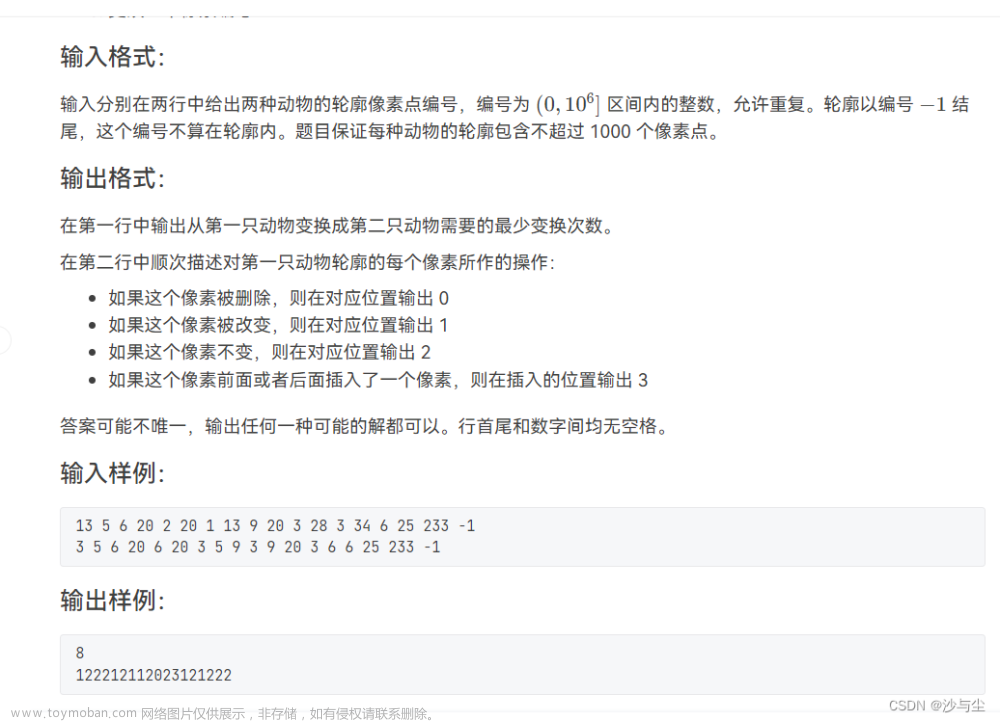
RC-u4 变牛的最快方法

题意
就是给你一堆操作修改上面的数组让他变成下面数组,输出最小修改次数和方案
思路
一眼dp,跑一遍dp记录方案数即可;
dp[i][j]表示从左往右修改,第一个数组的i位等于第二个数组的j位的最小修改方案.
c++能过代码
/*made in sxh*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define lowbit(x) x & -x
#define endl '\n'
//#define int long long
#define mem(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof a)
#define x first
#define y second
#define pb push_back
#define bug1(x) cout << x << endl
#define bug2(x, y) cout << x << ' ' << y << endl
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define bug3(x, y, z) cout << x << ' ' << y << ' ' << z << endl
const int N = 1e3 + 10, mod = 1e9 + 7;
int i, j, k, n, m, l, a[N], b[N], x, y;
bool p[N][N];
void init()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
mt19937 rnd(time(0));
}
vector<int> c, d;
int dp[N][N], pt[N][N];
pii pp[N][N];
void bfs()
{
queue<pii> q;
q.push({0, 0});
while (q.size())
{
int x = q.front().first, y = q.front().second;
q.pop();
p[x][y]=false;
if (dp[x][y] > dp[c.size()][d.size()])
continue;
if (x == c.size() && y == d.size())
continue;
if (x < c.size() && y < d.size())
{
if (c[x] != d[y])
{
if (dp[x + 1][y + 1] > dp[x][y] + 1)
{
dp[x + 1][y + 1] = dp[x][y] + 1;
pp[x + 1][y + 1] = {x, y};
pt[x + 1][y + 1] = 1;
if (!p[x + 1][y + 1])
q.push({x + 1, y + 1});
p[x + 1][y + 1] = 1;
}
}
else
{
if (dp[x + 1][y + 1] > dp[x][y])
{
dp[x + 1][y + 1] = dp[x][y];
pp[x + 1][y + 1] = {x, y};
pt[x + 1][y + 1] = 2;
if (!p[x + 1][y + 1])
q.push({x + 1, y + 1});
p[x + 1][y + 1] = 1;
}
}
}
if (x < c.size())
{
if (dp[x + 1][y] > dp[x][y] + 1)
{
dp[x + 1][y] = dp[x][y] + 1;
pp[x + 1][y] = {x, y};
pt[x + 1][y] = 0;
if (!p[x + 1][y])
q.push({x + 1, y});
p[x + 1][y] = 1;
}
}
if (y < d.size())
{
if (dp[x][y + 1] > dp[x][y] + 1)
{
dp[x][y + 1] = dp[x][y] + 1;
pp[x][y + 1] = {x, y};
pt[x][y + 1] = 3;
if (!p[x][y + 1])
q.push({x, y + 1});
p[x][y + 1] = 1;
}
}
}
}
signed main()
{
init();
memset(dp, 0x3f, sizeof dp);
dp[0][0] = 0;
while (cin >> n && n != -1)
{
c.push_back(n);
}
while (cin >> n && n != -1)
{
d.push_back(n);
}
bfs();
cout << dp[c.size()][d.size()] << endl;
pii cnt = {c.size(), d.size()};
vector<int> ans;
while (cnt.x||cnt.y)
{
ans.push_back(pt[cnt.x][cnt.y]);
cnt = pp[cnt.x][cnt.y];
}
reverse(ans.begin(), ans.end());
for (int i : ans)
cout << i;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
RC-u5 养老社区

输入样例
11
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 5
2 6
3 7
3 8
4 9
4 10
1 11
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 9 10
输出样例文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-522071.html
14
思路
先lca搞出来任意两点之间的距离。然后按照距离相同的练成一个图,给两点不同种族的连上边,这样就转化成无向图的三元环计数问题=w=。
相关知识点请自行搜索。(数据主要是太水了)
自言自语
1.数据实在是太水了,结果三元环的优化也完全不需要,把交换那行删掉也是完全能过的。。。
2.样例也没有菊花图的情况,自己跑了一遍菊花图的情况是稳t的,本地开O2跑了8s。。。(边太多了,跑不出来也正常hh)
C++能过代码文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-522071.html
/*made in sxh*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define lowbit(x) x & -x
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
#define mem(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof a)
#define x first
#define y second
#define pb push_back
#define bug1(x) cout << x << endl
#define bug2(x, y) cout << x << ' ' << y << endl
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define bug3(x, y, z) cout << x << ' ' << y << ' ' << z << endl
const int N = 2e3 + 10, mod = 1e9 + 7;
int i, j, k, n, m, l, a[N], b[N], d[N], x, y;
bool p[N];
vector<int> mp[N];
int dep[N], tr[N][25];
void init()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
mt19937 rnd(time(0));
}
void dfs(int x, int fa)
{
for (int i = 1; i < 20; i++)
tr[x][i] = tr[tr[x][i - 1]][i - 1];
for (auto i : mp[x])
{
if (i == fa)
continue;
dep[i] = dep[x] + 1;
tr[i][0] = x;
dfs(i, x);
}
}
int lca(int x, int y)
{
if (dep[x] > dep[y])
swap(x, y);
for (int i = 19; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (dep[x] <= dep[tr[y][i]])
y = tr[y][i];
}
if (x != y)
{
for (int i = 19; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (tr[x][i] != tr[y][i])
{
x = tr[x][i];
y = tr[y][i];
}
}
x = tr[x][0];
}
return x;
}
vector<pii> sd[N];
signed main()
{
init();
cin >> n;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> x >> y;
mp[x].push_back(y);
mp[y].push_back(x);
}
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
dep[1]=1;
dfs(1, -1);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (j = i + 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (a[i] == a[j])
continue;
int t = lca(i, j);
t = dep[i] + dep[j] - dep[t] * 2;
sd[t].push_back({i, j});
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
d[i] = 0, mp[i].clear();
for (auto j : sd[i])
{
d[j.first]++;
d[j.second]++;
}
for (auto j : sd[i])
{
//if (d[j.first] > d[j.second] || (d[j.first] == d[j.second] && j.first > j.second))
// swap(j.first, j.second);
mp[j.first].push_back(j.second);
}
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
for (auto k : mp[j])
p[k] = 1;
for (auto k : mp[j])
{
for (auto u : mp[k])
if (p[u])
ans++;
}
for (auto k : mp[j])
p[k] = 0;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
到了这里,关于2022 RoboCom 世界机器人开发者大赛-本科组(国赛)R4,R5题解的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!