目录
一、前期准备
1. 搭建语言类
2. 文本处理函数
3. 文件读取函数
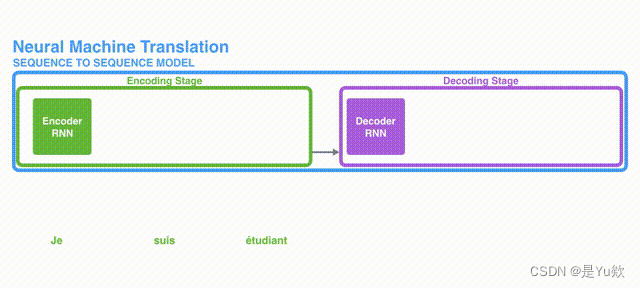
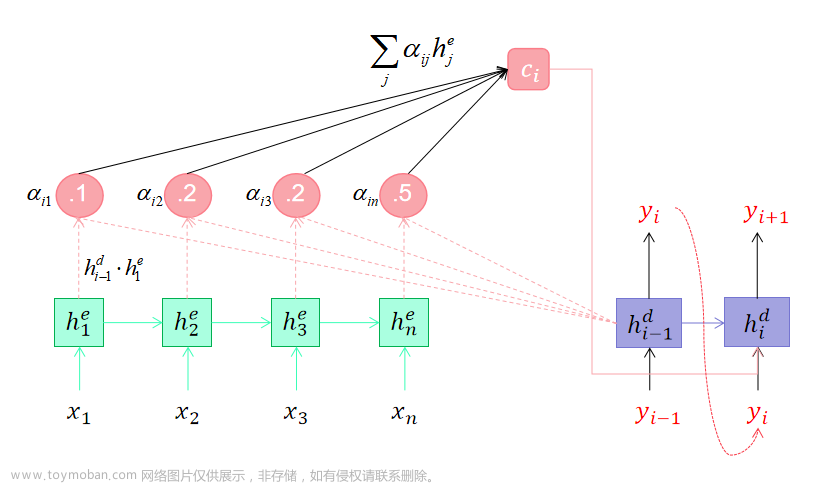
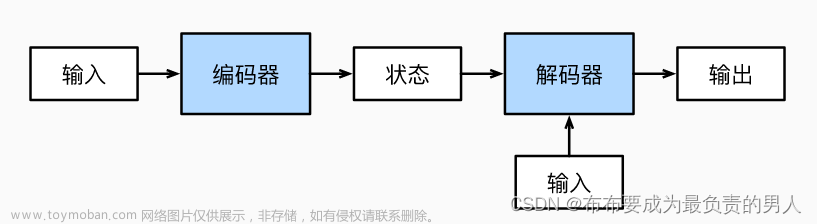
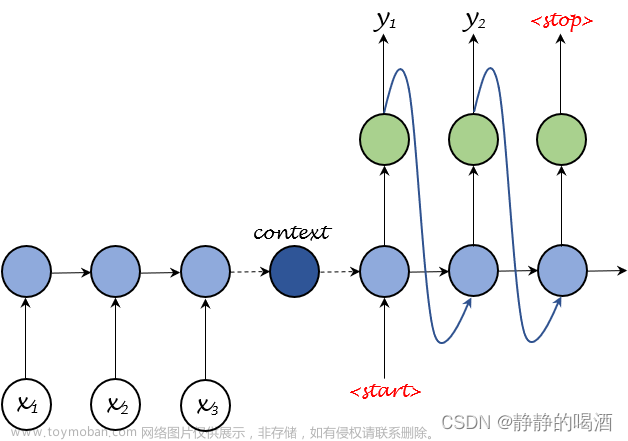
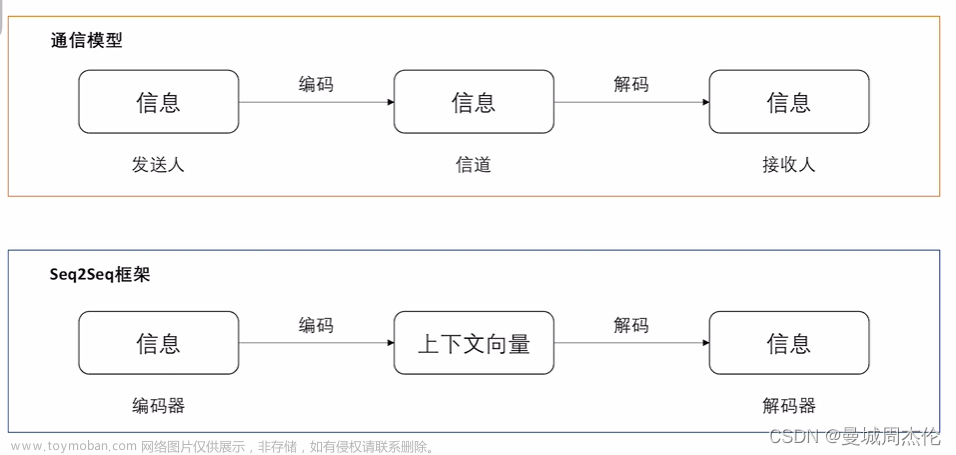
二、Seq2Seq 模型
1. 编码器(Encoder)
2. 解码器(Decoder)
三、训练
1. 数据预处理
2. 训练函数
四、训练与评估
🍨 本文为[🔗365天深度学习训练营]内部限免文章(版权归 *K同学啊* 所有)
🍖 作者:[K同学啊]
📌 本周任务:
●结合训练中N5周的内容理解本文代码
数据集:eng-fra.txt

一、前期准备
from __future__ import unicode_literals, print_function, division
from io import open
import unicodedata
import string
import re
import random
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch import optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(device)
cuda
1. 搭建语言类
定义了两个常量 SOS_token 和 EOS_token,其分别代表序列的开始和结束。 Lang 类,用于方便对语料库进行操作:
●word2index 是一个字典,将单词映射到索引
●word2count 是一个字典,记录单词出现的次数
●index2word 是一个字典,将索引映射到单词
●n_words 是单词的数量,初始值为 2,因为序列开始和结束的单词已经被添加
SOS_token = 0
EOS_token = 1
# 语言类,方便对语料库进行操作
class Lang:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
self.word2index = {}
self.word2count = {}
self.index2word = {0: "SOS", 1: "EOS"}
self.n_words = 2 # Count SOS and EOS
def addSentence(self, sentence):
for word in sentence.split(' '):
self.addWord(word)
def addWord(self, word):
if word not in self.word2index:
self.word2index[word] = self.n_words
self.word2count[word] = 1
self.index2word[self.n_words] = word
self.n_words += 1
else:
self.word2count[word] += 1
2. 文本处理函数
def unicodeToAscii(s):
return ''.join(
c for c in unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s)
if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn'
)
# 小写化,剔除标点与非字母符号
def normalizeString(s):
s = unicodeToAscii(s.lower().strip())
s = re.sub(r"([.!?])", r" \1", s)
s = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z.!?]+", r" ", s)
return s
3. 文件读取函数
def readLangs(lang1, lang2, reverse=False):
print("Reading lines...")
# 以行为单位读取文件
lines = open('%s-%s.txt'%(lang1,lang2), encoding='utf-8').\
read().strip().split('\n')
# 将每一行放入一个列表中
# 一个列表中有两个元素,A语言文本与B语言文本
pairs = [[normalizeString(s) for s in l.split('\t')] for l in lines]
# 创建Lang实例,并确认是否反转语言顺序
if reverse:
pairs = [list(reversed(p)) for p in pairs]
input_lang = Lang(lang2)
output_lang = Lang(lang1)
else:
input_lang = Lang(lang1)
output_lang = Lang(lang2)
return input_lang, output_lang, pairs
MAX_LENGTH = 10 # 定义语料最长长度
eng_prefixes = (
"i am ", "i m ",
"he is", "he s ",
"she is", "she s ",
"you are", "you re ",
"we are", "we re ",
"they are", "they re "
)
def filterPair(p):
return len(p[0].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and \
len(p[1].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and p[1].startswith(eng_prefixes)
def filterPairs(pairs):
# 选取仅仅包含 eng_prefixes 开头的语料
return [pair for pair in pairs if filterPair(pair)]
def prepareData(lang1, lang2, reverse=False):
# 读取文件中的数据
input_lang, output_lang, pairs = readLangs(lang1, lang2, reverse)
print("Read %s sentence pairs" % len(pairs))
# 按条件选取语料
pairs = filterPairs(pairs[:])
print("Trimmed to %s sentence pairs" % len(pairs))
print("Counting words...")
# 将语料保存至相应的语言类
for pair in pairs:
input_lang.addSentence(pair[0])
output_lang.addSentence(pair[1])
# 打印语言类的信息
print("Counted words:")
print(input_lang.name, input_lang.n_words)
print(output_lang.name, output_lang.n_words)
return input_lang, output_lang, pairs
input_lang, output_lang, pairs = prepareData('eng', 'fra', True)
print(random.choice(pairs))

二、Seq2Seq 模型
1. 编码器(Encoder)
class EncoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size):
super(EncoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size)
self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
embedded = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1)
output = embedded
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden)
return output, hidden
def initHidden(self):
return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)
2. 解码器(Decoder)
class DecoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size):
super(DecoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_size, hidden_size)
self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size)
self.out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
output = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1)
output = F.relu(output)
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden)
output = self.softmax(self.out(output[0]))
return output, hidden
def initHidden(self):
return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)
三、训练
1. 数据预处理
def indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence):
return [lang.word2index[word] for word in sentence.split(' ')]
# 将数字化的文本,转化为tensor数据
def tensorFromSentence(lang, sentence):
indexes = indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence)
indexes.append(EOS_token)
return torch.tensor(indexes, dtype=torch.long, device=device).view(-1, 1)
# 输入pair文本,输出预处理好的数据
def tensorsFromPair(pair):
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, pair[0])
target_tensor = tensorFromSentence(output_lang, pair[1])
return (input_tensor, target_tensor)
2. 训练函数
teacher_forcing_ratio = 0.5
def train(input_tensor, target_tensor,
encoder, decoder,
encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer,
criterion, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
# 编码器初始化
encoder_hidden = encoder.initHidden()
# grad属性归零
encoder_optimizer.zero_grad()
decoder_optimizer.zero_grad()
input_length = input_tensor.size(0)
target_length = target_tensor.size(0)
# 用于创建一个指定大小的全零张量(tensor),用作默认编码器输出
encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder.hidden_size, device=device)
loss = 0
# 将处理好的语料送入编码器
for ei in range(input_length):
encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder(input_tensor[ei], encoder_hidden)
encoder_outputs[ei] = encoder_output[0, 0]
# 解码器默认输出
decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device)
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden
use_teacher_forcing = True if random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratio else False
# 将编码器处理好的输出送入解码器
if use_teacher_forcing:
# Teacher forcing: Feed the target as the next input
for di in range(target_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden = decoder(decoder_input, decoder_hidden)
loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_tensor[di])
decoder_input = target_tensor[di] # Teacher forcing
else:
# Without teacher forcing: use its own predictions as the next input
for di in range(target_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden = decoder(decoder_input, decoder_hidden)
topv, topi = decoder_output.topk(1)
decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach() # detach from history as input
loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_tensor[di])
if decoder_input.item() == EOS_token:
break
loss.backward()
encoder_optimizer.step()
decoder_optimizer.step()
return loss.item() / target_length
import time
import math
def asMinutes(s):
m = math.floor(s / 60)
s -= m * 60
return '%dm %ds' % (m, s)
def timeSince(since, percent):
now = time.time()
s = now - since
es = s / (percent)
rs = es - s
return '%s (- %s)' % (asMinutes(s), asMinutes(rs))
def trainIters(encoder,decoder,n_iters,print_every=1000,
plot_every=100,learning_rate=0.01):
start = time.time()
plot_losses = []
print_loss_total = 0 # Reset every print_every
plot_loss_total = 0 # Reset every plot_every
encoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(encoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
decoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(decoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# 在 pairs 中随机选取 n_iters 条数据用作训练集
training_pairs = [tensorsFromPair(random.choice(pairs)) for i in range(n_iters)]
criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
for iter in range(1, n_iters + 1):
training_pair = training_pairs[iter - 1]
input_tensor = training_pair[0]
target_tensor = training_pair[1]
loss = train(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder,
decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion)
print_loss_total += loss
plot_loss_total += loss
if iter % print_every == 0:
print_loss_avg = print_loss_total / print_every
print_loss_total = 0
print('%s (%d %d%%) %.4f' % (timeSince(start, iter / n_iters),
iter, iter / n_iters * 100, print_loss_avg))
if iter % plot_every == 0:
plot_loss_avg = plot_loss_total / plot_every
plot_losses.append(plot_loss_avg)
plot_loss_total = 0
return plot_losses
四、训练与评估
hidden_size = 256
encoder1 = EncoderRNN(input_lang.n_words, hidden_size).to(device)
attn_decoder1 = DecoderRNN(hidden_size, output_lang.n_words).to(device)
plot_losses = trainIters(encoder1, attn_decoder1, 100000, print_every=5000)
 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-526822.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-526822.html
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#隐藏警告
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") # 忽略警告信息
# plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 100 # 分辨率
epochs_range = range(len(plot_losses))
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3))
plt.subplot(1, 1, 1)
plt.plot(epochs_range, plot_losses, label='Training Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training Loss')
plt.show()
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-526822.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-526822.html
到了这里,关于NLP实战6:seq2seq翻译实战-Pytorch复现-小白版的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!