赛题介绍
在分布式系统中某个节点发生故障时,故障会沿着分布式系统的拓扑结构进行传播,造成自身节点及其邻接节点相关的KPI指标和发生大量日志异常。本次比赛提供分布式数据库的故障特征数据和标签数据,其中特征数据是系统发生故障时的KPI指标数据,KPI指标包括由feature0、feature1 …feature106共107个指标,标签数据为故障类别数据,共6个类别,用0、1、2、3、4、5分别表示6个故障,参赛人员可根据这些数据,借助机器学习、深度学习、web等技术搭建故障诊断系统,该系统支持用户上传训练集对模型进行训练和模型下载,同时支持用户上传单条或多条测试语句进行测试并可视化测试结果,支持测试结果下载。
baseline: DecisionTree
数据分析
读取数据
df = pd.read_csv('data/train/train.csv', index_col=None)
判断是否有缺失值
df.isnull().any()
'''
output: True即为存在缺失值
sample_id False
feature0 True
feature1 True
feature2 True
feature3 True
...
feature103 True
feature104 True
feature105 False
feature106 True
label False
Length: 109, dtype: bool
'''
数据标准化及缺失值填充
# 数据标准化
features = df.iloc[:, 1:-1]
numeric_features = features.dtypes[features.dtypes != 'object'].index
features[numeric_features] = features[numeric_features].apply(
lambda x: (x - x.mean()) / (x.std())
)
# 在标准化数据之后,所有均值消失,因此我们可以将缺失值设置为0
features[numeric_features] = features[numeric_features].fillna(0)
features_labels = pd.concat([features, df[['label']]], axis=1)
train_features = pd.concat([df[['sample_id']], features], axis=1)
train_label = df[['sample_id', 'label']]
df = pd.concat([train_features, train_label[['label']]], axis=1)
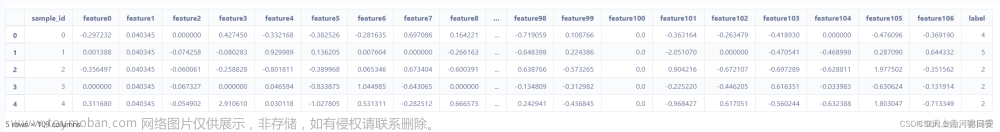
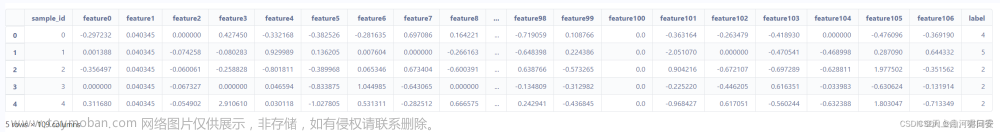
观察数据基本信息
# 观察前五行数据
df.head()
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-514446.html
# 数据大小
df.shape
'''
output:
(6296, 109)
'''
df.dtypes
'''
output:
sample_id int64
feature0 float64
feature1 float64
feature2 float64
feature3 float64
...
feature103 float64
feature104 float64
feature105 float64
feature106 float64
label int64
Length: 109, dtype: object
'''
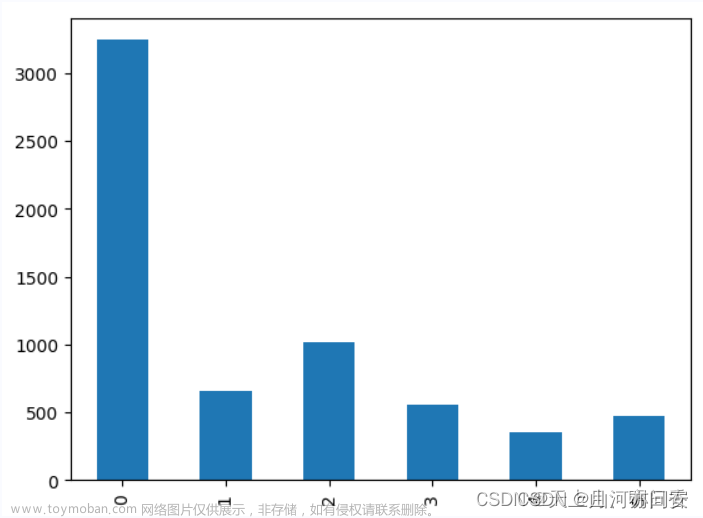
# 类别分布
df['label'].value_counts().sort_index().plot(kind='bar')
plt.show()
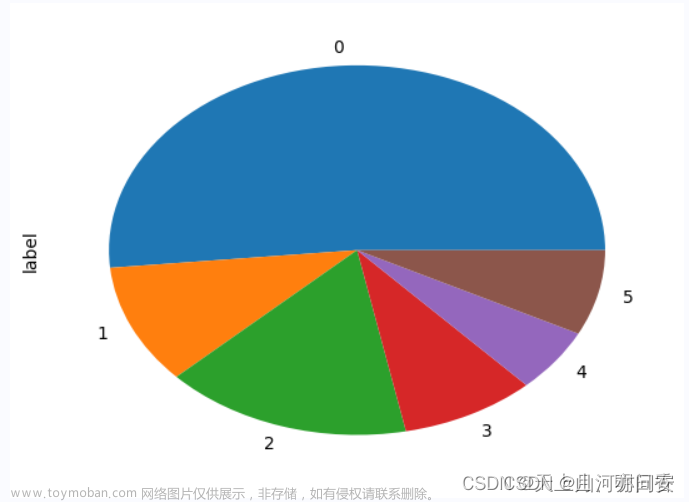
df['label'].value_counts().sort_index().plot(kind='pie')
plt.show()
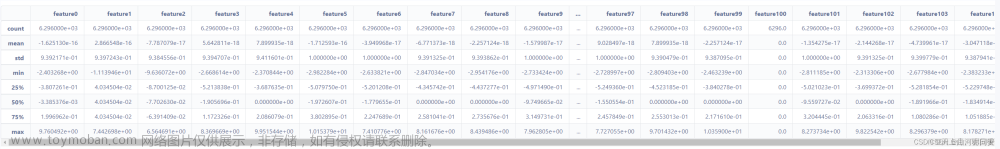
features.describe()
# 分组的平均数据统计
label_Summary = features_labels.groupby('label')
label_Summary.mean()
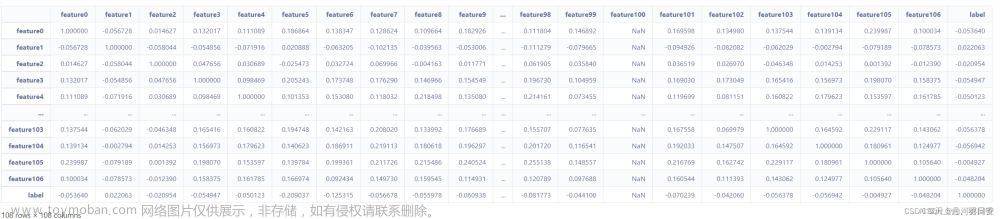
# 相关性矩阵
corr = features_labels.corr()
sns.set_context({'figure.figsize':[100, 100]})
fig = sns.heatmap(corr,
xticklabels=corr.columns.values,
yticklabels=corr.columns.values)
heatmap = fig.get_figure()
heatmap.savefig('work/heatmap.png', dpi=300)
corr
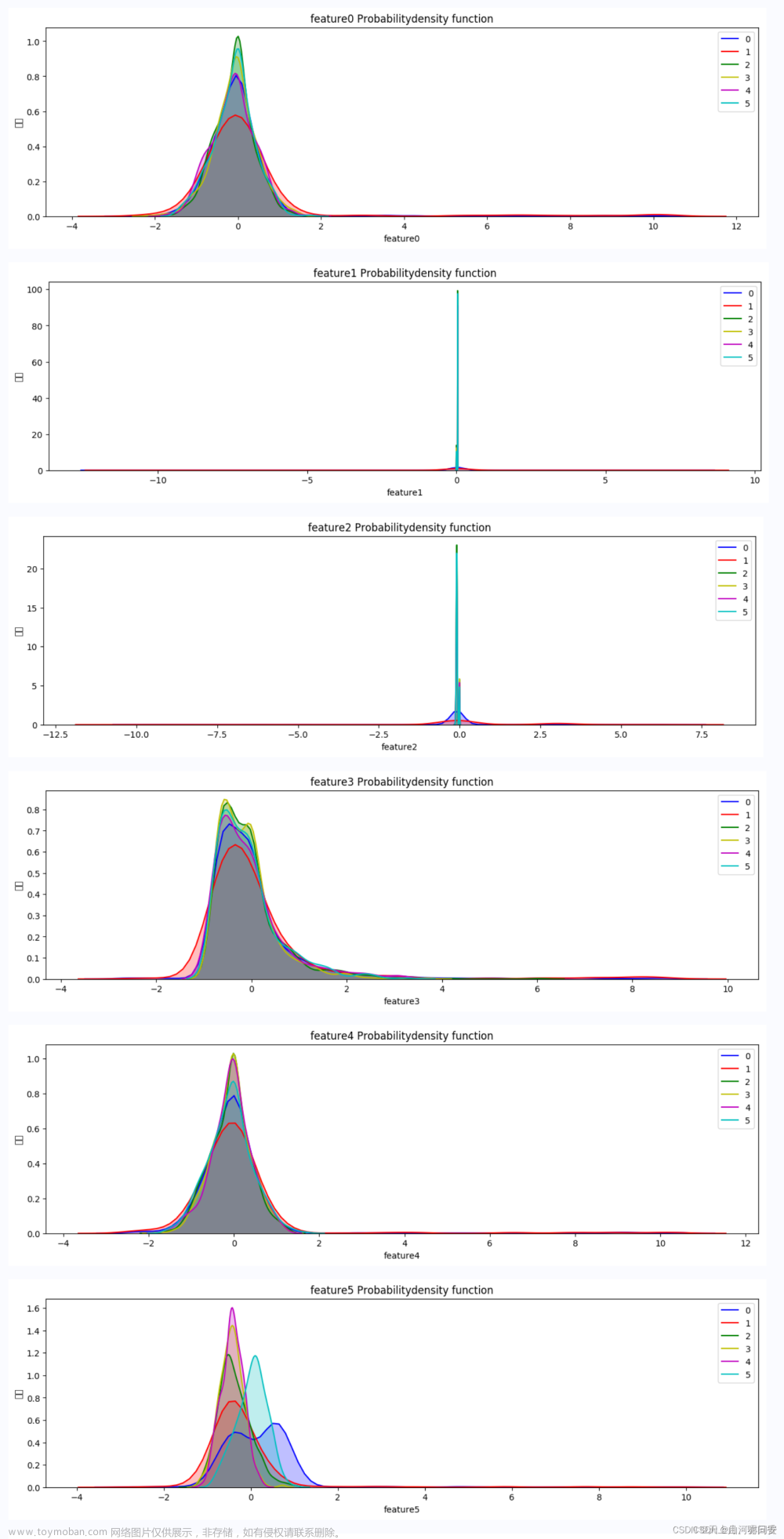
# 各个特征的概率密度函数
feature_names = features.columns.values.tolist()
for name in feature_names:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 4), )
ax = sns.kdeplot(df.loc[(df['label'] == 0), name], color='b', shade=True, label='0')
ax = sns.kdeplot(df.loc[(df['label'] == 1), name], color='r', shade=True, label='1')
ax = sns.kdeplot(df.loc[(df['label'] == 2), name], color='g', shade=True, label='2')
ax = sns.kdeplot(df.loc[(df['label'] == 3), name], color='y', shade=True, label='3')
ax = sns.kdeplot(df.loc[(df['label'] == 4), name], color='m', shade=True, label='4')
ax = sns.kdeplot(df.loc[(df['label'] == 5), name], color='c', shade=True, label='5')
ax.set(xlabel=name, ylabel='频率')
plt.title('{} Probabilitydensity function'.format(name))
plt.savefig('work/{}的概率密度函数图.png'.format(name))
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-514446.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-514446.html
划分数据集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
target_name = 'label'
x = df.drop(['sample_id', 'label'], axis=1)
y = df[['label']]
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
x, y, test_size=0.15, random_state=123, stratify=y)
模型训练
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
# 实例化
dtree = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(
criterion='entropy',
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.01
)
# train
dtree = dtree.fit(x_train, y_train)
评价指标计算
# 指标计算 参数:array
def metrics_calculate(pred, y_test, txt_path):
TP = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
FP = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
FN = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
for i in range(len(y_test)):
if pred[i] == 0 and y_test[i] == 0:
TP[0] += 1
if pred[i] != 0 and y_test[i] == 0:
FN[0] += 1
if pred[i] == 0 and y_test[i] != 0:
FP[0] += 1
if pred[i] == 1 and y_test[i] == 1:
TP[1] += 1
if pred[i] != 1 and y_test[i] == 1:
FN[1] += 1
if pred[i] == 1 and y_test[i] != 1:
FP[1] += 1
if pred[i] == 2 and y_test[i] == 2:
TP[2] += 1
if pred[i] != 2 and y_test[i] == 2:
FN[2] += 1
if pred[i] == 2 and y_test[i] != 2:
FP[2] += 1
if pred[i] == 3 and y_test[i] == 3:
TP[3] += 1
if pred[i] != 3 and y_test[i] == 3:
FN[3] += 1
if pred[i] == 3 and y_test[i] != 3:
FP[3] += 1
if pred[i] == 4 and y_test[i] == 4:
TP[4] += 1
if pred[i] != 4 and y_test[i] == 4:
FN[4] += 1
if pred[i] == 4 and y_test[i] != 4:
FP[4] += 1
if pred[i] == 5 and y_test[i] == 5:
TP[5] += 1
if pred[i] != 5 and y_test[i] == 5:
FN[5] += 1
if pred[i] == 5 and y_test[i] != 5:
FP[5] += 1
Precision = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
Recall = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
F1 = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
Precision[0] = TP[0] / (TP[0] + FP[0])
Precision[1] = TP[1] / (TP[1] + FP[1])
Precision[2] = TP[2] / (TP[2] + FP[2])
Precision[3] = TP[3] / (TP[3] + FP[3])
Precision[4] = TP[4] / (TP[4] + FP[4])
Precision[5] = TP[5] / (TP[5] + FP[5])
for i in range(6):
print('Precision: {}\n'.format(Precision[i]))
Recall[0] = TP[0] / (TP[0] + FN[0])
Recall[1] = TP[1] / (TP[1] + FN[1])
Recall[2] = TP[2] / (TP[2] + FN[2])
Recall[3] = TP[3] / (TP[3] + FN[3])
Recall[4] = TP[4] / (TP[4] + FN[4])
Recall[5] = TP[5] / (TP[5] + FN[5])
for i in range(6):
print('Recall: {}\n'.format(Recall[i]))
F1[0] = (2 * Precision[0] * Recall[0]) / (Precision[0] + Recall[0])
F1[1] = (2 * Precision[1] * Recall[1]) / (Precision[1] + Recall[1])
F1[2] = (2 * Precision[2] * Recall[2]) / (Precision[2] + Recall[2])
F1[3] = (2 * Precision[3] * Recall[3]) / (Precision[3] + Recall[3])
F1[4] = (2 * Precision[4] * Recall[4]) / (Precision[4] + Recall[4])
F1[5] = (2 * Precision[5] * Recall[5]) / (Precision[5] + Recall[5])
for i in range(6):
print('F1: {}\n'.format(F1[i]))
Macro_Precision = sum([Precision[0], Precision[1], Precision[2],
Precision[3], Precision[4], Precision[5]]) / 6
Macro_Recall = sum([Recall[0], Recall[1], Recall[2],
Recall[3], Recall[4], Recall[5]]) / 6
Macro_F1 = sum([F1[0], F1[1], F1[2], F1[3], F1[4], F1[5]]) / 6
l_sum = sum([TP[0], TP[1], TP[2], TP[3], TP[4], TP[5]])
m_sum = l_sum + sum([FP[0], FP[1], FP[2], FP[3], FP[4], FP[5]])
n_sum = l_sum + sum([FN[0], FN[1], FN[2], FN[3], FN[4], FN[5]])
Micro_Precision = l_sum / m_sum
print('Micro_Precision: {}\n'.format(Micro_Precision))
Micro_Recall = l_sum / n_sum
print('Micro_Recall: {}\n'.format(Micro_Recall))
Micro_F1 = (2 * Micro_Precision * Micro_Recall) / (Micro_Precision + Micro_Recall)
print('Micro_F1: {}\n'.format(Micro_F1))
f = open(txt_path, 'a', encoding='utf-8')
for i in range(6):
f.write('类别{}: '.format(i))
f.write('\n')
f.write('Precision: {:.2f}%'.format(Precision[i] * 100))
f.write('\n')
f.write('Recall: {:.2f}%'.format(Recall[i] * 100))
f.write('\n')
f.write('F1: {:.2f}'.format(F1[i]))
f.write('\n')
f.write('Macro_Precision: {:.2f}%'.format(Macro_Precision * 100))
f.write('\n')
f.write('Macro_Recall: {:.2f}%'.format(Macro_Recall * 100))
f.write('\n')
f.write('Macro_F1: {:.2f}'.format(Macro_F1))
f.write('\n')
f.write('Micro_Precision: {:.2f}%'.format(Micro_Precision * 100))
f.write('\n')
f.write('Micro_Recall: {:.2f}%'.format(Micro_Recall * 100))
f.write('\n')
f.write('Micro_F1: {:.2f}'.format(Micro_F1))
f.write('\n')
f.close()
验证模型
# 验证
pred = dtree.predict(x_test)
y_test = y_test.reshape((-1, ))
txt_path = 'work/result_RandomForest.txt'
metrics_calculate(pred, y_test, txt_path)
'''
Precision: 0.8382066276803118
Precision: 0.6823529411764706
Precision: 0.7553956834532374
Precision: 0.7368421052631579
Precision: 0.972972972972973
Precision: 0.8157894736842105
Recall: 0.8829568788501027
Recall: 0.5858585858585859
Recall: 0.6907894736842105
Recall: 0.8433734939759037
Recall: 0.6792452830188679
Recall: 0.8732394366197183
F1: 0.86
F1: 0.6304347826086957
F1: 0.7216494845360826
F1: 0.7865168539325843
F1: 0.7999999999999999
F1: 0.8435374149659864
Micro_Precision: 0.8052910052910053
Micro_Recall: 0.8052910052910053
Micro_F1: 0.8052910052910053
'''
到了这里,关于第十二届“中国软件杯”大赛:A10-基于机器学习的分布式系统故障诊断系统——baseline(一)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!