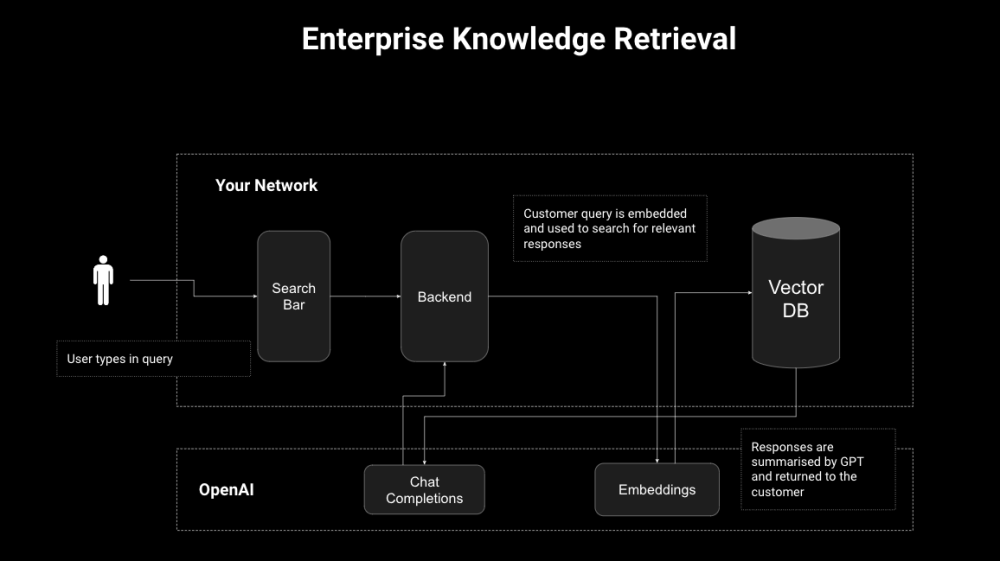
Large Language Models (LLMs) 的能力或者知识来自两方面:模型在训练时候的输入;模型训练好后以提示词方式输入到模型中的知识source knowledge。检索增强就是指后期输入到模型中的附加信息。
文本分段
按顺序安装包:
!pip install -qU \
datasets==2.12.0 \
apache_beam \
mwparserfromhell
!pip install -qU \
langchain==0.0.162 \
openai==0.27.7 \
tiktoken==0.4.0 \
"pinecone-client[grpc]"==2.2.2
from datasets import load_dataset
# 下载维基百科资料
data = load_dataset("wikipedia", "20220301.simple", split='train[:10000]')
# 分词工具
import tiktoken
tiktoken.encoding_for_model('gpt-3.5-turbo')
import tiktoken
tokenizer = tiktoken.get_encoding('cl100k_base')
# 计算分词后的token数 create the length function
def tiktoken_len(text):
tokens = tokenizer.encode(
text,
disallowed_special=()
)
return len(tokens)
# 使用 RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter 将整段文本分割,限定每个片段的最大token数
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=400,
chunk_overlap=20,
length_function=tiktoken_len, #计量token数
separators=["\n\n", "\n", " ", ""]
)
# 使用方式
chunks = text_splitter.split_text(data[6]['text'])[:3]
# 计算token数
tiktoken_len(chunks[0])
构建 Embedding
import os
# 设置OPENAI_API_KEY get openai api key from platform.openai.com
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY') or 'OPENAI_API_KEY'
from langchain.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
# 向量化的模型
model_name = 'text-embedding-ada-002'
embed = OpenAIEmbeddings(
model=model_name,
openai_api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY
)
# 测试文本
texts = [
'this is the first chunk of text',
'then another second chunk of text is here']
res = embed.embed_documents(texts)
print(len(res), len(res[0]))
>>>2 1536 # 向量长度为 1536
存储向量
使用 Pinecone 存储向量。
index_name = 'langchain-retrieval-augmentation'
import pinecone
# find API key in console at app.pinecone.io
PINECONE_API_KEY = os.getenv('PINECONE_API_KEY') or 'PINECONE_API_KEY'
# find ENV (cloud region) next to API key in console
PINECONE_ENVIRONMENT = os.getenv('PINECONE_ENVIRONMENT') or 'PINECONE_ENVIRONMENT'
pinecone.init(
api_key=YOUR_API_KEY,
environment=YOUR_ENV
)
if index_name not in pinecone.list_indexes():
# we create a new index
pinecone.create_index(
name=index_name,
metric='cosine',
dimension=len(res[0]) # 1536 dim of text-embedding-ada-002
)
# 连接库索引
index = pinecone.GRPCIndex(index_name)
print(index.describe_index_stats()) # 库索引统计信息
>>>{'dimension': 1536,
'index_fullness': 0.1,
'namespaces': {'': {'vector_count': 27437}},
'total_vector_count': 27437}
按批将数据插入索引库中
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
from uuid import uuid4
# 批量大小
batch_limit = 100
texts = []
metadatas = []
for i, record in enumerate(tqdm(data)):
# 维基百科中文本原始信息 first get metadata fields for this record
metadata = {
'wiki-id': str(record['id']),
'source': record['url'],
'title': record['title']
}
# 文本分段 now we create chunks from the record text
record_texts = text_splitter.split_text(record['text'])
# 为每一个分段文本创建元信息:j第几个片段 text片段文本 其它几个维基百科字段:wiki-id、source、title create individual metadata dicts for each chunk
record_metadatas = [{"chunk": j, "text": text, **metadata} for j, text in enumerate(record_texts)]
# append these to current batches
texts.extend(record_texts)
metadatas.extend(record_metadatas)
# if we have reached the batch_limit we can add texts
if len(texts) >= batch_limit:
ids = [str(uuid4()) for _ in range(len(texts))]
embeds = embed.embed_documents(texts)
index.upsert(vectors=zip(ids, embeds, metadatas))
texts = []
metadatas = []
if len(texts) > 0:
ids = [str(uuid4()) for _ in range(len(texts))]
embeds = embed.embed_documents(texts)
index.upsert(vectors=zip(ids, embeds, metadatas))
向量查询
from langchain.vectorstores import Pinecone
text_field = "text" # 需要查询出来的字段
# 向量化的模型
model_name = 'text-embedding-ada-002'
embed = OpenAIEmbeddings(
model=model_name,
openai_api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY
)
# switch back to normal index for langchain
index = pinecone.Index(index_name)
vectorstore = Pinecone(
index, embed.embed_query, text_field
)
# 查询信息
query = "who was Benito Mussolini?"
vectorstore.similarity_search(
query, # our search query
k=3 # return 3 most relevant docs
)
检索信息结合LLM
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
# completion llm
llm = ChatOpenAI(
openai_api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY,
model_name='gpt-3.5-turbo',
temperature=0.0
)
qa = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=llm,
chain_type="stuff",
retriever=vectorstore.as_retriever()
)
print(qa.run(query))
>>>'Benito Mussolini was an Italian politician and journalist who served as the Prime Minister of Italy from 1922 until 1943.'
有时 LLM 回答不着边,没有完全按照提供的信息回答,可以通过 RetrievalQAWithSourcesChain 使得回答更可信,模型会返回参考的来源信息文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-594342.html
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQAWithSourcesChain
qa_with_sources = RetrievalQAWithSourcesChain.from_chain_type(
llm=llm,
chain_type="stuff",
retriever=vectorstore.as_retriever()
)
print(qa_with_sources(query))
>>>{'question': 'who was Benito Mussolini?',
'answer': 'Benito Mussolini was an Italian politician and journalist who was the Prime Minister of Italy from 1922 until 1943.',
'sources': 'https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Benito%20Mussolini, https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fascism'}
参考:
Fixing Hallucination with Knowledge Bases
Retrieval Augmentation文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-594342.html
到了这里,关于LangChain(4)检索增强 Retrieval Augmentation的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!