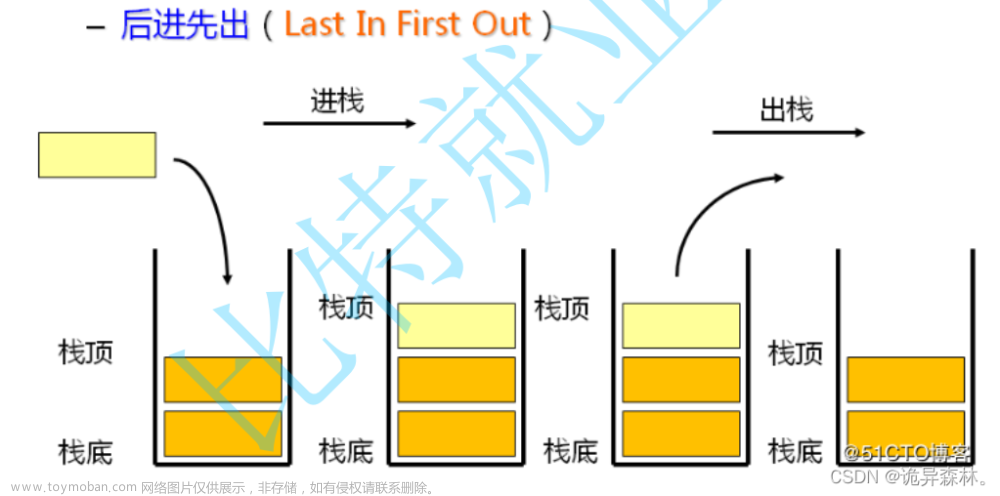
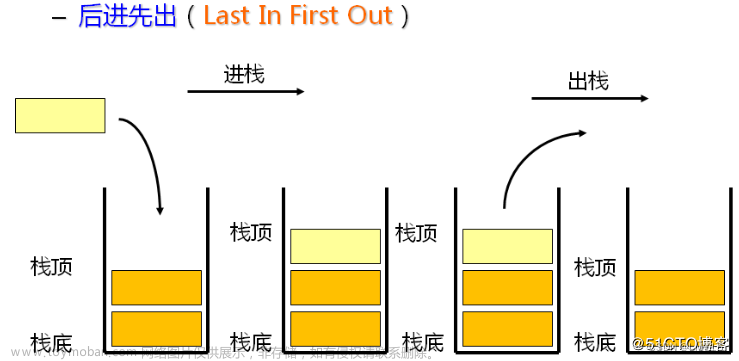
1、栈

(1)Stack.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void STInit(ST* pst);
void STDestroy(ST* pst);
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* pst);
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);
bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
int STSize(ST* pst);
(2)Stack.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Stack.h"
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
//pst->top = -1; //top指向栈顶数据
pst->top = 0; //top指向栈顶数据的下一个
pst->capacity = 0;
}
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
pst->top = 0;
}
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
if (pst->top == pst->capacity) //top指向栈顶数据的下一个,下一个元素的下标数就是当前已有元素总数
{
int newCapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tem = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tem == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tem;
pst->capacity = newCapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!STEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!STEmpty(pst));
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
(3)Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Stack.h"
int main()
{
ST st;
STInit(&st);
STPush(&st, 1);
STPush(&st, 2);
printf("%d ", STTop(&st));
STPop(&st);
printf("%d ", STTop(&st));
printf("\n");
STPush(&st, 2);
STPush(&st, 3);
STPush(&st, 4);
while (!STEmpty(&st))
{
printf("%d ", STTop(&st));
STPop(&st);
}
STDestroy(&st);
return 0;
}

2、队列
 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-578780.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-578780.html
(1)Queue.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
(2)Queue.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail\n");
return;
}
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->data = x;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
assert(pq->phead == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
//1、一个节点
//2、多个节点
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else
{
//头删
QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//return pq->phead == NULL && pq->ptail == NULL;
return pq->size == 0;
}
(3)Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Queue.h"
int main()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
QueuePush(&q, 5);
printf("Size:%d\n", QueueSize(&q));
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
return 0;
}
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-578780.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-578780.html
到了这里,关于栈和队列【数据结构】的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!