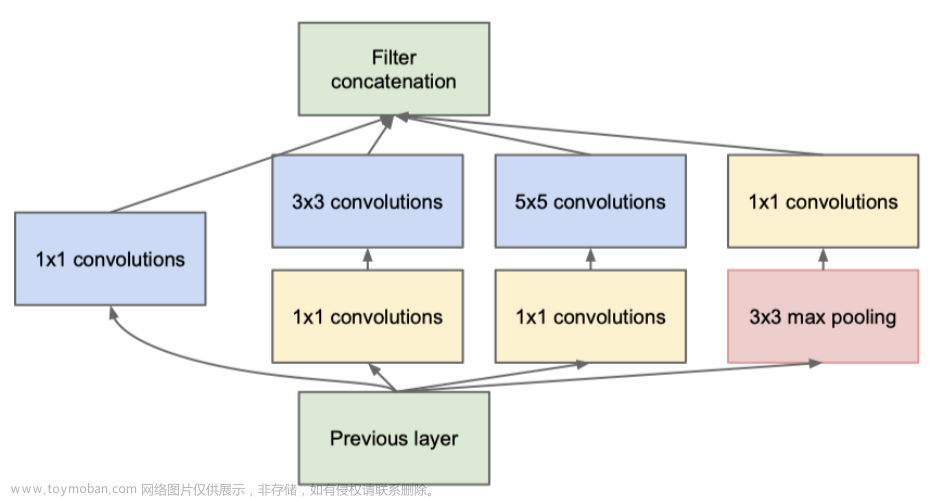
传统机器学习与深度学习的特征工程


卷积层:原始输入中间提取有用的一个局部特征
激活函数:用于增加模型的一些非线性,可以让模型学习更加复杂模式
池化层:用于减少数据的维度
特征向量

pytorch实现minist代码解析

首先继承nn.Module类的一个子类ConvNet,super方法就是在调用nn.Module的一个__init__方法,确保__init__方法中定义的属性和方法都可以在ConvNet中使用
归一化


损失函数

计算图

Mnist分类
获取Mnist数据集,预处理,输出一张图像
import torch
print(torch.__version__)
#win用户
DEVICE=torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
#mac用户
DEVICE=torch.device('mps' if torch.backends.mps.is_available() else 'cpu')
print('当前设备',DEVICE)

#将图像嵌入输出的单元格
%matplotlib inline
from pathlib import Path # 处理文件路径
import requests
DATA_PATH = Path("data")
PATH = DATA_PATH / "mnist"
PATH.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
URL = "http://deeplearning.net/data/mnist/"
FILENAME = "mnist.pkl.gz"
if not (PATH / FILENAME).exists():
content = requests.get(URL + FILENAME).content
(PATH / FILENAME).open("wb").write(content)
import pickle
import gzip
with gzip.open((PATH / FILENAME).as_posix(), "rb") as f:
((x_train, y_train), (x_valid, y_valid), (x_test, y_test)) = pickle.load(f, encoding="latin-1")
print("x_train: ", type(x_train), x_train.dtype, x_train.size, x_train.shape, "; y_train: ", y_train.shape)

print("x_valid: ", type(x_valid), x_valid.dtype, x_valid.size, x_valid.shape, "; y_valid: ", y_valid.shape)

from matplotlib import pyplot
pyplot.imshow(x_train[2].reshape((28, 28)), cmap="gray")

y_train[:10]

x_train, y_train, x_valid, y_valid = map(
lambda x: torch.tensor(x, device=DEVICE),
(x_train, y_train, x_valid, y_valid)
)
print("x_train: ", x_train, "; y_train: ", y_train)
x_train[0]
import torch.nn.functional as F
loss_func = F.cross_entropy # 损失函数,传入预测、真实值的标签
def model(xb):
xb = xb.to(DEVICE)
return xb.mm(weights) + bias # x*w+b
bs = 64
xb = x_train[0:bs] # 64, 784
yb = y_train[0:bs] # 真实标签
weights = torch.randn([784, 10], dtype = torch.float, requires_grad = True)
bias = torch.zeros(10, requires_grad = True)
weights = weights.to(DEVICE)
bias = bias.to(DEVICE)
print(loss_func(model(xb), yb))

补充:关于map函数的例子
def square(x):
return x**2
numbers=[1,2,3,4,5]
squares=map(square,numbers)
print(list(squares))

也就是map函数第一个参数是函数,第二个参数是数值,将函数作用于数值
面向工具包编程
from torch import nn # 提供神经网网络的类和函数 ,nn.Module
class Mnist_NN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self): # 设计房屋图纸
super(Mnist_NN, self).__init__()
self.hidden1 = nn.Linear(784, 256) # 784-输入层,256-隐藏层1
self.hidden2 = nn.Linear(256, 128)
self.out = nn.Linear(128, 10)
def forward(self, x): # 实际造房子
x2 = F.relu(self.hidden1(x)) # x: [bs, 784], w1: [784, 256], b1: [256] -> x2:[bs,256]
x3 = F.relu(self.hidden2(x2)) # x2: [bs, 256], w2:[256, 128], b2[128] -> x3[bs, 128]
x_out = self.out(x3) # x3: [bs, 128], w3: [128, 10], b3[10] -> x_out: [bs, 10]
return x_out
net = Mnist_NN().to(DEVICE)
print(net)

print(net.hidden1.weight)

for name, parameter in net.named_parameters():
print(name, parameter)
使用TensorDataset和DataLoader来简化数据预处理
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
train_ds = TensorDataset(x_train, y_train) #torch.utils.data.Dataset
train_dl = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
valid_ds = TensorDataset(x_valid, y_valid)
valid_dl = DataLoader(valid_ds, batch_size=bs)
data_iter = iter(train_dl)
batch_x, batch_y = next(data_iter)
print(batch_x.shape, batch_y.shape)
print(batch_y)

batch_x, batch_y = next(data_iter)
print(batch_x.shape, batch_y.shape)
print(batch_y)

def get_data(train_bs, valid_bs, bs): # 创建数据加载器
return (
DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=bs, shuffle=True),
DataLoader(valid_ds, batch_size=bs)
)
from torch import optim
def get_model():
model = Mnist_NN().to(DEVICE)
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01) # model.parameters()包含了所有的权重和偏执参数
return model, optimizer
注:adam相比于SGD是引入了一个惯性,相当于一个平行四边形的一个合成法则
def loss_batch(model, loss_func, xb, yb, opt=None):
loss = loss_func(model(xb), yb)
if opt is not None: # 此时是训练集
opt.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
opt.step()
return loss.item(), len(xb)
opt为True是训练集测试损失,opt为None是验证集测试损失
import numpy as np
def fit(epoch, model, loss_func, opt, train_dl, valid_dl):
for step in range(epoch):
model.train()
for xb, yb in train_dl:
loss_batch(model, loss_func, xb, yb, opt)
model.eval() # 考试
with torch.no_grad():
losses, nums = zip(
*[loss_batch(model, loss_func, xb, yb) for xb, yb in valid_dl] # "*"——解包/解开
)
# print(f"losses: {losses}")
# print(f"nums: {nums}")
val_loss = np.sum(np.multiply(losses, nums)) / np.sum(nums) # 加权平均损失
print('当前step: '+str(step), '验证集损失: '+str(val_loss))
train_dl, valid_dl = get_data(train_ds, valid_ds, bs=64)
model, optimizer = get_model()
fit(30, model, loss_func, optimizer, train_dl, valid_dl)

计算验证集准确率
torch.set_printoptions(precision=4, sci_mode=False)
for xb, yb in valid_dl:
output = model(xb)
print(output)
print(output.shape)
break
for xb, yb in valid_dl:
output = model(xb)
probs = torch.softmax(output, dim=1)
print(probs)
print(probs.shape)
break
for xb, yb in valid_dl:
output = model(xb)
probs = torch.softmax(output, dim=1)
preds = torch.argmax(probs, dim=1)
print(preds)
print(preds.shape)
break
correct_predict = 0 # 计数正确预测图片的数目
total_quantity = 0 # 计数验证集总数
for xb, yb in valid_dl:
output = model(xb)
probs = torch.softmax(output, dim=1)
preds = torch.argmax(probs, dim=1)
total_quantity += yb.size(0)
# print(yb.size(0))
# print((preds == yb).sum())
# print((preds == yb).sum().item())
correct_predict += (preds == yb).sum().item()
print(f"验证集的准确率是: {100 * correct_predict / total_quantity} % ")

气温预测
回归
import numpy as np # 矩阵运算
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
%matplotlib inline
features = pd.read_csv('temps.csv')
features.head()

print("数据维度: ", features.shape)

# 处理时间数据
import datetime
years = features['year']
months = features['month']
days = features['day']
dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
dates[:5]

dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in dates]
dates[:5]

plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')
fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize = (10, 10))
fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation=45) #x轴翻转45度
# 标签值
ax1.plot(dates, features['actual'])
ax1.set_xlabel(''); ax1.set_ylabel('Temoerature'); ax1.set_title('Actual Max Temp')
# 昨天温度
ax2.plot(dates, features['temp_1'])
ax2.set_xlabel(''); ax2.set_ylabel('Temoerature'); ax2.set_title('Previous Max Temp')
# 前天温度
ax3.plot(dates, features['temp_2'])
ax3.set_xlabel('Date'); ax3.set_ylabel('Temoerature'); ax3.set_title('Two Days Prior Max Temp')
# 朋友预测温度
ax4.plot(dates, features['friend'])
ax4.set_xlabel('Date'); ax4.set_ylabel('Temoerature'); ax4.set_title('Friend Max Temp')


features = pd.get_dummies(features)
features.head()

labels = np.array(features['actual'])
# 在特征中去掉标签
features = features.drop('actual', axis=1)
feature_list = list(features.columns)
features = np.array(features)
features.shape

from sklearn import preprocessing
input_features = preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit_transform(features)
input_features[:5]
构建神经网络
x = torch.tensor(input_features, dtype = float)
y = torch.tensor(labels, dtype=float)
print(x.shape, y.shape)
# 权重初始化
weights = torch.randn((14, 128), dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
biases = torch.randn(128, dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
weights2 = torch.randn((128, 1), dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
biases2 = torch.randn(1, dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
learning_rate = 0.001
losses = []
for i in range(1000):
hidden = x.mm(weights) + biases
hidden = torch.relu(hidden)
predictions = hidden.mm(weights2) + biases2
loss = torch.mean((predictions - y)**2)
losses.append(loss.item())
if i % 100 == 0:
print(f"loss: {loss}")
# 反向传播
loss.backward()
# 更新,相当于optim.step()
weights.data.add_(- learning_rate * weights.grad.data)
biases.data.add_(- learning_rate * biases.grad.data)
weights2.data.add_(- learning_rate * weights2.grad.data)
biases2.data.add_(- learning_rate * biases2.grad.data)
# 清空梯度,optim.zero_grad()
weights.grad.data.zero_()
biases.grad.data.zero_()
weights2.grad.data.zero_()
biases2.grad.data.zero_()

调包
import torch.optim as optim
# 数据准备
# 将数据都转化为tensor张量
x = torch.tensor(input_features, dtype = torch.float)
y = torch.tensor(labels, dtype=torch.float).view(-1, 1) # 改成(n, 1)
print(x.shape, y.shape)
model = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(14, 128),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(128, 1)
)
# 均方误差MSE
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
losses = [] # 存储每一次迭代的损失
for i in range(3000):
predictions = model(x) # [348, 1]
loss = criterion(predictions, y)
losses.append(loss.item())
if i % 200 == 0:
print(f"loss: {loss.item()}")
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()

预测训练结果
x = torch.tensor(input_features, dtype = torch.float)
predict = model(x).data.numpy()
dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in dates]
# 创建一个表格来存日期和对应的真实标签
true_data = pd.DataFrame(data = {'date': dates, 'actual': labels})
# 创建一个表格来存日期和对应的预测值
predictions_data = pd.DataFrame(data = {'date': dates, 'prediction': predict.reshape(-1)})
predict.shape, predict.reshape(-1).shape

true_data[:5]

predictions_data[:5]

画图对比
# 真实值
plt.plot(true_data['date'], true_data['actual'], 'b-', label = "actual")
# 预测值
plt.plot(predictions_data['date'], predictions_data['prediction'], 'ro', label = "prediction")
plt.xticks(rotation = 60)
plt.legend()
 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-613559.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-613559.html
# 真实值
plt.plot(true_data['date'], true_data['actual'], 'b-', label = "actual")
# 预测值
plt.plot(predictions_data['date'], predictions_data['prediction'], 'ro', label = "prediction")
plt.xticks(rotation = 60)
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('Date'); plt.ylabel('Maximum Tempurate(F)'); plt.title('Actual and Predicted Values')
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-613559.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-613559.html
到了这里,关于Mnist分类与气温预测任务的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!