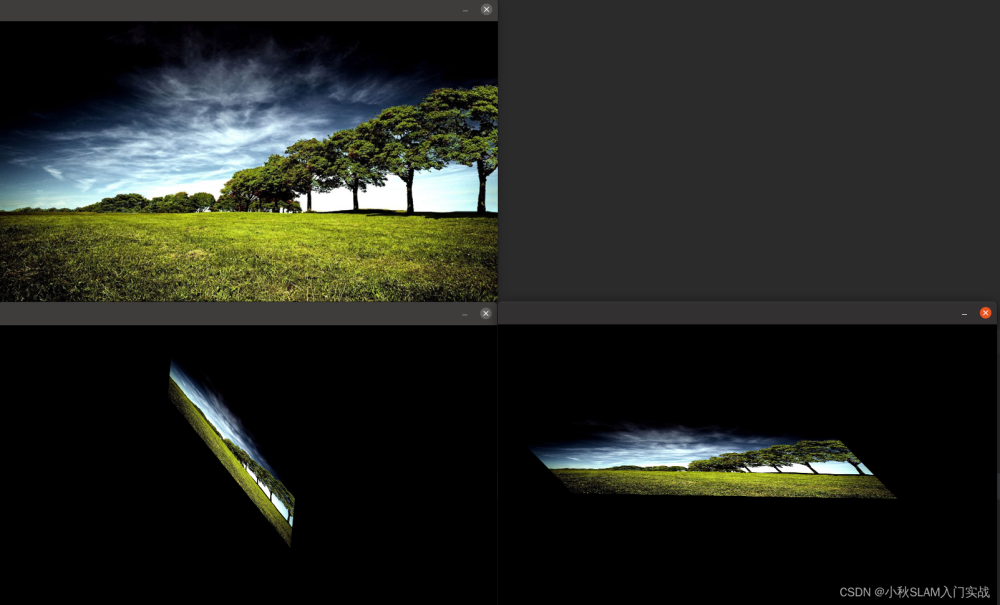
#python opencv 多尺度,平移,缩放,旋转等模板匹配法
##多尺度缩放与旋转的均为模板图
import cv2
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import time
# 图片旋转函数-保持图像不被裁剪且去除黑边
def ImageRotate(img, angle,borderValue=255): # img:输入图片;newIm:输出图片;angle:旋转角度(°)
height, width = img.shape[:2] # 输入(H,W,C),取 H,W 的值
center = (width // 2, height // 2) # 绕图片中心进行旋转
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, -angle, 1.0)
cos = np.abs(M[0, 0])
sin = np.abs(M[0, 1])
nW = int((height * sin) + (width * cos))
nH = int((height * cos) + (width * sin))
M[0, 2] += (nW / 2) - center[0]
M[1, 2] += (nH / 2) - center[1]
image_rotation = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (nW, nH),borderValue=borderValue)
return image_rotation
#金字塔下采样---弃用(没进行深入理解)
def ImagePyrDown(image,NumLevels):
for i in range(NumLevels):
image = cv2.pyrDown(image) #pyrDown下采样
return image
# 旋转匹配函数(输入参数分别为模板图像、待匹配图像)
def RatationMatch(modelpicture, searchpicture):
searchtmp, modeltmp = searchpicture.copy(),modelpicture.copy()
# 使用matchTemplate对原始灰度图像和图像模板进行匹配
mask = np.zeros_like(modeltmp, np.uint8)
pts = np.where(modeltmp == 0)
mask[pts[0], pts[1]] = 255
print('searchtmp:',searchtmp.shape,modeltmp.shape)
res = cv2.matchTemplate(searchtmp, modeltmp, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED,mask)
min_val, max_val, min_indx, max_indx = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)
location = max_indx
temp = max_val
angle = 0 # 当前旋转角度记录为0
tic = time.time()
# 以步长为5进行第一次粗循环匹配
for i in range(-90, 181, 5):
newIm = ImageRotate(modeltmp, i)
mask = np.zeros_like(newIm, np.uint8)
pts = np.where(newIm == 0)
mask[pts[0], pts[1]] = 255
#cv2.imshow('--mask', mask)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
#cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#mask[newIm[:]==0]=255
res = cv2.matchTemplate(searchtmp, newIm, cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED,mask)
min_val, max_val, min_indx, max_indx = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)
#print(min_val, max_val, min_indx, max_indx)
if max_val > temp:
location = max_indx
temp = max_val
angle = i
#print('angle:',angle)
#draw_result(searchtmp, newIm, (location[0], location[1]))
#modelpicture00 = ImageRotate(modelpicture, angle)
#cv2.imshow('--modelpicture00', modelpicture00)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
#cv2.destroyAllWindows()
toc = time.time()
#ss = ImageRotate(modelpicture, angle)
#draw_result(searchpicture, ss, (location[0],location[1]))
print('第一次粗循环匹配所花时间为:' + str(1000 * (toc - tic)) + 'ms'+'------angle:'+str(angle))
tic = time.time()
# 在当前最优匹配角度周围10的区间以1为步长循环进行循环匹配计算
for j in range(angle - 5, angle + 6):
newIm = ImageRotate(modeltmp, j)
#print('jj:',j)
res = cv2.matchTemplate(searchtmp, newIm, cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED)
min_val, max_val, min_indx, max_indx = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)
if max_val > temp:
location = max_indx
temp = max_val
angle = j
#print('angel2:',angle)
#draw_result(searchtmp, newIm, (location[0], location[1]))
toc = time.time()
print('在当前最优匹配角度周围10的区间以1为步长循环进行循环匹配所花时间为:' + str(1000 * (toc - tic)) + 'ms'+'-----angle:'+str(angle))
tic = time.time()
# 在当前最优匹配角度周围2的区间以0.1为步长进行循环匹配计算
k_angle = angle - 1
for k in range(0, 19):
k_angle = k_angle + 0.1
#print('k_angle:',k_angle)
newIm = ImageRotate(modeltmp, k_angle)
res = cv2.matchTemplate(searchtmp, newIm, cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED)
min_val, max_val, min_indx, max_indx = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)
if max_val > temp:
location = max_indx
temp = max_val
angle = k_angle
#draw_result(searchtmp, newIm, (location[0], location[1]))
toc = time.time()
print('在当前最优匹配角度周围2的区间以0.1为步长进行循环匹配所花时间为:' + str(1000 * (toc - tic)) + 'ms'+"---angle:"+str(angle))
location_x = location[0]
location_y = location[1]
#angle = -angle
match_point = {'angle': angle,"temp":temp, 'point': (location_x, location_y)}
#print(match_point)
return match_point
def scale_resize(img,scale):
# 要缩小图像,建议选择:cv2.INTER_AREA;如果要放大图像,cv2.INTER_CUBIC效果更好但是速度慢
if scale <= 1:
method = cv2.INTER_AREA
else:
method = cv2.INTER_CUBIC
newh = int(img.shape[1] * scale)
neww = int(img.shape[0] * scale)
new_dim = [neww, newh]
resizedimg = cv2.resize(img, new_dim, method)
return resizedimg
def run_main(templeimg, img):
imgW,imgH = img.shape[0],img.shape[1]
#初试:使用matchTemplate对原始灰度图像和图像模板进行匹配
mask = np.zeros_like(templeimg, np.uint8)
pts = np.where(templeimg == 0)
mask[pts[0], pts[1]] = 255
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img, templeimg, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED,mask)
min_val, max_val, min_indx, max_indx = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)
location_best = max_indx
temp_best = max_val
angle_best = 0 # 当前旋转角度记录为0
best_scale_img = img.copy()
#print(location_best)
for scale in np.linspace(3.0, 0, 100)[::-1]:
#要缩小图像,建议选择:cv2.INTER_AREA;如果要放大图像,cv2.INTER_CUBIC效果更好但是速度慢
if scale<=1:
method = cv2.INTER_AREA
else:
method = cv2.INTER_CUBIC
newh = int(templeimg.shape[1]*scale)
neww = int(templeimg.shape[0] * scale )
new_dim = [neww,newh]
# 业务要求:目标文件长度至少为img的宽的二分之一
if max(neww,newh) <(min(img.shape[0],img.shape[1])/2):
continue
if (neww>imgW) or(newh>imgH) :
continue
resizedtempleimg = cv2.resize(templeimg, new_dim, method)
resizedtempleimgcopy = resizedtempleimg.copy()
# ------旋转匹配 match_point = {'angle': angle,"temp":temp, 'point': (location_x, location_y)}
match_points = RatationMatch(resizedtempleimgcopy, img)
temp = match_points['temp']
angle = match_points['angle']
point = match_points['point']
if temp_best<temp:
temp_best = temp
location_best = point
angle_best = angle
best_temple_img1 = resizedtempleimg.copy()
#print('scale:',scale)
match_point_best = {'angle': angle_best, "temp": temp_best, 'point': (location_best[0], location_best[1]),'best_temple_img1':best_temple_img1}
return match_point_best
# 画图
def draw_result(src, temp, match_point):
print('match_point:',match_point,temp.shape)
#cv2.circle(src, match_point, 3, 0, 2, 8, 0)
cv2.rectangle(src, match_point,
(match_point[0] + temp.shape[1], match_point[1] + temp.shape[0]),
(0, 0, 0), 1)
#con = np.hstack((src,temp))
cv2.imshow('result', src)
#cv2.imshow('temp', temp)
cv2.waitKey()
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = cv2.imread("./data/point_img.png", 0)
templeimg = cv2.imread("./data/07point_temple.png", 0)
cv2.imshow('img------ori', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
cv2.imshow('templeimg------ori', templeimg)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#templeimg = ImageRotate(templeimg, 180)#顺时针
#cv2.imshow('ImageRotate', templeimg)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
#cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#主程序---旋转的为模板图,多尺度放大缩小的是模板图
match_points =run_main(templeimg, img)
best_temple_img1 = match_points["best_temple_img1"]
print("主程序,最终返回结果:",match_points)
#模型图像旋转最佳状态
TmpImage= ImageRotate(best_temple_img1, match_points['angle'])
cv2.imshow("TmpImage", TmpImage)
cv2.waitKey()
#画图最终结果
draw_result(img, TmpImage, match_points['point'])
#下一步计划:
#根据模板识别的区域,对img的轮廓进行筛选
#指针最准的角度为,针尖中心点的坐标
#传统的方法,还是需要大量的参数阈值控制,太鸡肋了,决定,只在数据量很少的冷启动项目阶段采用传统方式。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-563339.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-563339.html
到了这里,关于python +opencv 多尺度缩放与旋转的模板匹配的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!