概述
AStar算法是一种图形搜索算法,常用于寻路。他是以广度优先搜索为基础,集Dijkstra算法和最佳优先(best fit)于一身的一种算法。
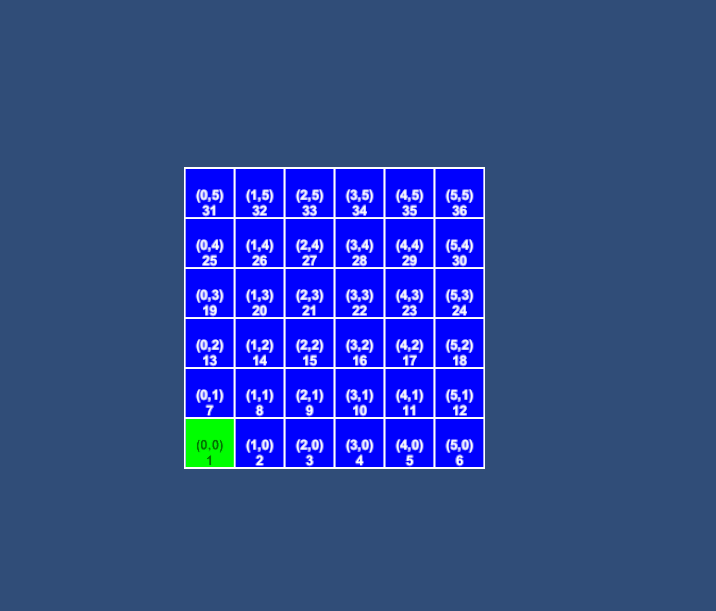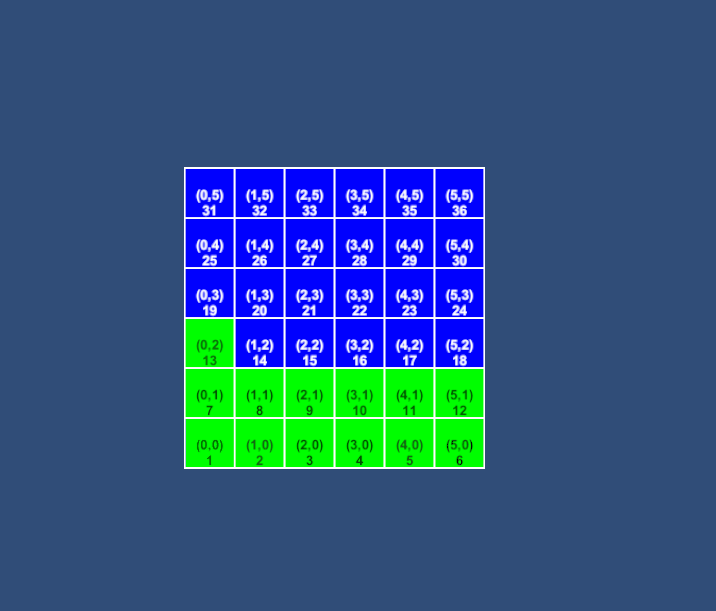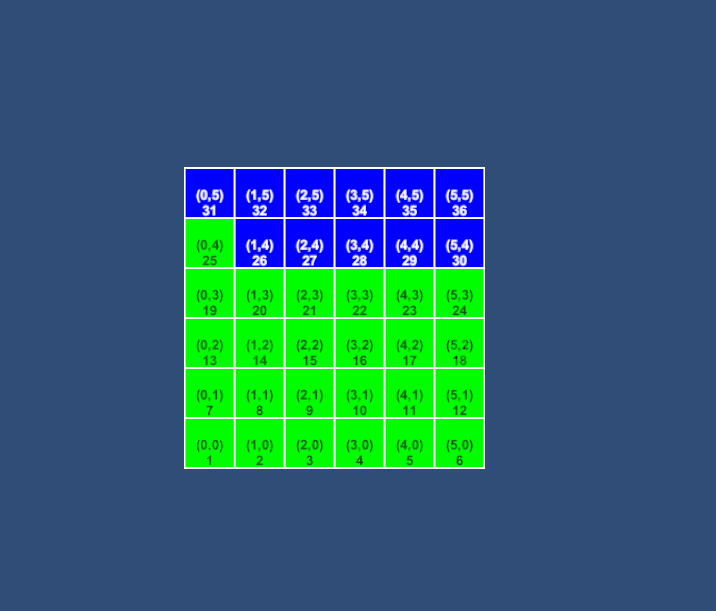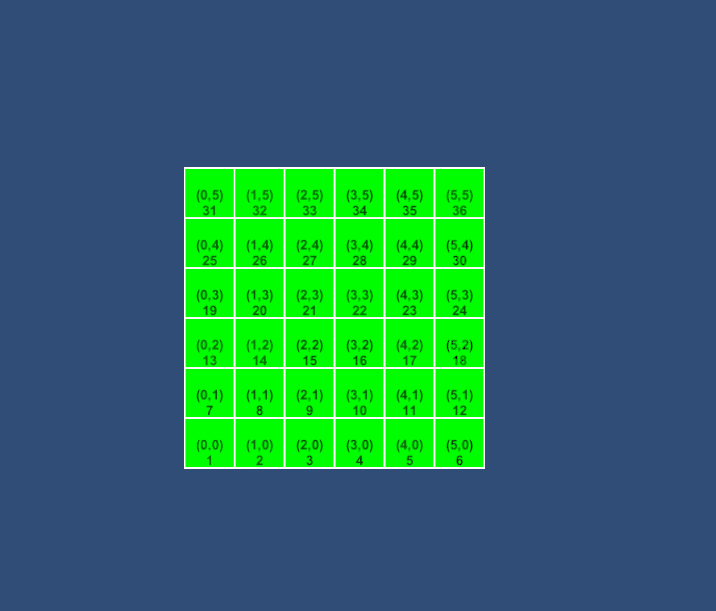
示例1:4向
示例2:8向 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-601263.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-601263.html
思路

递归的通过估值函数找到最佳路径,估值函数与距离相关,也有可能与通过代价系数相关(例如平地系数为1,坡地系数为2),有三个参数:文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-601263.html
- G:起点点到当前点的代价
- H: 当前点到终点的代价
- F: F = G + H 与最佳路径权重负相关的参数
过程大概:
代码示例
位置定义
public struct Vec2
{
public int x;
public int y;
public Vec2(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public static Vec2 Zero
{
get
{
return new Vec2(0, 0);
}
}
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
if (!(obj is Vec2))
return false;
var o = (Vec2)obj;
return x == o.x && y == o.y;
}
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return x.GetHashCode() + y.GetHashCode();
}
public static Vec2 operator +(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return new Vec2(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y);
}
public static Vec2 operator *(Vec2 a, int n)
{
return new Vec2(a.x * n, a.y * n);
}
public static Vec2 operator *(int n, Vec2 a)
{
return new Vec2(a.x * n, a.y * n);
}
public static bool operator ==(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y;
}
public static bool operator !=(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return !(a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y);
}
}
方向定义
public enum EDir
{
Up = 0,
Down = 1,
Left = 2,
Right = 3,
UpLeft = 4,
UpRight = 5,
DownLeft = 6,
DownRight = 7,
}
public abstract class CheckDirPol
{
abstract public Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> GetDir();
}
public class CheckDir4Pol : CheckDirPol
{
private Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> dirDict = new Dictionary<EDir, Vec2>
{
{EDir.Up, new Vec2(0, 1) },
{EDir.Down, new Vec2(0, -1) },
{EDir.Left, new Vec2(-1, 0) },
{EDir.Right, new Vec2(1, 0) },
};
override public Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> GetDir()
{
return dirDict;
}
}
public class CheckDir8Pol : CheckDirPol
{
private Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> dirDict = new Dictionary<EDir, Vec2>
{
{EDir.Up, new Vec2(0, 1) },
{EDir.Down, new Vec2(0, -1) },
{EDir.Left, new Vec2(-1, 0) },
{EDir.Right, new Vec2(1, 0) },
{EDir.UpLeft, new Vec2(-1, 1) },
{EDir.UpRight, new Vec2(1, 1) },
{EDir.DownLeft, new Vec2(-1, -1) },
{EDir.DownRight, new Vec2(1, -1) },
};
override public Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> GetDir()
{
return dirDict;
}
}
- 运用策略模式的技巧,以实现4向,8向搜索切换
估值函数
public abstract class EvaPol
{
abstract public float Calc(Vec2 a, Vec2 b);
}
public class MANEvaPol : EvaPol
{
override public float Calc(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return Mathf.Abs(a.x - b.x) + Mathf.Abs(a.y - b.y);
}
}
- 直接使用曼哈顿距离作为代价
节点定义
public class Node
{
public int id;
public Vec2 pos;
public float g;
public float h;
public float f;
public Vec2 prePos;
public bool hasPrePos;
public Node(Vec2 pos)
{
this.pos = pos;
}
public void SetPrePos(Vec2 pos)
{
prePos = pos;
hasPrePos = true;
}
}
算法上下文定义
Context context;
EvaPol disPol;
CheckDirPol checkDirPol;
public struct Context
{
public Vec2 end;
public Vec2 start;
public Node[,] nodes;
public List<Node> open;
public List<Node> close;
public int[,] map;
public List<Vec2> result;
public Vec2 size;
}
寻路算法
初始化
public void Init(Vec2 start, Vec2 end, int[,] map)
{
var x = map.GetLength(0);
var y = map.GetLength(1);
context = new Context()
{
start = start,
end = end,
open = new List<Node>(),
close = new List<Node>(),
map = map,
result = new List<Vec2>(),
size = new Vec2(x, y),
};
context.nodes = new Node[x, y];
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < x; j++)
context.nodes[i, j] = new Node(new Vec2(i, j));
disPol = new MANEvaPol();
//checkDirPol = new CheckDir4Pol();
checkDirPol = new CheckDir8Pol();
}
获取路径
public List<Vec2> GetResult()
{
return context.result;
}
寻路
寻路入口
public void FindPath()
{
var s = context.start;
var sn = context.nodes[s.x, s.y];
sn.g = 0;
sn.h = disPol.Calc(s, context.end);
sn.f = sn.g + sn.h;
context.open.Add(sn);
FindArrangement(sn);
}
递归函数
void FindArrangement(Node node)
{
context.close.Add(node);
context.open.Remove(node);
if (node.pos == context.end)
{
SetResult(node);
return;
}
CheckRound(node);
if (context.open.Count == 0)
return;
Node next = context.open[0];
for (int i = 1; i < context.open.Count; i++)
if (context.open[i].f < next.f)
next = context.open[i];
FindArrangement(next);
}
检查周围节点
void CheckRound(Node node)
{
var dirDict = checkDirPol.GetDir();
foreach (var pair in dirDict)
{
var dir = node.pos + pair.Value;
if (IsBlock(dir))
continue;
var dn = context.nodes[dir.x, dir.y];
if (context.close.Contains(dn))
continue;
if (context.open.Contains(dn))
TryOverridePath(node, dn);
else
{
dn.g = disPol.Calc(dn.pos, context.start);
dn.h = disPol.Calc(dn.pos, context.end);
dn.f = dn.g + dn.h;
dn.SetPrePos(node.pos);
context.open.Add(dn);
}
}
}
// 若是从邻节点到该节点路径更优,则替换更新
void TryOverridePath(Node a, Node b)
{
var g = a.g + disPol.Calc(a.pos, b.pos);
if (g < b.g)
{
b.g = g;
b.SetPrePos(a.pos);
}
}
bool IsBlock(Vec2 pos)
{
return !InMap(pos) || context.map[pos.x, pos.y] == 1;
}
bool InMap(Vec2 pos)
{
var x = pos.x;
var y = pos.y;
var size = context.size;
return x >= 0 && x < size.x && y >= 0 && y < size.y;
}
生成路径
void SetResult(Node node)
{
Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>();
while(node.hasPrePos)
{
q.Enqueue(node);
node = context.nodes[node.prePos.x, node.prePos.y];
}
while(q.Count > 0)
{
context.result.Add(q.Dequeue().pos);
}
}
完整代码
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public struct Vec2
{
public int x;
public int y;
public Vec2(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public static Vec2 Zero
{
get
{
return new Vec2(0, 0);
}
}
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
if (!(obj is Vec2))
return false;
var o = (Vec2)obj;
return x == o.x && y == o.y;
}
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return x.GetHashCode() + y.GetHashCode();
}
public static Vec2 operator +(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return new Vec2(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y);
}
public static Vec2 operator *(Vec2 a, int n)
{
return new Vec2(a.x * n, a.y * n);
}
public static Vec2 operator *(int n, Vec2 a)
{
return new Vec2(a.x * n, a.y * n);
}
public static bool operator ==(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y;
}
public static bool operator !=(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return !(a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y);
}
}
public enum EDir
{
Up = 0,
Down = 1,
Left = 2,
Right = 3,
UpLeft = 4,
UpRight = 5,
DownLeft = 6,
DownRight = 7,
}
public class AstarFindPath
{
public class Node
{
public int id;
public Vec2 pos;
public float g;
public float h;
public float f;
public Vec2 prePos;
public bool hasPrePos;
public Node(Vec2 pos)
{
this.pos = pos;
}
public void SetPrePos(Vec2 pos)
{
prePos = pos;
hasPrePos = true;
}
}
public abstract class EvaPol
{
abstract public float Calc(Vec2 a, Vec2 b);
}
public class MANEvaPol : EvaPol
{
override public float Calc(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return Mathf.Abs(a.x - b.x) + Mathf.Abs(a.y - b.y);
}
}
public abstract class CheckDirPol
{
abstract public Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> GetDir();
}
public class CheckDir4Pol : CheckDirPol
{
private Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> dirDict = new Dictionary<EDir, Vec2>
{
{EDir.Up, new Vec2(0, 1) },
{EDir.Down, new Vec2(0, -1) },
{EDir.Left, new Vec2(-1, 0) },
{EDir.Right, new Vec2(1, 0) },
};
override public Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> GetDir()
{
return dirDict;
}
}
public class CheckDir8Pol : CheckDirPol
{
private Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> dirDict = new Dictionary<EDir, Vec2>
{
{EDir.Up, new Vec2(0, 1) },
{EDir.Down, new Vec2(0, -1) },
{EDir.Left, new Vec2(-1, 0) },
{EDir.Right, new Vec2(1, 0) },
{EDir.UpLeft, new Vec2(-1, 1) },
{EDir.UpRight, new Vec2(1, 1) },
{EDir.DownLeft, new Vec2(-1, -1) },
{EDir.DownRight, new Vec2(1, -1) },
};
override public Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> GetDir()
{
return dirDict;
}
}
public struct Context
{
public Vec2 end;
public Vec2 start;
public Node[,] nodes;
public List<Node> open;
public List<Node> close;
public int[,] map;
public List<Vec2> result;
public Vec2 size;
}
Context context;
EvaPol disPol;
CheckDirPol checkDirPol;
public void Init(Vec2 start, Vec2 end, int[,] map)
{
var x = map.GetLength(0);
var y = map.GetLength(1);
context = new Context()
{
start = start,
end = end,
open = new List<Node>(),
close = new List<Node>(),
map = map,
result = new List<Vec2>(),
size = new Vec2(x, y),
};
context.nodes = new Node[x, y];
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < x; j++)
context.nodes[i, j] = new Node(new Vec2(i, j));
disPol = new MANEvaPol();
//checkDirPol = new CheckDir4Pol();
checkDirPol = new CheckDir8Pol();
}
public void FindPath()
{
var s = context.start;
var sn = context.nodes[s.x, s.y];
sn.g = 0;
sn.h = disPol.Calc(s, context.end);
sn.f = sn.g + sn.h;
context.open.Add(sn);
FindArrangement(sn);
}
public List<Vec2> GetResult()
{
return context.result;
}
void FindArrangement(Node node)
{
context.close.Add(node);
context.open.Remove(node);
if (node.pos == context.end)
{
SetResult(node);
return;
}
CheckRound(node);
if (context.open.Count == 0)
return;
Node next = context.open[0];
for (int i = 1; i < context.open.Count; i++)
if (context.open[i].f < next.f)
next = context.open[i];
FindArrangement(next);
}
void SetResult(Node node)
{
Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>();
while(node.hasPrePos)
{
q.Enqueue(node);
node = context.nodes[node.prePos.x, node.prePos.y];
}
while(q.Count > 0)
{
context.result.Add(q.Dequeue().pos);
}
}
void CheckRound(Node node)
{
var dirDict = checkDirPol.GetDir();
foreach (var pair in dirDict)
{
var dir = node.pos + pair.Value;
if (IsBlock(dir))
continue;
var dn = context.nodes[dir.x, dir.y];
if (context.close.Contains(dn))
continue;
if (context.open.Contains(dn))
TryOverridePath(node, dn);
else
{
dn.g = disPol.Calc(dn.pos, context.start);
dn.h = disPol.Calc(dn.pos, context.end);
dn.f = dn.g + dn.h;
dn.SetPrePos(node.pos);
context.open.Add(dn);
}
}
}
void TryOverridePath(Node a, Node b)
{
var g = a.g + disPol.Calc(a.pos, b.pos);
if (g < b.g)
{
b.g = g;
b.SetPrePos(a.pos);
}
}
bool IsBlock(Vec2 pos)
{
return !InMap(pos) || context.map[pos.x, pos.y] == 1;
}
bool InMap(Vec2 pos)
{
var x = pos.x;
var y = pos.y;
var size = context.size;
return x >= 0 && x < size.x && y >= 0 && y < size.y;
}
}
到了这里,关于AStar寻路算法的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!