顺序表的插入、删除、查找位置、按位置读取元素、清空、地址打印
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#define LTST_MAX_LENGTH 10
/**
*Liner list of integers. The key is data.*/
typedef struct SequentialList {
int actualLength;
int data[LTST_MAX_LENGTH];
}*SequentialListPtr;
/**
*Outout the list.
*/
void outputList(SequentialListPtr paraList) {
for (int i = 0; i < paraList->actualLength; i++) {
printf("%d ", paraList->data[i]);
}//of for i
printf("\r\n");
}//of outputlist
/**
*Output the memeory for the list.
*/
void outputMemory(SequentialListPtr paraListPtr) {
printf("The address of the structure: %ld\r\n", paraListPtr);
printf("The address of the actualLength: %ld\r\n", ¶ListPtr->actualLength);
printf("The address of the data: %ld\r\n", ¶ListPtr->data);
printf("The address of the actual data: %ld\r\n", ¶ListPtr->data[0]);
printf("The address of the second data: %ld\r\n", ¶ListPtr->data[1]);
}//of outputMemory
/**
*Initialize a sequential list.No error checking for this function.初始化顺序列表 此函数无错误检查 在线
*@oaram paraListPtr The pointer to the list.It must be a pointer to change the list.
*@param paraValues An int array storing all elements.
*/
SequentialListPtr sequentialListInit(int paraData[], int paraLength) {
SequentialListPtr resultPtr = (SequentialListPtr)malloc(sizeof(struct SequentialList));
for (int i = 0; i < paraLength; i++) {
resultPtr->data[i] = paraData[i];
}//of for i
resultPtr->actualLength = paraLength;
return resultPtr;
}//of sequentialListInit
/**
*Insert an element into a sequential linear list.
*@param paraListPtr The pointer to the list.It must be a pointer to change the list.
*@param paraPosition The position,e.g.,0 standsfor inserting at the frist position.
*@param paraValue The value to be inserted.
*/
void sequentialListInsert(SequentialListPtr paraListPtr, int paraPosition, int paraValue) {
//Step 1.Space check.
if (paraListPtr->actualLength >= LTST_MAX_LENGTH) {
printf("Cannot insert element:list full.\r\n");
return;
}//of if
//Step 2.Position check.
if (paraPosition < 0) {
printf("Cannot insert element:negative position unsupported. ");
return;
}//of if
if (paraPosition > paraListPtr->actualLength) {
printf("Cannot insret element:the position %d is bigger than the list length %d.\n", paraPosition, paraListPtr->actualLength);
return;
}//of if
//Step 3.Move the remaining part.
for (int i = paraListPtr->actualLength; i > paraPosition; i--) {
paraListPtr->data[i] = paraListPtr->data[i - 1];
}//of for i
//Step 4.Insert
paraListPtr->data[paraPosition] = paraValue;
//Step 5.Update the length.
paraListPtr->actualLength++;
}//of sequentialListInsert
/**
*Test the insert function.
*/
void sequentialInsertTest() {
int i;
int tempArray[5] = { 3,5,2,7,4 };
printf("---- sequentialInsretTest begins.----\n");
//Initialize.
SequentialListPtr tempList = sequentialListInit(tempArray, 5);
printf("After initialization,the list is: ");
outputList(tempList);
//Insert to the first.
printf("Now insert to the first,the list is: ");
sequentialListInsert(tempList, 0, 8);
outputList(tempList);
//Insert to the last.
printf("Now insert to the last,the list is: ");
sequentialListInsert(tempList, 6, 9);
outputList(tempList);
//Insert beyond the tail.
printf("Now insert beyond the tail.\r\n");
sequentialListInsert(tempList, 8, 9);
printf("The list is: ");
outputList(tempList);
//Insert to position 3.
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("Inserting %d.\r\n", (i + 10));
sequentialListInsert(tempList, 0, (i + 10));
outputList(tempList);
} //of for i
printf("----sequentialInsertTest ends.----\r\n");
}//of sequentialInsertTest
/**
*Delete an element from a sequential linear list.
*@param paraListPtr The pointer to the list.It must be a pointer to change the list.
*@param paraPosition The position,e.g.,0 stands for inserting at the first position.
*@return The deleted value.
*/
int sequentialListDelete(SequentialListPtr paraListPtr, int paraPosition) {
//Step 1.Position check.
if (paraPosition < 0) {
printf("Invalid position:%d.\r\n", paraPosition);
return -1;
}//of if
if (paraPosition >= paraListPtr->actualLength) {
printf("Cannot delete element:the position %d is beyond the list length %d.\r\n", paraPosition, paraListPtr->actualLength);
return -1;
}//of if
//Step 2.Move the remaining part.
int resultValue = paraListPtr->data[paraPosition];
for (int i = paraPosition; i < paraListPtr->actualLength; i++) {
paraListPtr->data[i] = paraListPtr->data[i + 1];
}//of for i
//Step 3.Update the length.
paraListPtr->actualLength--;
//Step 4.Reurn the value.
return resultValue;
}//of sequentialListDelete
/**
*Test the delete function.
*/
void sequentialDeleteTest() {
int tempArray[5] = { 3,5,2,7,4 };
printf("----sequentialDeleteTest begins.----\r\n");
//Initialize.
SequentialListPtr tempList = sequentialListInit(tempArray, 5);
printf("After initialization,the list is: ");
outputList(tempList);
//Delete the first.
printf("Now delete the first,the list is: ");
sequentialListDelete(tempList, 0);
outputList(tempList);
//Delete to the last.
printf("Now delete the last,the list is: ");
outputList(tempList);
//Delete the second.
printf("Now delete the second,the list is: ");
sequentialListDelete(tempList, 1);
outputList(tempList);
//Delete the second.
printf("Now delete the (-6)th,the list is: ");
sequentialListDelete(tempList, -6);
outputList(tempList);
printf("----sequentialDeleteTest ends.----\r\n");
outputMemory(tempList);
}//of sequentialDeleteTest
/**
*Locate an element in the list.
*@param paraListPtr The pointer to the list.
*@param paraValue the indicated value.
*@return The position of the value,or -1 indicating not exists
*/
int locateElement(SequentialListPtr paraListPtr, int paraValue) {
for (int i = 0; i < paraListPtr->actualLength; i++) {
if (paraListPtr->data[i] == paraValue) {
return 1;
}//of if
}//of for i
return -1;
}//of locateElement
/**
*Clear elements in the list.
*@param oaraListPtr The pointer to the list.
*@return The position of the value,or -1 indicating not exists
*/
void clearList(SequentialListPtr paraListPtr) {
paraListPtr->actualLength = 0;
}//of clearList
/**
The entrance.
*/
void main() {
sequentialInsertTest();
sequentialDeleteTest();
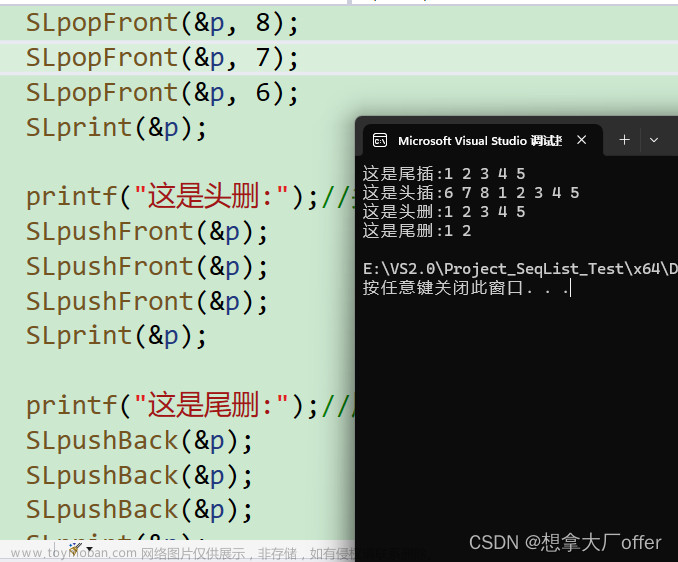
}//of main---- sequentialInsretTest begins.----
After initialization,the list is: 3 5 2 7 4
Now insert to the first,the list is: 8 3 5 2 7 4
Now insert to the last,the list is: 8 3 5 2 7 4 9
Now insert beyond the tail.
Cannot insret element:the position 8 is bigger than the list length 7.
The list is: 8 3 5 2 7 4 9
Inserting 10.
10 8 3 5 2 7 4 9
Inserting 11.
11 10 8 3 5 2 7 4 9
Inserting 12.
12 11 10 8 3 5 2 7 4 9
Inserting 13.
Cannot insert element:list full.
12 11 10 8 3 5 2 7 4 9
Inserting 14.
Cannot insert element:list full.
12 11 10 8 3 5 2 7 4 9
----sequentialInsertTest ends.----
----sequentialDeleteTest begins.----
After initialization,the list is: 3 5 2 7 4
Now delete the first,the list is: 5 2 7 4
Now delete the last,the list is: 5 2 7 4
Now delete the second,the list is: 5 7 4
Now delete the (-6)th,the list is: Invalid position:-6.
5 7 4
----sequentialDeleteTest ends.----
The address of the structure: -359099328
The address of the actualLength: -359099328
The address of the data: -359099324
The address of the actual data: -359099324
The address of the second data: -359099320 1.顺序表的插入操作时,如果规定了最大长度,那么一定在插入前要检查,检查是否超过了最大长度,检查插入位置是否合理。
2.插入分为头插,尾插,指定位置插入; 如果顺序表满了则不能再插入
3.malloc 分配的内存在堆区,free 释放分配的内存文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-513844.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-513844.html
到了这里,关于西柚闵帆老师数据结构第二次课——顺序表的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!