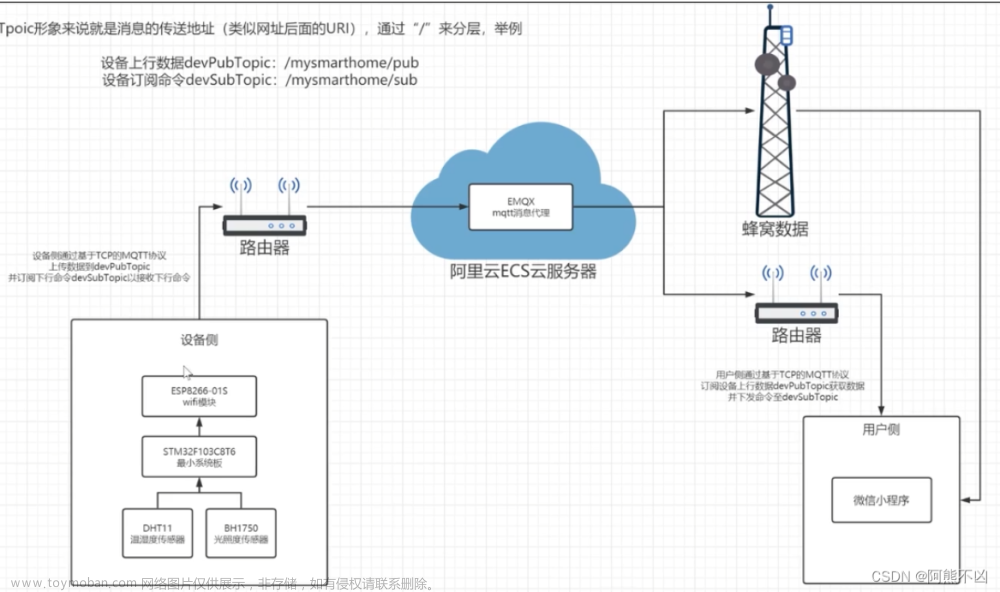
一,项目介绍
软件环境: C语言
硬件环境: STM32G030C8TX单片机开发板
开发工具: Linux平台GCC交叉编译环境以及ukeil
(1)边缘网关概念
边缘网关是部署在网络边缘侧的网关,通过网络联接、协议转换等功能联接物理和数字世界,提供轻量化的联接管理、实时数据分析及应用管理功能。比较常见的就是智能家居中智能音箱(蓝牙网关)+路由器(wifi网关),工厂里的工业网关等。它们通常扮演着一个区域内中心网关的功能,即负责终端设备的网络连接,也负责各终端数据的采集以及远程控制。同时,又提供数据上云的功能。

(2)包含知识点
两大网联网场景:消费物联网、工业物联网两大场景全覆盖
边缘网关新概念:物联网边缘网关中边缘采集、边缘计算两大主流技术
基础综合运用:C、shell、Makefile、C++、QT、单片机、数据库等基础知识大融合
Linux开发技术点:进程间通信、多线程程序设计、文件操作、网络编程、应用协议
物联网主流通信技术:Json、Modbus、mqtt
各种调试工具学习:mqtt.fx、modbus slave、modbus poll、wireshark、网络调试、串口调试等
二,产品需求矩阵
上位机:搜索界面,设备信息显示和控制界面,监控界面 ,历史数据查询,边缘计算
网关:上报模块,公有云模块,搜索响应模块,数据存储模块,内置网页,各采集模块,视频流模块
设备端:stm32模块,modbus模块
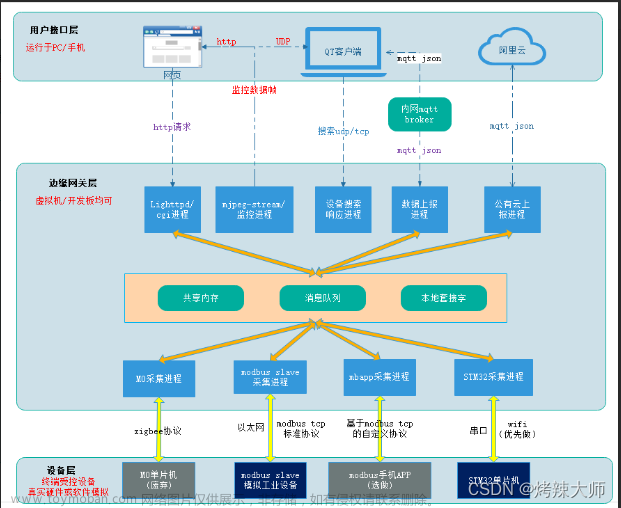
三,全局点表
点表使用
真实物联网场景中,点表通过客户端界面(上位机或者web页面)编辑,生成json文件后下发给设备,设备解析使用。
四,modbus采集进程
modbus采集模块实现了modbus工业设备的通信对接,向上通过modbusTCP协议采集单片机的数据,并刷新到共享内存,以便上报模块进程使用。向下接收来自上报模块的JSON控制指令,解析后,转换为标准的modbusTCP指令后通过网络发送给设备,实现设备的控制。
(1)主程序:
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&head);
FILE *fd = fopen("./node.json", "r");
if (fd == NULL)
{
perror("fopen err\n");
}
//定位文件末尾操作
fseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END);
//计算文件的大小
int len = ftell(fd);
//定位文件开头操作
fseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET);
char *p = (char *)malloc(len + 1);
fread(p, 1, len, fd);
cJSON *root = NULL;
//把传入的字符串转成cJSON的结构(反序列化)
root = cJSON_Parse(p);
if (root == NULL)
{
perror("err parse\n");
//return -1;
}
//版本
cJSON *item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "version");
printf("version =%s\n", item->valuestring);
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "mb_dev");
char *IP = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "addr")->valuestring;
int pot = cJSON_GetObjectItem(item, "port")->valueint;
printf("ip=%s port=%d\n", IP, pot); //解析端口和设备地址
//解析modbus
cJSON *ROO = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "modbus");
cJSON *tem = cJSON_GetObjectItem(ROO, "data");
int array_size = cJSON_GetArraySize(tem); //数组的大小
cJSON *JS_tem = tem->child; //子对象
for (int i = 0; i < array_size; i++)
{
struct mb_node_list *arr = (struct mb_node_list *)malloc(sizeof(struct mb_node_list));
printf("key=%d\n", cJSON_GetObjectItem(JS_tem, "key")->valueint);
printf("name=%s\n", cJSON_GetObjectItem(JS_tem, "name")->valuestring);
printf("addr=%d\n", cJSON_GetObjectItem(JS_tem, "addr")->valueint);
printf("type=%d\n", cJSON_GetObjectItem(JS_tem, "type")->valueint);
arr->node.key = cJSON_GetObjectItem(JS_tem, "key")->valueint;
arr->node.addr = cJSON_GetObjectItem(JS_tem, "addr")->valueint;
list_add(&arr->list, &head);
JS_tem = JS_tem->next;
}
//1,创建实例
//modbus_t *ctx = modbus_new_tcp(argv[1], atoi(argv[2]));
modbus_t *ctx = modbus_new_tcp(IP, pot);
//2,设置从机ID
modbus_set_slave(ctx, 1);
//3,和主机进行连接
int slave = modbus_connect(ctx);
if (slave != 0)
{
perror("connect err");
return -1;
}
else
{
printf("连接成功!!!!\n");
}
//数据采集线程
if (pthread_create(&tid, NULL, mythread, ctx) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create err");
return -1;
}
//指令控制
if (pthread_create(&tid, NULL, controlthread, ctx) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create_control err");
return -1;
}
pthread_detach(tid);
while (1)
;
//6,释放Modbus实例
modbus_free(ctx);
//7,关闭套接字
modbus_close(ctx);
return 0;
}
(2)数据采集线程:
//数据采集线程
void *mythread(void *arg)
{
uint16_t data[1024] = {};
uint16_t data1[1024] = {};
uint8_t dest[1024] = {};
int ret = -1;
ret = shm_init(¶, "shm_test", MAX_NODE_SIZE); //初始化
if (ret < 0)
{
perror("shm_init err\n");
//return -1;
}
//获取共享内存的地址并将其赋值给指针变量addr
void *addr = shm_getaddr(¶);
if (addr == NULL)
{
perror("shm_getaddr err\n");
//return -1;
}
int *p = NULL;
p = addr;
printf("Address=%p\n", p);
int *num = addr;
struct std_node *add = (addr + sizeof(int));
modbus_t *ctx = (modbus_t *)arg;
while (1)
{
sleep(2);
list_for_each(pos, &head)
{
tmp1 = list_entry(pos, struct mb_node_list, list);
//温度
if (tmp1->node.key == 101)
{
modbus_read_input_registers(ctx, tmp1->node.addr - 1, 2, data);
}
//湿度
else if (tmp1->node.key == 102)
{
modbus_read_input_registers(ctx, tmp1->node.addr - 1, 2, data + 2);
}
//空调开关
else if (tmp1->node.key == 103)
{
modbus_read_bits(ctx, tmp1->node.addr - 1, 2, dest);
//printf("空调开关= %u ", dest[0]);
}
//空调的温度,
//读取保持寄存器(功能码 0x3)
else if (tmp1->node.key == 104)
{
modbus_read_registers(ctx, tmp1->node.addr , 2, data1);
}
//风扇开关
else if (tmp1->node.key == 105)
{
modbus_read_bits(ctx, tmp1->node.addr - 1, 2, dest + 2);
}
//风扇档位1档,2档,3档
else if (tmp1->node.key == 106)
{
modbus_read_registers(ctx, tmp1->node.addr , 2, data1 + 2);
}
printf("温度寄存器= %u 湿度寄存器= %u\n", data[0], data[2]);
printf("空调温度的监测= %u 风扇的档位=%u\n", data1[0], data1[2]);
printf("空调开关的状态:=%u 风扇开关的状态:=%u\n", dest[0], dest[1]);
}
/* 读取的方式
modbus_read_input_registers(ctx, 0, 4, data);
//读输入寄存器的值,可读取多个连续输入寄存器的值(对应功能码为0x04)
//温度,湿度
printf("温度寄存器= %u 湿度寄存器= %u\n", data[0], data[2]);
//空调的温度,风扇档位1档,2档,3档
//读取保持寄存器(功能码 0x3)
modbus_read_registers(ctx, 0, 4, data1);
printf("空调温度的监测= %u 风扇的档位=%u\n", data1[0], data1[2]);
//空调开关和风扇开关
//读取线圈或者离散量输出状态(功能码 0x1)
modbus_read_bits(ctx, 0, 4, dest);
printf("空调开关的状态:=%u 风扇开关的状态:=%u\n", dest[0], dest[1]);
*/
for (int i = 0; i < *num; i++)
{
if (add[i].key == 101) //温度
{
add[i].new_val.f_val = modbus_get_float_dcba(data);
printf("Temperature sensor=%f\n", add[i].new_val.f_val);
if (add[i].new_val.f_val != 0)
{
add[i].ret = 0;
}
else
{
add[i].ret = -1;
printf("Temperature sensor err:=%d\n", add[i].ret);
}
}
else if (add[i].key == 102) //湿度
{
add[i].new_val.f_val = modbus_get_float_dcba(data + 2);
printf("Humidity sensor=%f\n", add[i].new_val.f_val);
if (add[i].new_val.f_val != 0)
{
add[i].ret = 0;
}
else
{
add[i].ret = -1;
printf("Humidity sensor err:=%d\n", add[i].ret);
}
}
else if (add[i].key == 103) //空调开关
{
add[i].new_val.b_val = dest[0];
printf("air conditioning switch=%d\n", add[i].new_val.b_val);
if (add[i].new_val.b_val != 0)
{
add[i].ret = 0;
}
else
{
add[i].ret = -1;
printf("air conditioning switch err:=%d\n", add[i].ret);
}
}
else if (add[i].key == 104) //空调的温度
{
add[i].new_val.f_val = modbus_get_float_dcba(data1);
printf("air conditioning temperature=%f\n", add[i].new_val.f_val);
if (add[i].new_val.f_val != 0)
{
add[i].ret = 0;
}
else
{
add[i].ret = -1;
printf("air conditioning temperature err:=%d\n", add[i].ret);
}
}
else if (add[i].key == 105) //风扇开关
{
add[i].new_val.b_val = dest[1];
printf("Fan switch=%d\n", add[i].new_val.b_val);
if (add[i].new_val.b_val != 0)
{
add[i].ret = 0;
}
else
{
add[i].ret = -1;
printf("Fan switch err:=%d\n", add[i].ret);
}
}
else if (add[i].key == 106) ///风扇档位控制,1档,2档,3档
{
add[i].new_val.f_val = modbus_get_float_dcba(data1 + 2);
printf("Fan switch control=%f\n", add[i].new_val.f_val);
if (add[i].new_val.f_val != 0)
{
add[i].ret = 0;
}
else
{
add[i].ret = -1;
printf("Fan switch err:=%d\n", add[i].ret);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
if (add[i].key == 101)
{
printf("key=%d new_val=%f\n", add[i].key, add[i].new_val.f_val);
}
else if (add[i].key == 102)
{
printf("key=%d new_val=%f\n", add[i].key, add[i].new_val.f_val);
}
else if (add[i].key == 103)
{
printf("key=%d new_val=%d\n", add[i].key, add[i].new_val.b_val);
}
else if (add[i].key == 104)
{
printf("key=%d new_val=%f\n", add[i].key, add[i].new_val.f_val);
}
else if (add[i].key == 105)
{
printf("key=%d new_val=%d\n", add[i].key, add[i].new_val.b_val);
}
else if (add[i].key == 106)
{
printf("key=%d new_val=%f\n", add[i].key, add[i].new_val.f_val);
}
}
sleep(1);
}
//free(tmp1);
// tmp1 = NULL;
shm_del(¶);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}(3)指令控制进程:
//指令控制
void *controlthread(void *arg)
{
modbus_t *ctx = (modbus_t *)arg;
struct msg msg;
//反序列化
msg.mtype = 1;
while (1)
{
// u_int16_t buf[4] = {444};
// u_int16_t buf1[4] = {1662};
//modbus_write_registers(ctx,40000,2,buf);
//modbus_write_registers(ctx,40002,2,buf1);
//modbus_write_registers(ctx,40003,2,buf);
//modbus_write_registers(ctx,40005,4,buf );
//modbus_write_register(ctx,0, 12);
//modbus_write_register(ctx,2, 12);
if (msg_queue_recv("modbus", &msg, sizeof(msg), 1, 0) > 0)
{
cJSON *root = cJSON_Parse(msg.mdata);
if (NULL == root)
{
printf("err parse\n");
//return -1;
}
//cJSON *item;
//item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "data"); //解析对象
//解析key的值
cJSON *login_key = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "key");
int identifying_Key = login_key->valueint;
printf("key=%d\n", identifying_Key); //打印此时的key值
//解析val的值
login_key = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "val");
int identifying_val = atoi(cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "val")->valuestring);
printf("val=%d\n", identifying_val);
//遍历链表
list_for_each(pos, &head)
{
tmp = list_entry(pos, struct mb_node_list, list);
if (identifying_Key == tmp->node.key)
{
if (identifying_Key == 103) //空调开关
{
modbus_write_bit(ctx, tmp->node.addr - 1, identifying_val);
}
else if (identifying_Key == 104) //空调温度控制
{
uint16_t buf[4];
modbus_set_float_dcba((float)atof(cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "val")->valuestring), buf);
modbus_write_registers(ctx, tmp->node.addr, 2, buf);
}
else if (identifying_Key == 105) //风扇开关
{
modbus_write_bit(ctx, tmp->node.addr - 1, identifying_val);
}
else if (identifying_Key == 106) //风扇档位控制,1档,2档,3档
{
uint16_t buf[4];
modbus_set_float_dcba((float)atof(cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "val")->valuestring), buf);
modbus_write_registers(ctx, tmp->node.addr, 2, buf);
}
}
}
}
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
pause();
}五,STM32
●STM32采集模块
stm32采集模块实现了stm32设备的通信对接,向上通过串口协议采集单片机的数据,
并刷新到共享内存,以便上报模块进程使用。
向下接收来自上报模块的JSON控制指令,解析后,
转换为相应的控制指令后通过串口发送给设备,实现设备的控制。
●单片机设备模块
单片机模拟了智能家居系统的设备场景,分别实现了传感器数据采集上报、设备的远程控制等功能。
通过ADC采集光敏传感器,并按照上报协议通过串口发送给网关设备。
接收来自网关的控制指令,通过JSON反序列化后,进行相应的设备控制。
呼吸灯来表示设备运行状态,按键模拟墙壁开关同步模拟灯光控制。
(1)需求分析
- 采集类传感器使用光敏度传感器。
- 蓝LED模拟智能灯,可以采集到灯状态并可远程控制;五向按键作为灯控开关(家居本地控制)。
- 绿色灯作为呼吸灯,1S闪烁一次,表示设备运行正常。
- 蓝灯表示网络连接状态,如果连接wifi并成功连接服务器后,蓝灯常亮(wifi连接模式)。
- 每隔2s采集一次传感器数据、智能灯的状态、电池电量信息,组包主动上报给网关。
- 接收来自网关的控制指令,并对智能灯做相应的控制。
(2)技术点分析
- GPIO
- 串口通信
- 串口中断
- GPIO中断
- 硬件定时器
- ADC采集
- 网络调试(wifi连接模式)
注意:这种方式很直观,发送前需要对发送的数据进行JSON的序列化动作。
- 单片机的栈空间比较小,如果使用
cJSON序列化时候,在串口调试助手发现输出不正常时,一般是栈空间不够了,此时可以考虑增大栈空间,可以直接从cubeMX直接进行调整。 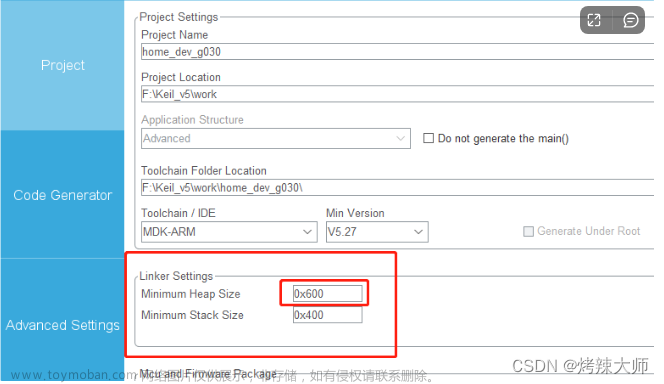
(3)Linux中采集和控制代码
主线程: // 读取串口数据(数据采集)
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
fd = open("/dev/ttyUSB0", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open err");
return -1;
}
else
printf("open device success\n");
serial_init(fd); //设置串口属性
//创建线程
pthread_t tid;
if (pthread_create(&tid, NULL, my_pthread, NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread create err");
return -1;
}
printf("this is father\n");
char buf[1024] = {0}; //存放读串口数据
static struct shm_param para;
int ret = -1;
// 创建共享内存
ret = shm_init(¶, "shm_test", 1024);
if (ret < 0)
{
return -1;
}
// 获取共享内存地址
struct std_node *addr = shm_getaddr(¶);
if (addr == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
while (1)
{
// 读取串口数据
if (read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf)) < 0)
{
perror("read err");
return -1;
}
printf("cj_buf=%s\n", buf);
// 反序列化
cJSON *root = cJSON_Parse(buf);
if (NULL == root)
{
printf("parse err\n");
return -1;
}
printf("*****反序列化*****\n");
cJSON *data = NULL;
cJSON *tmp = NULL;
cJSON *item = NULL;
data = cJSON_GetObjectItem(root, "data");
int n = cJSON_GetArraySize(data);
struct std_node buffer[n - 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
tmp = cJSON_GetArrayItem(data, i);
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(tmp, "key");
buffer[i].key = item->valueint;
printf("%s=%d\n", item->string, item->valueint);
item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(tmp, "val");
if (buffer[i].key == 301) //传感器
{
buffer[i].type = 3;
buffer[i].dev_type = buffer[i].key / 100;
buffer[i].old_val.f_val = item->valueint;
buffer[i].new_val.f_val = item->valueint;
}
else if (buffer[i].key == 302) //电池
{
buffer[i].type = 2;
buffer[i].dev_type = buffer[i].key / 100;
buffer[i].old_val.i_val = item->valueint;
buffer[i].new_val.i_val = item->valueint;
}
else if (buffer[i].key == 303) //灯状态
{
buffer[i].type = 2;
buffer[i].dev_type = buffer[i].key / 100;
buffer[i].old_val.i_val = item->valueint;
buffer[i].new_val.i_val = item->valueint;
}
//打印查看采集的值
printf("%s=%d\n", item->string, item->valueint);
buffer[i].ret = 0;
}
cJSON_Delete(root);
}
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
return 0;
}线程://从消息队列中读cjson(控制指令通过串口发给单片机)
void *my_pthread(void *arg)
{
printf("this is son\n");
struct msgbuf r_buf;
cJSON *r = cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON *d = cJSON_CreateArray();
cJSON_AddItemToObject(r, "data", d);
cJSON *i = cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToArray(d, i);
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(i, "key", 303);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(i, "name", "light");
cJSON_AddStringToObject(i, "val", "1");
char *q = cJSON_PrintUnformatted(r);
r_buf.mtype = 1;
strcpy(r_buf.mdata, q);
msg_queue_send("stm32", &r_buf, sizeof(r_buf), 0);
printf("r_buf=%s\n", r_buf.mdata);
free(q);
cJSON_Delete(r);
while (1)
{
//从消息队列中读cjson
struct msgbuf recv_buf;
int t = msg_queue_recv("stm32", &recv_buf, sizeof(recv_buf), 0, 0);
if (t < 0)
{
perror("msg recv err");
return NULL;
}
printf("%s\n", recv_buf.mdata);
// 反序列化
cJSON *msg_root = cJSON_Parse(recv_buf.mdata);
if (NULL == msg_root)
{
printf("parse err\n");
return NULL;
}
int msg_key, msg_val;
cJSON *msg_item = NULL;
cJSON *msg_data = cJSON_GetObjectItem(msg_root, "data");
int cout = cJSON_GetArraySize(msg_data);
printf("*************\n");
for (int i = 0; i < cout; i++)
{
cJSON *tmp = cJSON_GetArrayItem(msg_data, i);
msg_item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(tmp, "key");
msg_key = msg_item->valueint;
printf("%s=%d\n", msg_item->string, msg_item->valueint);
msg_item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(tmp, "name");
printf("%s=%s\n", msg_item->string, msg_item->valuestring);
msg_item = cJSON_GetObjectItem(tmp, "val");
msg_val = atoi(msg_item->valuestring);
printf("%s=%s\n", msg_item->string, msg_item->valuestring);
}
cJSON_Delete(msg_root);
// 序列化
if (msg_key == 303)
{
cJSON *root = cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON *data = cJSON_CreateArray();
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "data", data);
cJSON *item3 = cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToArray(data, item3);
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(item3, "key", 303);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(item3, "name", "light");
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(item3, "val", msg_val);
char *p = cJSON_PrintUnformatted(root);
printf("ctronl_cjson=%s\n", p);
//写串口
if (write(fd, p, strlen(p)) < 0)
{
perror("write err");
return NULL;
}
free(p);
cJSON_Delete(root);
}
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}(4)ukeil工程
main.c() LED灯五项按键中断, 串口接受控制指令,ADC采集
五项按键
//按键中断
void HAL_GPIO_EXTI_Rising_Callback(uint16_t GPIO_Pin)
{
if(GPIO_Pin==GPIO_PIN_8)
{
HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(GPIOB,GPIO_PIN_1);
while(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOA,GPIO_PIN_8));//抬手检测
}
}串口接受控制指令
//每次达到上述条件后,会触发此中断,每次触发中断缓冲区数据就是完整一包数据
void HAL_UARTEx_RxEventCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart, uint16_t Size)
{
if(huart->Instance == USART1)
{
// printf("RxBuf is %s\n", RxBuf);
//这里来解析命令,并做出相应的反应
// char dev_name[32]={0};
cJSON* recv_root=cJSON_Parse(RxBuf);
// if(NULL==recv_root)
// {
// printf("parse err\n");
// }
cJSON*recv_data=cJSON_GetObjectItem(recv_root,"data");
int count=cJSON_GetArraySize(recv_data);
for(int i=0;i<count;i++)
{
cJSON*tmp=cJSON_GetArrayItem(recv_data,i);
// printf("********zhongduan*******\n");
cJSON* recv_item=NULL;
recv_item=cJSON_GetObjectItem(tmp,"key");
// printf("%s=%d\n", recv_item->string, recv_item->valueint);
int key=recv_item->valueint;
// recv_item=cJSON_GetObjectItem(tmp,"name");
// printf("%s=%s\n", recv_item->string, recv_item->valuestring);
// strcpy(dev_name,recv_item->valuestring);
recv_item=cJSON_GetObjectItem(tmp,"val");
// printf("%s=%d\n", recv_item->string, recv_item->valueint);
int val=recv_item->valueint;
// int val=atoi(recv_item->valueint);
//控制灯
if(key==303)
{
//开灯
if(val==1)
{
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
}
//关灯
else if(val==0)
{
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_SET);
}
}
cJSON_Delete(recv_root);
}
memset(RxBuf,0,1024);
//再次设置此中断
HAL_UARTEx_ReceiveToIdle_IT(&huart1,RxBuf,1024);
}
}ADC采集 ,LED灯,呼吸灯
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
while (1)
{
//呼吸灯
for(int i=995;i>=0;i--)
{
TIM3->CCR3=i;
HAL_Delay(1);
}
for(int i=0;i<995;i++)
{
TIM3->CCR3=i;
HAL_Delay(1);
}
// 启动adc开始转换
HAL_ADC_Start(&hadc1);
// 获取转换结果
while(!(ADC1->ISR&(1<<2)));
bat=HAL_ADC_GetValue(&hadc1);
while(!(ADC1->ISR&(1<<3)));
light=HAL_ADC_GetValue(&hadc1);
// 停止转换
HAL_ADC_Stop(&hadc1);
// printf("bat=%d light=%d\n",bat,light);
// HAL_Delay(10);
if(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOB,GPIO_PIN_1)==GPIO_PIN_SET)
{
// printf("led_off\n");
led_val=0;
}else
{
// printf("led_on\n");
led_val=1;
}
//序列化封装为json格式
cJSON* root=cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON* data=cJSON_CreateArray();
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root,"data",data);
cJSON* item=cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToArray(data,item);
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(item,"key",301);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(item,"name","sensor");
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(item,"val",light);
cJSON* item2=cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToArray(data,item2);
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(item2,"key",302);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(item2,"name","bat");
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(item2,"val",bat);
cJSON* item3=cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToArray(data,item3);
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(item3,"key",303);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(item3,"name","light");
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(item3,"val",led_val);
char *p = cJSON_PrintUnformatted(root);
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1,p,strlen(p),1000);
// printf("cjson=%s\n",p);
free(p);
cJSON_Delete(root);
//lcd屏显示
sprintf(lcd_sensor,"%d\n",light);
sprintf(lcd_bat,"%d\n",bat);
sprintf(lcd_led,"%d\n",led_val);
Gui_DrawFont_GBK16(25,30,WHITE,RED,"sensor:");
Gui_DrawFont_GBK16(80,30,WHITE,RED,lcd_sensor);
Gui_DrawFont_GBK16(35,45,WHITE,RED,"bat:");
Gui_DrawFont_GBK16(78,45,WHITE,RED,lcd_bat);
Gui_DrawFont_GBK16(35,60,WHITE,RED,"LED:");
Gui_DrawFont_GBK16(78,60,WHITE,RED,lcd_led);
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
}
相关知识:
1,JSON数据交换格式
2,内核链表
3,共享内存,消息队列
通信组件(!!!!!!!!!!)
以下组件依赖临时目录,必须提前创建(tmp目录是内存型目录,如果重启了系统会消失,所以每次重启后注意重新创建下)文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-588260.html
mkdir /tmp/ipc/shmem -p
mkdir /tmp/ipc/msgqueue/peer -p4,GIT文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-588260.html
总结:
- 强化编程基础
- 迅速拓展知识面,训练自己的学习能力
- 了解企业开发流程,提前感受团队项目开发过程
到了这里,关于项目名称:智能家居边缘网关项目的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!