初识哈希
哈希表是一种查找效率及其高的算法,最理想的情况下查询的时间复杂度为O(1)。
unordered_map容器通过key访问单个元素要比map快,但它通常在遍历元素子集的范围迭代方面效率较低。
底层结构
unordered系列的关联式容器之所以效率更高,是因为底层采用了哈希的结构。
哈希是通过对
key进行映射,然后通过映射值直接去拿到要的数据,效率更高,平衡树的查找是通过依次比对,相对而言就会慢一些。
- 插入元素:通过计算出元素的映射值,来后通过映射值把元素插入到储存的位置当中。
- 搜索元素:通过计算元素的映射值来取得元素。
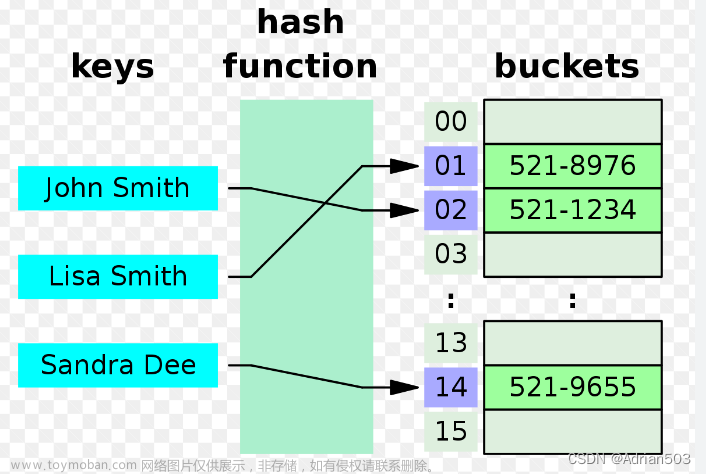
哈希方法中使用的转换函数称之为哈希(散列)函数,构造出来的结构叫做哈希表(散列表)
例: 集合 {1,7,6,4,5,9,11,21};
哈希函数为:hash(key)=key%capacity,capacity为底层空间的最大值。
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 21 4 5 6 9 1%10=1、4%10=4、7%10=10…
但如果我要插入一个11怎么办?
这就是一个经典的问题,哈希冲突
哈希冲突
解决哈希冲突的两种常见方式就是:闭散列和开散列。
闭散列
闭散列也叫开放寻址法,当发生冲突的时候我就往后面去找,假如1和11去%10都等于1,但是1先去把1号坑位占了,那么11肯定不能把1的坑位抢了,只能往后找有没有没有被占的坑位,有的话就放11,这个方法叫做线性探测法。
但是我要删除某个值该怎么办呢?
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 21 4 5 6 9 例如这段数据,我把11删掉之后
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 21 4 5 6 9 2的位置就空出来了,当我想要去找21的时候会发现找不到,因为找某个值和插入某个值是一样的,先确定映射值,如果不是当前值就往后面找,如果为空就找完了,这里2为空,不能继续往后找了,就要返回查找失败了,但是21是存在的呀,所以可以对每一个哈希节点进行标记,在每一个节点中记录一个状态值,是Empty还是Exit还是Delete,这样就可以避免上述情况了。
定义哈希节点
//枚举状态
enum State
{
Empty,
Exit,
Delete
};
template<class K,class V>
struct Hash_Node
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
State _state = Empty;
};
定义哈希表
template<class K,class V>
class Hash_table
{
public:
typedef Hash_Node<K, V> Node;
private:
vector<Node> _tables;
size_t _size=0;
};
哈希表什么情况下进行扩容?如何扩容?

Insert()函数
bool Insert(const pair<K,V>& key)
{
//查重
if (Find(key.first))
{
return false;
}
//扩容
if (_tables.size()==0||10*_size / _tables.size()>=7)
{
//大于7需要扩容
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : 2 * _tables.size();
Hash_table<K, V>newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newSize);//新表
//复用Insert函数
for (auto& e : _tables)
{
if (e._state == Exit)
{
newHT.Insert(e._kv);
}
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
}
//线性探测
size_t hashi = key.first % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._state == Exit)
{
hashi++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
_tables[hashi]._kv = key;
_tables[hashi]._state = Exit;
_size++;
return true;
}
Find()函数
Hash_Node<K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0) return nullptr;
size_t start = key % _tables.size();
size_t begin = start;
while (_tables[start]._state != Empty)
{
if (_tables[start]._state != Delete && _tables[start]._kv.first == key)
{
return &_tables[start];
}
start++;
start %= _tables.size();
if (begin == start)
{
break;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
样例测试
void test1()
{
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,21,31,41,51,61,71,81,91,101 };
Hash_table<int, int>hs;
for (auto e : arr)
{
hs.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
}
测试结果如下:

可以看到都是被成功的插入了。
线性探测的优先:简单方便。
线性探测的缺点:一旦发生哈希冲突了,所有的冲突都会堆积在一块,会导致查找的效率变得很低。
二次探测
二次探测其实就是每次跳过
i的平方个间隔,原来的线性探测是一个一个往后找。
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Exit Exit Exit 比如在1发生了哈希冲突,那么线性探测就会去找2位置,然后再找3位置,直到找到空为止。
但二次探测是1没有,i=1,i的平方等于1,找2位置,i=2,i的平方等于4,找5位置,发现没有元素,就直接占位,二次探测可以让数据更加分散,降低哈希冲突的发生率。
size_t start = hash(kv.first) % _tables.size();
size_t i = 0;
size_t hashi = start;
// 二次探测
while (_tables[hashi]._state == Exit)
{
++i;
hashi = start + i*i;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv;
_tables[hashi]._state = EXIST;
++_size;
以上的哈希表只能用来映射int类型的值,如果是其他类型就不行了,这里可以增加一个仿函数来兼容其他类型,这里最重要的是string类型了,如何才能将string类型转换为一个数值。
我们可以把ASCII码相加,就能得到key了,但是面对以下场景就会哈希冲突了。
string str1="abc"; string str2="acb"; string str3="cba";这里有大佬得出过一个结论
hash = hash * 131 + ch,这样可以降低哈希碰撞的概率。
HashFunc()仿函数
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
//特例化模板参数来解决string的问题
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t val = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
{
val *= 131;
val += ch;
}
return val;
}
};
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//闭散列
namespace mudan
{
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
//特例化模板参数来解决string的问题
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t val = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
{
val *= 131;
val += ch;
}
return val;
}
};
enum State
{
Empty,
Exit,
Delete
};
template<class K,class V>
struct Hash_Node
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
State _state = Empty;
};
template<class K,class V,class Hash=HashFunc<K>>
class Hash_table
{
public:
typedef Hash_Node<K, V> Node;
bool Insert(const pair<K,V>& key)
{
//查重
if (Find(key.first))
{
return false;
}
//扩容
if (_tables.size()==0||10*_size / _tables.size()>=7)
{
//大于7需要扩容
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : 2 * _tables.size();
Hash_table<K, V>newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newSize);//新表
//复用Insert函数
for (auto &e : _tables)
{
if (e._state == Exit)
{
newHT.Insert(e._kv);
}
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
}
Hash hash;
//线性探测
size_t hashi = hash(key.first) % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._state == Exit)
{
hashi++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
_tables[hashi]._kv = key;
_tables[hashi]._state = Exit;
_size++;
return true;
}
Hash_Node<K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0) return nullptr;
Hash hash;
size_t start = hash(key) % _tables.size();
size_t begin = start;
while (_tables[start]._state != Empty)
{
if (_tables[start]._state != Delete && _tables[start]._kv.first == key)
{
return &_tables[start];
}
start++;
start %= _tables.size();
if (begin == start)
{
break;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
private:
vector<Node> _tables;
size_t _size;
};
void TestHT2()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
//HashTable<string, int, HashFuncString> countHT;
Hash_table<string, int> countHT;
for (auto& str : arr)
{
auto ptr = countHT.Find(str);
if (ptr)
{
ptr->_kv.second++;
}
else
{
countHT.Insert(make_pair(str, 1));
}
}
}
void test1()
{
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,21,31,41,51,61,71,81,91,101 };
Hash_table<int, int>hs;
for (auto e : arr)
{
hs.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
}
}
可以看到映射也成功了。


对于之前说的问题也解决了。
string str1="abc";
string str2="acb";
string str3="cba";
Erase()函数
这个就简单了,Erase不是真正意义上把这个数字从数组当中删掉,而是改变状态,把状态改成Delete即可。
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Hash_Node<K, V>* ret = Find(key);
if (ret)
{
ret->_state = Delete;
--_size;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
全部的代码
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//闭散列
namespace mudan
{
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
//特例化模板参数来解决string的问题
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t val = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
{
val *= 131;
val += ch;
}
return val;
}
};
enum State
{
Empty,
Exit,
Delete
};
template<class K,class V>
struct Hash_Node
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
State _state = Empty;
};
template<class K,class V,class Hash=HashFunc<K>>
class Hash_table
{
public:
typedef Hash_Node<K, V> Node;
bool Insert(const pair<K,V>& key)
{
//查重
if (Find(key.first))
{
return false;
}
//扩容
if (_tables.size()==0||10*_size / _tables.size()>=7)
{
//大于7需要扩容
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : 2 * _tables.size();
Hash_table<K, V>newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newSize);//新表
//复用Insert函数
for (auto &e : _tables)
{
if (e._state == Exit)
{
newHT.Insert(e._kv);
}
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
}
Hash hash;
//线性探测
size_t hashi = hash(key.first) % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._state == Exit)
{
hashi++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
_tables[hashi]._kv = key;
_tables[hashi]._state = Exit;
_size++;
return true;
}
Hash_Node<K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0) return nullptr;
Hash hash;
size_t start = hash(key) % _tables.size();
size_t begin = start;
while (_tables[start]._state != Empty)
{
if (_tables[start]._state != Delete && _tables[start]._kv.first == key)
{
return &_tables[start];
}
start++;
start %= _tables.size();
if (begin == start)
{
break;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Hash_Node<K, V>* ret = Find(key);
if (ret)
{
ret->_state = Delete;
--_size;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
private:
vector<Node> _tables;
size_t _size=0;
};
void TestHT2()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
//HashTable<string, int, HashFuncString> countHT;
Hash_table<string, int> countHT;
for (auto& str : arr)
{
auto ptr = countHT.Find(str);
if (ptr)
{
ptr->_kv.second++;
}
else
{
countHT.Insert(make_pair(str, 1));
}
}
}
void test1()
{
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,21,31,41,51,61,71,81,91,101 };
Hash_table<int, int>hs;
for (auto e : arr)
{
hs.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
}
void TestHT3()
{
HashFunc<string> hash;
cout << hash("abcd") << endl;
cout << hash("bcad") << endl;
cout << hash("eat") << endl;
cout << hash("ate") << endl;
cout << hash("abcd") << endl;
cout << hash("aadd") << endl << endl;
cout << hash("abcd") << endl;
cout << hash("bcad") << endl;
cout << hash("eat") << endl;
cout << hash("ate") << endl;
cout << hash("abcd") << endl;
cout << hash("aadd") << endl << endl;
}
}
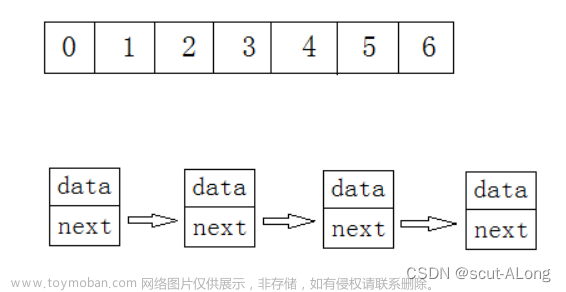
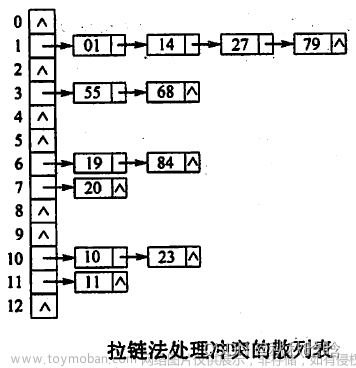
开散列

开散列如上图所示,他有一个桶子来表示key值,然后key值相同的(哈希冲突的)就都连接到这个桶的key对应的位置下面。
这个桶其实就是一个指针数组。
定义哈希节点
template<class K,class V>
struct HashNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode<K,V>* _next;
HashNode(const pair<K,V>& data)
:_kv(data)
,_next(nullptr)
{}
};
定义哈希表
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
public:
private:
vector<Node*>_tables;
size_t _size=0;
};
Insert()函数
插入操作头插和尾插都很快,这里由于定义的是单链表,就选择头插了。
插入过程如下图所示:
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-610977.html
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& key)
{
Hash hash;
//去重
if (Find(key.first)) return false;
//负载因子等于1就要扩容了
if (_size == _tables.size())
{
size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10:2 * _tables.size();
vector<Node*>newTables;
newTables.resize(newsize);
for (int i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = hash(cur->_kv.first) % newTables.size();
cur->_next =newTables[hashi];
newTables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;//销毁原来的桶
}
_tables.swap(newTables);
}
//头插
// head
// 1 2头插,2->next=1,head=2;
size_t hashi = hash(key.first) % _tables.size();
Node* newnode = new Node(key);
newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_size;
return true;
}
Find()函数
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
{
return nullptr;
}
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
//没找到,返回空
return nullptr;
}
Erase()函数
和链表的和删除一摸一样文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-610977.html
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
{
return nullptr;
}
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
// 1、头删
// 2、中间删
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
--_size;
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return false;
}
总代码
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//闭散列
namespace mudan
{
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
//特例化模板参数来解决string的问题
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t val = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
{
val *= 131;
val += ch;
}
return val;
}
};
enum State
{
Empty,
Exit,
Delete
};
template<class K,class V>
struct Hash_Node
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
State _state = Empty;
};
template<class K,class V,class Hash=HashFunc<K>>
class Hash_table
{
public:
typedef Hash_Node<K, V> Node;
bool Insert(const pair<K,V>& key)
{
//查重
if (Find(key.first))
{
return false;
}
//扩容
if (_tables.size()==0||10*_size / _tables.size()>=7)
{
//大于7需要扩容
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : 2 * _tables.size();
Hash_table<K, V>newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newSize);//新表
//复用Insert函数
for (auto &e : _tables)
{
if (e._state == Exit)
{
newHT.Insert(e._kv);
}
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
}
Hash hash;
//线性探测
size_t hashi = hash(key.first) % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._state == Exit)
{
hashi++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
_tables[hashi]._kv = key;
_tables[hashi]._state = Exit;
_size++;
return true;
}
Hash_Node<K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0) return nullptr;
Hash hash;
size_t start = hash(key) % _tables.size();
size_t begin = start;
while (_tables[start]._state != Empty)
{
if (_tables[start]._state != Delete && _tables[start]._kv.first == key)
{
return &_tables[start];
}
start++;
start %= _tables.size();
if (begin == start)
{
break;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Hash_Node<K, V>* ret = Find(key);
if (ret)
{
ret->_state = Delete;
--_size;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
private:
vector<Node> _tables;
size_t _size=0;
};
void TestHT2()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
//HashTable<string, int, HashFuncString> countHT;
Hash_table<string, int> countHT;
for (auto& str : arr)
{
auto ptr = countHT.Find(str);
if (ptr)
{
ptr->_kv.second++;
}
else
{
countHT.Insert(make_pair(str, 1));
}
}
}
void test1()
{
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,21,31,41,51,61,71,81,91,101 };
Hash_table<int, int>hs;
for (auto e : arr)
{
hs.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
}
void TestHT3()
{
HashFunc<string> hash;
cout << hash("abcd") << endl;
cout << hash("bcad") << endl;
cout << hash("eat") << endl;
cout << hash("ate") << endl;
cout << hash("abcd") << endl;
cout << hash("aadd") << endl << endl;
cout << hash("abcd") << endl;
cout << hash("bcad") << endl;
cout << hash("eat") << endl;
cout << hash("ate") << endl;
cout << hash("abcd") << endl;
cout << hash("aadd") << endl << endl;
}
}
namespace mudan1
{
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
//特例化模板参数来解决string的问题
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t val = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
{
val *= 131;
val += ch;
}
return val;
}
};
template<class K,class V>
struct HashNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode<K,V>* _next;
HashNode(const pair<K,V>& data)
:_kv(data)
,_next(nullptr)
{}
};
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& key)
{
Hash hash;
//去重
if (Find(key.first)) return false;
//负载因子等于1就要扩容了
if (_size == _tables.size())
{
size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10:2 * _tables.size();
vector<Node*>newTables;
newTables.resize(newsize);
for (int i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = hash(cur->_kv.first) % newTables.size();
cur->_next =newTables[hashi];
newTables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;//销毁原来的桶
}
_tables.swap(newTables);
}
//头插
// head
// 1 2头插,2->next=1,head=2;
size_t hashi = hash(key.first) % _tables.size();
Node* newnode = new Node(key);
newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_size;
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
{
return nullptr;
}
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
//没找到,返回空
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
{
return nullptr;
}
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
// 1、头删
// 2、中间删
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
--_size;
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return false;
}
private:
vector<Node*>_tables;
size_t _size=0;
};
void TestHT1()
{
int a[] = { 1, 11, 4, 15, 26, 7, 44,55,99,78 };
HashTable<int, int> ht;
for (auto e : a)
{
ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
ht.Insert(make_pair(22, 22));
}
}
到了这里,关于哈希表的简单模拟实现的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!