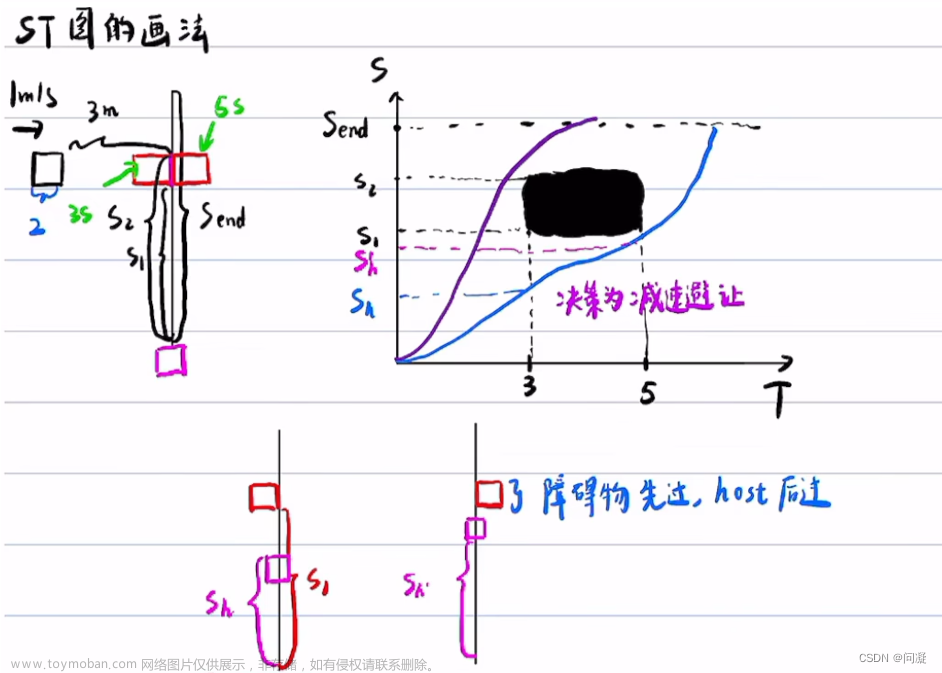
顺着之前学习public road planner 的路径规划中lane follow的task,在得到的规划路径上再进行速度规划。大致思路为先利用ST Graph,将障碍物、限速等投影在ST图上,利用全局搜索方法DP算法得到决策,开辟一个凸空间,在利用最优化方法(二次优化和非线性优化)进行速度规划。
在进行速度规划之前,首先需要注意:速度规划和路径规划时的坐标系差异。
路径规划的frenet坐标系为参考线,速度规划的frenet坐标系为路径规划规划出来的path。
1. ST_BOUNDS_DECIDER

所在路径为\modules\planning\tasks\deciders\st_bounds_decider
这个decider主要执行的就是计算st_graph中的st_drivable_boundary。
主要由三个模块计算组成:
1.根据车辆动力学计算得到的smax和smin
2.由参考速度行驶得到的smin和smax
3.由障碍物计算得到的可行驶区域smin和smax
分别对应的时st_driving_limits,st_guide_line,由于这两个类较好理解,没有单独拿出来分析。
第三个对应的st_obstacles_processor这个类在之前的文章学习过:
Apollo Planning学习(8)-------ST_OBSTACLES_PROCESSOR
最后st_bounds_decider将这些整合起来,在st_graph中画一个每一时刻的上下限范围。
- st_bounds_decider
#include "modules/planning/tasks/deciders/st_bounds_decider/st_bounds_decider.h"
#include <limits>
#include <memory>
#include "modules/planning/common/st_graph_data.h"
#include "modules/planning/tasks/deciders/st_bounds_decider/st_obstacles_processor.h"
namespace apollo {
namespace planning {
using apollo::common::ErrorCode;
using apollo::common::Status;
using apollo::planning_internal::StGraphBoundaryDebug;
using apollo::planning_internal::STGraphDebug;
namespace {
// STBoundPoint contains (t, s_min, s_max)
using STBoundPoint = std::tuple<double, double, double>;
// STBound is a vector of STBoundPoints
using STBound = std::vector<STBoundPoint>;
// ObsDecSet is a set of decision for new obstacles.
using ObsDecSet = std::vector<std::pair<std::string, ObjectDecisionType>>;
} // namespace
STBoundsDecider::STBoundsDecider(
const TaskConfig& config,
const std::shared_ptr<DependencyInjector>& injector)
: Decider(config, injector) {
ACHECK(config.has_st_bounds_decider_config());
st_bounds_config_ = config.st_bounds_decider_config();
}
Status STBoundsDecider::Process(Frame* const frame,
ReferenceLineInfo* const reference_line_info) {
// Initialize the related helper classes.
InitSTBoundsDecider(*frame, reference_line_info);
// Sweep the t-axis, and determine the s-boundaries step by step.
STBound regular_st_bound;
STBound regular_vt_bound;
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> st_guide_line;
Status ret = GenerateRegularSTBound(®ular_st_bound, ®ular_vt_bound,
&st_guide_line);
if (!ret.ok()) {
ADEBUG << "Cannot generate a regular ST-boundary.";
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, ret.error_message());
}
if (regular_st_bound.empty()) {
const std::string msg = "Generated regular ST-boundary is empty.";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
StGraphData* st_graph_data = reference_line_info_->mutable_st_graph_data();
st_graph_data->SetSTDrivableBoundary(regular_st_bound, regular_vt_bound);
// Record the ST-Graph for good visualization and easy debugging.
auto all_st_boundaries = st_obstacles_processor_.GetAllSTBoundaries();
std::vector<STBoundary> st_boundaries;
for (const auto& st_boundary : all_st_boundaries) {
st_boundaries.push_back(st_boundary.second);
}
ADEBUG << "Total ST boundaries = " << st_boundaries.size();
STGraphDebug* st_graph_debug = reference_line_info->mutable_debug()
->mutable_planning_data()
->add_st_graph();
RecordSTGraphDebug(st_boundaries, regular_st_bound, st_guide_line,
st_graph_debug);
return Status::OK();
}
// 入参1:Frame类对象,储存了一个规划周期的所有数据,如规划起始点,规划轨迹,参考线,车辆状态,routing路由信息等;
// 入参2:一个参考线信息类对象reference_line_info,这上面信息很多,障碍物列表,对个障碍物决策,以及个障碍物以及自车在ST图上的投影等
// 这里把入参参考线信息里的path_data路径数据和path_decision路径决策都拿出来了
void STBoundsDecider::InitSTBoundsDecider(
const Frame& frame, ReferenceLineInfo* const reference_line_info) {
const PathData& path_data = reference_line_info->path_data();
PathDecision* path_decision = reference_line_info->path_decision();
// Map all related obstacles onto ST-Graph.
auto time1 = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
st_obstacles_processor_.Init(path_data.discretized_path().Length(),
st_bounds_config_.total_time(), path_data,
path_decision, injector_->history());
// 将地图障碍物边界转换至st图上
st_obstacles_processor_.MapObstaclesToSTBoundaries(path_decision);
auto time2 = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
std::chrono::duration<double> diff = time2 - time1;
ADEBUG << "Time for ST Obstacles Processing = " << diff.count() * 1000
<< " msec.";
// Initialize Guide-Line and Driving-Limits.
// 初始化引导线和驾驶限制,这里其实是一个常量默认期望速度15m/s,约54kph
static constexpr double desired_speed = 15.0;
// If the path_data optimization is guided from a reference path of a
// reference trajectory, use its reference speed profile to select the st
// bounds in LaneFollow Hybrid Mode
// 如果从参考轨迹的参考路径引导路径数据优化,则使用其参考速度曲线选择车道跟随混合模式中的st界限
// 如果路径数据优化被一个参考路径引导,用它参考的速度规划来选择这个ST的边界在车道跟随的混合模式中?
// 这个混合模式应该是指的apollo端到端决策和基于规则决策的混合模式
// 如果路径数据是朝着参考轨迹优化的,这里is_optimized_towards_trajectory_reference默认为false,直接看else
// 引导线就是直接以期望速度15m/s匀速运动?st_guide_line_就是以期望速度匀速行驶的S插值功能的一个类
if (path_data.is_optimized_towards_trajectory_reference()) {
st_guide_line_.Init(desired_speed,
injector_->learning_based_data()
->learning_data_adc_future_trajectory_points());
} else {
st_guide_line_.Init(desired_speed);
}
// 定义了最大加速度2.5,最大减速度5.0,最大速度1.5倍期望速度
static constexpr double max_acc = 2.5;
static constexpr double max_dec = 5.0;
static constexpr double max_v = desired_speed * 1.5;
// STDrivingLimits这个类其实就是根据车辆最大加减速的限制计算处相应时间可以到达的s这个类就是实现这样一个功能,
// 这里就是对这样一个类对象进行初始化,同时输入规划起始点的速度
st_driving_limits_.Init(max_acc, max_dec, max_v,
frame.PlanningStartPoint().v());
}
// 这个函数就是产生FALLBACK的ST边界,就是规划求解失败后的ST边界
Status STBoundsDecider::GenerateFallbackSTBound(STBound* const st_bound,
STBound* const vt_bound) {
// Initialize st-boundary.
for (double curr_t = 0.0; curr_t <= st_bounds_config_.total_time();
curr_t += kSTBoundsDeciderResolution) {
st_bound->emplace_back(curr_t, std::numeric_limits<double>::lowest(),
std::numeric_limits<double>::max());
vt_bound->emplace_back(curr_t, std::numeric_limits<double>::lowest(),
std::numeric_limits<double>::max());
}
// Sweep-line to get detailed ST-boundary.
for (size_t i = 0; i < st_bound->size(); ++i) {
double t, s_lower, s_upper, lower_obs_v, upper_obs_v;
std::tie(t, s_lower, s_upper) = st_bound->at(i);
std::tie(t, lower_obs_v, upper_obs_v) = vt_bound->at(i);
ADEBUG << "Processing st-boundary at t = " << t;
// Get Boundary due to driving limits
// 给定时间t,根据车辆动力学计算以s为单位的行驶极限。return std::pair<double, double>
auto driving_limits_bound = st_driving_limits_.GetVehicleDynamicsLimits(t);
s_lower = std::fmax(s_lower, driving_limits_bound.first);
s_upper = std::fmin(s_upper, driving_limits_bound.second);
ADEBUG << "Bounds for s due to driving limits are "
<< "s_upper = " << s_upper << ", s_lower = " << s_lower;
// Get Boundary due to obstacles
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> available_s_bounds;
std::vector<ObsDecSet> available_obs_decisions;
/*
* 给定一个时间t,得到上下s边界。如果边界是根据先前的决定定义的,则只使用一个边界填充“available_s_bounds”。
* 否则,用所有候选项填写“available_s_bound”,用相应的可能障碍决策填写“available _obs_decisions”。
* 求得自车所有可能s边界available_s_bounds及其对应得决策列表available_obs_decisions,
* 其实就是看自车可以挤到块空隙里去,不同得空隙对应不同得上下边界以及决策。
*/
if (!st_obstacles_processor_.GetSBoundsFromDecisions(
t, &available_s_bounds, &available_obs_decisions)) {
const std::string msg =
"Failed to find a proper boundary due to obstacles.";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
/*
// STBoundPoint contains (t, s_min, s_max)
using STBoundPoint = std::tuple<double, double, double>;
// STBound is a vector of STBoundPoints
using STBound = std::vector<STBoundPoint>;
// ObsDecSet is a set of decision for new obstacles.
using ObsDecSet = std::vector<std::pair<std::string, ObjectDecisionType>>;
*/
std::vector<std::pair<STBoundPoint, ObsDecSet>> available_choices;
ADEBUG << "Available choices are:";
for (int j = 0; j < static_cast<int>(available_s_bounds.size()); ++j) {
ADEBUG << " (" << available_s_bounds[j].first << ", "
<< available_s_bounds[j].second << ")";
// 将刚才从getsboundsfromdecision函数中获得的数据放入available_choices这个容器中
available_choices.emplace_back(
std::make_tuple(0.0, available_s_bounds[j].first,
available_s_bounds[j].second),
available_obs_decisions[j]);
}
RemoveInvalidDecisions(driving_limits_bound, &available_choices);
// 总是选择最保守的选择。
if (!available_choices.empty()) {
// 选择最保守的决策。
auto top_choice_s_range = available_choices.front().first;
auto top_choice_decision = available_choices.front().second;
for (size_t j = 1; j < available_choices.size(); ++j) {
// 就是一个个找s_min最小的,将最小的留下
if (std::get<1>(available_choices[j].first) <
std::get<1>(top_choice_s_range)) {
top_choice_s_range = available_choices[j].first;
top_choice_decision = available_choices[j].second;
}
}
// 为没有决策的障碍设置决策。
bool is_limited_by_upper_obs = false;
bool is_limited_by_lower_obs = false;
// 说明其被障碍物限制了下限不能太慢;并设定标志位
if (s_lower < std::get<1>(top_choice_s_range)) {
s_lower = std::get<1>(top_choice_s_range);
is_limited_by_lower_obs = true;
}
// 说明其被障碍物限制了上限不能太快;并设定标志位
if (s_upper > std::get<2>(top_choice_s_range)) {
s_upper = std::get<2>(top_choice_s_range);
is_limited_by_upper_obs = true;
}
st_obstacles_processor_.SetObstacleDecision(top_choice_decision);
// Update st-guide-line, st-driving-limit info, and v-limits.
std::pair<double, double> limiting_speed_info;
if (st_obstacles_processor_.GetLimitingSpeedInfo(t,
&limiting_speed_info)) {
st_driving_limits_.UpdateBlockingInfo(
t, s_lower, limiting_speed_info.first, s_upper,
limiting_speed_info.second);
st_guide_line_.UpdateBlockingInfo(t, s_lower, true);
st_guide_line_.UpdateBlockingInfo(t, s_upper, false);
if (is_limited_by_lower_obs) {
lower_obs_v = limiting_speed_info.first;
}
if (is_limited_by_upper_obs) {
upper_obs_v = limiting_speed_info.second;
}
}
} else {
const std::string msg = "No valid st-boundary exists.";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
// Update into st_bound
st_bound->at(i) = std::make_tuple(t, s_lower, s_upper);
vt_bound->at(i) = std::make_tuple(t, lower_obs_v, upper_obs_v);
}
return Status::OK();
}
// 产生常规的ST边界
Status STBoundsDecider::GenerateRegularSTBound(
STBound* const st_bound, STBound* const vt_bound,
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>>* const st_guide_line) {
// Initialize st-boundary.
for (double curr_t = 0.0; curr_t <= st_bounds_config_.total_time();
curr_t += kSTBoundsDeciderResolution) {
st_bound->emplace_back(curr_t, std::numeric_limits<double>::lowest(),
std::numeric_limits<double>::max());
vt_bound->emplace_back(curr_t, std::numeric_limits<double>::lowest(),
std::numeric_limits<double>::max());
}
// Sweep-line to get detailed ST-boundary.
for (size_t i = 0; i < st_bound->size(); ++i) {
double t, s_lower, s_upper, lower_obs_v, upper_obs_v;
std::tie(t, s_lower, s_upper) = st_bound->at(i);
std::tie(t, lower_obs_v, upper_obs_v) = vt_bound->at(i);
ADEBUG << "Processing st-boundary at t = " << t;
// Get Boundary due to driving limits
auto driving_limits_bound = st_driving_limits_.GetVehicleDynamicsLimits(t);
s_lower = std::fmax(s_lower, driving_limits_bound.first);
s_upper = std::fmin(s_upper, driving_limits_bound.second);
ADEBUG << "Bounds for s due to driving limits are "
<< "s_upper = " << s_upper << ", s_lower = " << s_lower;
// Get Boundary due to obstacles
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> available_s_bounds;
std::vector<ObsDecSet> available_obs_decisions;
if (!st_obstacles_processor_.GetSBoundsFromDecisions(
t, &available_s_bounds, &available_obs_decisions)) {
const std::string msg =
"Failed to find a proper boundary due to obstacles.";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
std::vector<std::pair<STBoundPoint, ObsDecSet>> available_choices;
ADEBUG << "Available choices are:";
for (int j = 0; j < static_cast<int>(available_s_bounds.size()); ++j) {
ADEBUG << " (" << available_s_bounds[j].first << ", "
<< available_s_bounds[j].second << ")";
available_choices.emplace_back(
std::make_tuple(0.0, available_s_bounds[j].first,
available_s_bounds[j].second),
available_obs_decisions[j]);
}
RemoveInvalidDecisions(driving_limits_bound, &available_choices);
// 到这感觉和GenerateFallbackSTBound()的任务一样
//-------------------------------------------------------
if (!available_choices.empty()) {
ADEBUG << "One decision needs to be made among "
<< available_choices.size() << " choices.";
double guide_line_s = st_guide_line_.GetGuideSFromT(t);
st_guide_line->emplace_back(t, guide_line_s);
// 排名决策,具体规则之后的这个函数会介绍
RankDecisions(guide_line_s, driving_limits_bound, &available_choices);
// Select the top decision.
auto top_choice_s_range = available_choices.front().first;
bool is_limited_by_upper_obs = false;
bool is_limited_by_lower_obs = false;
// s_lower,s_upper已在之前用运动学初值算了一个值,最大加减速度对应的s
// 说明其被障碍物限制了下限不能太慢;并设定标志位
if (s_lower < std::get<1>(top_choice_s_range)) {
s_lower = std::get<1>(top_choice_s_range);
is_limited_by_lower_obs = true;
}
// 说明其被障碍物限制了上限不能太快;并设定标志位
if (s_upper > std::get<2>(top_choice_s_range)) {
s_upper = std::get<2>(top_choice_s_range);
is_limited_by_upper_obs = true;
}
// 为没有决策的障碍设置决策。
auto top_choice_decision = available_choices.front().second;
st_obstacles_processor_.SetObstacleDecision(top_choice_decision);
// 更新st指导线、st驾驶限制信息和v限制。
std::pair<double, double> limiting_speed_info;
// 根据障碍物的不同决策,算出自车的在每个时刻的速度限制上下限。
if (st_obstacles_processor_.GetLimitingSpeedInfo(t,
&limiting_speed_info)) {
// 然后st_driving_limits_调用UpdateBlockingInfo()函数更新阻塞信息
// 把当前的s的上下边界,速度的上下边界及对应的时间更新到st_driving_limits的类成员里。
st_driving_limits_.UpdateBlockingInfo(
t, s_lower, limiting_speed_info.first, s_upper,
limiting_speed_info.second);
// 然后又st_guide_line_引导线也调用UpdateBlockingInfo()函数更新t时刻的引导线,
// 用求出的S上下界去限制t时刻引导线s不能超出这个范围。
st_guide_line_.UpdateBlockingInfo(t, s_lower, true);
st_guide_line_.UpdateBlockingInfo(t, s_upper, false);
// 如果s被下方的的障碍物限制住了,那么自车速度下限lower_obs_v不能小于下方障碍物的上斜边ST斜率速度 limiting_speed_info.first
if (is_limited_by_lower_obs) {
lower_obs_v = limiting_speed_info.first;
}
// 如果s被上方的的障碍物限制住了,那么自车速度上限upper_obs_v不能小于上方障碍物的下斜边ST斜率速度 limiting_speed_info.second
if (is_limited_by_upper_obs) {
upper_obs_v = limiting_speed_info.second;
}
}
} else {
const std::string msg = "No valid st-boundary exists.";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
// 然后更新t时刻的st_bound和vt_bound
st_bound->at(i) = std::make_tuple(t, s_lower, s_upper);
vt_bound->at(i) = std::make_tuple(t, lower_obs_v, upper_obs_v);
}
return Status::OK();
}
// 移除无效决策
// 此函数传入参数的第一个参数是st图运动学最大加速度和最大减速度的边界
// 传入的第二个参数是一个包含可行区域的边界和决策
// 什么叫无效边界,这个函数的逻辑解释的无效边界就是第二个参数中的可行区域边界的s下界超出了最大加速度能到达的s或其上界甚至低于最大减速度到达的s
void STBoundsDecider::RemoveInvalidDecisions(
std::pair<double, double> driving_limit,
std::vector<std::pair<STBoundPoint, ObsDecSet>>* available_choices) {
// Remove those choices that don't even fall within driving-limits.
size_t i = 0;
while (i < available_choices->size()) {
double s_lower = 0.0;
double s_upper = 0.0;
std::tie(std::ignore, s_lower, s_upper) = available_choices->at(i).first;
if (s_lower > driving_limit.second || s_upper < driving_limit.first) {
// Invalid bound, should be removed.
if (i != available_choices->size() - 1) {
swap(available_choices->at(i),
available_choices->at(available_choices->size() - 1));
}
available_choices->pop_back();
} else {
// Valid bound, proceed to the next one.
++i;
}
}
}
// 这个函数大体原则就是空间尽量大,尽量包含引导线的排在前面,排在最前面的就是top_choice,就是最后要选用的那套决策和gap。
void STBoundsDecider::RankDecisions(
double s_guide_line, std::pair<double, double> driving_limit,
std::vector<std::pair<STBoundPoint, ObsDecSet>>* available_choices) {
// 对现有决策进行排序。
bool has_swaps = true;
while (has_swaps) {
has_swaps = false;
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(available_choices->size()) - 1; ++i) {
double A_s_lower = 0.0;
double A_s_upper = 0.0;
std::tie(std::ignore, A_s_lower, A_s_upper) =
available_choices->at(i).first;
double B_s_lower = 0.0;
double B_s_upper = 0.0;
std::tie(std::ignore, B_s_lower, B_s_upper) =
available_choices->at(i + 1).first;
ADEBUG << " Range ranking: A has s_upper = " << A_s_upper
<< ", s_lower = " << A_s_lower;
ADEBUG << " Range ranking: B has s_upper = " << B_s_upper
<< ", s_lower = " << B_s_lower;
// 如果两者都不大于可通过的阈值,则应选择具有较大空间的一个。
double A_room = std::fmin(driving_limit.second, A_s_upper) -
std::fmax(driving_limit.first, A_s_lower);
double B_room = std::fmin(driving_limit.second, B_s_upper) -
std::fmax(driving_limit.first, B_s_lower);
if (A_room < kSTPassableThreshold || B_room < kSTPassableThreshold) {
if (A_room < B_room) {
swap(available_choices->at(i + 1), available_choices->at(i));
has_swaps = true;
ADEBUG << "Swapping to favor larger room.";
}
continue;
}
// Should select the one with overlap to guide-line
// 如果相邻的两个gap s上下界之差都大于等于3m,就将包含引导线的那个gap排在前面
bool A_contains_guideline =
A_s_upper >= s_guide_line && A_s_lower <= s_guide_line;
bool B_contains_guideline =
B_s_upper >= s_guide_line && B_s_lower <= s_guide_line;
if (A_contains_guideline != B_contains_guideline) {
if (!A_contains_guideline) {
swap(available_choices->at(i + 1), available_choices->at(i));
has_swaps = true;
ADEBUG << "Swapping to favor overlapping with guide-line.";
}
continue;
}
}
}
}
// 此函数的主要功能是把获取t时刻自车S上下界过程中的中间量全部都存放到入参指针st_graph_debug里用来debug
void STBoundsDecider::RecordSTGraphDebug(
const std::vector<STBoundary>& st_graph_data, const STBound& st_bound,
const std::vector<std::pair<double, double>>& st_guide_line,
planning_internal::STGraphDebug* const st_graph_debug) {
if (!FLAGS_enable_record_debug || !st_graph_debug) {
ADEBUG << "Skip record debug info";
return;
}
// 绘制ST障碍物边界。
for (const auto& boundary : st_graph_data) {
auto boundary_debug = st_graph_debug->add_boundary();
boundary_debug->set_name(boundary.id());
if (boundary.boundary_type() == STBoundary::BoundaryType::YIELD) {
boundary_debug->set_type(StGraphBoundaryDebug::ST_BOUNDARY_TYPE_YIELD);
ADEBUG << "Obstacle ID = " << boundary.id() << ", decision = YIELD";
} else if (boundary.boundary_type() == STBoundary::BoundaryType::OVERTAKE) {
boundary_debug->set_type(StGraphBoundaryDebug::ST_BOUNDARY_TYPE_OVERTAKE);
ADEBUG << "Obstacle ID = " << boundary.id() << ", decision = OVERTAKE";
} else {
boundary_debug->set_type(StGraphBoundaryDebug::ST_BOUNDARY_TYPE_UNKNOWN);
ADEBUG << "Obstacle ID = " << boundary.id() << ", decision = UNKNOWN";
}
for (const auto& point : boundary.points()) {
auto point_debug = boundary_debug->add_point();
point_debug->set_t(point.x());
point_debug->set_s(point.y());
}
}
// 绘制所选ST边界。
auto boundary_debug = st_graph_debug->add_boundary();
boundary_debug->set_name("Generated ST-Boundary");
boundary_debug->set_type(
StGraphBoundaryDebug::ST_BOUNDARY_TYPE_DRIVABLE_REGION);
for (const auto& st_bound_pt : st_bound) {
auto point_debug = boundary_debug->add_point();
double t = 0.0;
double s_lower = 0.0;
std::tie(t, s_lower, std::ignore) = st_bound_pt;
point_debug->set_t(t);
point_debug->set_s(s_lower);
ADEBUG << "(" << t << ", " << s_lower << ")";
}
for (int i = static_cast<int>(st_bound.size()) - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
auto point_debug = boundary_debug->add_point();
double t = 0.0;
double s_upper = 0.0;
std::tie(t, std::ignore, s_upper) = st_bound[i];
point_debug->set_t(t);
point_debug->set_s(s_upper);
ADEBUG << "(" << t << ", " << s_upper << ")";
}
// 绘制生成st_bounds时使用的st_guide_line
for (const auto& st_points : st_guide_line) {
auto* speed_point = st_graph_debug->add_speed_profile();
speed_point->set_t(st_points.first);
speed_point->set_s(st_points.second);
}
}
} // namespace planning
} // namespace apollo
2. SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER

所在路径为\modules\planning\tasks\deciders\speed_bounds_decider
SpeedBoundsPrioriDecider本质就是SpeedBoundsDecider这个类,主要作用是生成一个相比于上一个task生成一个更加细致(增加了速度可行驶边界)的st图,为了后面DP做准备。
关于speed_limit_decider和st_boundary_mapper这两个类主要是辅佐SpeedBoundsDecider这个类。
这里主要分析SpeedBoundsDecider,主要处理逻辑为
- 将障碍物映射到st图中
- 沿路径创建速度限制
- 获取路径长度作为第1个图形中的s轴搜索边界
- 获取时间持续时间作为st图中的t轴搜索边界
- 构建最终的st图形
函数如下
#include "modules/planning/tasks/deciders/speed_bounds_decider/speed_bounds_decider.h"
#include <algorithm>
#include <limits>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "modules/common/vehicle_state/vehicle_state_provider.h"
#include "modules/planning/common/path/path_data.h"
#include "modules/planning/common/planning_context.h"
#include "modules/planning/common/planning_gflags.h"
#include "modules/planning/common/st_graph_data.h"
#include "modules/planning/common/util/common.h"
#include "modules/planning/tasks/deciders/speed_bounds_decider/speed_limit_decider.h"
#include "modules/planning/tasks/deciders/speed_bounds_decider/st_boundary_mapper.h"
using apollo::common::ErrorCode;
using apollo::common::Status;
using apollo::common::TrajectoryPoint;
using apollo::planning_internal::StGraphBoundaryDebug;
using apollo::planning_internal::STGraphDebug;
SpeedBoundsDecider::SpeedBoundsDecider(
const TaskConfig &config,
const std::shared_ptr<DependencyInjector> &injector)
: Decider(config, injector) {
ACHECK(config.has_speed_bounds_decider_config());
speed_bounds_config_ = config.speed_bounds_decider_config();
}
Status SpeedBoundsDecider::Process(
Frame *const frame, ReferenceLineInfo *const reference_line_info) {
// retrieve data from frame and reference_line_info
// 初始化相关数据
const PathData &path_data = reference_line_info->path_data();
const TrajectoryPoint &init_point = frame->PlanningStartPoint();
const ReferenceLine &reference_line = reference_line_info->reference_line();
PathDecision *const path_decision = reference_line_info->path_decision();
// 1. 将障碍物映射到st图中
auto time1 = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
// 初始化boundary_mapper,为了调用该类中的其他函数做铺垫
STBoundaryMapper boundary_mapper(
speed_bounds_config_, reference_line, path_data,
path_data.discretized_path().Length(), speed_bounds_config_.total_time(),
injector_);
if (!FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary) {
path_decision->EraseStBoundaries();
}
// 根据不同障碍物对应不同的决策在st graph中画出来
// 如果失败,则报错
if (boundary_mapper.ComputeSTBoundary(path_decision).code() ==
ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR) {
const std::string msg = "Mapping obstacle failed.";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
auto time2 = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
std::chrono::duration<double> diff = time2 - time1;
ADEBUG << "Time for ST Boundary Mapping = " << diff.count() * 1000
<< " msec.";
std::vector<const STBoundary *> boundaries;
// 遍历每个障碍物
for (auto *obstacle : path_decision->obstacles().Items()) {
// 获得障碍物的id
const auto &id = obstacle->Id();
// 障碍物的st边界
const auto &st_boundary = obstacle->path_st_boundary();
// 如果st边界不是空的,进入if
if (!st_boundary.IsEmpty()) {
// 如果该st边界类型是keep clear 则设置为不是阻塞障碍物,反之,则相反
if (st_boundary.boundary_type() == STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {
path_decision->Find(id)->SetBlockingObstacle(false);
} else {
path_decision->Find(id)->SetBlockingObstacle(true);
}
boundaries.push_back(&st_boundary);
}
}
const double min_s_on_st_boundaries = SetSpeedFallbackDistance(path_decision);
// 2. 沿路径创建速度限制
SpeedLimitDecider speed_limit_decider(speed_bounds_config_, reference_line,
path_data);
SpeedLimit speed_limit;
/*
根据这些规则来获得新的速度限制,并存入speed_limit中
1.车道本身限制
2.向心加速度限制
3.无人车绕行障碍物的速度限制
*/
// 如果失败则,则返回报错
if (!speed_limit_decider
.GetSpeedLimits(path_decision->obstacles(), &speed_limit)
.ok()) {
const std::string msg = "Getting speed limits failed!";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
// 3. 获取路径长度作为第1个图形中的s轴搜索边界
const double path_data_length = path_data.discretized_path().Length();
// 4. 获取时间持续时间作为st图中的t轴搜索边界
const double total_time_by_conf = speed_bounds_config_.total_time();
// 将生成的st图形数据加载回框架
StGraphData *st_graph_data = reference_line_info_->mutable_st_graph_data();
// 添加st_graph调试信息,并将指针保存到st_graph_data以用于优化器日志记录
auto *debug = reference_line_info_->mutable_debug();
STGraphDebug *st_graph_debug = debug->mutable_planning_data()->add_st_graph();
st_graph_data->LoadData(boundaries, min_s_on_st_boundaries, init_point,
speed_limit, reference_line_info->GetCruiseSpeed(),
path_data_length, total_time_by_conf, st_graph_debug);
// 创建并记录st_graph调试信息
RecordSTGraphDebug(*st_graph_data, st_graph_debug);
return Status::OK();
}
double SpeedBoundsDecider::SetSpeedFallbackDistance(
PathDecision *const path_decision) {
// Set min_s_on_st_boundaries to guide speed fallback.
static constexpr double kEpsilon = 1.0e-6;
double min_s_non_reverse = std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity();
double min_s_reverse = std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity();
// 遍历每一个障碍物
for (auto *obstacle : path_decision->obstacles().Items()) {
const auto &st_boundary = obstacle->path_st_boundary();
// 如果st边界是空的,则跳过
if (st_boundary.IsEmpty()) {
continue;
}
// 障碍物st边界左下角点
const auto left_bottom_point_s = st_boundary.bottom_left_point().s();
// 障碍物st边界右下角点
const auto right_bottom_point_s = st_boundary.bottom_right_point().s();
const auto lowest_s = std::min(left_bottom_point_s, right_bottom_point_s);b
// 如果同一个障碍物左下角点的s不等于右下角点的s
if (left_bottom_point_s - right_bottom_point_s > kEpsilon) {
if (min_s_reverse > lowest_s) {
min_s_reverse = lowest_s;
}
} else if (min_s_non_reverse > lowest_s) {
min_s_non_reverse = lowest_s;
}
}
min_s_reverse = std::max(min_s_reverse, 0.0);
min_s_non_reverse = std::max(min_s_non_reverse, 0.0);
return min_s_non_reverse > min_s_reverse ? 0.0 : min_s_non_reverse;
}
void SpeedBoundsDecider::RecordSTGraphDebug(
const StGraphData &st_graph_data, STGraphDebug *st_graph_debug) const {
if (!FLAGS_enable_record_debug || !st_graph_debug) {
ADEBUG << "Skip record debug info";
return;
}
for (const auto &boundary : st_graph_data.st_boundaries()) {
auto boundary_debug = st_graph_debug->add_boundary();
boundary_debug->set_name(boundary->id());
switch (boundary->boundary_type()) {
case STBoundary::BoundaryType::FOLLOW:
boundary_debug->set_type(StGraphBoundaryDebug::ST_BOUNDARY_TYPE_FOLLOW);
break;
case STBoundary::BoundaryType::OVERTAKE:
boundary_debug->set_type(
StGraphBoundaryDebug::ST_BOUNDARY_TYPE_OVERTAKE);
break;
case STBoundary::BoundaryType::STOP:
boundary_debug->set_type(StGraphBoundaryDebug::ST_BOUNDARY_TYPE_STOP);
break;
case STBoundary::BoundaryType::UNKNOWN:
boundary_debug->set_type(
StGraphBoundaryDebug::ST_BOUNDARY_TYPE_UNKNOWN);
break;
case STBoundary::BoundaryType::YIELD:
boundary_debug->set_type(StGraphBoundaryDebug::ST_BOUNDARY_TYPE_YIELD);
break;
case STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR:
boundary_debug->set_type(
StGraphBoundaryDebug::ST_BOUNDARY_TYPE_KEEP_CLEAR);
break;
}
for (const auto &point : boundary->points()) {
auto point_debug = boundary_debug->add_point();
point_debug->set_t(point.x());
point_debug->set_s(point.y());
}
}
for (const auto &point : st_graph_data.speed_limit().speed_limit_points()) {
common::SpeedPoint *speed_point = st_graph_debug->add_speed_limit();
speed_point->set_s(point.first);
speed_point->set_v(point.second);
}
}
3. SPEED_HEURISTIC_OPTIMIZER

所在路径为\modules\planning\tasks\optimizers\path_time_heuristic
主要作用就是利用动态规划&回溯的方法在ST图中搜索出一系列可行的速度点集。
关于速度动态规划知乎上有很多大佬总结的很好,可以按照下面链接依次学习:
Planning 基于动态规划的速度规划
Apollo 6.0的EM Planner (3):速度规划的动态规划DP过程
4. SPEED_DECIDER

其所在位置为\modules\planning\tasks\deciders\path_decider
这个task的作用是依据DP搜索的speed_profile,设置障碍物标签。
与路径决策器思路一致,当路径规划器完成路径规划以后,可以得到一条经过path library打分的最优路径,path decider就需要对静态障碍物做标签的更新,尤其是那些不在特殊路况下的障碍物,但是没有对动态障碍物进行处理。
这时候在速度规划器完成未来8s或者未来前向距离150m的规划以后,也已经得出了一条未来每个时刻无人车出现在参考线上的位置,再配合事先已经规划好的path,就可以完成对动态障碍物的标签更新。
具体的实现逻辑都在speed_decider这个类中:
#include "modules/planning/tasks/deciders/speed_decider/speed_decider.h"
#include <algorithm>
#include <memory>
#include "cyber/common/log.h"
#include "cyber/time/clock.h"
#include "modules/common/configs/vehicle_config_helper.h"
#include "modules/common/util/util.h"
#include "modules/common_msgs/perception_msgs/perception_obstacle.pb.h"
#include "modules/planning/common/planning_context.h"
#include "modules/planning/common/planning_gflags.h"
#include "modules/common_msgs/planning_msgs/decision.pb.h"
#include "modules/planning/tasks/utils/st_gap_estimator.h"
namespace apollo {
namespace planning {
using apollo::common::ErrorCode;
using apollo::common::Status;
using apollo::common::VehicleConfigHelper;
using apollo::common::math::Vec2d;
using apollo::cyber::Clock;
using apollo::perception::PerceptionObstacle;
SpeedDecider::SpeedDecider(const TaskConfig& config,
const std::shared_ptr<DependencyInjector>& injector)
: Task(config, injector) {}
common::Status SpeedDecider::Execute(Frame* frame,
ReferenceLineInfo* reference_line_info) {
Task::Execute(frame, reference_line_info);
init_point_ = frame_->PlanningStartPoint();
adc_sl_boundary_ = reference_line_info_->AdcSlBoundary();
reference_line_ = &reference_line_info_->reference_line();
if (!MakeObjectDecision(reference_line_info->speed_data(),
reference_line_info->path_decision())
.ok()) {
const std::string msg = "Get object decision by speed profile failed.";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
return Status::OK();
}
SpeedDecider::STLocation SpeedDecider::GetSTLocation(
const PathDecision* const path_decision, const SpeedData& speed_profile,
const STBoundary& st_boundary) const {
if (st_boundary.IsEmpty()) {
return BELOW;
}
STLocation st_location = BELOW;
bool st_position_set = false;
const double start_t = st_boundary.min_t();
const double end_t = st_boundary.max_t();
for (size_t i = 0; i + 1 < speed_profile.size(); ++i) {
const STPoint curr_st(speed_profile[i].s(), speed_profile[i].t());
const STPoint next_st(speed_profile[i + 1].s(), speed_profile[i + 1].t());
if (curr_st.t() < start_t && next_st.t() < start_t) {
continue;
}
if (curr_st.t() > end_t) {
break;
}
if (!FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary) {
common::math::LineSegment2d speed_line(curr_st, next_st);
// 如果障碍物的boundary与speed_line由重叠,则st_location = CROSS
if (st_boundary.HasOverlap(speed_line)) {
ADEBUG << "speed profile cross st_boundaries.";
st_location = CROSS;
if (!FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary) {
// 如果障碍物的边界类型是KEEP_CLEAR,判断speed_profile是否与stboundary有交叉,这个函数后面会说到
if (st_boundary.boundary_type() ==
STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {
// 如果这个函数返回的是false,就说明speed_profile的最后一点的速度小于KeepClearSlowSpeed
// 且speed_profile最后一点的s小于keep_clear_st_boundary.max_s()
// 则说明adc在st图上位于障碍物的下方
if (!CheckKeepClearCrossable(path_decision, speed_profile,
st_boundary)) {
st_location = BELOW;
}
}
}
break;
}
}
// note: st_position可以通过检查两个st点来计算,但我们需要迭代所有st点以确保没有交叉
if (!st_position_set) {
// 本质就是通过向量叉乘判断位置
if (start_t < next_st.t() && curr_st.t() < end_t) {
STPoint bd_point_front = st_boundary.upper_points().front();
double side = common::math::CrossProd(bd_point_front, curr_st, next_st);
st_location = side < 0.0 ? ABOVE : BELOW;
st_position_set = true;
}
}
}
return st_location;
}
// 如果这个函数返回的是false,就说明speed_profile的最后一点的速度小于KeepClearSlowSpeed
// 且speed_profile最后一点的s小于keep_clear_st_boundary.max_s()
// 则说明adc在st图上位于障碍物的下方
bool SpeedDecider::CheckKeepClearCrossable(
const PathDecision* const path_decision, const SpeedData& speed_profile,
const STBoundary& keep_clear_st_boundary) const {
bool keep_clear_crossable = true;
const auto& last_speed_point = speed_profile.back();
double last_speed_point_v = 0.0;
if (last_speed_point.has_v()) {
last_speed_point_v = last_speed_point.v();
} else {
const size_t len = speed_profile.size();
if (len > 1) {
const auto& last_2nd_speed_point = speed_profile[len - 2];
last_speed_point_v = (last_speed_point.s() - last_2nd_speed_point.s()) /
(last_speed_point.t() - last_2nd_speed_point.t());
}
}
static constexpr double kKeepClearSlowSpeed = 2.5; // m/s
ADEBUG << "last_speed_point_s[" << last_speed_point.s()
<< "] st_boundary.max_s[" << keep_clear_st_boundary.max_s()
<< "] last_speed_point_v[" << last_speed_point_v << "]";
if (last_speed_point.s() <= keep_clear_st_boundary.max_s() &&
last_speed_point_v < kKeepClearSlowSpeed) {
keep_clear_crossable = false;
}
return keep_clear_crossable;
}
// 这个注意传入参数pathdecision表示一条路径上的所有障碍物决策,单一条
bool SpeedDecider::CheckKeepClearBlocked(
const PathDecision* const path_decision,
const Obstacle& keep_clear_obstacle) const {
bool keep_clear_blocked = false;
// 检查是否与其他停止强重叠
for (const auto* obstacle : path_decision->obstacles().Items()) {
if (obstacle->Id() == keep_clear_obstacle.Id()) {
continue;
}
const double obstacle_start_s = obstacle->PerceptionSLBoundary().start_s();
const double adc_length =
VehicleConfigHelper::GetConfig().vehicle_param().length();
const double distance =
obstacle_start_s - keep_clear_obstacle.PerceptionSLBoundary().end_s();
// 如果障碍物是阻挡障碍物且该障碍物的起始点减去keepclear障碍物的末尾点的s方向的距离大于0&&小于半个车长
// 就认为keep_clear_blocked = true
if (obstacle->IsBlockingObstacle() && distance > 0 &&
distance < (adc_length / 2)) {
keep_clear_blocked = true;
break;
}
}
return keep_clear_blocked;
}
// “太近”取决于如果障碍物以当前速度行驶并且自我车辆使用了一些合理的减速,自我车辆是否会撞到前方障碍物
bool SpeedDecider::IsFollowTooClose(const Obstacle& obstacle) const {
if (!obstacle.IsBlockingObstacle()) {
return false;
}
if (obstacle.path_st_boundary().min_t() > 0.0) {
return false;
}
const double obs_speed = obstacle.speed();
const double ego_speed = init_point_.v();
if (obs_speed > ego_speed) {
return false;
}
const double distance =
obstacle.path_st_boundary().min_s() - FLAGS_min_stop_distance_obstacle;
static constexpr double lane_follow_max_decel = 3.0;
static constexpr double lane_change_max_decel = 3.0;
auto* planning_status = injector_->planning_context()
->mutable_planning_status()
->mutable_change_lane();
double distance_numerator = std::pow((ego_speed - obs_speed), 2) * 0.5;
double distance_denominator = lane_follow_max_decel;
if (planning_status->has_status() &&
planning_status->status() == ChangeLaneStatus::IN_CHANGE_LANE) {
distance_denominator = lane_change_max_decel;
}
return distance < distance_numerator / distance_denominator;
}
Status SpeedDecider::MakeObjectDecision(
const SpeedData& speed_profile, PathDecision* const path_decision) const {
// 如果速度规划数据大小小于2,退出
if (speed_profile.size() < 2) {
const std::string msg = "dp_st_graph failed to get speed profile.";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
// 遍历每个障碍物
for (const auto* obstacle : path_decision->obstacles().Items()) {
auto* mutable_obstacle = path_decision->Find(obstacle->Id());
// 获得每个障碍物在path上的stboundary
const auto& boundary = mutable_obstacle->path_st_boundary();
if (boundary.IsEmpty() || boundary.max_s() < 0.0 ||
boundary.max_t() < 0.0 ||
boundary.min_t() >= speed_profile.back().t()) {
AppendIgnoreDecision(mutable_obstacle);
continue;
}
// 对于已有纵向决策的障碍物,横向未设置的添加ignore决策
if (obstacle->HasLongitudinalDecision()) {
AppendIgnoreDecision(mutable_obstacle);
continue;
}
// 对于虚拟障碍物,如果中心点不在车道上,则跳过
if (obstacle->IsVirtual()) {
const auto& obstacle_box = obstacle->PerceptionBoundingBox();
if (!reference_line_->IsOnLane(obstacle_box.center())) {
continue;
}
}
// 遇到行人始终停止
if (CheckStopForPedestrian(*mutable_obstacle)) {
ObjectDecisionType stop_decision;
// 如果障碍物是行人,在障碍物纵向决策上添加stop_decision
if (CreateStopDecision(*mutable_obstacle, &stop_decision,
-FLAGS_min_stop_distance_obstacle)) {
mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph/pedestrian",
stop_decision);
}
continue;
}
auto location = GetSTLocation(path_decision, speed_profile, boundary);
if (!FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary) {
if (boundary.boundary_type() == STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {
if (CheckKeepClearBlocked(path_decision, *obstacle)) {
location = BELOW;
}
}
}
// 根据adc和障碍物在st图上的boundary的位置关系,来创建决策
switch (location) {
// adc在st图上位于障碍物boundary下方时
case BELOW:
// 如果障碍物类型是禁停类型,在障碍物纵向决策设置为停止
if (boundary.boundary_type() == STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {
ObjectDecisionType stop_decision;
if (CreateStopDecision(*mutable_obstacle, &stop_decision, 0.0)) {
mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph/keep_clear",
stop_decision);
}
}
// 检查adc是否跟随障碍物,如果是则进入下面的判断
else if (CheckIsFollow(*obstacle, boundary)) {
// 低速减速停止
// 判断是否跟的太近,如果跟的太近,在障碍物纵向决策设置为停止
if (IsFollowTooClose(*mutable_obstacle)) {
ObjectDecisionType stop_decision;
if (CreateStopDecision(*mutable_obstacle, &stop_decision,
-FLAGS_min_stop_distance_obstacle)) {
mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph/too_close",
stop_decision);
}
}
// 如果没有跟的太近,在障碍物纵向决策设置为跟车
else { // 高速或低速加速
// FOLLOW decision
ObjectDecisionType follow_decision;
if (CreateFollowDecision(*mutable_obstacle, &follow_decision)) {
mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph",
follow_decision);
}
}
}
// 如果都不是就在障碍物纵向决策设置为让行
else {
// YIELD decision
ObjectDecisionType yield_decision;
if (CreateYieldDecision(*mutable_obstacle, &yield_decision)) {
mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph",
yield_decision);
}
}
break;
// adc在st图上位于障碍物上方
case ABOVE:
// 如果障碍物类型是禁停类型,在障碍物纵向决策设置为忽略
if (boundary.boundary_type() == STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {
ObjectDecisionType ignore;
ignore.mutable_ignore();
mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph", ignore);
}
// 如果障碍物不是禁停类型,其他类型一律超车处理
else {
// OVERTAKE decision
ObjectDecisionType overtake_decision;
if (CreateOvertakeDecision(*mutable_obstacle, &overtake_decision)) {
mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph/overtake",
overtake_decision);
}
}
break;
// adc在st图上与障碍物有交叉
case CROSS:
// 判断障碍物类型是否为阻塞障碍物,如果是则在障碍物纵向决策设置为停止
if (mutable_obstacle->IsBlockingObstacle()) {
ObjectDecisionType stop_decision;
if (CreateStopDecision(*mutable_obstacle, &stop_decision,
-FLAGS_min_stop_distance_obstacle)) {
mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph/cross",
stop_decision);
}
const std::string msg = absl::StrCat(
"Failed to find a solution for crossing obstacle: ",
mutable_obstacle->Id());
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
break;
default:
AERROR << "Unknown position:" << location;
}
AppendIgnoreDecision(mutable_obstacle);
}
return Status::OK();
}
// 给障碍物决策添加ignore决策
void SpeedDecider::AppendIgnoreDecision(Obstacle* obstacle) const {
ObjectDecisionType ignore_decision;
ignore_decision.mutable_ignore();
// 如果障碍物没有横向决策就添加ignore
if (!obstacle->HasLongitudinalDecision()) {
obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph", ignore_decision);
}
// 如果障碍物没有纵向决策就添加ignore
if (!obstacle->HasLateralDecision()) {
obstacle->AddLateralDecision("dp_st_graph", ignore_decision);
}
}
bool SpeedDecider::CreateStopDecision(const Obstacle& obstacle,
ObjectDecisionType* const stop_decision,
double stop_distance) const {
const auto& boundary = obstacle.path_st_boundary();
// TODO(all): this is a bug! Cannot mix reference s and path s!
// Replace boundary.min_s() with computed reference line s
// fence is set according to reference line s.
double fence_s = adc_sl_boundary_.end_s() + boundary.min_s() + stop_distance;
if (boundary.boundary_type() == STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {
fence_s = obstacle.PerceptionSLBoundary().start_s();
}
const double main_stop_s =
reference_line_info_->path_decision()->stop_reference_line_s();
if (main_stop_s < fence_s) {
ADEBUG << "Stop fence is further away, ignore.";
return false;
}
const auto fence_point = reference_line_->GetReferencePoint(fence_s);
// set STOP decision
auto* stop = stop_decision->mutable_stop();
stop->set_distance_s(stop_distance);
auto* stop_point = stop->mutable_stop_point();
stop_point->set_x(fence_point.x());
stop_point->set_y(fence_point.y());
stop_point->set_z(0.0);
stop->set_stop_heading(fence_point.heading());
if (boundary.boundary_type() == STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {
stop->set_reason_code(StopReasonCode::STOP_REASON_CLEAR_ZONE);
}
PerceptionObstacle::Type obstacle_type = obstacle.Perception().type();
ADEBUG << "STOP: obstacle_id[" << obstacle.Id() << "] obstacle_type["
<< PerceptionObstacle_Type_Name(obstacle_type) << "]";
return true;
}
bool SpeedDecider::CreateFollowDecision(
const Obstacle& obstacle, ObjectDecisionType* const follow_decision) const {
const double follow_speed = init_point_.v();
const double follow_distance_s =
-StGapEstimator::EstimateProperFollowingGap(follow_speed);
const auto& boundary = obstacle.path_st_boundary();
const double reference_s =
adc_sl_boundary_.end_s() + boundary.min_s() + follow_distance_s;
const double main_stop_s =
reference_line_info_->path_decision()->stop_reference_line_s();
if (main_stop_s < reference_s) {
ADEBUG << "Follow reference_s is further away, ignore.";
return false;
}
auto ref_point = reference_line_->GetReferencePoint(reference_s);
// set FOLLOW decision
auto* follow = follow_decision->mutable_follow();
follow->set_distance_s(follow_distance_s);
auto* fence_point = follow->mutable_fence_point();
fence_point->set_x(ref_point.x());
fence_point->set_y(ref_point.y());
fence_point->set_z(0.0);
follow->set_fence_heading(ref_point.heading());
PerceptionObstacle::Type obstacle_type = obstacle.Perception().type();
ADEBUG << "FOLLOW: obstacle_id[" << obstacle.Id() << "] obstacle_type["
<< PerceptionObstacle_Type_Name(obstacle_type) << "]";
return true;
}
bool SpeedDecider::CreateYieldDecision(
const Obstacle& obstacle, ObjectDecisionType* const yield_decision) const {
PerceptionObstacle::Type obstacle_type = obstacle.Perception().type();
double yield_distance = StGapEstimator::EstimateProperYieldingGap();
const auto& obstacle_boundary = obstacle.path_st_boundary();
const double yield_distance_s =
std::max(-obstacle_boundary.min_s(), -yield_distance);
const double reference_line_fence_s =
adc_sl_boundary_.end_s() + obstacle_boundary.min_s() + yield_distance_s;
const double main_stop_s =
reference_line_info_->path_decision()->stop_reference_line_s();
if (main_stop_s < reference_line_fence_s) {
ADEBUG << "Yield reference_s is further away, ignore.";
return false;
}
auto ref_point = reference_line_->GetReferencePoint(reference_line_fence_s);
// set YIELD decision
auto* yield = yield_decision->mutable_yield();
yield->set_distance_s(yield_distance_s);
yield->mutable_fence_point()->set_x(ref_point.x());
yield->mutable_fence_point()->set_y(ref_point.y());
yield->mutable_fence_point()->set_z(0.0);
yield->set_fence_heading(ref_point.heading());
ADEBUG << "YIELD: obstacle_id[" << obstacle.Id() << "] obstacle_type["
<< PerceptionObstacle_Type_Name(obstacle_type) << "]";
return true;
}
bool SpeedDecider::CreateOvertakeDecision(
const Obstacle& obstacle,
ObjectDecisionType* const overtake_decision) const {
const auto& velocity = obstacle.Perception().velocity();
const double obstacle_speed =
common::math::Vec2d::CreateUnitVec2d(init_point_.path_point().theta())
.InnerProd(Vec2d(velocity.x(), velocity.y()));
const double overtake_distance_s =
StGapEstimator::EstimateProperOvertakingGap(obstacle_speed,
init_point_.v());
const auto& boundary = obstacle.path_st_boundary();
const double reference_line_fence_s =
adc_sl_boundary_.end_s() + boundary.min_s() + overtake_distance_s;
const double main_stop_s =
reference_line_info_->path_decision()->stop_reference_line_s();
if (main_stop_s < reference_line_fence_s) {
ADEBUG << "Overtake reference_s is further away, ignore.";
return false;
}
auto ref_point = reference_line_->GetReferencePoint(reference_line_fence_s);
// set OVERTAKE decision
auto* overtake = overtake_decision->mutable_overtake();
overtake->set_distance_s(overtake_distance_s);
overtake->mutable_fence_point()->set_x(ref_point.x());
overtake->mutable_fence_point()->set_y(ref_point.y());
overtake->mutable_fence_point()->set_z(0.0);
overtake->set_fence_heading(ref_point.heading());
PerceptionObstacle::Type obstacle_type = obstacle.Perception().type();
ADEBUG << "OVERTAKE: obstacle_id[" << obstacle.Id() << "] obstacle_type["
<< PerceptionObstacle_Type_Name(obstacle_type) << "]";
return true;
}
bool SpeedDecider::CheckIsFollow(const Obstacle& obstacle,
const STBoundary& boundary) const {
const double obstacle_l_distance =
std::min(std::fabs(obstacle.PerceptionSLBoundary().start_l()),
std::fabs(obstacle.PerceptionSLBoundary().end_l()));
if (obstacle_l_distance > FLAGS_follow_min_obs_lateral_distance) {
return false;
}
// move towards adc
if (boundary.bottom_left_point().s() > boundary.bottom_right_point().s()) {
return false;
}
static constexpr double kFollowTimeEpsilon = 1e-3;
static constexpr double kFollowCutOffTime = 0.5;
if (boundary.min_t() > kFollowCutOffTime ||
boundary.max_t() < kFollowTimeEpsilon) {
return false;
}
// cross lane but be moving to different direction
if (boundary.max_t() - boundary.min_t() < FLAGS_follow_min_time_sec) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool SpeedDecider::CheckStopForPedestrian(const Obstacle& obstacle) const {
const auto& perception_obstacle = obstacle.Perception();
// 如果障碍物决策类型不是PEDESTRIAN,退出,返回false
if (perception_obstacle.type() != PerceptionObstacle::PEDESTRIAN) {
return false;
}
const auto& obstacle_sl_boundary = obstacle.PerceptionSLBoundary();
// 如果障碍物的ends小于starts,退出,返回false
if (obstacle_sl_boundary.end_s() < adc_sl_boundary_.start_s()) {
return false;
}
// 从PlanningContext读取行人停止时间
auto* mutable_speed_decider_status = injector_->planning_context()
->mutable_planning_status()
->mutable_speed_decider();
// 建立一个存放障碍物id对应行人停止时间的哈希表
std::unordered_map<std::string, double> stop_time_map;
for (const auto& pedestrian_stop_time :
mutable_speed_decider_status->pedestrian_stop_time()) {
// 逐个添加
stop_time_map[pedestrian_stop_time.obstacle_id()] =
pedestrian_stop_time.stop_timestamp_sec();
}
const std::string& obstacle_id = obstacle.Id();
// 更新静态行人的停车时间戳以查看计时器检查静态行人的停止计时器
static constexpr double kSDistanceStartTimer = 10.0;
static constexpr double kMaxStopSpeed = 0.3;
static constexpr double kPedestrianStopTimeout = 4.0;
bool result = true;
if (obstacle.path_st_boundary().min_s() < kSDistanceStartTimer) {
// 计算障碍物的速度
const auto obstacle_speed = std::hypot(perception_obstacle.velocity().x(),
perception_obstacle.velocity().y());
// 如果障碍物的速度大于最大停止速度,从stop_time_map删除该障碍物
if (obstacle_speed > kMaxStopSpeed) {
stop_time_map.erase(obstacle_id);
}
// 如果障碍物的速度小于最大停止速度
else {
// 判断stop_time_map中是否已有这个障碍物,如果没有,进入
if (stop_time_map.count(obstacle_id) == 0) {
// 添加时间戳
stop_time_map[obstacle_id] = Clock::NowInSeconds();
ADEBUG << "add timestamp: obstacle_id[" << obstacle_id << "] timestamp["
<< Clock::NowInSeconds() << "]";
}
// 如果已经有这个障碍物了
else {
// 检查时间戳
double stop_timer = Clock::NowInSeconds() - stop_time_map[obstacle_id];
ADEBUG << "stop_timer: obstacle_id[" << obstacle_id << "] stop_timer["
<< stop_timer << "]";
// 如果停止时间大于行人停止时间,退出,返回false
if (stop_timer >= kPedestrianStopTimeout) {
result = false;
}
}
}
}
// 将行人停止时间写入PlanningContext
mutable_speed_decider_status->mutable_pedestrian_stop_time()->Clear();
for (const auto& stop_time : stop_time_map) {
auto pedestrian_stop_time =
mutable_speed_decider_status->add_pedestrian_stop_time();
pedestrian_stop_time->set_obstacle_id(stop_time.first);
pedestrian_stop_time->set_stop_timestamp_sec(stop_time.second);
}
return result;
}
} // namespace planning
} // namespace apollo
流程图总结这个函数的主要逻辑为:
(注意这个stlocation是adc在st图上位于障碍物的什么位置
above:adc在st图上位于障碍物的上方
below:adc在st图上位于障碍物的下方
cross:adc在st图上位与障碍物有交叉)
5. SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
SpeedBoundsFinalDecider对应的Decider同样是SpeedBoundsDecider,和SpeedBoundsPrioriDecider不同的是配置参数,从Apollo中的默认配置参数来看,SpeedBoundsFinalDecider会根据DP过程生成的决策结果和更小的boundary_buffer生成更加精确的STBoundary。
default_task_config: {
task_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER
speed_bounds_decider_config {
total_time: 7.0
boundary_buffer: 0.25
max_centric_acceleration_limit: 2.0
point_extension: 0.0
lowest_speed: 2.5
static_obs_nudge_speed_ratio: 0.6
dynamic_obs_nudge_speed_ratio: 0.8
}
}
default_task_config: {
task_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
speed_bounds_decider_config {
total_time: 7.0
boundary_buffer: 0.1
max_centric_acceleration_limit: 2.0
point_extension: 0.0
lowest_speed: 2.5
static_obs_nudge_speed_ratio: 0.6
dynamic_obs_nudge_speed_ratio: 0.8
}
}
6. PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
最后这里关于优化,速度优化是既有二次规划也有非线性优化,我这里在知乎上找了几篇大佬的文章。
可以按照下面链接依次学习:
Planning 基于二次规划的速度规划
Planning 基于非线性规划的速度规划
Apollo 6.0的EM Planner (4):速度规划的二次规划QP过程文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-524634.html
最后,关于st规划先学习到这里了。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-524634.html
到了这里,关于Apollo Planning学习(9)-------速度规划的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!