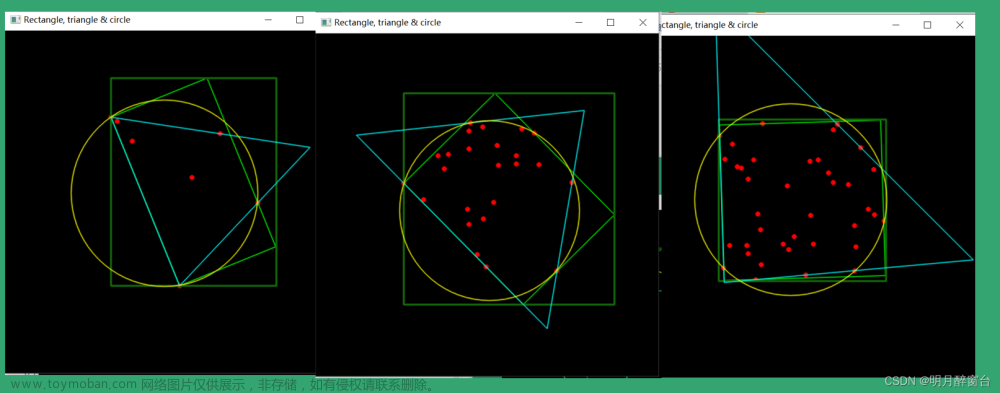
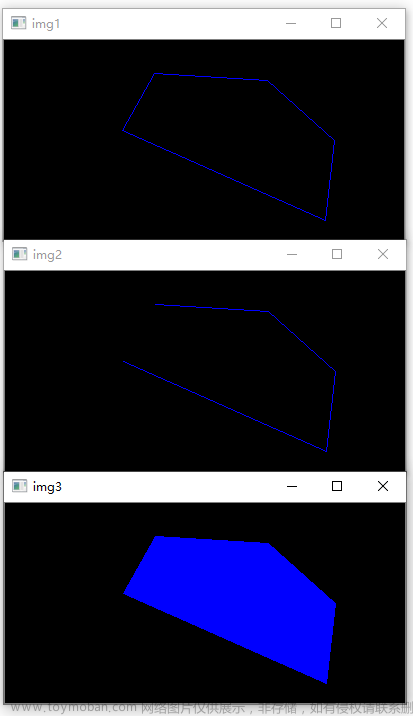
多边形边的插值
算法描述及提问:
给定一个最小长度,对多边形的每一条边不断的对半插值,使得插值后的每一条边都要不大于最小长度。
测试ChatGPT - 中文版 VSCode插件。
Chat GPT给出的结果:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
struct Point {
double x;
double y;
};
double distance(const Point& p1, const Point& p2) {
double dx = p2.x - p1.x;
double dy = p2.y - p1.y;
return std::sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
std::vector<Point> interpolatePolygon(const std::vector<Point>& polygon, double minLength) {
std::vector<Point> interpolatedPoints;
for (size_t i = 0; i < polygon.size(); i++) {
size_t j = (i + 1) % polygon.size();
double segmentDistance = distance(polygon[i], polygon[j]);
if (segmentDistance <= minLength) {
interpolatedPoints.push_back(polygon[i]); // 将原始顶点添加到插值点列表
} else {
int numInterpolatedPoints = static_cast<int>(segmentDistance / minLength);
double stepSize = segmentDistance / (numInterpolatedPoints + 1);
for (int k = 1; k <= numInterpolatedPoints; k++) {
double factor = stepSize * k / segmentDistance;
double newX = polygon[i].x + factor * (polygon[j].x - polygon[i].x);
double newY = polygon[i].y + factor * (polygon[j].y - polygon[i].y);
interpolatedPoints.push_back({newX, newY}); // 添加插值点到列表
}
}
}
return interpolatedPoints;
}
int main() {
// 定义多边形的顶点
std::vector<Point> polygon = {
{0.0, 0.0}, {2.0, 0.0}, {2.0, 2.0}, {0.0, 2.0}
};
double minLength = 1.0;
// 进行边均匀插值并打印结果
std::vector<Point> interpolatedPoints = interpolatePolygon(polygon, minLength);
for (const auto& point : interpolatedPoints) {
std::cout << "Interpolated Point: (" << point.x << ", " << point.y << ")\n";
}
return 0;
}

显然是错误的。
正确的结果:
修改后的结果1
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
struct Point {
double x;
double y;
};
double distance(const Point& p1, const Point& p2) {
double dx = p2.x - p1.x;
double dy = p2.y - p1.y;
return std::sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
std::vector<Point> interpolatePolygon(const std::vector<Point>& polygon, double minLength) {
std::vector<Point> interpolatedPoints;
for (size_t i = 0; i < polygon.size(); i++) {
size_t j = (i + 1) % polygon.size();
double segmentDistance = distance(polygon[i], polygon[j]);
if (segmentDistance <= minLength) {
interpolatedPoints.push_back(polygon[i]); // 将原始顶点添加到插值点列表
}
else {
int numInterpolatedPoints = ceil(segmentDistance / minLength);
double stepSize = segmentDistance / numInterpolatedPoints;
for (int k = 1; k <= numInterpolatedPoints; k++) {
double factor = stepSize * k / segmentDistance;
double newX = polygon[i].x + factor * (polygon[j].x - polygon[i].x);
double newY = polygon[i].y + factor * (polygon[j].y - polygon[i].y);
interpolatedPoints.push_back({ newX, newY }); // 添加插值点到列表
}
}
}
return interpolatedPoints;
}
int main() {
// 定义多边形的顶点
std::vector<Point> polygon = {
{0.0, 0.0}, {2.0, 0.0}, {2.0, 2.0}, {0.0, 2.0}
};
double minLength = 2;
// 进行边均匀插值并打印结果
std::vector<Point> interpolatedPoints = interpolatePolygon(polygon, minLength);
for (const auto& point : interpolatedPoints) {
std::cout << "Interpolated Point: (" << point.x << ", " << point.y << ")\n";
}
return 0;
}
修改后的结果2
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
struct Point {
double x;
double y;
};
double distance(const Point& p1, const Point& p2) {
double dx = p2.x - p1.x;
double dy = p2.y - p1.y;
return std::sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
std::vector<Point> interpolatePolygon(const std::vector<Point>& polygon, double minLength) {
std::vector<Point> interpolatedPoints;
int numVertices = polygon.size();
std::vector<double> segmentLengths(numVertices);
// 计算各边长度
for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) {
int nextIndex = (i + 1) % numVertices;
segmentLengths[i] = distance(polygon[i], polygon[nextIndex]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) {
int nextIndex = (i + 1) % numVertices;
double dx = polygon[nextIndex].x - polygon[i].x;
double dy = polygon[nextIndex].y - polygon[i].y;
double segmentDistance = distance(polygon[i], polygon[nextIndex]);
interpolatedPoints.push_back(polygon[i]);
if (segmentDistance > minLength) {
int n = ceil(segmentDistance / minLength);
int p = ceil(n / 2);
for (int j = 0; j < p*2-1; j++) {
double newX = polygon[i].x + pow(0.5,p) * dx*(1+j);
double newY = polygon[i].y + pow(0.5,p) * dy*(1+j);
interpolatedPoints.push_back({ newX, newY });
}
}
}
return interpolatedPoints;
}
int main() {
// 定义多边形的顶点
std::vector<Point> polygon = {
{0.0, 0.0}, {2.0, 0.0}, {2.0, 2.0}, {0.0, 2.0}
};
double minLength = 1.5;
// 进行边均匀插值并打印结果
std::vector<Point> interpolatedPoints = interpolatePolygon(polygon, minLength);
for (const auto& point : interpolatedPoints) {
std::cout << "Interpolated Point: (" << point.x << ", " << point.y << ")\n";
}
return 0;
}
总结
使用ChatGPT-中文版 VSCode,基本可以写出一个简单的算法,但是正确与否还需要个人Debug及修改,可以节省一部分时间和精力。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-527665.html
参考
1、https://blog.csdn.net/mrbaolong/article/details/131585575?csdn_share_tail=%7B%22type%22%3A%22blog%22%2C%22rType%22%3A%22article%22%2C%22rId%22%3A%22131585575%22%2C%22source%22%3A%22mrbaolong%22%7D文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-527665.html
到了这里,关于多边形边的插值的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!