编写使用中断的按键驱动程序
-
对于使用中断的按键驱动,内核自带的驱动程序
drivers/input/keyboard/gpio_keys.c就可以,需要做的只是修改设备树指定引脚及键值 -
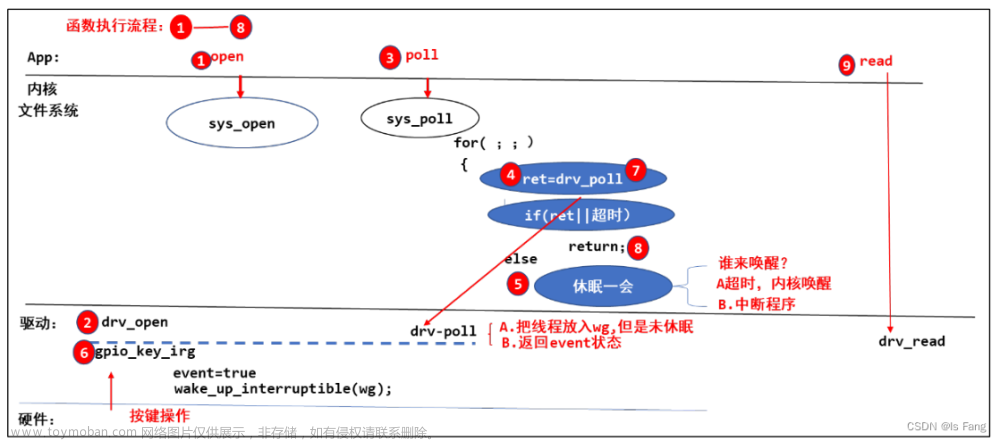
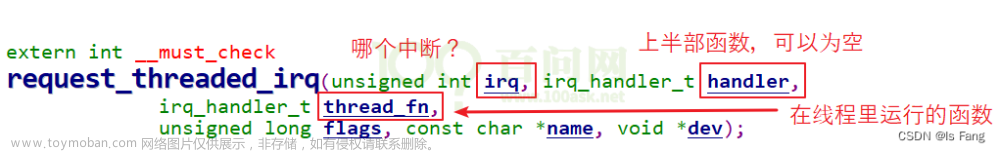
中断是引入其他基础知识的前提:休眠-唤醒、POLL 机制、异步通知、定时器、中断的线程化处理都离不开中断
编程思路
设备树相关
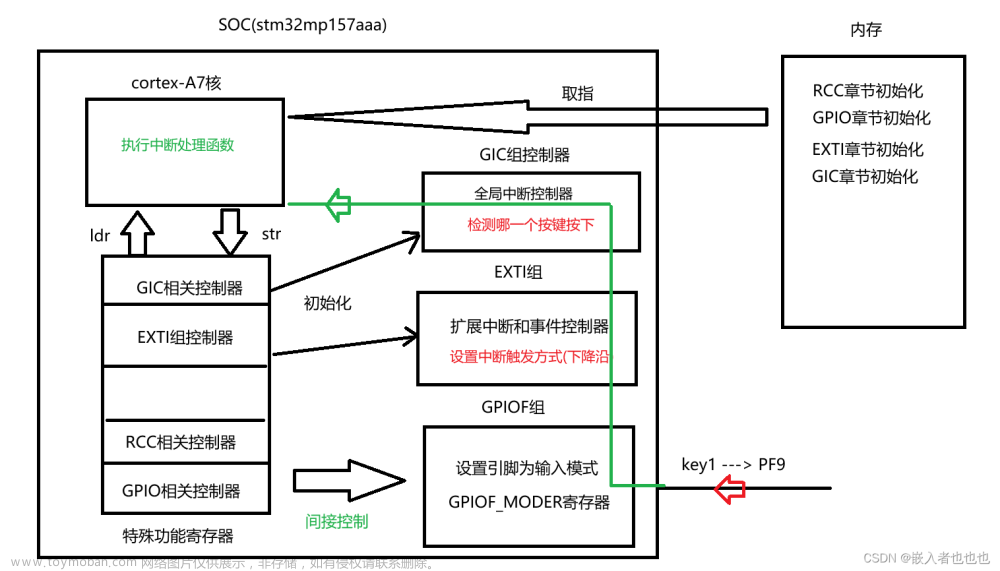
查看原理图确定按键使用的引脚,再在设备树中添加节点,在节点里指定中断信息
例子:
gpio_keys_first {
compatible = "first_key,gpio_key";
gpios = <&gpio5 1 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH
&gpio4 14 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>;
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&key1_pinctrl
&key2_pinctrl>;
};
注意:在设备树里面可以不用设置中断,因为Linux 系统中异常与中断里面提到对于 GPIO,可以在驱动程序里面使用 gpio_to_irq 或 gpiod_to_irq 获得中断号
驱动代码相关
- 首先要获得中断号
- 然后编写中断处理函数;
- 最后 request_irq。
代码
修改设备树文件
对于一个引脚要用作中断时,
- a) 要通过 PinCtrl 把它设置为 GPIO 功能;【ST 公司对于 STM32MP157 系列芯片,GPIO 为默认模式 不需要再进行配置Pinctrl 信息】
- b) 表明自身:是哪一个 GPIO 模块里的哪一个引脚【修改设备树】
打开内核的设备树文件:arch/arm/boot/dts/stm32mp157c-100ask-512d-lcd-v1.dts
gpio_keys_first {
compatible = "first_key,gpio_key";
gpios = <&gpiog 3 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW
&gpiog 2 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>;
};
与此同时,需要把用到引脚的节点禁用
注意,如果其他设备树文件也用到该节点,需要设置属性为disabled状态,在arch/arm/boot/dts目录下执行如下指令查找哪些设备树用到该节点
grep "&gpiog" * -nr
如果用到该节点,需要添加属性去屏蔽:
status = "disabled";
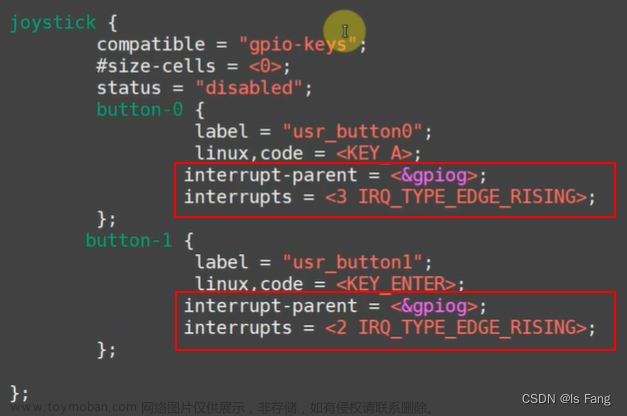
gpio_key_drv.c
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include <linux/gpio/consumer.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/of_irq.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
struct gpio_key{
int gpio;
struct gpio_desc *gpiod;
int flag;
int irq;
} ;
static struct gpio_key *gpio_keys_first;
//中断处理函数,参数是request_irq函数参数的最后一个
static irqreturn_t gpio_key_isr(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct gpio_key *gpio_key = dev_id;//获取的是引脚的电平,因为设置了上升沿和下降沿都触发
int val;
val = gpiod_get_value(gpio_key->gpiod);
printk("key %d %d\n", gpio_key->gpio, val);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
/* 1. 从platform_device获得GPIO
* 2. gpio=>irq
* 3. request_irq
*/
static int gpio_key_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int err;
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;//platform_device 里面有device结构体
int count;
int i;
enum of_gpio_flags flag;
unsigned flags = GPIOF_IN;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
count = of_gpio_count(node);
if (!count)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, there isn't any gpio available\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_first = kzalloc(sizeof(struct gpio_key) * count, GFP_KERNEL);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
gpio_keys_first[i].gpio = of_get_gpio_flags(node, i, &flag);
if (gpio_keys_first[i].gpio < 0)
{
printk("%s %s line %d, of_get_gpio_flags fail\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
gpio_keys_first[i].gpiod = gpio_to_desc(gpio_keys_first[i].gpio);
gpio_keys_first[i].flag = flag & OF_GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW;
//如果设备树里面是低电平有效,则flags或上GPIO子系统里面的低电平有效的宏定义(注意有F)
if (flag & OF_GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW)
flags |= GPIOF_ACTIVE_LOW;
//读出引脚的逻辑值
err = devm_gpio_request_one(&pdev->dev, gpio_keys_first[i].gpio, flags, NULL);
gpio_keys_first[i].irq = gpio_to_irq(gpio_keys_first[i].gpio);//从 GPIO 获得中断号,该中断号是使用request_irq的参数之一
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
err = request_irq(gpio_keys_first[i].irq, gpio_key_isr, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "my_gpio_key", &gpio_keys_first[i]);
}
return 0;
}
static int gpio_key_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
//int err;
struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node;
int count;
int i;
count = of_gpio_count(node);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
free_irq(gpio_keys_first[i].irq, &gpio_keys_first[i]);
}
kfree(gpio_keys_first);
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id my_keys[] = {
{ .compatible = "first_key,gpio_key" },
{ },
};
/* 1. 定义platform_driver */
static struct platform_driver gpio_keys_driver = {
.probe = gpio_key_probe,
.remove = gpio_key_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "my_gpio_key",
.of_match_table = my_keys,
},
};
/* 2. 在入口函数注册platform_driver */
static int __init gpio_key_init(void)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
err = platform_driver_register(&gpio_keys_driver);
return err;
}
/* 3. 有入口函数就应该有出口函数:卸载驱动程序时,就会去调用这个出口函数
* 卸载platform_driver
*/
static void __exit gpio_key_exit(void)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
platform_driver_unregister(&gpio_keys_driver);
}
/* 7. 其他完善:提供设备信息,自动创建设备节点 */
module_init(gpio_key_init);
module_exit(gpio_key_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
Makefile
# 1. 使用不同的开发板内核时, 一定要修改KERN_DIR
# 2. KERN_DIR中的内核要事先配置、编译, 为了能编译内核, 要先设置下列环境变量:
# 2.1 ARCH, 比如: export ARCH=arm64
# 2.2 CROSS_COMPILE, 比如: export CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu-
# 2.3 PATH, 比如: export PATH=$PATH:/home/book/100ask_roc-rk3399-pc/ToolChain-6.3.1/gcc-linaro-6.3.1-2017.05-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin
# 注意: 不同的开发板不同的编译器上述3个环境变量不一定相同,
# 请参考各开发板的高级用户使用手册
KERN_DIR = /home/book/100ask_stm32mp157_pro-sdk/Linux-5.4
all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules
clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean
rm -rf modules.order
# 参考内核源码drivers/char/ipmi/Makefile
# 要想把a.c, b.c编译成ab.ko, 可以这样指定:
# ab-y := a.o b.o
# obj-m += ab.o
obj-m += gpio_key_drv.o
编译测试
首先要设置 ARCH、CROSS_COMPILE、PATH 这三个环境变量后,进入 ubuntu 上板子内核源码的目录,在Linux内核源码根目录下,执行如下命令即可编译 dtb 文件:
make dtbs V=1
编译好的文件在路径由DTC指定,移植设备树到开发板的共享文件夹中,先保存源文件,然后覆盖源文件,重启后会挂载新的设备树,进入该目录查看是否有新添加的设备节点
cd /sys/firmware/devicetree/base
编译驱动程序,在Makefile文件目录下执行make指令,此时,目录下有编译好的内核模块gpio_key_drv.ko移植到开发板上
确定一下烧录系统:cat /proc/mounts,查看boot分区挂载的位置,将其重新挂载在boot分区:mount /dev/mmcblk2p2 /boot,然后将共享文件夹里面的设备树文件拷贝到boot目录下,这样的话设备树文件就在boot目录下文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-610622.html
cp /mnt/stm32mp157c-100ask-512d-lcd-v1.dtb /boot
重启后挂载,运行文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-610622.html
insmod gpio_key_drv.ko // 装载驱动程序
到了这里,关于STM32MP157驱动开发——按键驱动(中断)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!