这个例子主要是使用android开发出一个简单的记事本应用,可以实现数据的增加、修改以及删除等操作。
主要参考:哔哩哔哩up主:子林android。
主要涉及的相关知识:
1、控件RecyclerView的使用
2、轻量级数据库SQLite的使用
3、activity之间的跳转以及参数传递
首先创建MainActivity
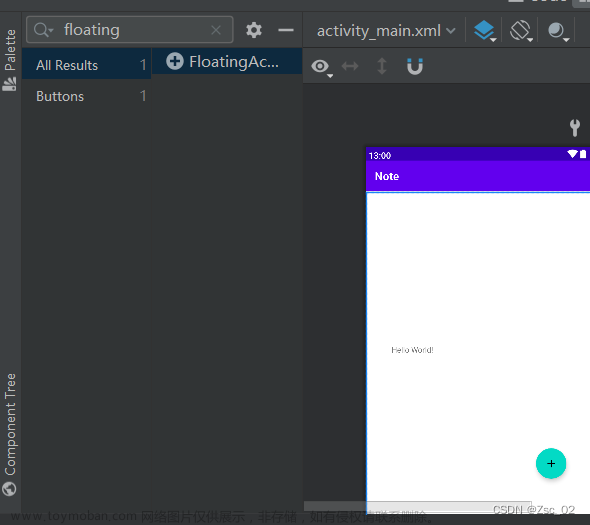
为方便这里使用的是帧布局FrameLayout,主要包含两个控件,一个是用于显示记事本相关信息的RecyclerView,另一个是用于进行添加记事信息FloatingActionButton按钮,布局文件代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/rlv"/>
<com.google.android.material.floatingactionbutton.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/btn_add"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/ic_baseline_add_24"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|right"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:background="@color/green_200"
android:onClick="add"/>
</FrameLayout>
接下来是对应的Java代码。首先是控件的一些初始化工作,这些在onCreate()函数中的 initView()中完成,MainActivity的对应代码如下:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private final String DB_Name="mySQLite.db";
private RecyclerView mRecyclerView;
private FloatingActionButton mButton;
private List<NewsBean> newsBeanList;
private NewsAdapter newsAdapter;
private MySQILOpenHelper mySQILOpenHelper;
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.N)
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
initData();
initEvent();
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
refreshDataFromDB();
}
private void refreshDataFromDB() {
newsBeanList=getDataFromDB();
newsAdapter.refreshData(newsBeanList);
}
private void initEvent() {
newsAdapter=new NewsAdapter(newsBeanList,this);
mRecyclerView.setAdapter(newsAdapter);
LinearLayoutManager layoutManager=new LinearLayoutManager(this);
mRecyclerView.setLayoutManager(layoutManager);
}
private void initData() {
newsBeanList= new ArrayList<>();
mySQILOpenHelper=new MySQILOpenHelper(this);
newsBeanList=getDataFromDB();
}
private List<NewsBean> getDataFromDB() {
return newsBeanList=mySQILOpenHelper.query();
}
private void initView() {
mRecyclerView=findViewById(R.id.rlv);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main,menu);
SearchView searchView= (SearchView) menu.findItem(R.id.menu_serach).getActionView();
searchView.setOnQueryTextListener(new SearchView.OnQueryTextListener() {
@Override
public boolean onQueryTextSubmit(String query) {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean onQueryTextChange(String newText) {
List<NewsBean> List = mySQILOpenHelper.queryByTitle(newText);
newsAdapter.refreshData(List);
return true;
}
});
return super.onCreateOptionsMenu(menu);
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(@NonNull MenuItem item) {
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
public void add(View view) {
Intent intent=new Intent(MainActivity.this,AddActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
*
注意:当其他Activity跳转到MainActivity时,由于生命周期的原因,onCreate()函数不在执行,因此此时必须重写onResume() 函数,在onResume()中重新查询数据库相关操作,并刷新当前适配器adapter对应数据,否则MainActivity界面不会有显示信息。
其次,RecyclerView的实现还需相关的数据源,以及两者之间的桥梁适配器adapter。记事本主要有三部分信息:标题、内容和创建时间。此处我们用一个标准的JavaBean类来封装这个实体类,并使其实现Serializable从而用于后文中activity之间跳转时自定义参数的传递,代码如下:
public class NewsBean implements Serializable {
private String title;
private String content;
private String createdTime;
private int id;
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public String getCreatedTime() {
return createdTime;
}
public void setCreatedTime(String createdTime) {
this.createdTime = createdTime;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "NewsBean{" +
"title='" + title + '\'' +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
", createdTime='" + createdTime + '\'' +
", id=" + id +
'}';
}
接下来定义一个名为NewsAdapter的适配器,继承自 RecyclerView.Adapter,代码如下,其中适配器中用到了一个布局文件new_layout.xml,用于指定记事本信息显示格式如下:

适配器NewsAdapter的代码如下
public class NewsAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<NewsAdapter.MyViewHolder> {
private List newsBeanList;
private LayoutInflater layoutInflater;
private Context context;
public NewsAdapter(List<NewsBean> newsBeanList, Context context) {
this.newsBeanList = newsBeanList;
this.context = context;
layoutInflater=LayoutInflater.from(context);
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return newsBeanList.size();
}
@NonNull
@Override
public MyViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.new_layout, parent, false);
MyViewHolder myViewHolder=new MyViewHolder(view);
return myViewHolder;
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull MyViewHolder holder, @SuppressLint("RecyclerView") int position) {
NewsBean newsBean = newsBeanList.get(position);
holder.tvContent.setText(newsBean.getContent());
holder.tvTitle.setText(newsBean.getTitle());
holder.tvTime.setText(newsBean.getCreatedTime());
holder.rlContainer.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent=new Intent(context, EditActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("new",newsBean);
context.startActivity(intent);
}
});
holder.rlContainer.setOnLongClickListener(new View.OnLongClickListener() {
@Override
public boolean onLongClick(View v) {
Dialog dialog=new Dialog(context,
android.R.style.ThemeOverlay_Material_Dialog_Alert);
View view = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.diag_layout, null);
TextView tvDelete=view.findViewById(R.id.tv_delete);
TextView tvEdit=view.findViewById(R.id.tv_edit);
tvDelete.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int row = mySQILOpenHelper.deleteFromDbById(newsBean.getId());
if(row>0){
deleteData(position);
Toast.makeText(context,"删除成功",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}else {
Toast.makeText(context,"删除失败",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
tvEdit.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent=new Intent(context, EditActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("new",newsBean);
context.startActivity(intent);
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
dialog.setContentView(view);
dialog.show();
return true;
}
});
}
public void refreshData(List<NewsBean>list){
this.newsBeanList=list;
notifyDataSetChanged();
//notifyDataSetChanged();
}
public void deleteData(int position){
newsBeanList.remove(position);
notifyItemRemoved(position);
}
class MyViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder{
TextView tvTitle,tvContent,tvTime;
ViewGroup rlContainer;
public MyViewHolder(@NonNull View itemView) {
super(itemView);
this.tvTime=itemView.findViewById(R.id.tv_time);
this.tvContent=itemView.findViewById(R.id.tv_content);
this.tvTitle=itemView.findViewById(R.id.tv_title);
this.rlContainer=itemView.findViewById(R.id.rl_item_container);
}
}
}
上述代码中,在viewHolder中为new_layout.xml整个区域设计了长按弹对话框模式(包含删除和编辑当前记事本信息),以及短按跳转至编辑界面的点击事件。
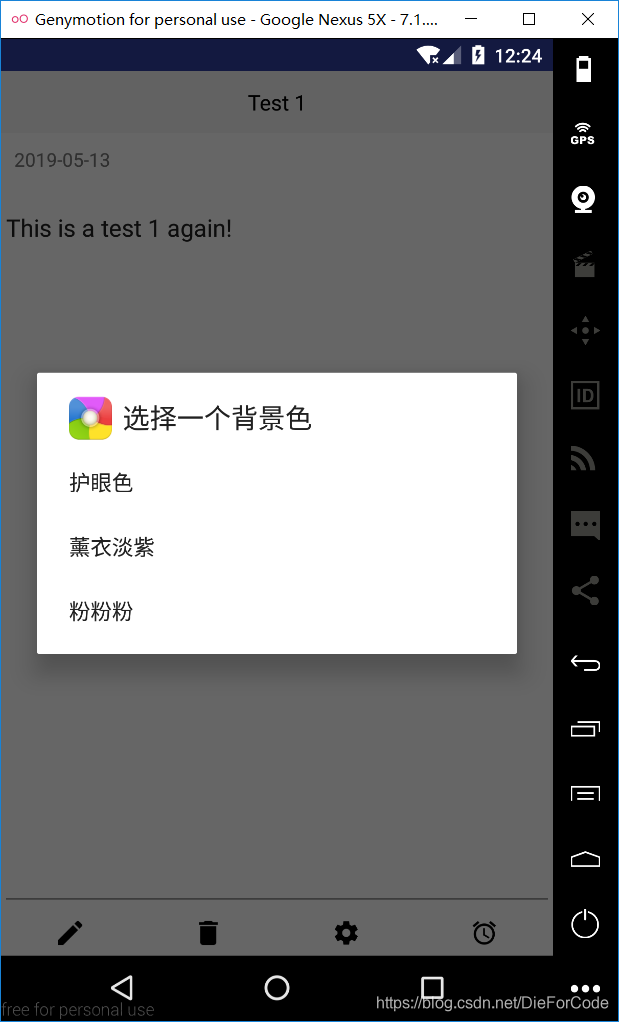
接下来是编辑界面和添加界面
分别创建名为AddActivity和EditActivity两个Activity,两个界面基本一致,界面如下:
对应的布局文件xml比较简单,详细代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".EditActivity"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="10dp">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:gravity="center_vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="标题"
android:textSize="30sp"/>
<EditText
android:padding="5dp"
android:background="@drawable/edit_bg"
android:id="@+id/et_edit_title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="内容"
android:textSize="30sp"/>
<EditText
android:padding="5dp"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:id="@+id/et_edit_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="250dp"
android:background="@drawable/edit_bg"/>
</LinearLayout>
<Button
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:id="@+id/save"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/btn_bg"
android:text="保存"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:onClick="save"/>
</LinearLayout>
接下来最重要的就是数据库SQLite的创建,这里使用数据库帮助类SQLiteOpenHelper 来实现,包含了增,删,改和查四种操作,其代码如下:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-518650.html
public class MySQILOpenHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private static final String DB_Name="mySQLite.db";
private static final String TABLE_NAME="note";
private static final String sql="create table "+TABLE_NAME+" (id integer primary key autoincrement,title text,content,text,createdTime text)";
public MySQILOpenHelper(Context context){
super(context,DB_Name,null,1);
}
/*public MySQILOpenHelper(Context context,String name){
super(context,name,null,1);
}*/
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
db.execSQL(sql);
}
public long insertData(NewsBean newsBean){
SQLiteDatabase db=getWritableDatabase();
ContentValues value=new ContentValues();
value.put("title",newsBean.getTitle());
value.put("content",newsBean.getContent());
value.put("createdTime",newsBean.getCreatedTime());
return db.insert(TABLE_NAME,null,value);
}
public int updateData(NewsBean newsBean){
//Log.d("TAG", "updateData: "+newsBean);
SQLiteDatabase db=getWritableDatabase();
ContentValues value=new ContentValues();
//value.put("id",newsBean.getId());
value.put("title",newsBean.getTitle());
value.put("content",newsBean.getContent());
value.put("createdTime",newsBean.getCreatedTime());
return db.update(TABLE_NAME,value,"id like ?",new String[]{String.valueOf(newsBean.getId())});
}
public List<NewsBean> query(){
SQLiteDatabase db=getWritableDatabase();
List<NewsBean>newsBeanList=new ArrayList<>();
Cursor cursor = db.query(TABLE_NAME, null, null, null, null, null, null);
if(cursor!=null){
while ((cursor.moveToNext())){
@SuppressLint("Range") int id=Integer.parseInt(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("id")));
@SuppressLint("Range") String title=cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("title"));
@SuppressLint("Range") String content=cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("content"));
@SuppressLint("Range") String createdTime=cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("createdTime"));
NewsBean newsBean=new NewsBean();
newsBean.setId(id);
newsBean.setCreatedTime(createdTime);
newsBean.setContent(content);
newsBean.setTitle(title);
newsBeanList.add(newsBean);
}
cursor.close();
}
return newsBeanList;
}
public List<NewsBean> queryByTitle(String title1){
if(TextUtils.isEmpty(title1))
{
return query();
}
SQLiteDatabase db=getWritableDatabase();
List<NewsBean>newsBeanList=new ArrayList<>();
Cursor cursor = db.query(TABLE_NAME, null, "title like ?", new String[]{"%"+title1+"%"}, null, null, null);
if(cursor!=null){
while ((cursor.moveToNext())){
@SuppressLint("Range") int id=Integer.parseInt(cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("id")));
//@SuppressLint("Range") String id=cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("id"));
@SuppressLint("Range") String title=cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("title"));
@SuppressLint("Range") String content=cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("content"));
@SuppressLint("Range") String createdTime=cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("createdTime"));
NewsBean newsBean=new NewsBean();
newsBean.setId(id);
newsBean.setCreatedTime(createdTime);
newsBean.setContent(content);
newsBean.setTitle(title);
newsBeanList.add(newsBean);
}
cursor.close();
}
return newsBeanList;
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
}
public int deleteFromDbById(int id) {
SQLiteDatabase db=getWritableDatabase();
return db.delete(TABLE_NAME,"id like ?",new String[]{String.valueOf(id)});
}
}
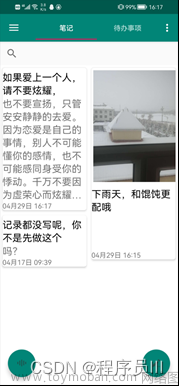
写到这里,基本上已经完成了一个简单记事本APP的开发,最后运行成功的界面如下:


 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-518650.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-518650.html
到了这里,关于实现一个简单的记事本APP的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!