);
setaspectratio(1, -1);
setbkcolor(WHITE);
cleardevice();
setlinecolor(BLACK);
setlinestyle(PS_SOLID, 2);
E_Cube Cube;
E_Transform3 Rotate;
Cube.GetPoint();
Cube.GetFacet();
for (; 1;) {
Cube.Draw();
Sleep(1000);
cleardevice();
Rotate.SetMatrix(Cube.GetVertexArrayName(), 8);
Rotate.E_RotateZ(PI / 6);
Rotate.E_RotateY(PI / 6);
Rotate.E_RotateX(PI / 6);
}
closegraph();
return 0;
}
- 效果展示

四、反射变换
-
坐标表示
- 以下依次为x轴、y轴、z轴的反射

- 以下依次为xoy面、zox面、yoz面反射

- 以下依次为x轴、y轴、z轴的反射
-
矩阵表示
这里只以x轴反射为例
-
变换矩阵
这里只以x轴反射为例
-
核心代码
void E_Transform3::E_ReflectZ()//z轴
{
Identity();
T[0][0] = -1; T[1][1] = -1; T[2][2] = 1;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void E_Transform3::E_ReflectX()//x轴
{
Identity();
T[0][0] = 1; T[1][1] = -1; T[2][2] = -1;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void E_Transform3::E_ReflectY()//y轴
{
Identity();
T[0][0] = -1; T[1][1] = 1; T[2][2] = -1;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void E_Transform3::E_ReflectZOX()//zox面
{
Identity();
T[0][0] = 1; T[1][1] = -1; T[2][2] = 1;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void E_Transform3::E_ReflectXOY()//xoy面
{
Identity();
T[0][0] = 1; T[1][1] = 1; T[2][2] = -1;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void E_Transform3::E_ReflectYOZ()//yoz面
{
Identity();
T[0][0] = -1; T[1][1] = 1; T[2][2] = 1;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
五、错切变换
-
坐标表示

-
矩阵表示

-
变换矩阵
 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-483846.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-483846.html -
核心代码
void E_Transform3::E_ShearX(double b, double c)
{
Identity();
T[0][2] = b; T[0][3] = c;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void E_Transform3::E_ShearY(double b, double c)
{
Identity();
T[1][0] = b; T[1][3] = c;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
void E_Transform3::E_ShearZ(double b, double c)
{
Identity();
T[2][0] = b; T[2][1] = c;
MultiplyMatrix();
}
到了这里,关于基于EasyX学习图形学中的三维几何变换【全】的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!