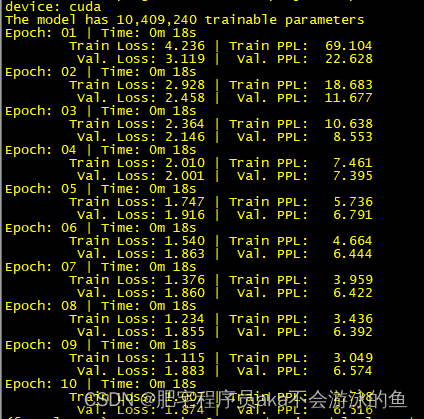
系列文章
【如何训练一个中英翻译模型】LSTM机器翻译seq2seq字符编码(一)
【如何训练一个中英翻译模型】LSTM机器翻译模型训练与保存(二)
【如何训练一个中英翻译模型】LSTM机器翻译模型部署(三)
【如何训练一个中英翻译模型】LSTM机器翻译模型部署之onnx(python)(四)
一、事情准备
这篇是在【如何训练一个中译英翻译器】LSTM机器翻译模型部署之onnx(python)(四)的基础上进行的,要用到文件为:
input_words.txt
target_words.txt
config.json
encoder_model-sim.onnx
decoder_model-sim.onnx
其中的onnx就是用来转为ncnn模型的,这里借助了onnx这个中间商,所以前面我们需要先通过onnxsim对模型进行simplify,要不然在模型转换时会出现op不支持的情况(模型转换不仅有中间商这个例子,目前还可以通过pnnx直接将pytorch模型转为ncnn,感兴趣的小伙伴可以去折腾下)
老规矩,先给出工具:
onnx2ncnn:https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn
netron:https://netron.app
二、模型转换
这里进行onnx转ncnn,通过命令进行转换
onnx2ncnn onnxModel/encoder_model-sim.onnx ncnnModel/encoder_model.param ncnnModel/encoder_model.bin
onnx2ncnn onnxModel/decoder_model-sim.onnx ncnnModel/decoder_model.param ncnnModel/decoder_model.bin
转换成功可以看到:
转换之后可以对模型进行优化,但是奇怪的是,这里优化了不起作用,去不了MemoryData这些没用的op
ncnnoptimize ncnnModel/encoder_model.param ncnnModel/encoder_model.bin ncnnModel/encoder_model.param ncnnModel/encoder_model.bin 1
ncnnoptimize ncnnModel/decoder_model.param ncnnModel/decoder_model.bin ncnnModel/decoder_model.param ncnnModel/decoder_model.bin 1
三、ncnn模型加载与推理(python版)
跟onnx的推理比较类似,就是函数的调用方法有点不同,这里先用python实现,验证下是否没问题,方面后面部署到其它端,比如android。
主要包括:模型加载、推理模型搭建跟模型推理,但要注意的是这里的输入输出名称需要在param这个文件里面获取。
采用netron分别查看encoder与decoder的网络结构,获取输入输出名称:
encoder:
输入输出分别如图
decoder:
输入
输出:
推理代码如下,推理过程感觉没问题,但是推理输出结果相差很大(对比过第一层ncnn与onnx的推理结果了),可能问题出在模型转换环节的精度损失上,而且第二层模型转换后网络输出结果不一致了,很迷,还没找出原因,但是以下的推理是能运行通过,只不过输出结果有问题
import numpy as np
import ncnn
# 加载字符
# 从 input_words.txt 文件中读取字符串
with open('config/input_words.txt', 'r') as f:
input_words = f.readlines()
input_characters = [line.rstrip('\n') for line in input_words]
# 从 target_words.txt 文件中读取字符串
with open('config/target_words.txt', 'r', newline='') as f:
target_words = [line.strip() for line in f.readlines()]
target_characters = [char.replace('\\t', '\t').replace('\\n', '\n') for char in target_words]
#字符处理,以方便进行编码
input_token_index = dict([(char, i) for i, char in enumerate(input_characters)])
target_token_index = dict([(char, i) for i, char in enumerate(target_characters)])
# something readable.
reverse_input_char_index = dict(
(i, char) for char, i in input_token_index.items())
reverse_target_char_index = dict(
(i, char) for char, i in target_token_index.items())
num_encoder_tokens = len(input_characters) # 英文字符数量
num_decoder_tokens = len(target_characters) # 中文文字数量
import json
with open('config/config.json', 'r') as file:
loaded_data = json.load(file)
# 从加载的数据中获取max_encoder_seq_length和max_decoder_seq_length的值
max_encoder_seq_length = loaded_data["max_encoder_seq_length"]
max_decoder_seq_length = loaded_data["max_decoder_seq_length"]
# Load the ncnn models for the encoder and decoder
encoderNet = ncnn.Net()
encoderNet.load_param("ncnnModel/encoder_model.param")
encoderNet.load_model("ncnnModel/encoder_model.bin")
decoderNet = ncnn.Net()
decoderNet.load_param("ncnnModel/decoder_model.param")
decoderNet.load_model("ncnnModel/decoder_model.bin")
def decode_sequence(input_seq):
# Encode the input as state vectors.
# print(input_seq)
ex_encoder = encoderNet.create_extractor()
ex_encoder.input("input_1", ncnn.Mat(input_seq))
states_value = []
_, LSTM_1 = ex_encoder.extract("lstm")
_, LSTM_2 = ex_encoder.extract("lstm_1")
states_value.append(LSTM_1)
states_value.append(LSTM_2)
# print(ncnn.Mat(input_seq))
# print(vgdgd)
# Generate empty target sequence of length 1.
target_seq = np.zeros((1, 1, 849))
# Populate the first character of target sequence with the start character.
target_seq[0, 0, target_token_index['\t']] = 1.
# this target_seq you can treat as initial state
# Sampling loop for a batch of sequences
# (to simplify, here we assume a batch of size 1).
stop_condition = False
decoded_sentence = ''
ex_decoder = decoderNet.create_extractor()
while not stop_condition:
#print(ncnn.Mat(target_seq))
print("---------")
ex_decoder.input("input_2", ncnn.Mat(target_seq))
ex_decoder.input("input_3", states_value[0])
ex_decoder.input("input_4", states_value[1])
_, output_tokens = ex_decoder.extract("dense")
_, h = ex_decoder.extract("lstm_1")
_, c = ex_decoder.extract("lstm_1_1")
print(output_tokens)
tk = []
for i in range(849):
tk.append(output_tokens[849*i])
tk = np.array(tk)
output_tokens = tk.reshape(1,1,849)
print(output_tokens)
# print(fdgd)
print(h)
print(c)
# output_tokens = np.array(output_tokens)
# output_tokens = output_tokens.reshape(1, 1, -1)
# # h = np.array(h)
# # c = np.array(c)
# print(output_tokens.shape)
# print(h.shape)
# print(c.shape)
#output_tokens, h, c = decoder_model.predict([target_seq] + states_value)
# Sample a token
# argmax: Returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis
# just like find the most possible char
sampled_token_index = np.argmax(output_tokens[0, -1, :])
# find char using index
sampled_char = reverse_target_char_index[sampled_token_index]
# and append sentence
decoded_sentence += sampled_char
# Exit condition: either hit max length
# or find stop character.
if (sampled_char == '\n' or len(decoded_sentence) > max_decoder_seq_length):
stop_condition = True
# Update the target sequence (of length 1).
# append then ?
# creating another new target_seq
# and this time assume sampled_token_index to 1.0
target_seq = np.zeros((1, 1, num_decoder_tokens))
target_seq[0, 0, sampled_token_index] = 1.
print(sampled_token_index)
# Update states
# update states, frome the front parts
states_value = [h, c]
return decoded_sentence
import numpy as np
input_text = "Call me."
encoder_input_data = np.zeros(
(1,max_encoder_seq_length, num_encoder_tokens),
dtype='float32')
for t, char in enumerate(input_text):
print(char)
# 3D vector only z-index has char its value equals 1.0
encoder_input_data[0,t, input_token_index[char]] = 1.
input_seq = encoder_input_data
decoded_sentence = decode_sequence(input_seq)
print('-')
print('Input sentence:', input_text)
print('Decoded sentence:', decoded_sentence)
decoder的模型输出为849*849,感觉怪怪的,然后我们把模型的输入固定下来看看是不是模型的问题。
打开decoder_model.param,把输入层固定下来,0=w 1=h 2=c,那么:
input_2:0=849 1=1 2=1
input_3:0=256 1=1
input_4:0=256 1=1
运行以下命令进行优化
ncnnoptimize ncnnModel/decoder_model.param ncnnModel/decoder_model.bin ncnnModel/decoder_model.param ncnnModel/decoder_model.bin 1
结果如下:
打开网络来看一下:
可以看到输出确实是849849(红色框),那就是模型转换有问题了
仔细看,能够看到有两个shape(蓝色框)分别为849跟8491,这两个不同维度的网络进行BinaryOP之后,就变成849849了,那么,我们把Reshape这个网络去掉试试(不把前面InnerProduct的输入维度有849reshape为8491),下面来看手术刀怎么操作。
我们需要在没经过固定维度并ncnnoptimize的模型上操作(也就是没经过上面0=w 1=h 2=c修改的模型上操作)
根据名字我们找到Reshape那一层:
然后找到与reshape那一层相连接的上一层(红色框)与下一层(蓝色框)
通过红色框与蓝色框里面的名字我们找到了上层与下层分别为InnerProduct与BinaryOp
这时候,把InnerProduct与BinaryOp接上,把Reshape删掉
再改一下最上面的层数,把19改为18,因为我们删掉了一层 保存之后再次执行
保存之后再次执行
ncnnoptimize ncnnModel/decoder_model.param ncnnModel/decoder_model.bin ncnnModel/decoder_model.param ncnnModel/decoder_model.bin 1
执行后可以看到网络层数跟blob数都更新了
这时候改一下固定一下输入层数,并运行ncnnoptimize,再打开netron看一下网络结构,可以看到输出维度正常了
但是通过推理结果还是不对,没找到原因,推理代码如下:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-606316.html
import numpy as np
import ncnn
# 加载字符
# 从 input_words.txt 文件中读取字符串
with open('config/input_words.txt', 'r') as f:
input_words = f.readlines()
input_characters = [line.rstrip('\n') for line in input_words]
# 从 target_words.txt 文件中读取字符串
with open('config/target_words.txt', 'r', newline='') as f:
target_words = [line.strip() for line in f.readlines()]
target_characters = [char.replace('\\t', '\t').replace('\\n', '\n') for char in target_words]
#字符处理,以方便进行编码
input_token_index = dict([(char, i) for i, char in enumerate(input_characters)])
target_token_index = dict([(char, i) for i, char in enumerate(target_characters)])
# something readable.
reverse_input_char_index = dict(
(i, char) for char, i in input_token_index.items())
reverse_target_char_index = dict(
(i, char) for char, i in target_token_index.items())
num_encoder_tokens = len(input_characters) # 英文字符数量
num_decoder_tokens = len(target_characters) # 中文文字数量
import json
with open('config/config.json', 'r') as file:
loaded_data = json.load(file)
# 从加载的数据中获取max_encoder_seq_length和max_decoder_seq_length的值
max_encoder_seq_length = loaded_data["max_encoder_seq_length"]
max_decoder_seq_length = loaded_data["max_decoder_seq_length"]
# Load the ncnn models for the encoder and decoder
encoderNet = ncnn.Net()
encoderNet.load_param("ncnnModel/encoder_model.param")
encoderNet.load_model("ncnnModel/encoder_model.bin")
decoderNet = ncnn.Net()
decoderNet.load_param("ncnnModel/decoder_model.param")
decoderNet.load_model("ncnnModel/decoder_model.bin")
def decode_sequence(input_seq):
# Encode the input as state vectors.
# print(input_seq)
ex_encoder = encoderNet.create_extractor()
ex_encoder.input("input_1", ncnn.Mat(input_seq))
states_value = []
_, LSTM_1 = ex_encoder.extract("lstm")
_, LSTM_2 = ex_encoder.extract("lstm_1")
states_value.append(LSTM_1)
states_value.append(LSTM_2)
# print(ncnn.Mat(input_seq))
# print(vgdgd)
# Generate empty target sequence of length 1.
target_seq = np.zeros((1, 1, 849))
# Populate the first character of target sequence with the start character.
target_seq[0, 0, target_token_index['\t']] = 1.
# this target_seq you can treat as initial state
# Sampling loop for a batch of sequences
# (to simplify, here we assume a batch of size 1).
stop_condition = False
decoded_sentence = ''
ex_decoder = decoderNet.create_extractor()
while not stop_condition:
#print(ncnn.Mat(target_seq))
print("---------")
ex_decoder.input("input_2", ncnn.Mat(target_seq))
ex_decoder.input("input_3", states_value[0])
ex_decoder.input("input_4", states_value[1])
_, output_tokens = ex_decoder.extract("dense")
_, h = ex_decoder.extract("lstm_1")
_, c = ex_decoder.extract("lstm_1_1")
print(output_tokens)
# print(ghfhf)
# tk = []
# for i in range(849):
# tk.append(output_tokens[849*i])
# tk = np.array(tk)
# output_tokens = tk.reshape(1,1,849)
# print(output_tokens)
# print(fdgd)
print(h)
print(c)
output_tokens = np.array(output_tokens)
output_tokens = output_tokens.reshape(1, 1, -1)
# # h = np.array(h)
# # c = np.array(c)
# print(output_tokens.shape)
# print(h.shape)
# print(c.shape)
#output_tokens, h, c = decoder_model.predict([target_seq] + states_value)
# Sample a token
# argmax: Returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis
# just like find the most possible char
sampled_token_index = np.argmax(output_tokens[0, -1, :])
# find char using index
sampled_char = reverse_target_char_index[sampled_token_index]
# and append sentence
decoded_sentence += sampled_char
# Exit condition: either hit max length
# or find stop character.
if (sampled_char == '\n' or len(decoded_sentence) > max_decoder_seq_length):
stop_condition = True
# Update the target sequence (of length 1).
# append then ?
# creating another new target_seq
# and this time assume sampled_token_index to 1.0
target_seq = np.zeros((1, 1, num_decoder_tokens))
target_seq[0, 0, sampled_token_index] = 1.
print(sampled_token_index)
# Update states
# update states, frome the front parts
states_value = [h, c]
return decoded_sentence
import numpy as np
input_text = "Call me."
encoder_input_data = np.zeros(
(1,max_encoder_seq_length, num_encoder_tokens),
dtype='float32')
for t, char in enumerate(input_text):
print(char)
# 3D vector only z-index has char its value equals 1.0
encoder_input_data[0,t, input_token_index[char]] = 1.
input_seq = encoder_input_data
decoded_sentence = decode_sequence(input_seq)
print('-')
print('Input sentence:', input_text)
print('Decoded sentence:', decoded_sentence)
参考文献:https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/issues/2586文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-606316.html
到了这里,关于【如何训练一个中英翻译模型】LSTM机器翻译模型部署之ncnn(python)(五)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!