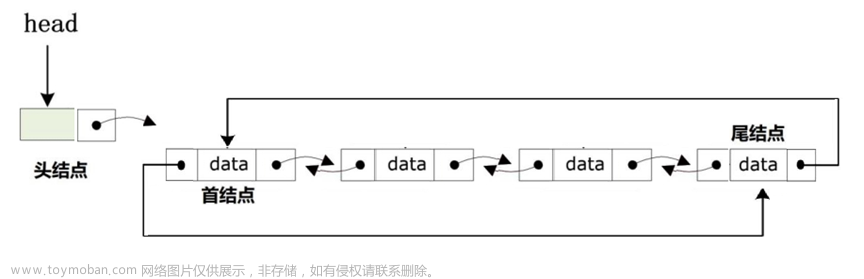
上一节我们谈到了链表的概念,以及链表的创建方法,忘记的小伙伴可以复习一下:
[算法通关村] 1.1 单向链表的创建
今天我们来探究一下链表的插入,链表的插入共有 3 种可能性,分别是在链表的头部插入、在中间插入,和在链表的尾部插入(追加),不同的插入位置对应着不同的代码,所以需要一个一个来探究。
在链表的中间插入
我们先来看一个新节点 nodeInsert 如何插入到位置为 1 < k < n+1 的原节点前面。(n 为链表长度)
不难想到,由于我们上一节中创建的是一个 “单向链表”,每一个节点仅知道下一个节点的位置,并不知道上一个节点的位置,就像 “猴子掰玉米” 一样。在插入过程中,为了不丢失节点,需要保证每一个节点都被引用(指向),才不会被 JVM 回收,我们可以看到如下的插入过程:
![[算法通关村] 1.2 链表的插入,算法通关村,算法,链表,数据结构](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2023/07/606650-1.gif)
首先需要将 nodeInsert.next 指向拟插入位置 k 的上一个节点的 next,即:
nodeInsert.next = current.next然后将 current.next 指向 nodeInsert,此时变量 current 指向节点的原 next 关系自动消失:(只能同时指向一个后继节点)
current.next = nodeInsert在链表的头部插入
在链表的头部插入需要移动头指针 head 。由于头插移动了头结点,内存地址发生变化,所以需要将返回的新节点赋与 linkedList,否则后续计算会出错。
首先将待插入节点 nodeInsert 的 next 变量指向头结点,然后移动头指针指向 nodeInsert 即可:
![[算法通关村] 1.2 链表的插入,算法通关村,算法,链表,数据结构](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2023/07/606650-2.gif)
代码实现如下:
nodeInsert.next = linkedList;
linkedList = nodeInsert;
return linkedList;
//上面 return 还可以这么写:
//return nodeInsert;
在链表的尾部插入
在链表的尾部插入主要有两步,首先需要一个指针(Node 型变量)指向尾结点,这就涉及到了链表的遍历,而在 “链表的中间插入” 环节,也会涉及到链表的遍历,我们可以将此代码复用:
// 移动指针到拟插入位置的前一个节点
int count = 1;
while (count < position - 1) {
current = current.next;
count++;
}然后只需要将尾结点 current.next 指向待插入的 nodeInsert 节点即可:
// 此代码可省略,实际上是赋予了 null 值
// 因无伤大雅,又与 “中间插入” 代码一致,故可复用
nodeInsert.next = current.next;
current.next = nodeInsert;插入过程的图形化展示如下:
![[算法通关村] 1.2 链表的插入,算法通关村,算法,链表,数据结构](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2023/07/606650-3.gif)
注意事项及完整代码
上述原理很容易理解,但在实际操作中,还需要判断插入位置是否越界,即:
- 最少在 position = 1 前插入(头部插入)
- 至多在 position = getLength(linkedList) + 1 前插入(尾部插入)
![[算法通关村] 1.2 链表的插入,算法通关村,算法,链表,数据结构](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2023/07/606650-4.png)
当插入位置 position 的值不满足上述要求时,我们会手动抛出一个异常:
// 短路或 先判断简单的
if (position < 1 || position > (getLength(linkedList) + 1)) {
throw new Exception("参数:拟插入位置 越界");
}其次,我们还需要查看待操作链表是否为一个空链表,这在方法 getLength 中就会进行判断,所以无需重复写判空语句:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-606650.html
public static int getLength(NewNode linkedList) throws Exception {
int length = 0;
NewNode current = linkedList;
while (current != null) {
length++;
current = current.next;
}
if (length == 0) {
throw new Exception("链表不存在");
}
return length;
}除此之外,还实现了 toString 方法用于遍历链表查看效果,该方法不是必须的。最后给出完整代码:文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-606650.html
class NewNode {
public int val;
public NewNode next;
NewNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
public class BasicLinkList {
/**
* 链表插入
*
* @param linkedList 链表头节点
* @param nodeInsert 待插入节点
* @param position 在该位置前插入
* @return 插入后得到的新链表(指向头节点)
*/
public static NewNode insertNode(NewNode linkedList, NewNode nodeInsert, int position) throws Exception {
// 越界判断:
// 最少在 position = 1 前插入(头插),
// 最多在 position = getLength(linkedList) + 1 前插入(尾插)
// 短路或 先判断简单的
if (position < 1 || position > (getLength(linkedList) + 1)) {
throw new Exception("参数:拟插入位置 越界");
}
//在链表开头插入
if (position == 1) {
nodeInsert.next = linkedList;
// return nodeInsert;
//上面return还可以这么写:
linkedList = nodeInsert;
return linkedList;
}
NewNode current = linkedList;
int count = 1;
// 移动指针到拟插入位置的前一个节点
while (count < position - 1) {
current = current.next;
count++;
}
nodeInsert.next = current.next;
current.next = nodeInsert;
return linkedList;
}
/**
* 获取链表长度
*
* @param linkedList 链表头节点
* @return 链表长度
*/
public static int getLength(NewNode linkedList) throws Exception {
int length = 0;
NewNode current = linkedList;
while (current != null) {
length++;
current = current.next;
}
if (length == 0) {
throw new Exception("链表不存在");
}
return length;
}
/**
* 输出链表
*
* @param head 头节点
*/
public static String toString(NewNode head) {
NewNode current = head;
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
while (current != null) {
stringBuilder.append(current.val).append("\t");
current = current.next;
}
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 先创建一个链表
NewNode linkedList = BasicLink.initLinkedList(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5});
NewNode newNode;
// 中间插入节点:在第 3 个节点前,插入 val = 30
newNode = new NewNode(30);
System.out.println(BasicLinkList.toString(BasicLinkList.insertNode(linkedList, newNode, 3)));
System.out.println("========");
// 头部插入节点:插入 val = 72
newNode = new NewNode(72);
// 由于头插移动了头结点,内存地址发生变化,所以需要将返回的新节点赋与 linkedList,否则后续计算会出错
linkedList = BasicLinkList.insertNode(linkedList, newNode, 1);
System.out.println(BasicLinkList.toString(linkedList));
System.out.println("========");
// 尾部插入节点:插入 val = 9
newNode = new NewNode(9);
System.out.println(BasicLinkList.toString(BasicLinkList.insertNode(linkedList, newNode, BasicLinkList.getLength(linkedList)+1)));
}
}到了这里,关于[算法通关村] 1.2 链表的插入的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!