本文基于Istio 1.18.0版本进行源码学习
4、服务发现:ServiceController
ServiceController是服务发现的核心模块,主要功能是监听底层平台的服务注册中心,将平台服务模型转换成Istio服务模型并缓存;同时根据服务的变化,触发相关服务的事件处理回调函数的执行
1)、ServiceController的核心接口
ServiceController可以同时支持多个服务注册中心,因为它包含不同的注册中心控制器,它们的聚合是通过抽象聚合接口(aggregate.Controller)完成的,该接口相关定义如下:
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/aggregate/controller.go
// 聚合所有底层注册中心的数据,并监控数据的变化
type Controller struct {
// meshConfig
meshHolder mesh.Holder
// The lock is used to protect the registries and controller's running status.
storeLock sync.RWMutex
// 注册中心的集合
registries []*registryEntry
// indicates whether the controller has run.
// if true, all the registries added later should be run manually.
running bool
// 控制器回调函数的集合,当添加了某一注册中心时,控制器会向其注册回调函数
handlers model.ControllerHandlers
// 按照集群区分的回调函数
handlersByCluster map[cluster.ID]*model.ControllerHandlers
model.NetworkGatewaysHandler
}
type registryEntry struct {
serviceregistry.Instance
// stop if not nil is the per-registry stop chan. If null, the server stop chan should be used to Run the registry.
stop <-chan struct{}
}
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/instance.go
// 注册中心接口
type Instance interface {
// 控制器接口
model.Controller
// 服务发现接口
model.ServiceDiscovery
// Provider backing this service registry (i.e. Kubernetes etc.)
Provider() provider.ID
// Cluster for which the service registry applies. Only needed for multicluster systems.
Cluster() cluster.ID
}
注册中心接口Instance实现了Istio通用的控制器接口Controller及服务发现接口ServiceDiscovery,接口定义如下:
// pilot/pkg/model/controller.go
// 控制器接口,用于注册事件处理回调函数
// 注册中心控制器会接收资源更新事件,并执行相应的事件处理回调函数
type Controller interface {
// Note: AppendXXXHandler is used to register high level handlers.
// For per cluster handlers, they should be registered by the `AppendXXXHandlerForCluster` interface.
// AppendServiceHandler notifies about changes to the service catalog.
// 注册服务的事件处理回调函数
AppendServiceHandler(f ServiceHandler)
// AppendWorkloadHandler notifies about changes to workloads. This differs from InstanceHandler,
// which deals with service instances (the result of a merge of Service and Workload)
// 注册服务实例的事件处理回调函数,主要是为了支持kubernetes service和istio serviceEntry交叉选择服务实例
AppendWorkloadHandler(f func(*WorkloadInstance, Event))
// Run until a signal is received
// 运行控制器
Run(stop <-chan struct{})
// HasSynced returns true after initial cache synchronization is complete
// 同步检查控制器的缓存
HasSynced() bool
}
// pilot/pkg/model/service.go
// 服务发现接口提供对服务模型的查询功能
type ServiceDiscovery interface {
NetworkGatewaysWatcher
// Services list declarations of all services in the system
// 查询网格中的所有服务
Services() []*Service
// GetService retrieves a service by host name if it exists
// 根据hostname查询服务
GetService(hostname host.Name) *Service
// InstancesByPort retrieves instances for a service on the given ports with labels that match
// any of the supplied labels. All instances match an empty tag list.
//
// For example, consider an example of catalog.mystore.com:
// Instances(catalog.myservice.com, 80) ->
// --> IstioEndpoint(172.16.0.1:8888), Service(catalog.myservice.com), Labels(foo=bar)
// --> IstioEndpoint(172.16.0.2:8888), Service(catalog.myservice.com), Labels(foo=bar)
// --> IstioEndpoint(172.16.0.3:8888), Service(catalog.myservice.com), Labels(kitty=cat)
// --> IstioEndpoint(172.16.0.4:8888), Service(catalog.myservice.com), Labels(kitty=cat)
//
// Calling Instances with specific labels returns a trimmed list.
// e.g., Instances(catalog.myservice.com, 80, foo=bar) ->
// --> IstioEndpoint(172.16.0.1:8888), Service(catalog.myservice.com), Labels(foo=bar)
// --> IstioEndpoint(172.16.0.2:8888), Service(catalog.myservice.com), Labels(foo=bar)
//
// Similar concepts apply for calling this function with a specific
// port, hostname and labels.
//
// Introduced in Istio 0.8. It is only called with 1 port.
// CDS (clusters.go) calls it for building 'dnslb' type clusters.
// EDS calls it for building the endpoints result.
// Consult istio-dev before using this for anything else (except debugging/tools)
// 根据服务及端口获取服务实例
InstancesByPort(svc *Service, servicePort int) []*ServiceInstance
// GetProxyServiceInstances returns the service instances that co-located with a given Proxy
//
// Co-located generally means running in the same network namespace and security context.
//
// A Proxy operating as a Sidecar will return a non-empty slice. A stand-alone Proxy
// will return an empty slice.
//
// There are two reasons why this returns multiple ServiceInstances instead of one:
// - A ServiceInstance has a single IstioEndpoint which has a single Port. But a Service
// may have many ports. So a workload implementing such a Service would need
// multiple ServiceInstances, one for each port.
// - A single workload may implement multiple logical Services.
//
// In the second case, multiple services may be implemented by the same physical port number,
// though with a different ServicePort and IstioEndpoint for each. If any of these overlapping
// services are not HTTP or H2-based, behavior is undefined, since the listener may not be able to
// determine the intended destination of a connection without a Host header on the request.
// 获取与sidecar代理相关的服务实例
GetProxyServiceInstances(*Proxy) []*ServiceInstance
// 获取proxy工作负载的标签
GetProxyWorkloadLabels(*Proxy) labels.Instance
// MCSServices returns information about the services that have been exported/imported via the
// Kubernetes Multi-Cluster Services (MCS) ServiceExport API. Only applies to services in
// Kubernetes clusters.
MCSServices() []MCSServiceInfo
AmbientIndexes
}
2)、ServiceController的初始化
Kubernetes ServiceController初始化流程如下:

核心方法是pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/kube/controller/controller.go中的NewController()方法,代码如下:
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/kube/controller/controller.go
func NewController(kubeClient kubelib.Client, options Options) *Controller {
// 实例化kubernetes注册中心的控制器
c := &Controller{
opts: options,
client: kubeClient,
queue: queue.NewQueueWithID(1*time.Second, string(options.ClusterID)),
servicesMap: make(map[host.Name]*model.Service),
nodeSelectorsForServices: make(map[host.Name]labels.Instance),
nodeInfoMap: make(map[string]kubernetesNode),
externalNameSvcInstanceMap: make(map[host.Name][]*model.ServiceInstance),
workloadInstancesIndex: workloadinstances.NewIndex(),
initialSyncTimedout: atomic.NewBool(false),
networkManager: initNetworkManager(options),
configCluster: options.ConfigCluster,
}
c.namespaces = kclient.New[*v1.Namespace](kubeClient)
if c.opts.SystemNamespace != "" {
registerHandlers[*v1.Namespace](
c,
c.namespaces,
"Namespaces",
func(old *v1.Namespace, cur *v1.Namespace, event model.Event) error {
if cur.Name == c.opts.SystemNamespace {
return c.onSystemNamespaceEvent(old, cur, event)
}
return nil
},
nil,
)
}
if c.opts.DiscoveryNamespacesFilter == nil {
c.opts.DiscoveryNamespacesFilter = namespace.NewDiscoveryNamespacesFilter(c.namespaces, options.MeshWatcher.Mesh().DiscoverySelectors)
}
c.initDiscoveryHandlers(options.MeshWatcher, c.opts.DiscoveryNamespacesFilter)
c.services = kclient.NewFiltered[*v1.Service](kubeClient, kclient.Filter{ObjectFilter: c.opts.DiscoveryNamespacesFilter.Filter})
// 注册service对应的事件处理回调函数
registerHandlers[*v1.Service](c, c.services, "Services", c.onServiceEvent, nil)
switch options.EndpointMode {
case EndpointSliceOnly:
c.endpoints = newEndpointSliceController(c)
default: // nolint: gocritic
log.Errorf("unknown endpoints mode: %v", options.EndpointMode)
fallthrough
case EndpointsOnly:
// 实例化endpointsController,注册endpoints对应的事件处理回调函数
c.endpoints = newEndpointsController(c)
}
// This is for getting the node IPs of a selected set of nodes
c.nodes = kclient.NewFiltered[*v1.Node](kubeClient, kclient.Filter{ObjectTransform: kubelib.StripNodeUnusedFields})
// 注册node对应的事件处理回调函数
registerHandlers[*v1.Node](c, c.nodes, "Nodes", c.onNodeEvent, nil)
c.podsClient = kclient.NewFiltered[*v1.Pod](kubeClient, kclient.Filter{
ObjectFilter: c.opts.DiscoveryNamespacesFilter.Filter,
ObjectTransform: kubelib.StripPodUnusedFields,
})
c.pods = newPodCache(c, c.podsClient, func(key types.NamespacedName) {
c.queue.Push(func() error {
return c.endpoints.sync(key.Name, key.Namespace, model.EventAdd, true)
})
})
// 注册pod对应的事件处理回调函数
registerHandlers[*v1.Pod](c, c.podsClient, "Pods", c.pods.onEvent, c.pods.labelFilter)
if features.EnableMCSServiceDiscovery || features.EnableMCSHost {
c.crdWatcher = crdwatcher.NewController(kubeClient)
}
if features.EnableAmbientControllers {
c.configController = options.ConfigController
c.ambientIndex = c.setupIndex()
}
c.exports = newServiceExportCache(c)
c.imports = newServiceImportCache(c)
c.meshWatcher = options.MeshWatcher
if c.opts.MeshNetworksWatcher != nil {
c.opts.MeshNetworksWatcher.AddNetworksHandler(func() {
c.reloadMeshNetworks()
c.onNetworkChange()
})
c.reloadMeshNetworks()
}
return c
}
NewController()方法中实例化了Kubernetes注册中心的控制器,Kubernetes注册中心的控制器定义如下:
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/kube/controller/controller.go
type Controller struct {
opts Options
client kubelib.Client
// 控制器的任务队列
queue queue.Instance
namespaces kclient.Client[*v1.Namespace]
services kclient.Client[*v1.Service]
// kubernetes的endpoints控制器抽象接口,支持endpoint和endpointSlice
endpoints kubeEndpointsController
// Used to watch node accessible from remote cluster.
// In multi-cluster(shared control plane multi-networks) scenario, ingress gateway service can be of nodePort type.
// With this, we can populate mesh's gateway address with the node ips.
nodes kclient.Client[*v1.Node]
crdWatcher *crdwatcher.Controller
// 多集群服务serviceExport的资源处理接口
exports serviceExportCache
// 多集群服务serviceImport的资源处理接口
imports serviceImportCache
// 包含kclient.Client[*v1.Pod]
pods *PodCache
crdHandlers []func(name string)
// service及pod实例的事件处理函数
handlers model.ControllerHandlers
namespaceDiscoveryHandlers []func(ns string, event model.Event)
// This is only used for test
stop chan struct{}
sync.RWMutex
// servicesMap stores hostname ==> service, it is used to reduce convertService calls.
// istio服务模型的缓存
servicesMap map[host.Name]*model.Service
// nodeSelectorsForServices stores hostname => label selectors that can be used to
// refine the set of node port IPs for a service.
nodeSelectorsForServices map[host.Name]labels.Instance
// map of node name and its address+labels - this is the only thing we need from nodes
// for vm to k8s or cross cluster. When node port services select specific nodes by labels,
// we run through the label selectors here to pick only ones that we need.
// Only nodes with ExternalIP addresses are included in this map !
// node的缓存
nodeInfoMap map[string]kubernetesNode
// externalNameSvcInstanceMap stores hostname ==> instance, is used to store instances for ExternalName k8s services
// externalName类型的服务实例缓存
externalNameSvcInstanceMap map[host.Name][]*model.ServiceInstance
// index over workload instances from workload entries
// 工作负载实例的索引
workloadInstancesIndex workloadinstances.Index
networkManager
// initialSyncTimedout is set to true after performing an initial processing timed out.
initialSyncTimedout *atomic.Bool
meshWatcher mesh.Watcher
podsClient kclient.Client[*v1.Pod]
ambientIndex *AmbientIndex
configController model.ConfigStoreController
configCluster bool
}
Controller中services、nodes、podsClient属性都是Client[T controllers.Object]类型的,Client[T controllers.Object]封装了对应的资源操作客户端,定义如下:
// pkg/kube/kclient/interfaces.go
// Client wraps a Kubernetes client providing cached read access and direct write access.
type Client[T controllers.Object] interface {
Reader[T]
Writer[T]
Informer[T]
}
Kubernetes控制器关键属性的初始化方式如下图:
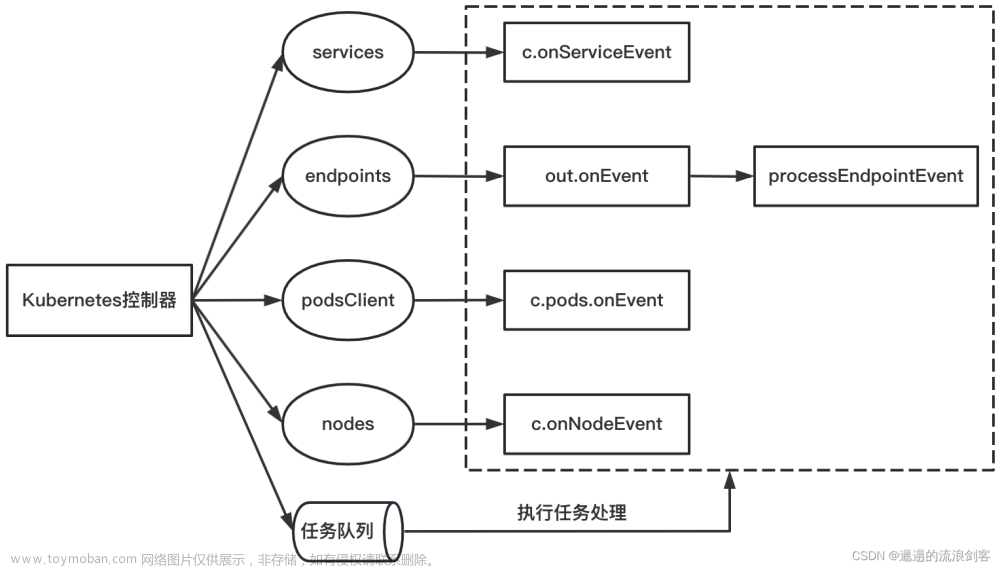
Kubernetes控制器的核心就是监听Kubernetes相关资源(Service、Endpoint、EndpointSlice、Pod、Node)的更新事件,执行相应的事件处理回调函数;并且进行从Kubernetes资源对象到Istio资源对象的转换,提供一定的缓存能力,主要是缓存Istio Service与WorkloadInstance
3)、ServiceController的工作机制
ServiceController为4种资源分别创建了Informer,用于监听Kubernetes资源的更新,并为其注册EventHandler
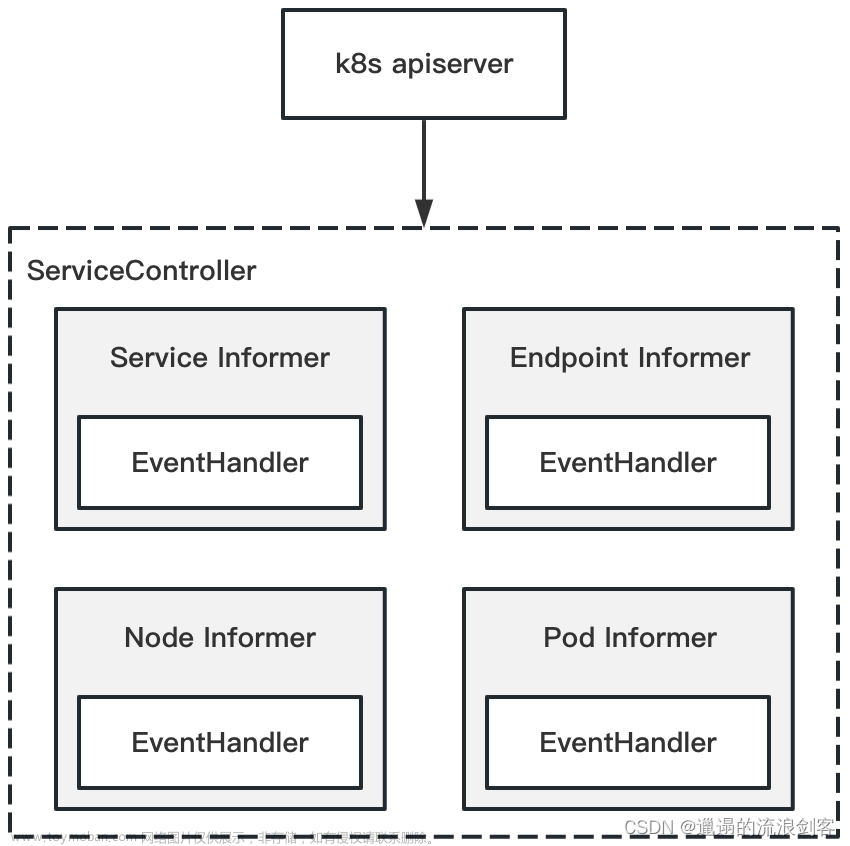
NewController()方法中调用registerHandlers()方法为4种资源注册EventHandler,registerHandlers()方法代码如下:
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/kube/controller/controller.go
func registerHandlers[T controllers.ComparableObject](c *Controller,
informer kclient.Informer[T], otype string,
handler func(T, T, model.Event) error, filter FilterOutFunc[T],
) {
// 包装传入的handler方法
wrappedHandler := func(prev, curr T, event model.Event) error {
curr = informer.Get(curr.GetName(), curr.GetNamespace())
if controllers.IsNil(curr) {
// this can happen when an immediate delete after update
// the delete event can be handled later
return nil
}
return handler(prev, curr, event)
}
informer.AddEventHandler(
controllers.EventHandler[T]{
AddFunc: func(obj T) {
incrementEvent(otype, "add")
// 创建资源处理任务并将其推送到任务队列
c.queue.Push(func() error {
return wrappedHandler(ptr.Empty[T](), obj, model.EventAdd)
})
},
UpdateFunc: func(old, cur T) {
if filter != nil {
if filter(old, cur) {
incrementEvent(otype, "updatesame")
return
}
}
incrementEvent(otype, "update")
c.queue.Push(func() error {
return wrappedHandler(old, cur, model.EventUpdate)
})
},
DeleteFunc: func(obj T) {
incrementEvent(otype, "delete")
c.queue.Push(func() error {
return handler(ptr.Empty[T](), obj, model.EventDelete)
})
},
})
}
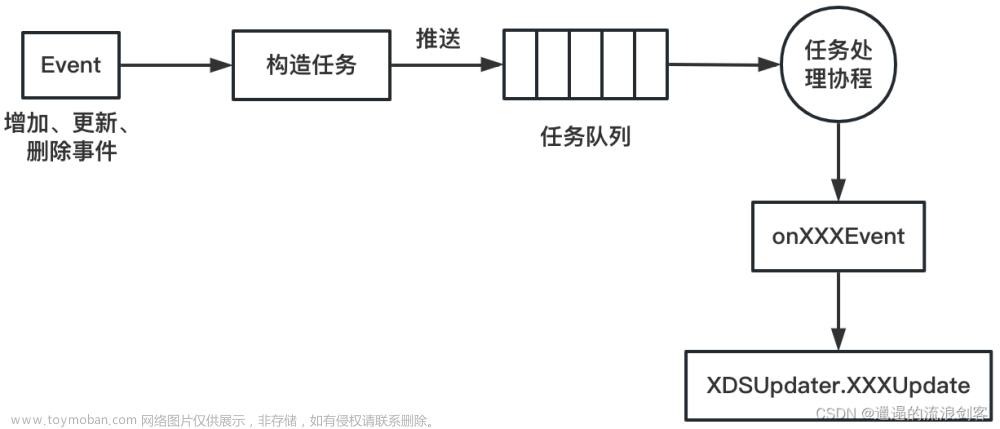
当监听到Service、Endpoint、Pod、Node资源更新时,EventHandler会创建资源处理任务并将其推送到任务队列,然后由任务处理协程阻塞式地接收任务对象,最终调用任务处理函数完成对资源对象的事件处理
1)Service事件处理
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/kube/controller/controller.go
func (c *Controller) onServiceEvent(_, curr *v1.Service, event model.Event) error {
log.Debugf("Handle event %s for service %s in namespace %s", event, curr.Name, curr.Namespace)
// Create the standard (cluster.local) service.
// 将kubernetes service转换成istio service
svcConv := kube.ConvertService(*curr, c.opts.DomainSuffix, c.Cluster())
switch event {
case model.EventDelete:
// 删除service
c.deleteService(svcConv)
default:
// 创建或更新service
c.addOrUpdateService(curr, svcConv, event, false)
}
return nil
}
func (c *Controller) addOrUpdateService(curr *v1.Service, currConv *model.Service, event model.Event, updateEDSCache bool) {
needsFullPush := false
// First, process nodePort gateway service, whose externalIPs specified
// and loadbalancer gateway service
if !currConv.Attributes.ClusterExternalAddresses.IsEmpty() {
needsFullPush = c.extractGatewaysFromService(currConv)
} else if isNodePortGatewayService(curr) {
// We need to know which services are using node selectors because during node events,
// we have to update all the node port services accordingly.
nodeSelector := getNodeSelectorsForService(curr)
c.Lock()
// only add when it is nodePort gateway service
c.nodeSelectorsForServices[currConv.Hostname] = nodeSelector
c.Unlock()
needsFullPush = c.updateServiceNodePortAddresses(currConv)
}
var prevConv *model.Service
// instance conversion is only required when service is added/updated.
instances := kube.ExternalNameServiceInstances(curr, currConv)
c.Lock()
prevConv = c.servicesMap[currConv.Hostname]
c.servicesMap[currConv.Hostname] = currConv
if len(instances) > 0 {
c.externalNameSvcInstanceMap[currConv.Hostname] = instances
}
c.Unlock()
// This full push needed to update ALL ends endpoints, even though we do a full push on service add/update
// as that full push is only triggered for the specific service.
if needsFullPush {
// networks are different, we need to update all eds endpoints
c.opts.XDSUpdater.ConfigUpdate(&model.PushRequest{Full: true, Reason: []model.TriggerReason{model.NetworksTrigger}})
}
shard := model.ShardKeyFromRegistry(c)
ns := currConv.Attributes.Namespace
// We also need to update when the Service changes. For Kubernetes, a service change will result in Endpoint updates,
// but workload entries will also need to be updated.
// TODO(nmittler): Build different sets of endpoints for cluster.local and clusterset.local.
if updateEDSCache || features.EnableK8SServiceSelectWorkloadEntries {
endpoints := c.buildEndpointsForService(currConv, updateEDSCache)
if len(endpoints) > 0 {
c.opts.XDSUpdater.EDSCacheUpdate(shard, string(currConv.Hostname), ns, endpoints)
}
}
// 更新服务缓存
c.opts.XDSUpdater.SvcUpdate(shard, string(currConv.Hostname), ns, event)
// 触发service事件处理函数
c.handlers.NotifyServiceHandlers(prevConv, currConv, event)
}
Service事件处理器会将根据事件的类型更新服务缓存,然后调用serviceHandlers的事件处理器进行回调。serviceHandlers是通过ServiceController的AppendServiceHandler()注册的,注册代码如下:
// pilot/pkg/bootstrap/server.go
func (s *Server) initRegistryEventHandlers() {
log.Info("initializing registry event handlers")
// Flush cached discovery responses whenever services configuration change.
serviceHandler := func(prev, curr *model.Service, event model.Event) {
needsPush := true
if event == model.EventUpdate {
needsPush = serviceUpdateNeedsPush(prev, curr)
}
if needsPush {
// 触发xds全量更新
pushReq := &model.PushRequest{
Full: true,
ConfigsUpdated: sets.New(model.ConfigKey{Kind: kind.ServiceEntry, Name: string(curr.Hostname), Namespace: curr.Attributes.Namespace}),
Reason: []model.TriggerReason{model.ServiceUpdate},
}
s.XDSServer.ConfigUpdate(pushReq)
}
}
// 注册service的事件处理函数
s.ServiceController().AppendServiceHandler(serviceHandler)
...
2)Endpoint事件处理
Endpoint事件处理器在NewController()中调用newEndpointsController()创建endpointsController的时候注册:
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/kube/controller/endpoints.go
func newEndpointsController(c *Controller) *endpointsController {
endpoints := kclient.NewFiltered[*v1.Endpoints](c.client, kclient.Filter{ObjectFilter: c.opts.GetFilter()})
out := &endpointsController{
endpoints: endpoints,
c: c,
}
// 注册endpoint对应的事件处理回调函数
registerHandlers[*v1.Endpoints](c, endpoints, "Endpoints", out.onEvent, endpointsEqual)
return out
}
func (e *endpointsController) onEvent(_, ep *v1.Endpoints, event model.Event) error {
return processEndpointEvent(e.c, e, ep.Name, ep.Namespace, event, ep)
}
Endpoint事件处理函数是processEndpointEvent(),实现如下:
// pilot/pkg/serviceregistry/kube/controller/endpointcontroller.go
func processEndpointEvent(c *Controller, epc kubeEndpointsController, name string, namespace string, event model.Event, ep any) error {
// Update internal endpoint cache no matter what kind of service, even headless service.
// As for gateways, the cluster discovery type is `EDS` for headless service.
// 更新eds
updateEDS(c, epc, ep, event)
if svc := c.services.Get(name, namespace); svc != nil {
// if the service is headless service, trigger a full push if EnableHeadlessService is true,
// otherwise push endpoint updates - needed for NDS output.
// 如果是headlessService,触发xds全量更新
if svc.Spec.ClusterIP == v1.ClusterIPNone {
for _, modelSvc := range c.servicesForNamespacedName(config.NamespacedName(svc)) {
c.opts.XDSUpdater.ConfigUpdate(&model.PushRequest{
Full: features.EnableHeadlessService,
// TODO: extend and set service instance type, so no need to re-init push context
ConfigsUpdated: sets.New(model.ConfigKey{Kind: kind.ServiceEntry, Name: modelSvc.Hostname.String(), Namespace: svc.Namespace}),
Reason: []model.TriggerReason{model.HeadlessEndpointUpdate},
})
return nil
}
}
}
return nil
}
func updateEDS(c *Controller, epc kubeEndpointsController, ep any, event model.Event) {
namespacedName := epc.getServiceNamespacedName(ep)
log.Debugf("Handle EDS endpoint %s %s in namespace %s", namespacedName.Name, event, namespacedName.Namespace)
var forgottenEndpointsByHost map[host.Name][]*model.IstioEndpoint
if event == model.EventDelete {
forgottenEndpointsByHost = epc.forgetEndpoint(ep)
}
shard := model.ShardKeyFromRegistry(c)
for _, hostName := range c.hostNamesForNamespacedName(namespacedName) {
var endpoints []*model.IstioEndpoint
if forgottenEndpointsByHost != nil {
endpoints = forgottenEndpointsByHost[hostName]
} else {
// 将endpoint转换成istio endpoint
endpoints = epc.buildIstioEndpoints(ep, hostName)
}
if features.EnableK8SServiceSelectWorkloadEntries {
svc := c.GetService(hostName)
if svc != nil {
fep := c.collectWorkloadInstanceEndpoints(svc)
endpoints = append(endpoints, fep...)
} else {
log.Debugf("Handle EDS endpoint: skip collecting workload entry endpoints, service %s/%s has not been populated",
namespacedName.Namespace, namespacedName.Name)
}
}
// 调用EDSUpdate
c.opts.XDSUpdater.EDSUpdate(shard, string(hostName), namespacedName.Namespace, endpoints)
}
}
最后调用XDSUpdater.EDSUpdate()进行EDS的缓存更新及触发xDS更新,代码如下:
// pilot/pkg/xds/eds.go
func (s *DiscoveryServer) EDSUpdate(shard model.ShardKey, serviceName string, namespace string,
istioEndpoints []*model.IstioEndpoint,
) {
inboundEDSUpdates.Increment()
// Update the endpoint shards
// 更新eds缓存
pushType := s.edsCacheUpdate(shard, serviceName, namespace, istioEndpoints)
// 触发xds更新
if pushType == IncrementalPush || pushType == FullPush {
// Trigger a push
s.ConfigUpdate(&model.PushRequest{
Full: pushType == FullPush,
ConfigsUpdated: sets.New(model.ConfigKey{Kind: kind.ServiceEntry, Name: serviceName, Namespace: namespace}),
Reason: []model.TriggerReason{model.EndpointUpdate},
})
}
}
func (s *DiscoveryServer) edsCacheUpdate(shard model.ShardKey, hostname string, namespace string,
istioEndpoints []*model.IstioEndpoint,
) PushType {
if len(istioEndpoints) == 0 {
// Should delete the service EndpointShards when endpoints become zero to prevent memory leak,
// but we should not delete the keys from EndpointIndex map - that will trigger
// unnecessary full push which can become a real problem if a pod is in crashloop and thus endpoints
// flip flopping between 1 and 0.
// 在endpoint变为0时,应该删除服务的endpointIndex,但是不能删除endpointIndex map中的键值,
// 因为假如这时pod状态在crash loop和ready之间跳变,就会引起不必要、频繁的xds全量更新
s.Env.EndpointIndex.DeleteServiceShard(shard, hostname, namespace, true)
log.Infof("Incremental push, service %s at shard %v has no endpoints", hostname, shard)
return IncrementalPush
}
pushType := IncrementalPush
// Find endpoint shard for this service, if it is available - otherwise create a new one.
// 找到服务的endpointShard,如果不存在,则创建一个新的
ep, created := s.Env.EndpointIndex.GetOrCreateEndpointShard(hostname, namespace)
// If we create a new endpoint shard, that means we have not seen the service earlier. We should do a full push.
// 如果创建了endpointShard,则需要触发xds全量更新
if created {
log.Infof("Full push, new service %s/%s", namespace, hostname)
pushType = FullPush
}
ep.Lock()
defer ep.Unlock()
newIstioEndpoints := istioEndpoints
// 支持发送unhealthy endpoints
if features.SendUnhealthyEndpoints.Load() {
oldIstioEndpoints := ep.Shards[shard]
newIstioEndpoints = make([]*model.IstioEndpoint, 0, len(istioEndpoints))
// Check if new Endpoints are ready to be pushed. This check
// will ensure that if a new pod comes with a non ready endpoint,
// we do not unnecessarily push that config to Envoy.
// Please note that address is not a unique key. So this may not accurately
// identify based on health status and push too many times - which is ok since its an optimization.
emap := make(map[string]*model.IstioEndpoint, len(oldIstioEndpoints))
nmap := make(map[string]*model.IstioEndpoint, len(newIstioEndpoints))
// Add new endpoints only if they are ever ready once to shards
// so that full push does not send them from shards.
for _, oie := range oldIstioEndpoints {
emap[oie.Address] = oie
}
for _, nie := range istioEndpoints {
nmap[nie.Address] = nie
}
needPush := false
for _, nie := range istioEndpoints {
if oie, exists := emap[nie.Address]; exists {
// If endpoint exists already, we should push if it's health status changes.
// 如果endpoint存在,判断其健康状态是否发生了变化,仅在发生变化时才需要进行xds推送
if oie.HealthStatus != nie.HealthStatus {
needPush = true
}
newIstioEndpoints = append(newIstioEndpoints, nie)
} else if nie.HealthStatus == model.Healthy {
// If the endpoint does not exist in shards that means it is a
// new endpoint. Only send if it is healthy to avoid pushing endpoints
// that are not ready to start with.
// 如果endpoint原来不存在,仅当其健康时进行xds推送
needPush = true
newIstioEndpoints = append(newIstioEndpoints, nie)
}
}
// Next, check for endpoints that were in old but no longer exist. If there are any, there is a
// removal so we need to push an update.
// 如果检查到endpoint原来存在,但是现在被删除了,则这时也需要进行xds推送
for _, oie := range oldIstioEndpoints {
if _, f := nmap[oie.Address]; !f {
needPush = true
}
}
if pushType != FullPush && !needPush {
log.Debugf("No push, either old endpoint health status did not change or new endpoint came with unhealthy status, %v", hostname)
pushType = NoPush
}
}
ep.Shards[shard] = newIstioEndpoints
// Check if ServiceAccounts have changed. We should do a full push if they have changed.
// 检查serviceAccount的变化
saUpdated := s.UpdateServiceAccount(ep, hostname)
// For existing endpoints, we need to do full push if service accounts change.
if saUpdated && pushType != FullPush {
// Avoid extra logging if already a full push
log.Infof("Full push, service accounts changed, %v", hostname)
pushType = FullPush
}
// Clear the cache here. While it would likely be cleared later when we trigger a push, a race
// condition is introduced where an XDS response may be generated before the update, but not
// completed until after a response after the update. Essentially, we transition from v0 -> v1 ->
// v0 -> invalidate -> v1. Reverting a change we pushed violates our contract of monotonically
// moving forward in version. In practice, this is pretty rare and self corrects nearly
// immediately. However, clearing the cache here has almost no impact on cache performance as we
// would clear it shortly after anyways.
// 清空xdsCache
s.Cache.Clear(sets.New(model.ConfigKey{Kind: kind.ServiceEntry, Name: hostname, Namespace: namespace}))
return pushType
}
Endpoint事件处理器根据Endpoint的变化更新与服务相关的缓存,判断本次Endpoint资源的更新是否需要触发全量的xDS更新。在服务网各种变化最多、最快的往往是Endpoint,因为增量EDS的更新能够大大降低系统的资源(CPU、内存、带宽)开销,提升服务网格的稳定性
参考:
《Istio权威指南 下》文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-605260.html
2.深入Istio源码:Pilot服务发现文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-605260.html
到了这里,关于Istio Pilot源码学习(二):ServiceController服务发现的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!