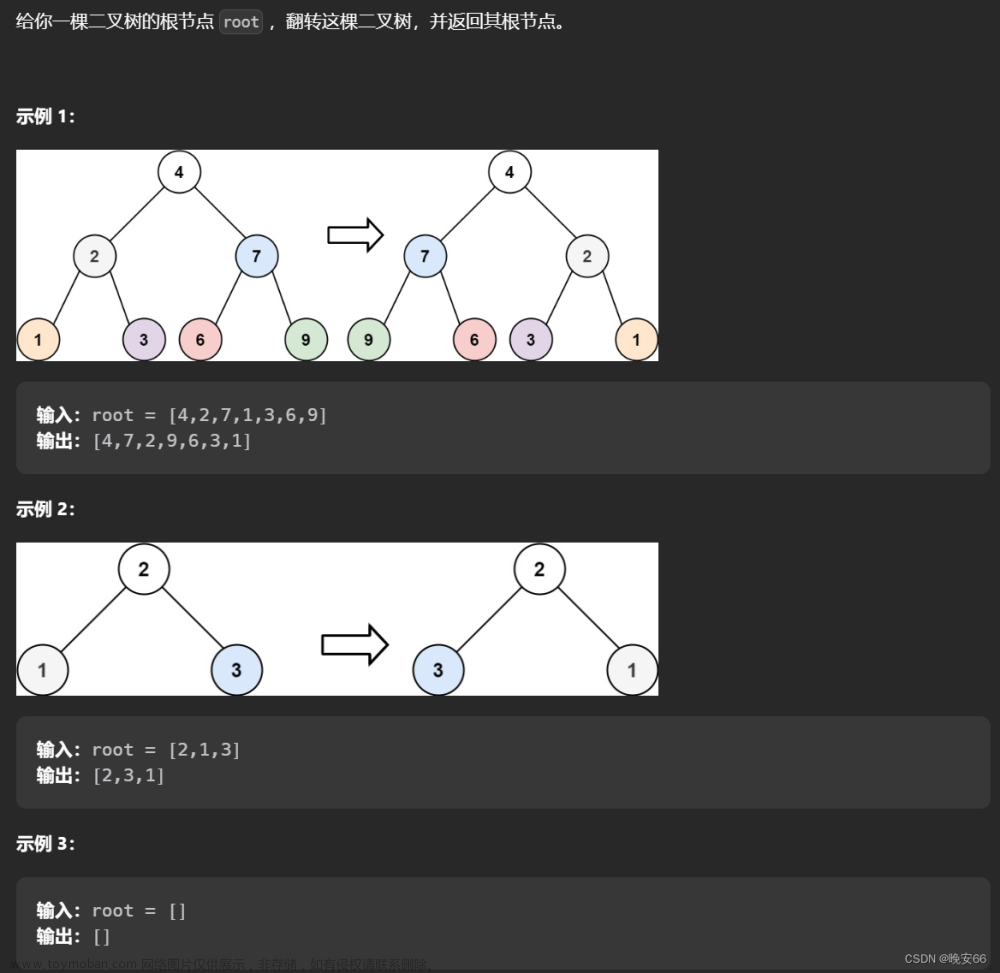
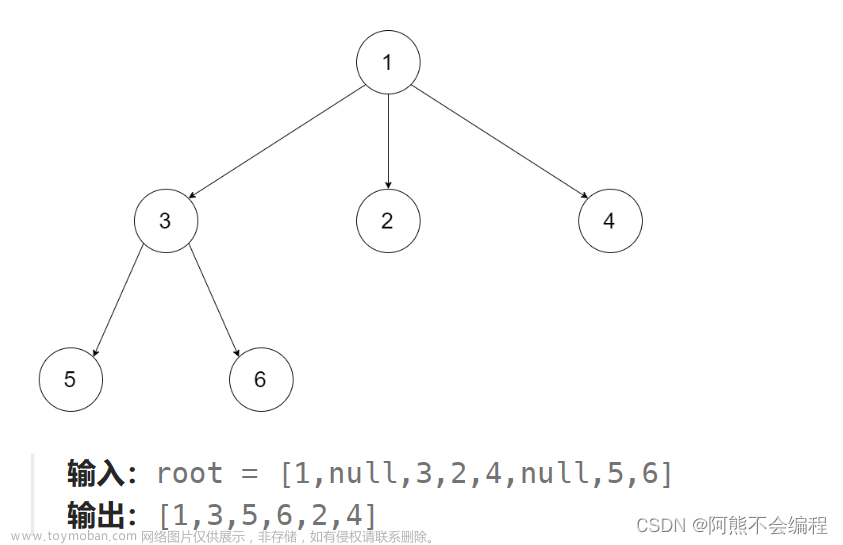
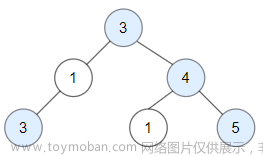
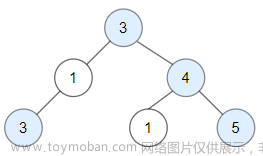
各位CSDN的uu们你们好呀,今天小雅兰的内容仍然是二叉树和Leetcode每日一题,下面,就让我们进入二叉树的世界吧!!!


这个题目需要重新定义一个函数,函数参数需要有左子树和右子树,题目所给定的函数无法解决问题。
bool _isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* leftRoot,struct TreeNode* rightRoot) { //左子树和右子树同时为空 if(leftRoot==NULL&&rightRoot==NULL) { return true; } //一棵树为空,另一棵树不为空 if((leftRoot==NULL&&rightRoot!=NULL)|| (leftRoot!=NULL&&rightRoot==NULL)) { return false; } //左子树的根和右子树的根不相等 //这就必然不对称 if(leftRoot->val!=rightRoot->val) { return false; } return _isSymmetric(leftRoot->left,rightRoot->right)&& _isSymmetric(leftRoot->right,rightRoot->left); } bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root){ return _isSymmetric(root->left,root->right); }




每个不为空的结点,都可以认为是一棵子树的根
//两棵树相同 bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q){ //两个都为空 if(p==NULL&&q==NULL) { return true; } //一个为空,另一个不为空 if((p==NULL&&q!=NULL)||(p!=NULL&&q==NULL)) { return false; } //根不相等 if(p->val!=q->val) { return false; } return isSameTree(p->left,q->left) &&isSameTree(p->right,q->right); } bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot){ if(root==NULL) { return false; } //root和subRoot相同 if(isSameTree(root,subRoot)) { return true; } //root的左子树与subRoot有相同或者root的右子树与subRoot有相同 //满足其中一个条件即可,所以用|| return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot)|| isSubtree(root->right,subRoot); }



递归里面传数组下标要注意!!!
每个栈帧里面都有一个数组下标!!!
所以要传数组下标的地址。
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root) { return root==NULL?0:TreeSize(root->left)+TreeSize(root->right)+1; } //递归里面传数组下标要注意!!! //每个栈帧里面都有一个i void preorder(struct TreeNode* root,int* a,int* pi) { if(root==NULL) { return; } a[(*pi)++]=root->val; preorder(root->left,a,pi); preorder(root->right,a,pi); } int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){ //root是输入型参数,returnSize是返回型参数 *returnSize=TreeSize(root); int* a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize*sizeof(int)); int i=0; preorder(root,a,&i); return a; }
当然,这个题目还有另外一种解法,就是把i作为全局变量,但是这样要特别注意,稍有不慎就会出错
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return root==NULL?0:TreeSize(root->left)+TreeSize(root->right)+1;
}
//递归里面传数组下标要注意!!!
//每个栈帧里面都有一个i
int i=0;
void preorder(struct TreeNode* root,int* a)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
a[i++]=root->val;
preorder(root->left,a);
preorder(root->right,a);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
//root是输入型参数,returnSize是返回型参数
*returnSize=TreeSize(root);
int* a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize*sizeof(int));
i=0;
preorder(root,a);
return a;
}

int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return root==NULL?0:TreeSize(root->left)+TreeSize(root->right)+1;
}
void inorder(struct TreeNode* root,int* a,int* pi)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
inorder(root->left,a,pi);
a[(*pi)++]=root->val;
inorder(root->right,a,pi);
}
int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
//root是输入型参数,returnSize是返回型参数
*returnSize=TreeSize(root);
int* a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize*sizeof(int));
int i=0;
inorder(root,a,&i);
return a;
}

int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return root==NULL?0:TreeSize(root->left)+TreeSize(root->right)+1;
}
void postorder(struct TreeNode* root,int* a,int* pi)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
postorder(root->left,a,pi);
postorder(root->right,a,pi);
a[(*pi)++]=root->val;
}
int* postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
//root是输入型参数,returnSize是返回型参数
*returnSize=TreeSize(root);
int* a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize*sizeof(int));
int i=0;
postorder(root,a,&i);
return a;
}
层序遍历
除了先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历外,还可以对二叉树进行层序遍历。设二叉树的根节点所在层数为1,层序遍历就是从所在二叉树的根节点出发,首先访问第一层的树根节点,然后从左到右访问第2层 上的节点,接着是第三层的节点,以此类推,自上而下,自左至右逐层访问树的结点的过程就是层序遍历。
1出来带2和4,2出来带3和NULL,4出来带和6
写这个代码的核心是得有一个队列!!!
Queue.h的内容:
#pragma once #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<stdbool.h> #include<assert.h> typedef struct BinaryTreeNode* QDataType; // 链式结构:表示队列 typedef struct QueueNode { struct QueueNode* next; QDataType data; }QueueNode; // 队列的结构 typedef struct Queue { QueueNode* phead;//头指针 QueueNode* ptail;//尾指针 int size; }Queue; // 初始化队列 void QueueInit(Queue* pq); // 销毁队列 void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq); // 队尾入队列 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x); // 队头出队列 void QueuePop(Queue* pq); // 获取队列头部元素 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq); // 获取队列队尾元素 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq); // 获取队列中有效元素个数 int QueueSize(Queue* pq); // 检测队列是否为空 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);Queue.c的内容:
#include"Queue.h" // 初始化队列 void QueueInit(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); pq->phead = NULL; pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; } // 销毁队列 void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); QueueNode* cur = pq->phead; while (cur != NULL) { QueueNode* next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; } // 队尾入队列 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x) { assert(pq); QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); return; } newnode->data = x; newnode->next = NULL; //是空队列的情况 if (pq->ptail == NULL) { assert(pq->phead == NULL); pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode; } else { pq->ptail->next = newnode; pq->ptail = newnode; } pq->size++; } // 检测队列是否为空 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->phead == NULL && pq->ptail == NULL; } // 队头出队列 void QueuePop(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); //1.一个结点 //2.多个结点 if (pq->phead->next == NULL) { free(pq->phead); pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL; } else { //相当于头删 QueueNode* next = pq->phead->next; free(pq->phead); pq->phead = next; } pq->size--; } // 获取队列头部元素 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); return pq->phead->data; } // 获取队列队尾元素 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); return pq->ptail->data; } // 获取队列中有效元素个数 int QueueSize(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->size; }
层序遍历源代码:
//层序遍历 void LevelOrder(BTNode* root) { Queue q; QueueInit(&q); if (root != NULL) { QueuePush(&q, root); } while (!QueueEmpty(&q)) { BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q); QueuePop(&q); printf("%d ", front->data); if (front->left != NULL) { QueuePush(&q, front->left); } if (front->right != NULL) { QueuePush(&q, front->right); } } printf("\n"); QueueDestroy(&q); }
二叉树销毁
//二叉树销毁 void BTreeDestroy(BTNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return; } BTreeDestroy(root->left); BTreeDestroy(root->right); free(root); }
通 过 前 序 遍 历 的 数 组 " A B D # # E # H # # C F # # G # # " 构 建 二 叉 树
根 左子树 右子树
#include <stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> typedef int BTDataType; typedef struct BinaryTreeNode { BTDataType data; struct BinaryTreeNode* left; struct BinaryTreeNode* right; }BTNode; BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x) { BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode)); if (node == NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); return NULL; } node->data = x; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; return node; } BTNode* CreatTree(char* a,int* pi) { if(a[*pi]=='#') { (*pi)++; return NULL; } BTNode* root=BuyNode(a[*pi]); (*pi)++; root->left=CreatTree(a,pi); root->right=CreatTree(a,pi); return root; } //中序 void InOrder(BTNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return; } InOrder(root->left); printf("%c ", root->data); InOrder(root->right); } int main() { char a[100]; scanf("%s",a); int i=0; BTNode*root=CreatTree(a,&i); InOrder(root); printf("\n"); return 0; }
判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
完全二叉树的特征是:层序遍历去走,它是连续的!!!
1出来带2和4,2出来带3和NULL,4出来带5和6,3出来带NULL和NULL,但是,3后面的NULL的后面竟然还有非空,这就证明此树是一棵非完全二叉树。
1出来带2和4,2出来带3和7,4出来带5和6,3出来带8和NULL,7出来带NULL和NULL,5出来带NULL和NULL,6出来带NULL和NULL,8出来带NULL和NULL,也就是说,队列里面的全都是空了,这一定是一棵完全二叉树。
//判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树 bool BTreeComplete(BTNode* root) { Queue q; QueueInit(&q); if (root != NULL) { QueuePush(&q, root); } while (!QueueEmpty(&q)) { BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q); QueuePop(&q); //遇到空就跳出循环 if (front == NULL) { break; } QueuePush(&q, front->left); QueuePush(&q, front->right); } //检查后面的结点有没有非空 //有非空,就不是完全二叉树 while (!QueueEmpty(&q)) { BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q); QueuePop(&q); if (front != NULL) { QueueDestroy(&q); return false; } } QueueDestroy(&q); return true; }
1.某完全二叉树按层次输出(同一层从左到右)的序列为 ABCDEFGH 。该完全二叉树的前序序列为( A )
A ABDHECFG
B ABCDEFGH
C HDBEAFCG
D HDEBFGCA
2.二叉树的先序遍历和中序遍历如下:先序遍历:EFHIGJK;中序遍历:HFIEJKG.则二叉树根结点为( A )
A E
B F
C G
D H
此题与中序遍历无关(中序遍历是迷惑人的),光看先序遍历就可以看出来,先序遍历就是根 左子树 右子树,所以E就是根结点。
但如果是想还原出这棵二叉树,中序遍历就很重要啦!!!
3.设一棵二叉树的中序遍历序列:badce,后序遍历序列:bdeca,则二叉树前序遍历序列为( D )。
A adbce
B decab
C debac
D abcde
后序遍历序列最后一个是a,所以a就是根节点!!!
4.某二叉树的后序遍历序列与中序遍历序列相同,均为 ABCDEF ,则按层次输出(同一层从左到右)的序列为( A )
A FEDCBA
B CBAFED
C DEFCBA
D ABCDEF
二叉树的性质
整个二叉树的源代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include"Queue.h"
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
return node1;
}//前序
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PrevOrder(root->left);
PrevOrder(root->right);
}//中序
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}//后序
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
二叉树结点个数
//int size = 0;//全局变量
//int BTreeSize(BTNode* root)
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// {
// return;
// }
// else
// {
// ++size;
// }
// BTreeSize(root->left);
// BTreeSize(root->right);
//}
二叉树结点个数
//int BTreeSize(BTNode* root)
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// {
// return 0;
// }
// else
// {
// return BTreeSize(root->left) + BTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
// }
//}
//二叉树结点个数
int BTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : BTreeSize(root->left) + BTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
//求叶子结点的个数
int BTreeleafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
return BTreeleafSize(root->left) + BTreeleafSize(root->right);
}//求二叉树的高度
int BTreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
int leftHeight = BTreeHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight = BTreeHeight(root->right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
}
// 二叉树第k层节点个数
int BTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
assert(k > 0);
if (root == NULL)//无论k是多少
{
return 0;
}
//root一定不为空
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
//root不为空并且k不为1
return BTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) + BTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
// 二叉树查找值为x的节点
BTNode* BTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (root->data == x)
{
return root;
}
BTNode* ret1 = BTreeFind(root->left, x);
if (ret1)
{
return ret1;
}
BTNode* ret2 = BTreeFind(root->right, x);
if (ret2)
{
return ret2;
}
return NULL;
}
//层序遍历
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root != NULL)
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", front->data);
if (front->left != NULL)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right != NULL)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
//二叉树销毁
void BTreeDestroy(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
BTreeDestroy(root->left);
BTreeDestroy(root->right);
free(root);
}
//判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
bool BTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root != NULL)
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
//遇到空就跳出循环
if (front == NULL)
{
break;
}
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
//检查后面的结点有没有非空
//有非空,就不是完全二叉树
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front != NULL)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
PrevOrder(root);
printf("\n");InOrder(root);
printf("\n");PostOrder(root);
printf("\n");/*BTreeSize(root);
printf("BTreeSize:%d\n", size);size = 0;
BTreeSize(root);
printf("BTreeSize:%d\n", size);size = 0;
BTreeSize(root);
printf("BTreeSize:%d\n", size);*/printf("BTreeSize:%d\n",BTreeSize(root));
printf("BTreeleafSize:%d\n", BTreeleafSize(root));
printf("BTreeHeight:%d\n", BTreeHeight(root));
printf("BTreeLevelKSize:%d\n", BTreeLevelKSize(root, 3));
printf("BTreeFind:%p\n", BTreeFind(root, 3));
LevelOrder(root);
BTreeDestroy(root);
root = NULL;return 0;
}
好啦,小雅兰的今日分享就到这里啦,还要继续加油学习噢!!!文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-576841.html
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-576841.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-576841.html
到了这里,关于二叉树(下)+Leetcode每日一题——“数据结构与算法”“对称二叉树”“另一棵树的子树”“二叉树的前中后序遍历”的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!