秋风阁-北溪入江流
Docker部署RabbitMq
version: '3.8'
services:
rabbitmq:
image: rabbitmq:3.11.19
container_name: rabbitmq
hostname: rabbitmq
ports:
# amqp协议通讯端口(对外服务必开)
- 5672:5672
# RabbitMq自带管理界面访问端口
- 15672:15672
environment:
- RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_VHOST=${vhost}
- RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=${user}
- RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=${password}
RabbitMq自带有专门的管理界面,可以在其管理界面对RabbitMq进行管理查看等操作。
RabbitMq的管理界面的对外端口为15672,当我们启动RabbitMq后,需要启动管理界面插件后才能访问界面。
# 进入容器内部
docker exec -it rabbitmq bash
# 启动插件,启动管理界面
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
Java直接操作RabbitMq
Maven导入依赖库
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId>
<version>5.18.0</version>
</dependency>
Java获取RabbitMq连接,基本配置
通过参数配置连接RabbitMq
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.After;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
public class TestMessageQueue {
private Connection connection;
private Channel channel;
@Before
public void before() throws IOException, TimeoutException{
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setUsername(${userName});
connectionFactory.setPassword(${password});
connectionFactory.setHost(${host});
connectionFactory.setPort(${port});
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(${virtualHost});
// 获取RabbitMq连接
this.connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
}
@After
public void after() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
// 关闭RabbitMq相关连接
this.connection.close();
}
}
通过amqp协议连接RabbitMq
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.security.KeyManagementException;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
public class TestMessageQueue {
private Connection connection;
private Channel channel;
@Before
public void before()
throws IOException, TimeoutException, URISyntaxException, NoSuchAlgorithmException, KeyManagementException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setUri("amqp://root:TIEta2023@47.109.103.123:9572/TieTa");
this.connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
this.channel = this.connection.createChannel();
}
@After
public void after() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
this.channel.close();
this.connection.close();
}
}
发布者模式(发送数据)
@Test
public void producer() throws IOException{
// 声明(创建)队列
this.channel.queueDeclarePassive(${queueName});
// 发送数据
this.channel.basicPublish("", ${queueName}, null, "你好 World!".getBytes());
}
- queueDeclarePassive: 创建或声明队列,当没有队列时会创建队列。通过此命令确保需要使用的队列的存在。
- basicPublish: 发送消息
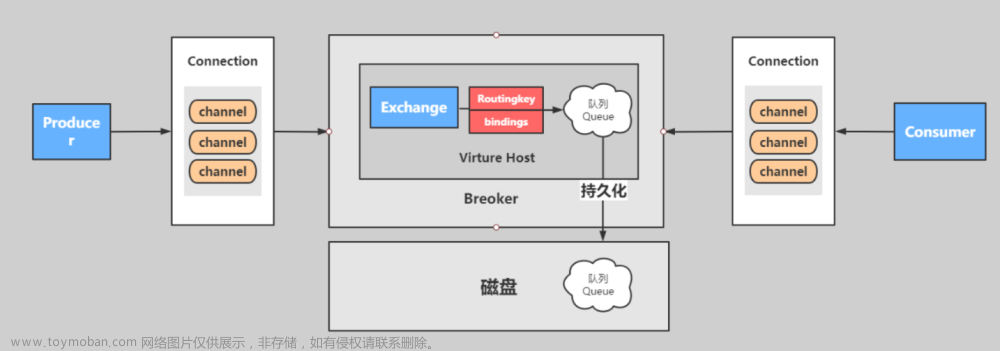
- exchange: 在RabbitMq中,发布者不会直接将信息推送到队列中,而是而是先将消息投递到exchange中,在由exchange转发到具体的队列,队列再将消息以推送或者拉取方式给消费者进行消费。消息队列通过在在消费者和生产者中引入了exchange的概念,当压力增长的情况下,可以通过配置exchange在不停机的情况下调整系统资源,缓解服务压力
- exchange为空表示设置为简单exchange模式
- routingKey: 传送到的队列名称
- props: 设置消息属性
- body: 消息内容,在RabbitMq中,通过流的方式传输信息,所以需要对传输内容进行编码
- exchange: 在RabbitMq中,发布者不会直接将信息推送到队列中,而是而是先将消息投递到exchange中,在由exchange转发到具体的队列,队列再将消息以推送或者拉取方式给消费者进行消费。消息队列通过在在消费者和生产者中引入了exchange的概念,当压力增长的情况下,可以通过配置exchange在不停机的情况下调整系统资源,缓解服务压力
消费者模式(接收数据)
@Test
public void consumer() throws IOException{
// 声明(创建)队列
this.channel.queueDeclarePassive(${queueName});
// 定义消费者
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
// 回调函数
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag,
Envelope envelope,
AMQP.BasicProperties properties,
byte[] body) throws IOException {
String msg = new String(body, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(msg);
}
};
/**
* 获取消息
* queue: 消息队列名称
* autoAck: 自动应答机制
* callback: 回调处理类
*/
channel.basicConsume(${queueName}, true, consumer);
}
- body: RabbitMq默认以流的方式传输数据,所以在接收到数据后,需要将其转换为需要的格式
- autoAck: 自动应答机制,通过ACK机制(消息确认机制)确认消息是否被正确接收,确保消息的正确传输,不会丢失
SpringBoot操作RabbitMq
引入依赖库
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
<version>3.1.1</version>
</dependency>
在spring-boot-starter-amqp库中,是通过依赖上面amqd-client库来获取对RabbitMq的支持
RabbitMq参数配置
在SpringBoot的配置文件application.yaml中添加如下配置文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-568092.html
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: ${host}
port: ${port}
username: ${userName}
password: ${password}
virtualHost: ${virtualHost}
发布者模式(发送数据)
@Component
public class MessageQueue {
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Autowired
public MessageQueue(RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate) {
this.rabbitTemplate = rabbitTemplate;
}
public void producer() {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(${queueName}, ${message});
}
}
消费者模式(接收数据)
@Component
public class MessageQueue {
@RabbitHandler
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue(${queueName}))
public void consumer(String msg) {
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
- queuesToDeclare: 当没有队列时会自动创建队列
清空队列
在RabbitMq中,发布者发送消息需要消费者进行消费,但是当消息队列无消费者的时候,发布者发送消息,消息将堆积在消息队列中,等到消费者上线时会全部发送给消费者。随着消息的堆积,消息可能已经过时了,此时没有必要在对现有的消息进行消费。所以可以清空队列,避免无效的消息消费。
在SpringBoot中通过调用RabbitAdmin.purgeQueue(queueName)进行消息队列的清空。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-568092.html
@Component
public class MessageQueue {
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
private RabbitAdmin rabbitAdmin;
@Autowired
public MessageQueue(RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate) {
this.rabbitTemplate = rabbitTemplate;
this.rabbitAdmin = new RabbitAdmin(this.rabbitTemplate);
}
public void queueName() {
this.rabbitAdmin.purgeQueue(queueName);
}
}
到了这里,关于Java操作RabbitMq并整合SpringBoot的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!