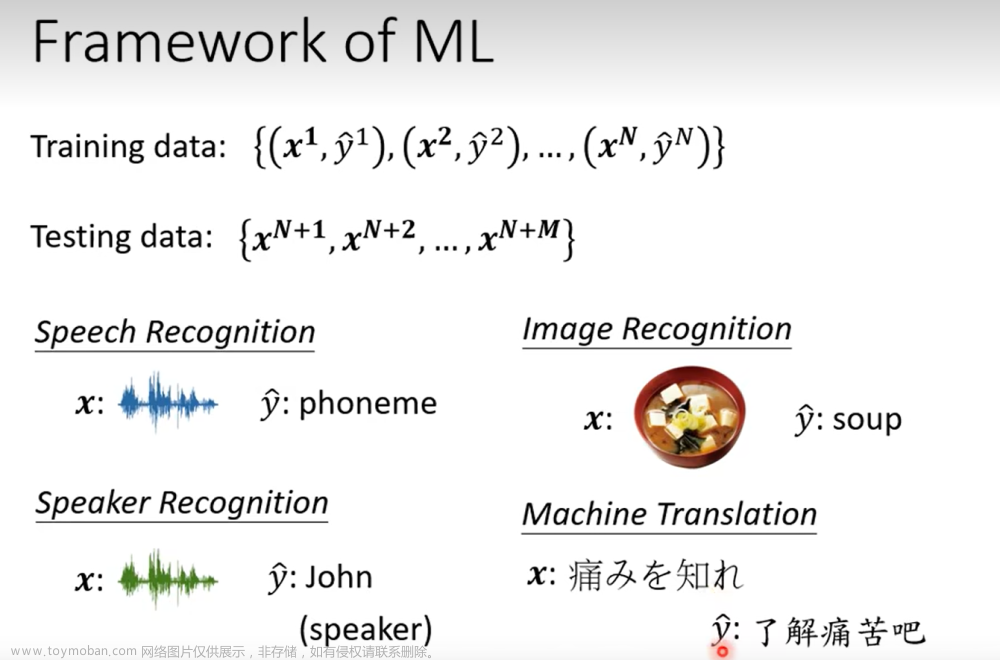
sigmoid函数
def sigmoid(x):
return 1.0 / (1+np.exp((-x)))
定义最小平方和损失函数
loss = torch.nn.MSELoss()
线性回归编程

如果不加噪音就成了正常的线性函数了,所以要加噪音。
torch.normal(0, 0.01, y.shape)
torch.normal(0, 0.01, y.shape)是一个用于生成服从正态分布的张量的函数。其中,0代表均值,0.01代表标准差,y.shape表示生成的张量的形状与y相同。具体而言,该函数会生成一个张量,其元素值是从均值为0、标准差为0.01的正态分布中随机采样得到的。
y.reshape((-1, 1))
y.reshape((-1, 1))是将张量y进行形状重塑的操作。通过该操作,可以将y转换为一个列向量,其中每个元素保持不变。
在PyTorch中,使用reshape函数对张量进行形状调整。参数(-1, 1)表示将y重塑为一个列向量,其中-1表示自动计算此维度的大小,而1表示列的维度大小为1。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-599874.html
y.reshape((-1, 1))将返回一个形状调整后的新张量,而原始的y张量保持不变。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-599874.html
手动实现线性回归
pip install d2l==0.17.6
import random
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
def synthetic_data(w,b,num_examples):
# 生成大小为(0,1),num_examples行,len(w)列的数据x , 此处是(1000,2)
X = torch.normal(0,1,(num_examples,len(w)))
# y = X*w + b
y = torch.matmul(X,w) + b
# y 加上噪音
y += torch.normal(0,0.01,y.shape)
return X,y.reshape((-1,1))
'''随机(小批量)梯度下降'''
def data_iter(batch_size,features,labels):
num_examples = features.shape[0]
'''生成0-999'''
indices = list(range(num_examples))
'''打乱0-999'''
random.shuffle(indices)
'''0-999中每次取一个batch_size'''
for i in range(0,num_examples,batch_size):
'''设置一个batch的索引'''
batch_indices = torch.tensor(indices[i:min(i+batch_size,num_examples)])
yield features[batch_indices],labels[batch_indices]
def plot_img(features,labels):
# 创建一个画板
d2l.set_figsize()
# 画一个散点图 (numpy格式的x,y,散点的像素大小)
d2l.plt.scatter(features[:, 1].detach().numpy(), labels.detach().numpy(), 1)
# 展示图像
d2l.plt.show()
true_w = torch.tensor([2,-3.4])
true_b = 4.2
features,labels = synthetic_data(true_w,true_b,1000)
# 画图显示特征和标签
# plot_img(features,labels)
batch_size = 10
for X,y in data_iter(batch_size,features,labels):
print(X,'\n',y)
break
# 初始化模型参数, w是个列,形状为两行1列,值符合0,0.01的分布
w = torch.normal(0,0.01,size=(2,1),requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1,requires_grad=True)
# 定义线性函数
def linreg(X,w,b):
return torch.matmul(X,w)+b
# 定义损失函数
def squared_loss(y_hat,y):
return (y_hat - y.reshape(y_hat.shape)) ** 2 /2
# 定义优化函数
def sgd(params,lr,batch_size):
'''小批量随机梯度下降'''
with torch.no_grad():
for param in params:
'''参数 = 参数 - 1/batch_size * -学习率 * 梯度'''
param -= lr * param.grad / batch_size
'''一个参数一个梯度,该下一个参数了比如是w2,所以要梯度清零'''
param.grad.zero_()
# 开始训练,定义参数和网络
lr = 0.03
num_epochs = 10
net = linreg
loss = squared_loss
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X,y in data_iter(batch_size,features,labels):
y_hat = net(X,w,b)
L = loss(y_hat,y)
# 计算的是每个样本的损失,所以要求和
L.sum().backward()
# 更新参数
sgd([w,b],lr,batch_size)
with torch.no_grad():
# w,b已经经过上面的更新函数更新过了,用更新后的w,b代入公式 计算损失
train_L = loss(net(features,w,b),labels)
print(f'epoch {epoch+1}, loss {float(train_L.mean()):f}')
到了这里,关于机器学习 & 深度学习编程笔记的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!