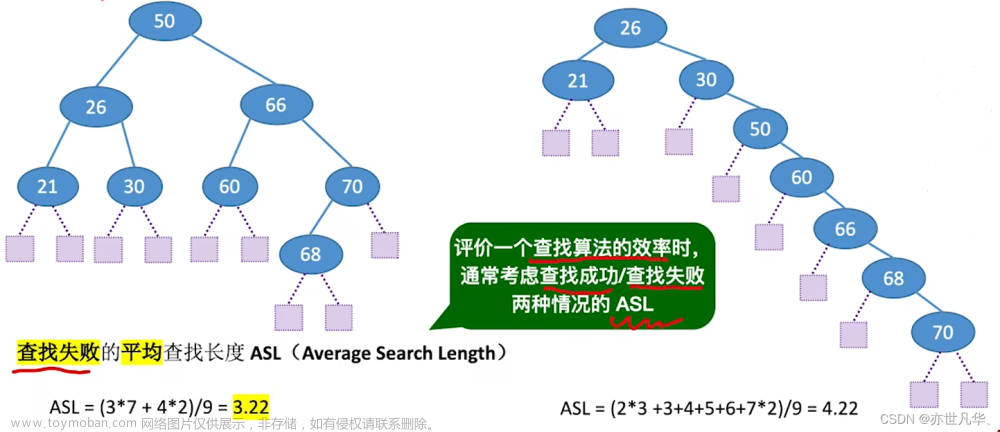
洛谷 P3369文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-534519.html
#include <iostream>
#include <istream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <chrono>
#include <ctime>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
#include <string>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iomanip>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <functional>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
template <typename _Type>
class Splay {
private:
template <typename _T>
struct SplayNode {
SplayNode() :data(), l(nullptr), r(nullptr),fa(nullptr), c(1), sub(1) {}
_T data;
SplayNode* l, * r,*fa;
int c, sub;//副本个数 子树节点个数
};
public:
typedef SplayNode<_Type> value_Type;
typedef SplayNode<_Type>* point;
public:
Splay() :m_root(nullptr), m_tot(0) {}
~Splay() { clear(m_root); }
void clear(typename Splay<_Type>::point& input);
public:
int GetSubCnt(typename Splay<_Type>::point node) {
if (node == nullptr) return 0;
return node->sub;
}
void flush(typename Splay<_Type>::point node) {
if (node == nullptr) return;
node->sub = GetSubCnt(node->l) + GetSubCnt(node->r) + node->c;
}
typename Splay<_Type>::point GetNode(_Type&& input);
public:
typename Splay<_Type>::point insert(_Type input);//插入
void remove(_Type input);//删除
typename Splay<_Type>::point find(_Type x);//查找x
typename Splay<_Type>::point splay(typename Splay<_Type>::point& input);//
typename Splay<_Type>::point findKth(int k); //查找第k大
int findRank(_Type x);
typename Splay<_Type>::point findPre(_Type x); //查找x前驱
typename Splay<_Type>::point findNext(_Type x);//查找x后继
public:
void rotate_left(typename Splay<_Type>::point& input); //左旋转
void rotate_right(typename Splay<_Type>::point& input); //右旋转
private:
typename Splay<_Type>::point m_root;
int m_tot;
};
//
template <class _Type>
typename Splay<_Type>::point Splay<_Type>::GetNode(_Type&& input) {
Splay<_Type>::point ret = new Splay<_Type>::value_Type();
if (ret)ret->data = input, m_tot++;
return ret;
}
template <class _Type>
void Splay<_Type>::clear(typename Splay<_Type>::point& input) {
if (input == nullptr) return;
clear(input->l);
clear(input->r);
input->l = nullptr;
input->r = nullptr;
delete(input);
input = nullptr;
}
template <class _Type>
typename Splay<_Type>::point Splay<_Type>::findKth(int k) //查找第k大
{
if (m_root == nullptr || k > m_tot) return nullptr;
Splay<_Type>::point cur = m_root;
while (cur) {
int l = GetSubCnt(cur->l);
int r = GetSubCnt(cur->r);
int m = cur->c;
if (k <= l) {
cur = cur->l;
}
else if (k <= l + m) {
return splay(cur);
}
else {
k -= l + m;
cur = cur->r;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
template <class _Type>
int Splay<_Type>::findRank(_Type x) {
Splay<_Type>::point cur = m_root;
int ans = 0;
while (cur) {
if (cur->data > x) {
cur = cur->l;
}
else if (cur->data < x) {
ans += GetSubCnt(cur->l) + cur->c;
cur = cur->r;
}
else break;
}
if (cur == nullptr) return ans + 1;
ans += GetSubCnt(cur->l) + 1;
splay(cur);
return ans;
}
template <class _Type>
typename Splay<_Type>::point Splay<_Type>::findPre(_Type x) //查找x前驱
{
Splay<_Type>::point cur = m_root, ret = nullptr;
while (cur) {
if (cur->data < x)ret = cur, cur = cur->r;
else cur = cur->l;
}
return splay(ret);
}
template <class _Type>
typename Splay<_Type>::point Splay<_Type>::findNext(_Type x)//查找x后继
{
Splay<_Type>::point cur = m_root, ret = nullptr;
while (cur) {
if (cur->data > x)ret = cur, cur = cur->l;
else cur = cur->r;
}
return splay(ret);
}
template <class _Type>
typename Splay<_Type>::point Splay<_Type>::find(_Type x)//查找x
{
Splay<_Type>::point cur = m_root;
while (cur) {
if (cur->data == x) {
break;
}
else if (cur->data > x) {
cur = cur->l;
}
else {
cur = cur->r;
}
}
return splay(cur);
}
template <class _Type>
typename Splay<_Type>::point Splay<_Type>::insert(_Type input)//插入
{
if (m_root == nullptr) return m_root = GetNode(std::forward<_Type>(input));
else {
Splay<_Type>::point cur = m_root;
while (cur) {
if (cur->data == input) {
cur->c++;
m_tot++;
break;
}
else if (cur->data > input) {
if (cur->l)cur = cur->l;
else {
cur->l = GetNode(std::forward<_Type>(input));
cur->l->fa = cur;
cur = cur->l;
break;
}
}
else {
if (cur->r)cur = cur->r;
else {
cur->r = GetNode(std::forward<_Type>(input));
cur->r->fa = cur;
cur = cur->r;
break;
}
}
}
return splay(cur);
}
}
template <class _Type>
void Splay<_Type>::remove(_Type input)//删除
{
Splay<_Type>::point p = find(input), l,r;
if (p == nullptr) return;
p = splay(p);
if (--p->c > 0)return;
if (p->l == nullptr) {
m_root = p->r;
if(p->r)p->r->fa = nullptr;
}
else if (p->r == nullptr) {
m_root = p->l;
if (p->l)p->l->fa = nullptr;
}
else {
//分裂成2棵子树
l = p->l;
r = p->r;
l->fa = r->fa = nullptr;
m_root = l;
l = findPre(p->data); //查找左子树的前驱 相当于左子树的最大值 没有右子树
//合并2棵子树
l->r = r;
r->fa = l;
}
delete p;
m_tot--;
flush(m_root);
}
template <class _Type>
typename Splay<_Type>::point Splay<_Type>::splay(typename Splay<_Type>::point& input)
{
if (input == nullptr) return nullptr;
while (input->fa) {
Splay<_Type>::point fa = input->fa, ffa = fa->fa;
bool bol = fa->l == input;
//父节点是根节点
if (!ffa) {
//左子树
if (bol) rotate_right(fa);
else rotate_left(fa);
}
else {
bool bofl = ffa->l == fa;
//LL
if (bofl && bol) {
rotate_right(ffa);
rotate_right(fa);
}
else if (!bofl && !bol) {
//RR
rotate_left(ffa);
rotate_left(fa);
}
else if (bofl && !bol) {
//LR
rotate_left(fa);
rotate_right(ffa);
}
else {
//RL
rotate_right(fa);
rotate_left(ffa);
}
}
}
return m_root = input;
}
template <class _Type>
void Splay<_Type>::rotate_left(typename Splay<_Type>::point& node)//左旋转
{
if (node == nullptr || node->r == nullptr) return;
Splay::point r = node->r;
Splay::point rl = r->l;
if (node->fa) {
if (node->fa->l == node) node->fa->l = r;
else node->fa->r = r;
}
r->fa = node->fa;
node->fa = r;
r->l = node;
node->r = rl;
if(rl)rl->fa = node;
node = r;
flush(node->l);
flush(node);
}
template <class _Type>
void Splay<_Type>::rotate_right(typename Splay<_Type>::point& node)//右旋转
{
if (node == nullptr || node->l == nullptr) return;
Splay::point l = node->l;
Splay::point lr = l->r;
if (node->fa) {
if (node->fa->l == node) node->fa->l = l;
else node->fa->r = l;
}
l->fa = node->fa;
node->fa = l;
l->r = node;
node->l = lr;
if(lr)lr->fa = node;
node = l;
flush(node->r);
flush(node);
}
//void rfIO()
//{
// FILE *stream1;
// freopen_s(&stream1,"in.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen_s(&stream1,"out.txt", "w", stdout);
//}
inline int read(int& x) {
char ch = getchar();
int f = 1; x = 0;
while (ch > '9' || ch < '0') { if (ch == '-')f = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') { x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); }
return x * f;
}
//void ReadFile() {
// FILE* stream1;
// freopen_s(&stream1,"in.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen_s(&stream1,"out.txt", "w", stdout);
//}
static auto speedup = []() {ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr); return nullptr; }();
int n;
int main()
{
Splay<int> tree;
cin >> n;
int a, b;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a >> b;
switch (a)
{
case 1:tree.insert(b); break;
case 2:tree.remove(b); break;
case 3:cout << tree.findRank(b) << endl; break;
case 4:
{
Splay<int>::point ret = tree.findKth(b);
if (ret == nullptr) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << ret->data << endl;
break;
}
case 5:
{
Splay<int>::point ret = tree.findPre(b);
if (ret == nullptr) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << ret->data << endl;
break;
}
case 6:
{
Splay<int>::point ret = tree.findNext(b);
if (ret == nullptr) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << ret->data << endl;
break;
}
default:
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-534519.html
到了这里,关于splay树的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!