MyBatis-Plus一级缓存和二级缓存
基本缓存问题
什么是缓存?
1.存在内存中的临时数据
2.将用户经常查询的数据放在缓存(内存)中,用户去查询数据就不用从磁盘上(关系型数据库 数据文件)查询,从缓存中查询,从而提高查询效率,解决了高并发系统的性能问题。
为什么使用缓存
减少和数据库的交互次数,减少系统开销或IO,提高系统效率
什么样的场景使用缓存?
经常查询同时不经常修改的数据。
Mybatis 缓存
MyBatis包含一个非常强大的查询缓存特性,它可以非常方便地定制和配置缓存。缓存可以极大地 提升查询效率。
一级缓存-MyBatis默认打开一级缓存、不允许关闭
一级缓存:也称为本地缓存,基于 PerpetualCache 的 HashMap 本地缓存,其存储作用域为SqlSession,用于保存用户在一次会话过程中查询的结果,用户一次会话中只能使用一个sqlSession,各个SqlSession之间的缓存相互隔离,当 Session flush 或 close 之后,该 SqlSession 中的所有 Cache 就将清空,MyBatis默认打开一级缓存、不允许关闭。
二级缓存(默认是开启)
注意:二级缓存的作用域不然更新了数据,还是使用查询到缓存的数据)
二级缓存(默认是开启)
也称为全局缓存,是mapper级别的缓存。二级缓存与一级缓存其机制相同,默认也是采用 PerpetualCache,HashMap 存储,所以默认也是本地缓存。不同之处在于其存储作用域为 Mapper(Namespace),可以在多个SqlSession之间共享,是针对一个表的查结果的存储,可以共享给所有针对这张表的查询的用户。也就是说对于mapper级别的缓存不同的sqlsession是可以共享的,并且可自定义存储源,如 Ehcache、Redis。默认开启二级缓存,但是还需要配置才可以使用。
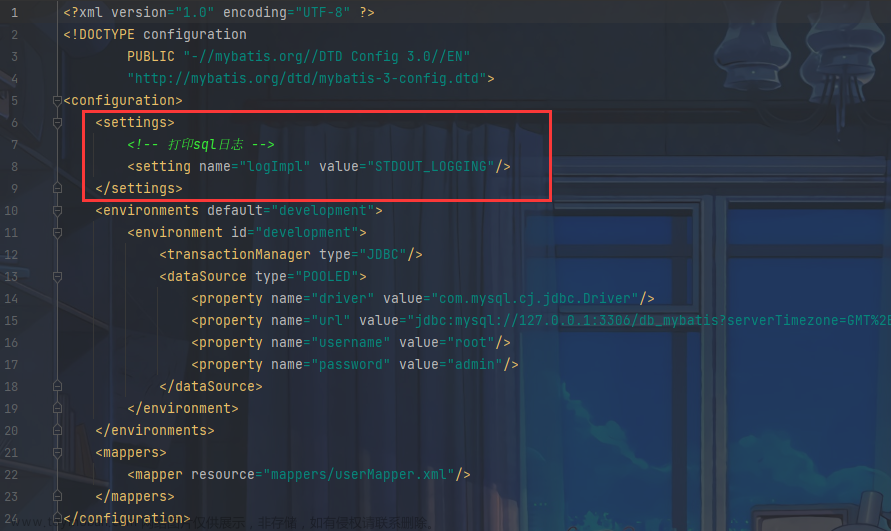
操作演示
第一步:在yml开启二级缓存
写配置: cache-enabled: true
# 配置MybatisPlus
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
# 将下划线映射为驼峰格式
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
# 是否开启缓存
cache-enabled: true
第二步: 在dao层添加注解设置缓存数据的时间
@CacheNamespace
flushInterval = 5000
ScheduledCache 缓存超过指定时间则清空,单位ms,不设置该属性则不使用ScheduledCache不自动回收缓存
@CacheNamespace(flushInterval = 5*60*1000,eviction = ScheduledCache.class,blocking = true)
public interface SysRoleMapper extends BaseMapper<SysRole> {
List<SysRole> userIdQueryRoleKeys(Long userId);
List<SysRole> queryRoleKeys(@Param("deptIds") List<Long> deptIds);
}
注意缓存对象要实现 Serializable 接口
// 注意缓存对象要实现 Serializable 接口
public class SysRole implements Serializable {
// 省略
}
@CacheNamespaceRef
(可选)在 XxxMapper.xml 上添加 ,并指定命名空间
如果项目中使用 Mapper.xml 写 SQL ,则配置如下, 如果没有,则跳过此步骤。
<cache-ref namespace="com.xxx.myProject.mapper.SysRole" />
此处为什么使用< cache-ref />,而不是 < cache /> ?
如果 使用 ,即 ,则 项目中出现两个key相同的缓存 ,即 XxxMapper.xml 中的缓存和 XxxMapper.java 中的缓存, 这两个缓存 肯定不会合并,谁覆盖谁呢 ?
实际上,MybatisPlus 内置很多常用方法,另外,开发者还可以在 XxxMapper.java 或者 XxxMapper.xml 自定义SQL, 这两处的SQL 都是 XxxMapper 下方法,对应的缓存 应该合并到一起, 因此应该使用 ,让 XxxMapper.xml 中的缓存 合并到 XxxMapper.java 的缓存中 。二级缓存作用于 namespace 针对于多个 sqlSession 共有,对于经常要获取最新数据的不建议使用二级缓存!
eviction 属性 缓存回收策略类 描述 作用
eviction=LruCache.class LruCache Least Recently Use, LRU缓存回收策略 当缓存达到上限,移除最近最少使用的对象
eviction=FifoCache.class FifoCache FIFO缓存回收策略 当缓存达到上限,移除最先进入缓存的数据
eviction=SoftCache.class SoftCache 软引用缓存回收策略 当JVM内存不足,自动清理
eviction=WeakCache.class WeakCache 弱引用缓存回收策略 只要触发gc,自动清理
flushInterval 属性 缓存定时回收类 作用
flushInterval = 5000 ScheduledCache 缓存超过指定时间则清空,单位ms,不设置该属性则不使用ScheduledCache不自动回收缓存
readWrite 属性 支持序列化的缓存 作用
readWrite = false SerializedCache 设置为true是规定缓存只读,设置为false时使用SerializedCache,相同的查询从缓存中得到结果对象的副本
blocking 属性 阻塞缓存 作用
blocking = true BlockingCache 设置为true时,基于java可重入锁,在缓存中get/set方法加锁,操作只有一个线程读写缓存
其他基本缓存实现类 描述 作用
LoggingCache 缓存日志 基本默认使用的缓存,输出对缓存的操作和缓存命中率等信息
SynchronizedCache 同步缓存 基于synchronized关键字实现,解决并发问题
TransactionCache 事务缓存 以事务的形式一次存入或移除多个缓存
SQL不想被缓存
顺便说一下,如果某个SQL不想被缓存,可以单独处理一下:
1、SQL走的是xml文件查询:配置useCache=“false”
2、SQL走的是注解形式:@Options(useCache=false)
如果你走的是xml,你在注解上使用这个注解,将不会起效
这些便是我对他俩的理解和使用过程注解写法:xml写法:
问题:MyBatis 二级缓存带来的问题
MyBatis 二级缓存使用的在某些场景下会出问题,来看一下为什么这么说。
假设,项目有一条 select 语句(已开启了 MyBatis 二级缓存):
select a.col1, a.col2, a.col3, b.col1, b.col2, b.col3
from tableA a, tableB b
where a.id= b.id
对于 tableA 与 tableB 的操作定义在两个Mapper中,分别叫做 MapperA 与 MapperB ,它们属于两个命名空间。
执行下面3个操作:
(1)MapperA 中执行上述 sql 语句查询这6个字段。
(2)tableB 表 更新了 col1 与 col2 两个字段 。
(3)MapperA 再次执行上述sql语句查询这6个字段(前提是没有执行过任何 insert、delete、update操作)。
此时问题就来了,即使第(2)步 tableB 更新了 col1 与 col2 两个字段,第(3)步 MapperA 走二级缓存,查询到的这6个字段依然是原来的这6个字段的值, 没有看到变化后的值。
因为我们从 CacheKey 的3组条件来看,
1.标签所在的Mapper的Namespace 标签的id属性,RowBounds 的 offset 和 limit 属性,RowBounds 是 MyBatis 用于处理分页的一个类,offset 默认为0,limit默认为Integer.MAX_VALUE ,以及 标签中定义的sql语句。
2.对于MapperA来说,其中的任何一个条件都没有变化,自然会将原结果返回。
3.这个问题对于MyBatis的二级缓存来说是一个无解的问题,因此使用MyBatis二级缓存有一个前提:必须保证所有的增删改查都在同一个命名空间下才行。对于多表联合查询,如果不在同一个命名空间下,则数据容易出现脏读。解决脏数据问题-(没法解决,不使用二级缓存,采用第三方缓存redis)
解决: 脏数据问题-(没法解决,不使用二级缓存,采用第三方缓存redis)
更改application.yml文件
##redis配置
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
redis:
database: 0
# Redis服务器地址
host: 127.0.0.1
# Redis服务器连接端口
port: 6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
password:
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
jedis:
pool:
max-idle: 8
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
max-wait: -1
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接
min-idle: 0
# 连接超时时间(毫秒)
timeout: 5000
mybatis-plus:
#开启二级缓存,使用redis配置
cache-enabled: true
定义RedisTemplate的bean交给spring管理,这里为了能将对象直接存取到redis中,进行了一些序列化的操作
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheWriter;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.time.Duration;
/**
* @class: RedisConfiguration
* redis的配置文件,template对映序列化规则,以及混村有效时间的设置
*/
public class RedisConfiguration {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl( Duration.ofHours(1)); // 设置缓存有效期一小时
return RedisCacheManager
.builder( RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(redisConnectionFactory))
.cacheDefaults(RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader())).build();
}
@Bean(value = "redisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
//Use Jackson 2Json RedisSerializer to serialize and deserialize the value of redis (default JDK serialization)
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
objectMapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
//将类名称序列化到json串中
objectMapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
//设置输入时忽略JSON字符串中存在而Java对象实际没有的属性
objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(objectMapper);
//Use String RedisSerializer to serialize and deserialize the key value of redis
RedisSerializer redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
//key
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
//value
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
}
自定义缓存管理
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisServerCommands;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.Cursor;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisCallback;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ScanOptions;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
/**
* @class: MybatisRedisCache
*/
@Slf4j
public class MybatisRedisCache implements Cache {
// 读写锁
private final ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(true);
//这里使用了redis缓存,使用springboot自动注入
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
private String id;
public MybatisRedisCache(final String id) {
if (id == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cache instances require an ID");
}
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return this.id;
}
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
if (redisTemplate == null) {
//由于启动期间注入失败,只能运行期间注入,这段代码可以删除
redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate<String, Object>) SpringUtil.getBean("redisTemplate");
}
if (value != null) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key.toString(), value);
}
}
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
if (redisTemplate == null) {
//由于启动期间注入失败,只能运行期间注入,这段代码可以删除
redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate<String, Object>) SpringUtil.getBean("redisTemplate");
}
try {
if (key != null) {
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key.toString());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error("缓存出错 ");
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
if (redisTemplate == null) {
//由于启动期间注入失败,只能运行期间注入,这段代码可以删除
redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate<String, Object>) SpringUtil.getBean("redisTemplate");
}
if (key != null) {
redisTemplate.delete(key.toString());
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
log.debug("清空缓存");
if (redisTemplate == null) {
redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate<String, Object>) SpringUtil.getBean("redisTemplate");
}
try {
Set<String> keys = scan(this.id);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(keys)) {
redisTemplate.delete(keys);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("清空缓存", e);
}
}
public Set<String> scan(String matchKey) {
if (redisTemplate == null) {
redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate<String, Object>) SpringUtil.getBean("redisTemplate");
}
Set<String> keys = redisTemplate.execute((RedisCallback<Set<String>>) connection -> {
Set<String> keysTmp = new HashSet<>();
Cursor<byte[]> cursor = connection.scan(new ScanOptions.ScanOptionsBuilder().match("*" + matchKey + "*").count(1000).build());
while (cursor.hasNext()) {
keysTmp.add(new String(cursor.next()));
}
return keysTmp;
});
return keys;
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
if (redisTemplate == null) {
//由于启动期间注入失败,只能运行期间注入,这段代码可以删除
redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate<String, Object>) SpringUtil.getBean("redisTemplate");
}
Long size = redisTemplate.execute((RedisCallback<Long>) RedisServerCommands::dbSize);
return size.intValue();
}
@Override
public ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() {
return this.readWriteLock;
}
}
工具类
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @class: SpringUtil
* 工具类
*/
@Component
public class SpringUtil implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
SpringUtil.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public static Object getBean(String name){
return applicationContext.getBean(name);
}
public static <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> clazz){
return applicationContext.getBean(name, clazz);
}
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz){
return applicationContext.getBean(clazz);
}
}
在mapper层中加入注解文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-487613.html
//redis缓存注解
@CacheNamespace(implementation= MybatisRedisCache.class,eviction= MybatisRedisCache.class)
public interface ElectronicFenceMapper extends BaseMapper<ElectronicFence> {
}
主启动类加入注解文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-487613.html
@EnableCaching
public class RedisText{
}
到了这里,关于MyBatis-Plus一级缓存和二级缓存-redis解决缓存的脏数据的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!