内核函数
定时器涉及函数参考内核源码:include\linux\timer.h
给定时器的各个参数赋值:
setup_timer(struct timer_list * timer,
void (*function)(unsigned long),
unsigned long data):
设置定时器:主要是初始化 timer_list 结构体,设置其中的函数、参数。
void add_timer(struct timer_list *timer):
- a) 向内核添加定时器。timer->expires 表示超时时间。
- b) 当超时时间到达,内核就会调用这个函数:timer->function(timer->data)。
修改定时器:
int mod_timer(struct timer_list *timer, unsigned long expires):
- a) 修改定时器的超时时间,
- b) 它等同于:del_timer(timer); timer->expires = expires; add_timer(timer);
- c) 但是更加高效。
修改定时器:
int del_timer(struct timer_list *timer)
内核定时器时间单位
编译内核时,可以在内核源码根目录下用“ls -a”看到一个隐藏文件.config,它就是内核配置文件。打开后可以看到如下这项:
CONFIG_HZ=100
这是硬件定时器,这表示内核每秒中会发生 100 次系统滴答中断(tick),这是 Linux 系统的心跳。每发生一次 tick 中断,全局变量 jiffies 就会累加 1。CONFIG_HZ=100 表示每个滴答是 10ms。定时器的时间就是基于 jiffies 的,我们修改超时时间时,一般使用这 2种方法:
① 在 add_timer 之前,直接修改:
timer.expires = jiffies + xxx; // xxx 表示多少个滴答后超时,也就是 xxx*10ms
timer.expires = jiffies + 2*HZ; // HZ 等于 CONFIG_HZ ,2*HZ 就相当于 2 秒
② 在 add_timer 之后,使用 mod_timer 修改:
mod_timer(&timer, jiffies + xxx); // xxx 表示多少个滴答后超时,也就是 xxx*10ms
mod_timer(&timer, jiffies + 2*HZ); // HZ 等于 CONFIG_HZ ,2*HZ 就相当于 2 秒
系统滴答中断(tick)与定时器的关系
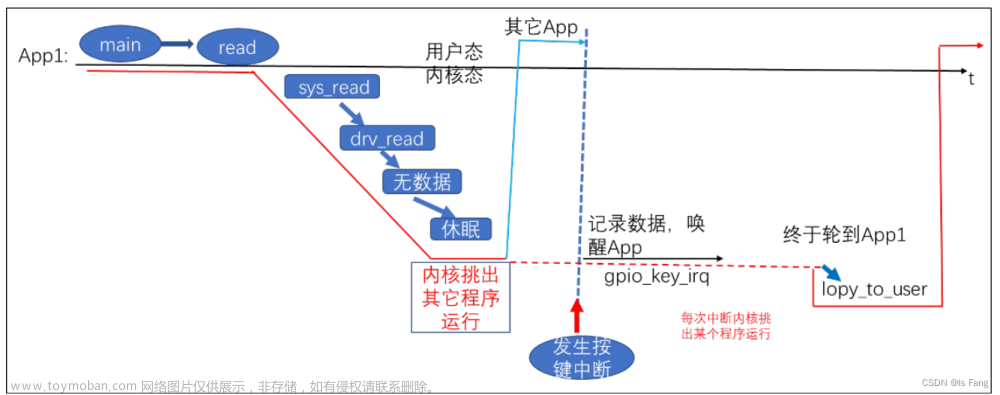
系统滴答中断是硬件中断,定时器是软件中断,每次执行完硬件中断后才执行软件中断,系统滴答中断设置为100HZ,表示10ms执行一次软件中断,判断全局变量jiffies 是否大于key_timer.expires,大于则调用对应的定时器处理函数
定时器方式的按键驱动程序(stm32mp157)(旧版本定时器)
使用定时器处理按键抖动

如果不处理抖动的话,用户只操作一次按键, GPIO 电平会反复变化,中断程序可能会上报多个数据,那么可以在 GPIO 中断中并不立刻记录按键值,而是修改定时器超时时间,10ms 后再处理如果 10ms 内又发生了 GPIO 中断,那就认为是抖动,这时再次修改超时时间为 10ms。只有 10ms 之内再无 GPIO 中断发生,那么定时器的函数才会被调用。在定时器函数中记录按键值。
button_test.c
实现功能:首先以非阻塞的方式读取环形缓冲区十次,然后以阻塞的方式读取按键的值
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <signal.h>
static int fd;
/*
* ./button_test /dev/my_gpio_key
*
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int val;
struct pollfd fds[1];
int timeout_ms = 5000;
int ret;
int flags;
int i;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s <dev>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开文件 */
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
//非阻塞的方式读取十次
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if (read(fd, &val, 4) == 4)
printf("get button: 0x%x\n", val);
else
printf("get button: -1\n");
}
//修改为阻塞的方式,是休眠唤醒机制,没有数据则休眠
flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags & ~O_NONBLOCK);
while (1)
{
if (read(fd, &val, 4) == 4)
printf("get button: 0x%x\n", val);
else
printf("while get button: -1\n");
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
gpio_key_drv.c
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include <linux/gpio/consumer.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/of_irq.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
struct gpio_key{
int gpio;
struct gpio_desc *gpiod;
int flag;
int irq;
struct timer_list key_timer;//每个按键都有定时器
} ;
static struct gpio_key *gpio_keys_first;
/* 主设备号 */
static int major = 0;
static struct class *gpio_key_class;
/* 环形缓冲区 */
#define BUF_LEN 128
static int g_keys[BUF_LEN];
static int r, w;
struct fasync_struct *button_fasync;
#define NEXT_POS(x) ((x+1) % BUF_LEN)
static int is_key_buf_empty(void)
{
return (r == w);
}
static int is_key_buf_full(void)
{
return (r == NEXT_POS(w));
}
static void put_key(int key)
{
if (!is_key_buf_full())
{
g_keys[w] = key;
w = NEXT_POS(w);
}
}
static int get_key(void)
{
int key = 0;
if (!is_key_buf_empty())
{
key = g_keys[r];
r = NEXT_POS(r);
}
return key;
}
static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(gpio_key_wait);
//定时中断函数:完成按键状态的返回
static void key_timer_expire(unsigned long data)
{
/* data ==> gpio */
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = data;
int val;
int key;
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
printk("key_timer_expire key %d %d\n", gpio_key->gpio, val);
key = (gpio_key->gpio << 8) | val;
put_key(key);
wake_up_interruptible(&gpio_key_wait);
kill_fasync(&button_fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
}
/* 实现对应的open/read/write等函数,填入file_operations结构体 */
static ssize_t gpio_key_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
//printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
int err;
int key;
if (is_key_buf_empty() && (file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK))
return -EAGAIN;
wait_event_interruptible(gpio_key_wait, !is_key_buf_empty());
key = get_key();
err = copy_to_user(buf, &key, 4);
return 4;
}
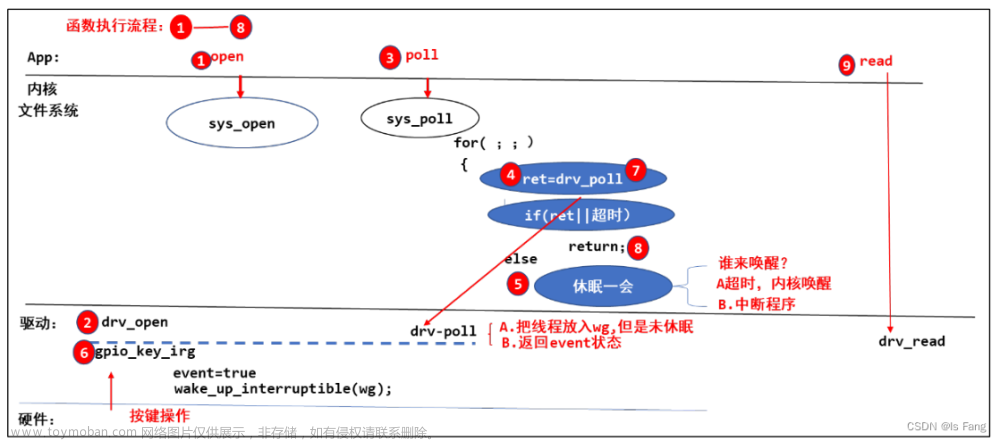
static unsigned int gpio_key_drv_poll(struct file *fp, poll_table * wait)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
poll_wait(fp, &gpio_key_wait, wait);
return is_key_buf_empty() ? 0 : POLLIN | POLLRDNORM;
}
static int gpio_key_drv_fasync(int fd, struct file *file, int on)
{
if (fasync_helper(fd, file, on, &button_fasync) >= 0)
return 0;
else
return -EIO;
}
/* 定义自己的file_operations结构体 */
static struct file_operations gpio_key_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = gpio_key_drv_read,
.poll = gpio_key_drv_poll,
.fasync = gpio_key_drv_fasync,
};
//按键中断处理函数不会直接返回按键的状态,而是通过调用定时器中断
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = dev_id;
printk("gpio_key_isr key %d irq happened\n", gpio_key->gpio);
mod_timer(&gpio_key->key_timer, jiffies + HZ/50);//使用HZ宏,定时器超时时间为20ms,如果超时时间到了,就会修改key_timer的值,导致key_timer_expire函数被调用
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
/* 1. 从platform_device获得GPIO
* 2. gpio=>irq
* 3. request_irq
*/
static int gpio_key_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int err;
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
enum of_gpio_flags flag;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
count = of_gpio_count(node);
if (!count)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, there isn't any gpio available\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_first= kzalloc(sizeof(struct gpio_key) * count, GFP_KERNEL);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
gpio_keys_first[i].gpio = of_get_gpio_flags(node, i, &flag);
if (gpio_keys_first[i].gpio < 0)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, of_get_gpio_flags fail\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_first[i].gpiod = gpio_to_desc(gpio_keys_first[i].gpio);
gpio_keys_first[i].flag = flag & OF_GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW;
gpio_keys_first[i].irq = gpio_to_irq(gpio_keys_first[i].gpio);
//每个按键都注册定时中断函数
setup_timer(&gpio_keys_first[i].key_timer, key_timer_expire, &gpio_keys_first[i]);
gpio_keys_first[i].key_timer.expires = ~0;
add_timer(&gpio_keys_first[i].key_timer);
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
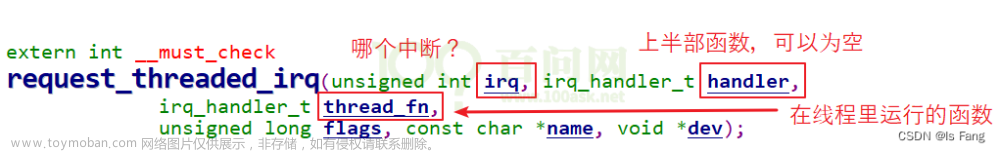
err = request_irq(gpio_keys_first[i].irq, gpio_key_isr, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "my_gpio_key", &gpio_keys_first[i]);
}
/* 注册file_operations */
major = register_chrdev(0, "my_gpio_key", &gpio_key_drv); /* /dev/gpio_key */
gpio_key_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "my_gpio_key_class");
if (IS_ERR(gpio_key_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "my_gpio_key");
return PTR_ERR(gpio_key_class);
}
device_create(gpio_key_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "my_gpio_key"); /* /dev/my_gpio_key */
return 0;
}
static int gpio_key_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
//int err;
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
device_destroy(gpio_key_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(gpio_key_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "my_gpio_key");
count = of_gpio_count(node);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
free_irq(gpio_keys_first[i].irq, &gpio_keys_first[i]);
del_timer(&gpio_keys_first[i].key_timer);
}
kfree(gpio_keys_first);
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id my_keys[] = {
{ .compatible = "first_key,gpio_key" },
{ },
};
/* 1. 定义platform_driver */
static struct platform_driver gpio_keys_driver = {
.probe = gpio_key_probe,
.remove = gpio_key_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "my_gpio_key",
.of_match_table = my_keys,
},
};
/* 2. 在入口函数注册platform_driver */
static int __init gpio_key_init(void)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
err = platform_driver_register(&gpio_keys_driver);
return err;
}
/* 3. 有入口函数就应该有出口函数:卸载驱动程序时,就会去调用这个出口函数
* 卸载platform_driver
*/
static void __exit gpio_key_exit(void)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
platform_driver_unregister(&gpio_keys_driver);
}
/* 7. 其他完善:提供设备信息,自动创建设备节点 */
module_init(gpio_key_init);
module_exit(gpio_key_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
Makefile
# 1. 使用不同的开发板内核时, 一定要修改KERN_DIR
# 2. KERN_DIR中的内核要事先配置、编译, 为了能编译内核, 要先设置下列环境变量:
# 2.1 ARCH, 比如: export ARCH=arm64
# 2.2 CROSS_COMPILE, 比如: export CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu-
# 2.3 PATH, 比如: export PATH=$PATH:/home/book/100ask_roc-rk3399-pc/ToolChain-6.3.1/gcc-linaro-6.3.1-2017.05-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin
# 注意: 不同的开发板不同的编译器上述3个环境变量不一定相同,
# 请参考各开发板的高级用户使用手册
KERN_DIR = /home/book/100ask_stm32mp157_pro-sdk/Linux-5.4
all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules
$(CROSS_COMPILE)gcc -o button_test button_test.c
clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean
rm -rf modules.order button_test
# 参考内核源码drivers/char/ipmi/Makefile
# 要想把a.c, b.c编译成ab.ko, 可以这样指定:
# ab-y := a.o b.o
# obj-m += ab.o
obj-m += gpio_key_drv.o
修改设备树文件

对于一个引脚要用作中断时,
- a) 要通过 PinCtrl 把它设置为 GPIO 功能;【ST 公司对于 STM32MP157 系列芯片,GPIO 为默认模式 不需要再进行配置Pinctrl 信息】
- b) 表明自身:是哪一个 GPIO 模块里的哪一个引脚【修改设备树】
打开内核的设备树文件:arch/arm/boot/dts/stm32mp157c-100ask-512d-lcd-v1.dts
gpio_keys_first {
compatible = "first_key,gpio_key";
gpios = <&gpiog 3 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW
&gpiog 2 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>;
};
与此同时,需要把用到引脚的节点禁用
注意,如果其他设备树文件也用到该节点,需要设置属性为disabled状态,在arch/arm/boot/dts目录下执行如下指令查找哪些设备树用到该节点
grep "&gpiog" * -nr
如果用到该节点,需要添加属性去屏蔽:
status = "disabled";

编译测试
首先要设置 ARCH、CROSS_COMPILE、PATH 这三个环境变量后,进入 ubuntu 上板子内核源码的目录,在Linux内核源码根目录下,执行如下命令即可编译 dtb 文件:
make dtbs V=1
编译好的文件在路径由DTC指定,移植设备树到开发板的共享文件夹中,先保存源文件,然后覆盖源文件,重启后会挂载新的设备树,进入该目录查看是否有新添加的设备节点
cd /sys/firmware/devicetree/base
编译驱动程序,在Makefile文件目录下执行make指令,此时,目录下有编译好的内核模块gpio_key_drv.ko和可执行文件button_test文件移植到开发板上
确定一下烧录系统:cat /proc/mounts,查看boot分区挂载的位置,将其重新挂载在boot分区:mount /dev/mmcblk2p2 /boot,然后将共享文件夹里面的设备树文件拷贝到boot目录下,这样的话设备树文件就在boot目录下
cp /mnt/stm32mp157c-100ask-512d-lcd-v1.dtb /boot
重启后挂载,运行
insmod -f gpio_key_drv.ko // 强制安装驱动程序
ls /dev/my_gpio_key
./button_test /dev/my_gpio_key & //后台运行,此时prink函数打印的内容看不到
然后按下按键文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-608038.html
定时器方式的按键驱动程序(stm32mp157)(新版本定时器)
高版本的定时器的函数和结构体发生变化,具体变化如下:


所以只需要修改timer_setup函数和定时器中断处理函数文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-608038.html
修改gpio_key_drv.c
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include <linux/gpio/consumer.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/of_irq.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
struct gpio_key{
int gpio;
struct gpio_desc *gpiod;
int flag;
int irq;
struct timer_list key_timer;//每个按键都有定时器
} ;
static struct gpio_key *gpio_keys_first;
/* 主设备号 */
static int major = 0;
static struct class *gpio_key_class;
/* 环形缓冲区 */
#define BUF_LEN 128
static int g_keys[BUF_LEN];
static int r, w;
struct fasync_struct *button_fasync;
#define NEXT_POS(x) ((x+1) % BUF_LEN)
static int is_key_buf_empty(void)
{
return (r == w);
}
static int is_key_buf_full(void)
{
return (r == NEXT_POS(w));
}
static void put_key(int key)
{
if (!is_key_buf_full())
{
g_keys[w] = key;
w = NEXT_POS(w);
}
}
static int get_key(void)
{
int key = 0;
if (!is_key_buf_empty())
{
key = g_keys[r];
r = NEXT_POS(r);
}
return key;
}
static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(gpio_key_wait);
//定时中断函数:完成按键状态的返回
//static void key_timer_expire(unsigned long data)
static void key_timer_expire(struct timer_list *t)
{
/* data ==> gpio */
//struct gpio_key *gpio_key = data;
//利用from_timer函数的定时器成员反算出结构体的指针,进而获得该结构体的所有信息
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = from_timer(gpio_key, t, key_timer);
int val;
int key;
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
printk("key_timer_expire key %d %d\n", gpio_key->gpio, val);
key = (gpio_key->gpio << 8) | val;
put_key(key);
wake_up_interruptible(&gpio_key_wait);
kill_fasync(&button_fasync, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
}
/* 实现对应的open/read/write等函数,填入file_operations结构体 */
static ssize_t gpio_key_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
//printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
int err;
int key;
if (is_key_buf_empty() && (file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK))
return -EAGAIN;
wait_event_interruptible(gpio_key_wait, !is_key_buf_empty());
key = get_key();
err = copy_to_user(buf, &key, 4);
return 4;
}
static unsigned int gpio_key_drv_poll(struct file *fp, poll_table * wait)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
poll_wait(fp, &gpio_key_wait, wait);
return is_key_buf_empty() ? 0 : POLLIN | POLLRDNORM;
}
static int gpio_key_drv_fasync(int fd, struct file *file, int on)
{
if (fasync_helper(fd, file, on, &button_fasync) >= 0)
return 0;
else
return -EIO;
}
/* 定义自己的file_operations结构体 */
static struct file_operations gpio_key_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = gpio_key_drv_read,
.poll = gpio_key_drv_poll,
.fasync = gpio_key_drv_fasync,
};
//按键中断处理函数不会直接返回按键的状态,而是通过调用定时器中断
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = dev_id;
printk("gpio_key_isr key %d irq happened\n", gpio_key->gpio);
mod_timer(&gpio_key->key_timer, jiffies + HZ/50);//使用HZ宏,定时器超时时间为20ms,如果超时时间到了,就会修改key_timer的值,导致key_timer_expire函数被调用
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
/* 1. 从platform_device获得GPIO
* 2. gpio=>irq
* 3. request_irq
*/
static int gpio_key_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int err;
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
enum of_gpio_flags flag;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
count = of_gpio_count(node);
if (!count)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, there isn't any gpio available\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_first= kzalloc(sizeof(struct gpio_key) * count, GFP_KERNEL);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
gpio_keys_first[i].gpio = of_get_gpio_flags(node, i, &flag);
if (gpio_keys_first[i].gpio < 0)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, of_get_gpio_flags fail\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_first[i].gpiod = gpio_to_desc(gpio_keys_first[i].gpio);
gpio_keys_first[i].flag = flag & OF_GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW;
gpio_keys_first[i].irq = gpio_to_irq(gpio_keys_first[i].gpio);
//每个按键都注册定时中断函数
//setup_timer(&gpio_keys_first[i].key_timer, key_timer_expire, &gpio_keys_first[i]);
timer_setup(&gpio_keys_first[i].key_timer, key_timer_expire, 0);
gpio_keys_first[i].key_timer.expires = ~0;
add_timer(&gpio_keys_first[i].key_timer);
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
err = request_irq(gpio_keys_first[i].irq, gpio_key_isr, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "my_gpio_key", &gpio_keys_first[i]);
}
/* 注册file_operations */
major = register_chrdev(0, "my_gpio_key", &gpio_key_drv); /* /dev/gpio_key */
gpio_key_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "my_gpio_key_class");
if (IS_ERR(gpio_key_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "my_gpio_key");
return PTR_ERR(gpio_key_class);
}
device_create(gpio_key_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "my_gpio_key"); /* /dev/my_gpio_key*/
return 0;
}
static int gpio_key_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
//int err;
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
device_destroy(gpio_key_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(gpio_key_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "my_gpio_key");
count = of_gpio_count(node);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
free_irq(gpio_keys_first[i].irq, &gpio_keys_first[i]);
del_timer(&gpio_keys_first[i].key_timer);
}
kfree(gpio_keys_first);
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id my_keys[] = {
{ .compatible = "first_key,gpio_key" },
{ },
};
/* 1. 定义platform_driver */
static struct platform_driver gpio_keys_driver = {
.probe = gpio_key_probe,
.remove = gpio_key_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "my_gpio_key",
.of_match_table = my_keys,
},
};
/* 2. 在入口函数注册platform_driver */
static int __init gpio_key_init(void)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
err = platform_driver_register(&gpio_keys_driver);
return err;
}
/* 3. 有入口函数就应该有出口函数:卸载驱动程序时,就会去调用这个出口函数
* 卸载platform_driver
*/
static void __exit gpio_key_exit(void)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
platform_driver_unregister(&gpio_keys_driver);
}
/* 7. 其他完善:提供设备信息,自动创建设备节点 */
module_init(gpio_key_init);
module_exit(gpio_key_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
到了这里,关于STM32MP157驱动开发——按键驱动(定时器)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!