连续折腾了多个晚上,又趁周末又花了一天时间,终于把powerlink协议移植成功到单片机上啦。本想放弃,但想了下不管我能不能用上,结个尾吧,分享给有需要的人。放弃并不难,但坚持一定很酷。为了移植测试这个协议花了不少血本。stm32开发板就买了两套,其中第一套板子在移植过程中发现内存不够用,型号买小啦,最后买了stm32F407ZGT6的开发板。
前言
STM32F407ZGT6芯片资源1M的falsh,192k的内存够用了。买的第一套Alientek的miniSTM32开发板芯片型号stm32F103RCT6,芯片资源256k的flash,48k的ram不够用(主要是ram不够用)。因为移植过程中发现这powerlink协议栈挺占内存的,rom倒是占的不大。
汇总下资源占用情况,分享给有需要的人参考。(资源包含嵌入式系统RTX内核源码和从站demo功能源码在内)
Program Size: Code=94008 RO-data=15352 RW-data=4204 ZI-data=62212
RW-data+ZI-data 内存占用 4204+62212 = 66416,超过60K了,主要是字典文件占用内存大。Rom占用:94k。
项目开源,欢迎测试评测。开源地址:powerlink-stm32: powerlink-stm32
GitHub - yangyongzhen/powerlink-stm32: openPOWERLINK stack on stm32 mcu transplant
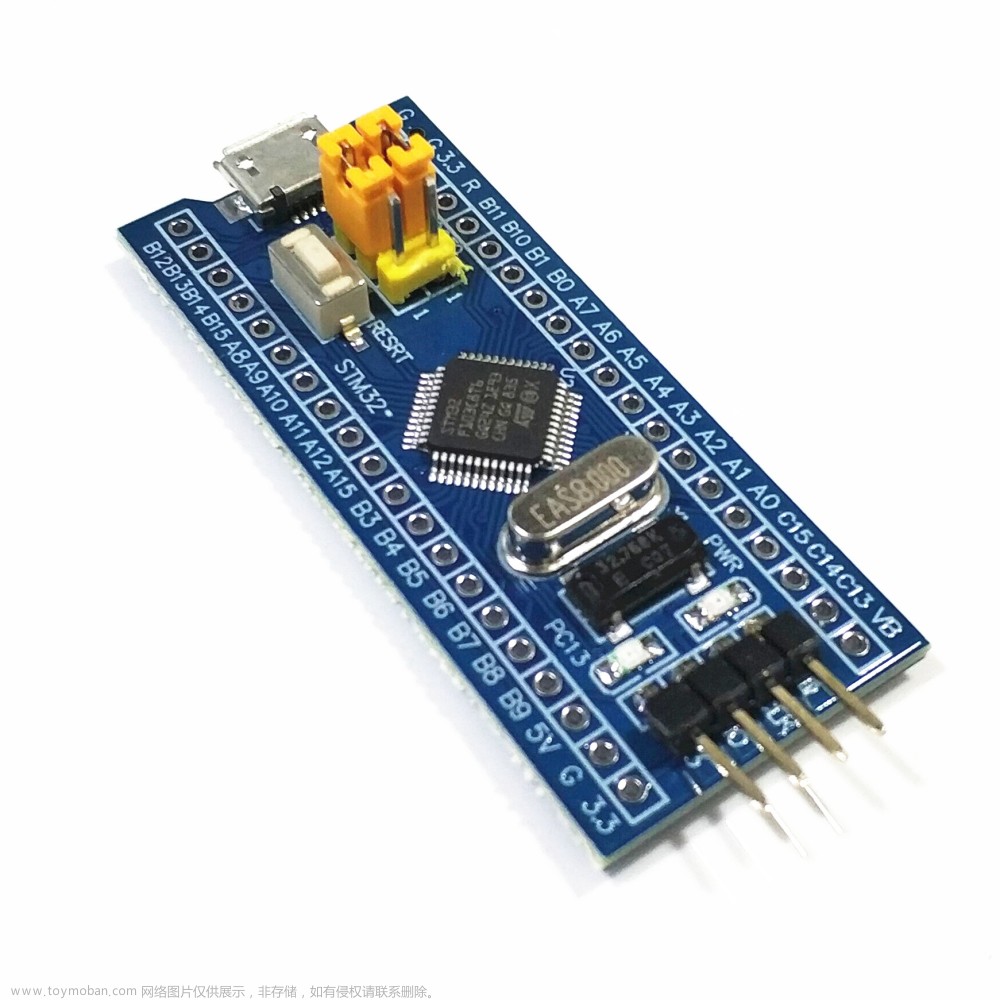
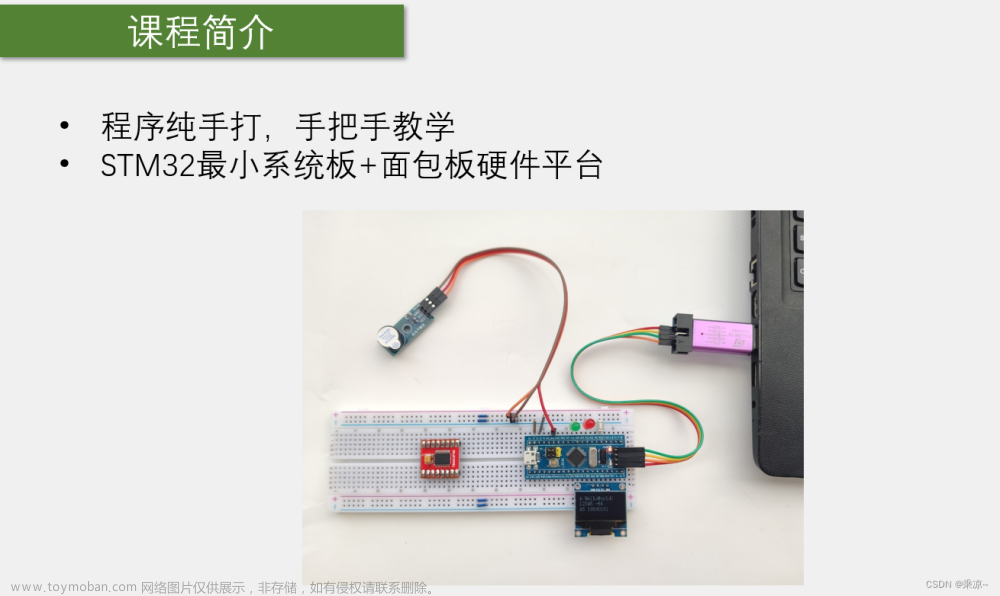
我使用的开发板如下图所示长这样:

移植工程结构:

从工程结构上看,我把涉及改动的文件都单独放到port文件夹了。里面涉及的文件挺多的,不过好在代码量不太大。使用Keil自带的RTX嵌入式内核系统的相关特性,移植不算难。
移植过程
协议栈移植
移植过程参考之前分享的一篇文章《POWERLINK协议源码(最新)在stm32单片机上的移植指南》POWERLINK协议源码(最新)在stm32单片机上的移植指南,把涉及的相关文件摘出来。
屏蔽掉跟系统或驱动相关的接口和编译错误,建立工程目录结构。
netif-stm32.c和target-stm32.c代码量不大,很好移植。
target-stm32.c中主要涉及target_msleep,target_enableGlobalInterrupt,target_getTickCount等的实现。使用RTX系统的相关api实现即可。target_setIpAdrs接口不需要,留空即可。
target-mutex.c文件移植:
/**
\brief Create Mutex
The function creates a mutex.
\param[in] mutexName_p The name of the mutex to create.
\param[out] pMutex_p Pointer to store the created mutex.
\return The function returns a tOplkError error code.
\retval kErrorOk Mutex was successfully created.
\retval kErrorNoFreeInstance An error occurred while creating the mutex.
\ingroup module_target
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
tOplkError target_createMutex(const char* mutexName_p,
OPLK_MUTEX_T* pMutex_p)
{
UNUSED_PARAMETER(mutexName_p);
pMutex_p = osMutexNew(NULL);
return kErrorOk;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
\brief Destroy Mutex
The function destroys a mutex.
\param[in] mutexId_p The ID of the mutex to destroy.
\ingroup module_target
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void target_destroyMutex(OPLK_MUTEX_T mutexId_p)
{
//CloseHandle(mutexId_p);
if(mutexId_p != NULL){
osMutexDelete(mutexId_p);
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
\brief Lock Mutex
The function locks a mutex.
\param[in] mutexId_p The ID of the mutex to lock.
\return The function returns a tOplkError error code.
\retval kErrorOk Mutex was successfully locked.
\retval kErrorNoFreeInstance An error occurred while locking the mutex.
\ingroup module_target
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
tOplkError target_lockMutex(OPLK_MUTEX_T mutexId_p)
{
tOplkError ret;
osStatus_t status;
ret = kErrorOk;
if (mutexId_p != NULL) {
status = osMutexAcquire(mutexId_p, osWaitForever);
if (status != osOK) {
// handle failure code
}
}
return ret;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
\brief Unlock Mutex
The function unlocks a mutex.
\param[in] mutexId_p The ID of the mutex to unlock.
\ingroup module_target
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void target_unlockMutex(OPLK_MUTEX_T mutexId_p)
{
//ReleaseMutex(mutexId_p);
osStatus_t status;
if (mutexId_p != NULL) {
status = osMutexRelease(mutexId_p);
if (status != osOK) {
// handle failure code
}
}
}
int target_lock(void)
{
target_enableGlobalInterrupt(FALSE);
return 0;
}
int target_unlock(void)
{
target_enableGlobalInterrupt(TRUE);
return 0;
}使用RTX的Mutex互斥量api接口,这部分很容易移植。
circbuf-stm32.c文件中,主要涉及加锁和解锁,也好移植。
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
\brief Lock circular buffer
The function enters a locked section of the circular buffer.
\param[in] pInstance_p Pointer to circular buffer instance.
\ingroup module_lib_circbuf
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void circbuf_lock(tCircBufInstance* pInstance_p)
{
osStatus_t waitResult;
tCircBufArchInstance* pArchInstance;
// Check parameter validity
ASSERT(pInstance_p != NULL);
pArchInstance = (tCircBufArchInstance*)pInstance_p->pCircBufArchInstance;
waitResult = osMutexAcquire(pArchInstance->lockMutex, osWaitForever);
switch (waitResult) {
case osOK:
break;
default:
DEBUG_LVL_ERROR_TRACE("%s() Mutex wait unknown error! Error:%ld\n",
__func__);
break;
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
\brief Unlock circular buffer
The function leaves a locked section of the circular buffer.
\param[in] pInstance_p Pointer to circular buffer instance.
\ingroup module_lib_circbuf
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void circbuf_unlock(tCircBufInstance* pInstance_p)
{
tCircBufArchInstance* pArchInstance;
// Check parameter validity
ASSERT(pInstance_p != NULL);
pArchInstance = (tCircBufArchInstance*)pInstance_p->pCircBufArchInstance;
osMutexRelease(pArchInstance->lockMutex);
}eventkcal-stm32.c文件移植:
这个参考了eventkcal-win32.c的实现,比 eventkcal-linux.c的简单些。使用RTX的信号量机制,实现替代也不难。
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
\brief Ethernet driver initialization
This function initializes the Ethernet driver.
\param[in] pEdrvInitParam_p Edrv initialization parameters
\return The function returns a tOplkError error code.
\ingroup module_edrv
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
tOplkError edrv_init(const tEdrvInitParam* pEdrvInitParam_p)
{
// Check parameter validity
ASSERT(pEdrvInitParam_p != NULL);
// Clear instance structure
OPLK_MEMSET(&edrvInstance_l, 0, sizeof(edrvInstance_l));
if (pEdrvInitParam_p->pDevName == NULL)
return kErrorEdrvInit;
// Save the init data
edrvInstance_l.initParam = *pEdrvInitParam_p;
edrvInstance_l.fStartCommunication = TRUE;
edrvInstance_l.fThreadIsExited = FALSE;
// If no MAC address was specified read MAC address of used
// Ethernet interface
if ((edrvInstance_l.initParam.aMacAddr[0] == 0) &&
(edrvInstance_l.initParam.aMacAddr[1] == 0) &&
(edrvInstance_l.initParam.aMacAddr[2] == 0) &&
(edrvInstance_l.initParam.aMacAddr[3] == 0) &&
(edrvInstance_l.initParam.aMacAddr[4] == 0) &&
(edrvInstance_l.initParam.aMacAddr[5] == 0))
{ // read MAC address from controller
getMacAdrs(edrvInstance_l.initParam.pDevName,
edrvInstance_l.initParam.aMacAddr);
}
edrvInstance_l.sock = socket(0, Sn_MR_MACRAW, 0,0);
if (edrvInstance_l.sock < 0)
{
DEBUG_LVL_ERROR_TRACE("%s() cannot open socket\n", __func__);
return kErrorEdrvInit;
}
edrvInstance_l.hThread = osThreadNew(workerThread,&edrvInstance_l,NULL);
// // wait until thread is started
// sem_wait(&edrvInstance_l.syncSem);
return kErrorOk;
}//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
\brief Event handler thread function
This function contains the main function for the event handler thread.
\param[in] arg Thread parameter. Used to get the instance structure.
\return The function returns the thread exit code.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
static void eventThread(void* arg)
{
const tEventkCalInstance* pInstance = (const tEventkCalInstance*)arg;
osStatus_t waitResult;
DEBUG_LVL_EVENTK_TRACE("Kernel event thread %d waiting for events...\n", GetCurrentThreadId());
while (!pInstance->fStopThread)
{
waitResult = osSemaphoreAcquire(pInstance->semKernelData, 100UL); // wait for max. 10 ticks for semaphore token to get available
switch (waitResult) {
case osOK:
if (eventkcal_getEventCountCircbuf(kEventQueueKInt) > 0)
{
eventkcal_processEventCircbuf(kEventQueueKInt);
}
else
{
if (eventkcal_getEventCountCircbuf(kEventQueueU2K) > 0)
{
eventkcal_processEventCircbuf(kEventQueueU2K);
}
}
break;
case osErrorResource:
DEBUG_LVL_ERROR_TRACE("kernel event osErrorResource!\n");
break;
case osErrorParameter:
DEBUG_LVL_ERROR_TRACE("kernel event osErrorParameter!\n");
break;
case osErrorTimeout:
DEBUG_LVL_ERROR_TRACE("kernel event timeout!\n");
break;
default:
DEBUG_LVL_ERROR_TRACE("%s() Semaphore wait unknown error! \n",
__func__);
break;
}
}
DEBUG_LVL_EVENTK_TRACE("Kernel event thread is exiting!\n");
}edrv-rawsock_stm32.c文件移植:
这个很重要,网格底层通信相关的都在这个文件里。使用w5500模块提供的api,操作原始MAC报文帧的方式实现。pthread_mutex_lock和sem_post这些linux系统的互斥量和信号量等,都用RTX提供的相关接口替换。
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
\brief Send Tx buffer
This function sends the Tx buffer.
\param[in,out] pBuffer_p Tx buffer descriptor
\return The function returns a tOplkError error code.
\ingroup module_edrv
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
tOplkError edrv_sendTxBuffer(tEdrvTxBuffer* pBuffer_p)
{
int sockRet;
// Check parameter validity
ASSERT(pBuffer_p != NULL);
FTRACE_MARKER("%s", __func__);
if (pBuffer_p->txBufferNumber.pArg != NULL)
return kErrorInvalidOperation;
if (getLinkStatus(edrvInstance_l.initParam.pDevName) == FALSE)
{
/* If there is no link, we pretend that the packet is sent and immediately call
* tx handler. Otherwise the stack would hang! */
if (pBuffer_p->pfnTxHandler != NULL)
{
pBuffer_p->pfnTxHandler(pBuffer_p);
}
}
else
{
//pthread_mutex_lock(&edrvInstance_l.mutex);
osMutexAcquire(edrvInstance_l.mutex,osWaitForever);
if (edrvInstance_l.pTransmittedTxBufferLastEntry == NULL)
{
edrvInstance_l.pTransmittedTxBufferLastEntry = pBuffer_p;
edrvInstance_l.pTransmittedTxBufferFirstEntry = pBuffer_p;
}
else
{
edrvInstance_l.pTransmittedTxBufferLastEntry->txBufferNumber.pArg = pBuffer_p;
edrvInstance_l.pTransmittedTxBufferLastEntry = pBuffer_p;
}
//pthread_mutex_unlock(&edrvInstance_l.mutex);
osMutexRelease(edrvInstance_l.mutex);
sockRet = send(edrvInstance_l.sock, (u_char*)pBuffer_p->pBuffer, (int)pBuffer_p->txFrameSize);
if (sockRet < 0)
{
DEBUG_LVL_EDRV_TRACE("%s() send() returned %d\n", __func__, sockRet);
return kErrorInvalidOperation;
}
else
{
packetHandler((u_char*)&edrvInstance_l, sockRet, pBuffer_p->pBuffer);
}
}
return kErrorOk;
}//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
\brief Edrv worker thread
This function implements the edrv worker thread. It is responsible to receive frames
\param[in,out] pArgument_p User specific pointer pointing to the instance structure
\return The function returns a thread error code.
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
static void workerThread(void* pArgument_p)
{
tEdrvInstance* pInstance = (tEdrvInstance*)pArgument_p;
int rawSockRet;
u_char aBuffer[EDRV_MAX_FRAME_SIZE];
DEBUG_LVL_EDRV_TRACE("%s(): ThreadId:%ld\n", __func__, syscall(SYS_gettid));
// signal that thread is successfully started
//sem_post(&pInstance->syncSem);
osSemaphoreRelease(pInstance->syncSem);
while (edrvInstance_l.fStartCommunication)
{
rawSockRet = recvfrom(edrvInstance_l.sock, aBuffer, EDRV_MAX_FRAME_SIZE, 0, 0);
if (rawSockRet > 0)
{
packetHandler(pInstance, rawSockRet, aBuffer);
}
}
edrvInstance_l.fThreadIsExited = TRUE;
}从站demo移植
移植从站的demo, demo_cn_console文件夹里的从站demo,在上述协议栈成功移植的基础上,这部分从站demo移植很简单。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-484283.html
/*
** main function
**
** Arguments:
** none
**
*/
int main (int argc, char* argv[])
{
tOplkError ret = kErrorOk;
tOptions opts;
// System Initialization
SystemCoreClockUpdate();
if (getOptions(argc, argv, &opts) < 0)
return 0;
LED_Initialize();
uart_init();
//stdout_init();
printf("hello test\r\n");
LED_On(2);
spi_init();
reset_w5500();
set_w5500_mac();
set_w5500_ip();
eventlog_init(opts.logFormat,
opts.logLevel,
opts.logCategory,
(tEventlogOutputCb)console_printlogadd);
initEvents(&fGsOff_l);
printf("----------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("openPOWERLINK console CN DEMO application\n");
printf("Using openPOWERLINK stack: %s\n", oplk_getVersionString());
printf("----------------------------------------------------\n");
eventlog_printMessage(kEventlogLevelInfo,
kEventlogCategoryGeneric,
"demo_cn_console: Stack version:%s Stack configuration:0x%08X",
oplk_getVersionString(),
oplk_getStackConfiguration());
ret = initPowerlink(CYCLE_LEN,
opts.devName,
aMacAddr_l,
opts.nodeId);
if (ret != kErrorOk)
goto Exit;
ret = initApp();
if (ret != kErrorOk)
goto Exit;
osKernelInitialize(); // Initialize CMSIS-RTOS
osThreadNew(Main_Loop_Thread, NULL, NULL); // Create application main thread
osThreadNew(LED_Blink_PortE, NULL, NULL); // Create application test thread
osKernelStart(); // Start thread execution
for (;;)
{
//Dummy infinite for loop.
}
Exit:
printf("openPOWERLINK console Exit\n");
shutdownApp();
shutdownPowerlink();
return 0;
}如何使用
完成上述移植过程后,需要下载到板子上运行。需要配置好串口管脚,方便串口输出日志调试看。spi的管脚也需要根据板子上的实际资源配置好。然后接上网线,先运行起来主站,然后运行从站,结合串口打印日志调试。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-484283.html
到了这里,关于POWERLINK协议在stm32单片机+w5500移植成功经验分享的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!