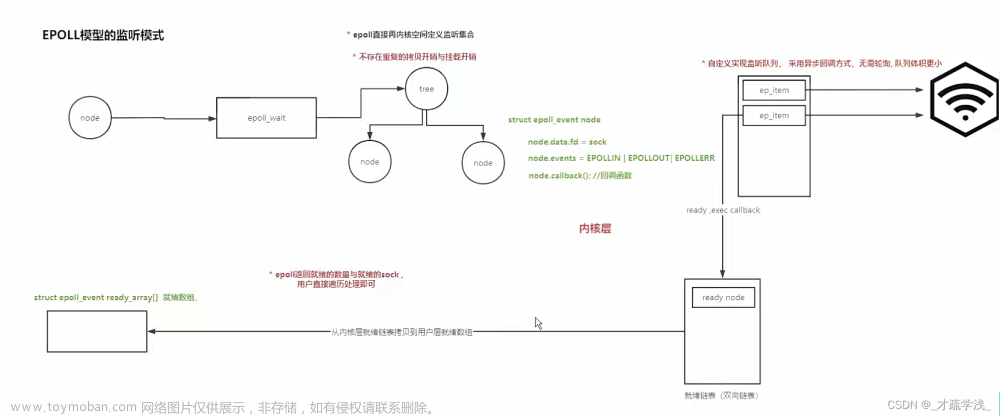
Linux内核poll,ppoll,epoll,select代码位置:
poll,ppoll,select相关内核实现在在fs/select.c中;
epoll_ctl和epoll_wait相关函数在fs/eventpoll.c中
epoll实测不支持监听普通文件,select可以,但是发现无论是可读、可写,其一直会返回准备就绪状态,所以select也无法实际用来监控普通文件,可用来监听物理设备如uart对应的ttyS0等。
epoll_ctl控制普通文件会返回-1,即EPERM,添加的fd不支持epoll。比如添加的是普通文件描述符内核设备文件poll file operations定义类似如下:


如下通过epoll实现监控IO变化:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <regex.h>
#include <libgen.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/timerfd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <sys/eventfd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/reboot.h>
#include <sys/resource.h>
#include <sys/prctl.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/sockios.h>
#include <linux/ethtool.h>
#include <linux/netlink.h>
static bool thread_start = 0;
static int32_t epoll_fd = -1;
static int32_t g_test_gpio_fd = -1;
static int32_t g_test_status_fd = -1;
static int test_action = 1;
typedef struct{
int8_t thread_name[OWN_THREAD_NAME_SIZE]; //thread name
pthread_t m_thead; //thread hanle
uint32_t thread_priority; //thread priority
uint32_t stack_depth; //stack size
void *thread_func; //thread func
void *para;
}OWN_thread_t;
#define OWN_THREAD_NAME_SIZE 20
#define TEST_PATH "/etc/test_value"
#define OWN_WAKE_GPIO_MAX_SIZE (10)
#define OWN_MIN_STACK 100*1024
#define F_FAIL -1
#define F_SUCCESS 1
#define EPOLL_TIMEOUT (1000)
#define OWN_BUFSIZE_4 4
#define OWN_THREAD_PRIORITY 3
#define OWN_test_THREAD_STACK_SIZE (18 * 1024)//byte(18kb)
int32_t OWN_thread_create(OWN_thread_t *threadin)
{
int32_t ret = -1;
if(threadin == NULL)
{
printf("threadin is null\n");
}
pthread_attr_t attr;
ret = pthread_attr_init(&attr);
if (ret != 0)
{
printf("pthread_attr_init Error\n");
return -1;
}
if(threadin->stack_depth < OWN_MIN_STACK)
{
threadin->stack_depth = OWN_MIN_STACK;
}
ret = pthread_attr_setstacksize(&attr, threadin->stack_depth);
if(ret != 0)
{
printf("pthread_attr_setstacksize %d Error=%d\n",threadin->stack_depth,ret);
return -1;
}
ret = pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
if(ret != 0)
{
printf("pthread_attr_setdetachstate Error=%d\n",ret);
return -1;
}
ret = pthread_create(&(threadin->m_thead), &attr, threadin->thread_func, (void *)(threadin->para));
pthread_attr_destroy (&attr);
if(ret != 0)
{
printf("pthread_create Error, ret=%d, err:%s\n", ret, strerror(errno));
return F_FAIL;
}
else
{
return F_SUCCESS;
}
return F_FAIL;
}
static void *OWN_thread_handler(void *arg)
{
static int32_t first_reload = 1;
int32_t fd_cnt = 0;
int32_t ret = 0;
int32_t i = 0;
int8_t value[OWN_BUFSIZE_4] = {0};
struct epoll_event events[OWN_WAKE_GPIO_MAX_SIZE];
int8_t value_status = 0;
while (thread_start)
{
memset(events, 0x0, sizeof(events));
fd_cnt = epoll_wait(epoll_fd, events, OWN_WAKE_GPIO_MAX_SIZE, EPOLL_TIMEOUT);
if(fd_cnt <= 0)
{
continue;
}
for(i = 0; i < fd_cnt; i++)
{
memset(value, 0x0, sizeof(value));
lseek(events[i].data.fd, 0, SEEK_SET);
ret = read(events[i].data.fd, value, sizeof(value));
value_status = atoi((const char *)value);
printf("value =%s value_status =%d ret : %d\n", value, value_status, ret);
if (events[i].events & EPOLLPRI && events[i].data.fd == g_test_gpio_fd)
{
printf("gpio test file \r\n");
if (test_action != NULL)
{
printf("callback test value =%s value_status =%d ret : %d\n", value, value_status, ret);
}
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
int ret = 0;
struct epoll_event evd = {0};
OWN_thread_t test_gpio_thread;
epoll_fd = epoll_create(OWN_WAKE_GPIO_MAX_SIZE);
if (epoll_fd < 0)
{
printf("epoll error \n");
}
g_test_gpio_fd = open(TEST_PATH , O_RDONLY | O_NONBLOCK);
if (g_test_gpio_fd < 0)
{
printf("open error \n");
}
memset(&evd, 0x0, sizeof(evd));
evd.data.fd = g_test_gpio_fd;
evd.events = EPOLLPRI;
ret = epoll_ctl(g_test_epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, epoll_fd, &evd);
if (ret < 0)
{
printf("epoll_ctl error \n");
}
thread_start = 1;
memset(&test_gpio_thread, 0, sizeof(test_gpio_thread));
snprintf((char*)test_gpio_thread.thread_name,OWN_THREAD_NAME_SIZE - 1, "Notify handle");
test_gpio_thread.thread_priority = OWN_THREAD_PRIORITY;
test_gpio_thread.stack_depth = OWN_test_THREAD_STACK_SIZE;
test_gpio_thread.thread_func = OWN_thread_handler;
test_gpio_thread.para = NULL;
ret = OWN_thread_create(&test_gpio_thread);
if (ret != F_SUCCESS) {
printf("OWN_thread_handler creation failure !\n");
}
while(1)
{
sleep(2);
}
return 0;
}select应用示例:如下实例为监听普通文件,发现返回值一直大于0,监听意义不大。可以将监听的设备改为ttyS0,则可以正常监控。
函数返回值如下:
>0:就绪描述字的正数目
-1:出错
0 :超时文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-523945.html
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <regex.h>
#include <libgen.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/timerfd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <sys/eventfd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/reboot.h>
#include <sys/resource.h>
#include <sys/prctl.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/spi/spidev.h>
#include <linux/sockios.h>
#include <linux/ethtool.h>
#include <linux/netlink.h>
static pthread_t test_thread;
int fd = 0;
static void *thread_func(void * arg);
int main(int argc, char * argv [ ])
{
int ret;
char buf[] = "hello test! ";
if (argc < 2)
{
return -1;
}
setbuf(stdout, NULL);
fd = open("/etc_rw/test_select", O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd > 0)
{
printf("Open success! \n");
}
else
{
printf("Open failure! \n");
}
if (pthread_create(&test_thread, NULL, thread_func, NULL) != 0)
{
printf("Failed to creat thread \n");
}
while (fd >= 0)
{
//ret = write(fd, (uint8_t*)buf, strlen(buf));
printf("Write fd value = %d, ret value = %d \n", fd, ret);
sleep(2);
}
return 0;
}
static void *thread_func(void * arg)
{
int ret;
fd_set fdset;
struct timeval timeout = {4, 0};
char buf[100] = {0};
timeout.tv_sec = 5;
timeout.tv_usec = 0;
while (fd >= 0)
{
FD_ZERO(&fdset);
FD_SET(fd, &fdset);
ret = select(fd + 1, &fdset, NULL, NULL, &timeout);
if (ret == -1)
{
printf("Failed to select \n");
}
else if (ret == 0)
{
printf("ret value is 0 \n");
timeout.tv_sec = 4;
timeout.tv_usec = 0;
}
else
{
if (FD_ISSET(fd, &fdset))
{
//do
// {
memset(buf, 0, 100);
ret = read(fd, buf, 100);
printf("Read ret = %d buf = %s \n", ret, buf);
// }while(ret == 200);
}
}
}
return (void *)1;
}
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-523945.html
到了这里,关于linux epoll/select使用区分和实例对比的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!