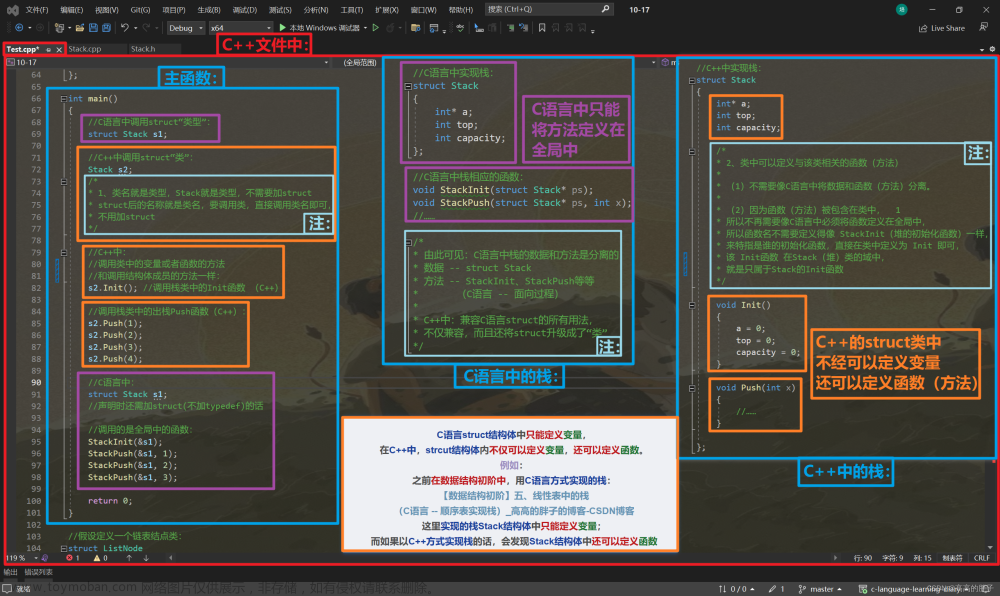
1.属性和行为作为整体




2.示例2-设计学生类

3.访问权限



4.class和struct的区别


5.成员属性设置为私有



6.设计案例1-立方体类










在main函数前重新补上isSame函数
在Cube类里面添加issamebyclass,利用成员函数判断两个立方体是否相等

自己写的代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Cube {
public: //行为
void setL(int l) {
m_L = l;
}
int getL() {
return m_L;
}
void setW(int w) {
m_W= w;
}
int getW() {
return m_W;
}
void setH(int h) {
m_H = h;
}
int getH() {
return m_H;
}
int calculateS() {
return 2 * (m_L * m_W + m_L * m_H + m_H * m_W);
}
int calculateV() {
return m_L * m_W * m_H;
}
bool IsSameByClass(Cube& c) {
if (getL() == c.getL() && getW() == c.getW() && getH() == c.getH()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private://属性
int m_L, m_W, m_H;
};
bool IsSame(Cube& c1, Cube& c2){
if (c1.getL() == c2.getL() && c1.getW() == c2.getW() && c1.getH() == c2.getH()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
Cube c1;
c1.setL(10), c1.setW(10), c1.setH(10);
cout << "c1_L=" << c1.getL() << "\tc1_W=" << c1.getW() << "\tc1_H=" << c1.getH()<<endl;
cout << "c1_S=" << c1.calculateS() << "\tc1_V=" << c1.calculateV() << endl<<endl;
Cube c2;
c2.setL(10), c2.setW(10), c2.setH(10);
cout << "c2_L=" << c2.getL() << "\tc2_W=" << c2.getW() << "\tc2_H=" << c2.getH() << endl;
cout << "c2_S=" << c2.calculateS() << "\tc2_V=" << c2.calculateV() << endl << endl;
bool flag = IsSame(c1,c2);
if (flag) {
cout << "两个立方体相等。" << endl << endl;
}
else {
cout << "两个立方体不相等。" << endl<<endl;
}
bool flag_2 = c1.IsSameByClass(c2);
if (flag_2) {
cout << "BYclass两个立方体相等。" << endl << endl;
}
else {
cout << "BYclass两个立方体不相等。" << endl << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-608370.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-608370.html
7.设计案例2-点和圆的关系
B站视频链接:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1et411b73Z/?p=105&spm_id_from=333.1007.top_right_bar_window_history.content.click&vd_source=fb8dcae0aee3f1aab700c21099045395 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-608370.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-608370.html
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "circle.h"
#include "point.h"
//class Point {
//public:
// void setX(float x) {
// m_X = x;
// }
// float getX() {
// return m_X;
// }
//
// void setY(float y) {
// m_Y = y;
// }
// float getY() {
// return m_Y;
// }
//
//private:
// float m_X, m_Y;
//};
//class Circle {
//public: //行为
// void setR(float r) {
// m_R = r;
// }
// float getR() {
// return m_R;
// }
//
// void setCenter(Point center) {
// m_Center = center;
// }
// Point getCenter() {
// return m_Center;
// }
//
//private://属性
// Point m_Center;
// float m_R;
//};
void isInCircle(Circle& c, Point& p)
{
float r = sqrt(pow(c.getCenter().getX() - p.getX(), 2) +
pow(c.getCenter().getY() - p.getY(), 2));
if (pow(c.getR(), 2) < pow(r, 2))
{
cout << "点在圆外" << endl;
}
else if (pow(c.getR(), 2) == pow(r, 2))
{
cout << "点在圆上" << endl;
}
else if (pow(r, 2) == 0)
{
cout << "点是圆心" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "点在圆内" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
Point p;
p.setX(0);
p.setY(9);
Point center;
center.setX(0);
center.setY(0);
Circle c;
c.setCenter(center);
c.setR(2);
isInCircle(c, p);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
point.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point {
public:
void setX(float x);
float getX();
void setY(float y);
float getY();
private:
float m_X, m_Y;
};
point.cpp
#include "point.h"
void Point::setX(float x) {
m_X = x;
}
float Point::getX() {
return m_X;
}
void Point::setY(float y) {
m_Y = y;
}
float Point::getY() {
return m_Y;
}
circle.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "point.h"
class Circle {
public: //行为
void setR(float r);
float getR();
void setCenter(Point center);
Point getCenter();
private://属性
Point m_Center;
float m_R;
};
circle.cpp
#include "circle.h"
void Circle::setR(float r) {
m_R = r;
}
float Circle::getR() {
return m_R;
}
void Circle::setCenter(Point center) {
m_Center = center;
}
Point Circle::getCenter() {
return m_Center;
}
到了这里,关于【C++】类和对象-封装的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!